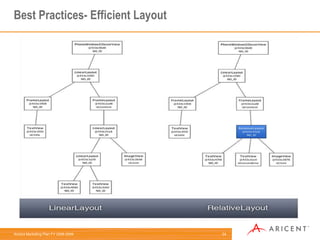
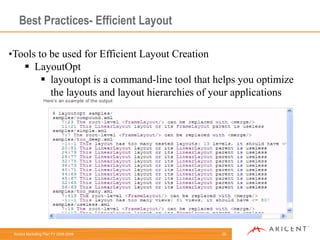
Linear layouts are more efficient than relative or absolute layouts for list items. Relative layouts are more flexible but also more expensive to render. Developers should use tools like LayoutOpt and TraceView to optimize layout hierarchies and identify performance bottlenecks. ProGuard can also help by removing unused code and optimizing code size.

















![7Common Mistakes(Android)- Which we should not doDo:onCreate{ // Create an AsyncTask for any I/O operation}Example for creating AsyncTask:private class DownloadFilesTask extends AsyncTask<URL, Integer, Long> { protected Long doInBackground(URL... urls) { int count = urls.length; long totalSize = 0; for (inti = 0; i < count; i++) { totalSize += Downloader.downloadFile(urls[i]); publishProgress((int) ((i / (float) count) * 100)); } return totalSize; }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bestpracticesandroid2010-110317040200-phpapp01/85/Best-practices-android_2010-19-320.jpg)