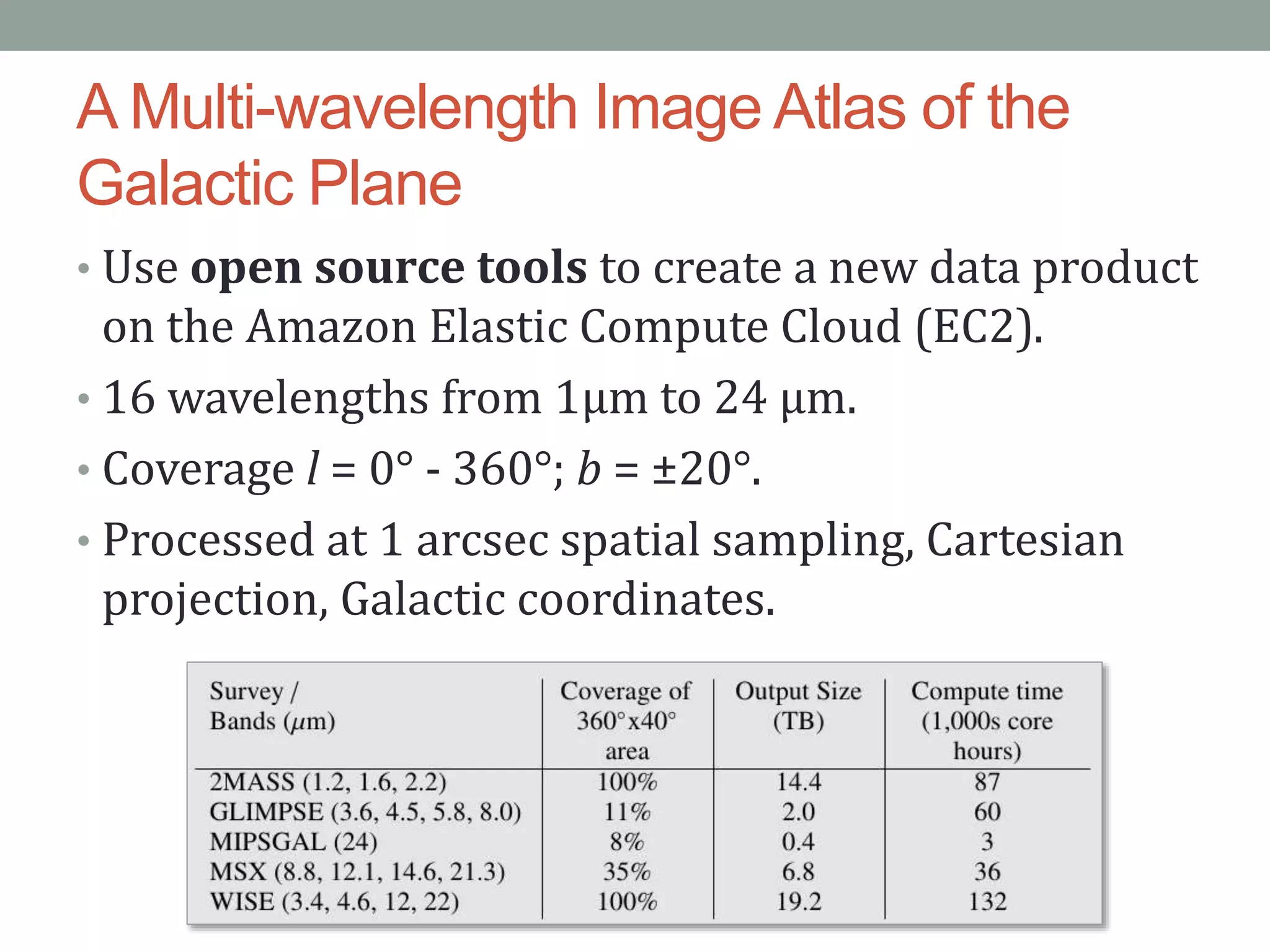
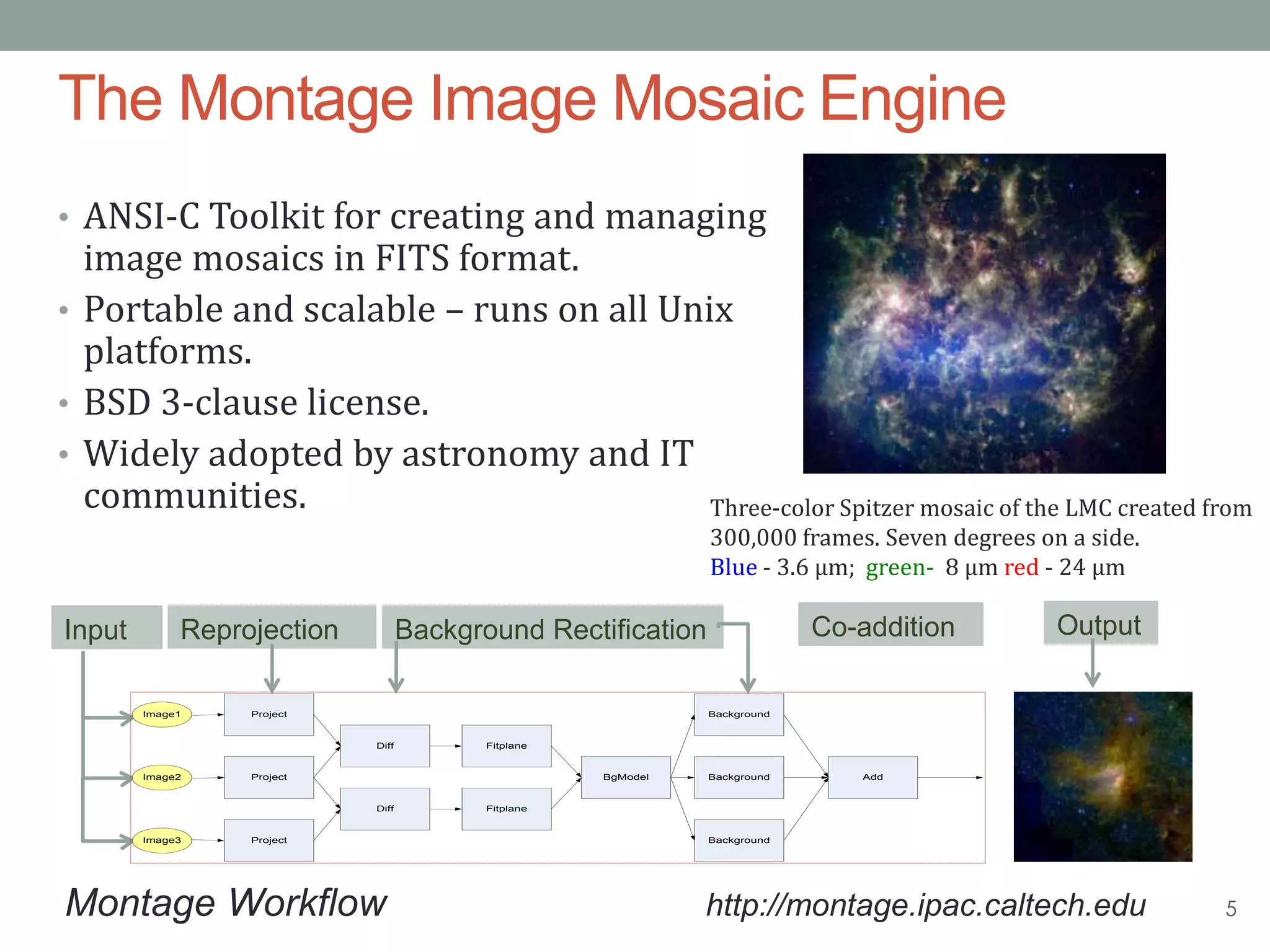
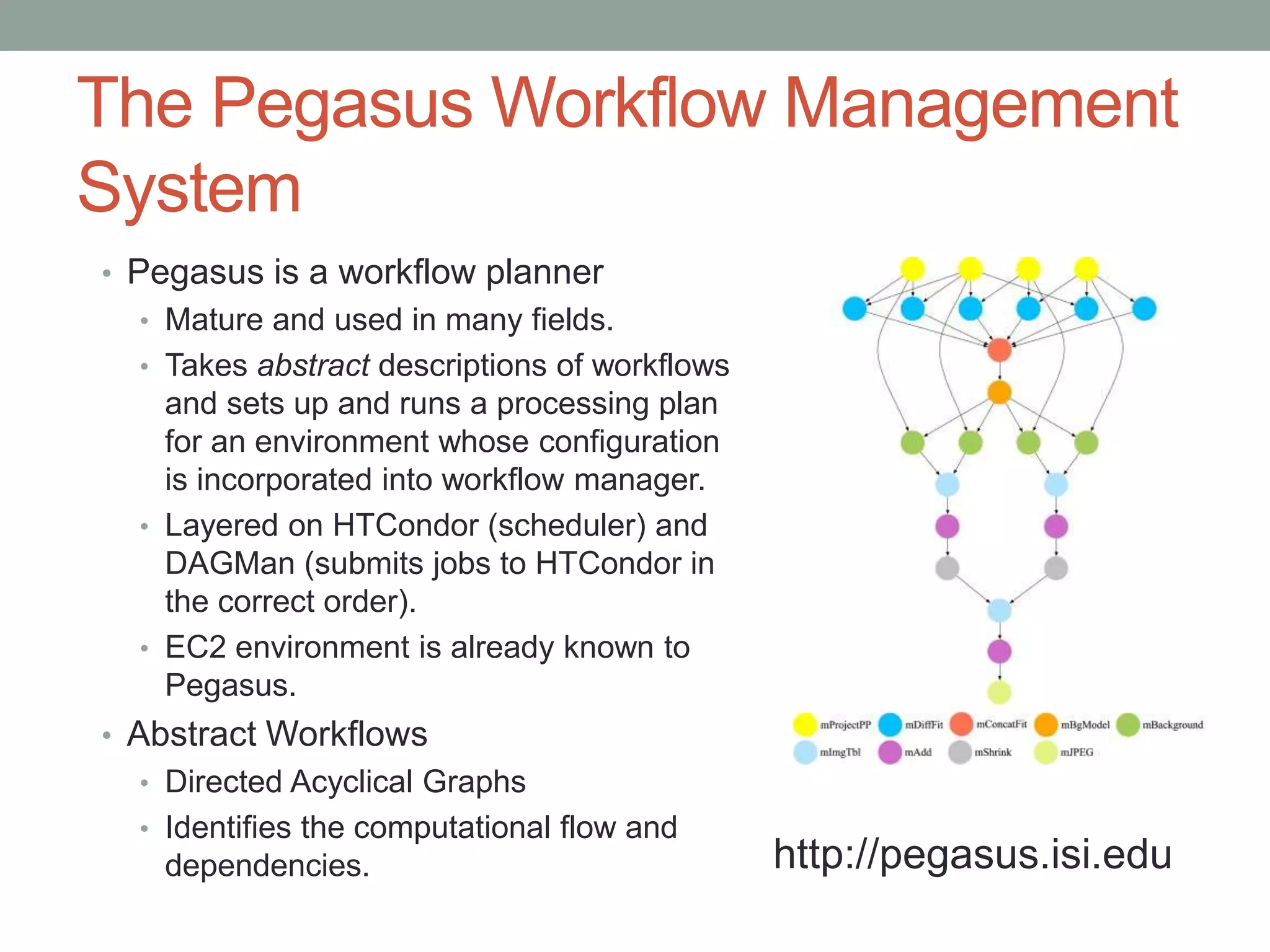
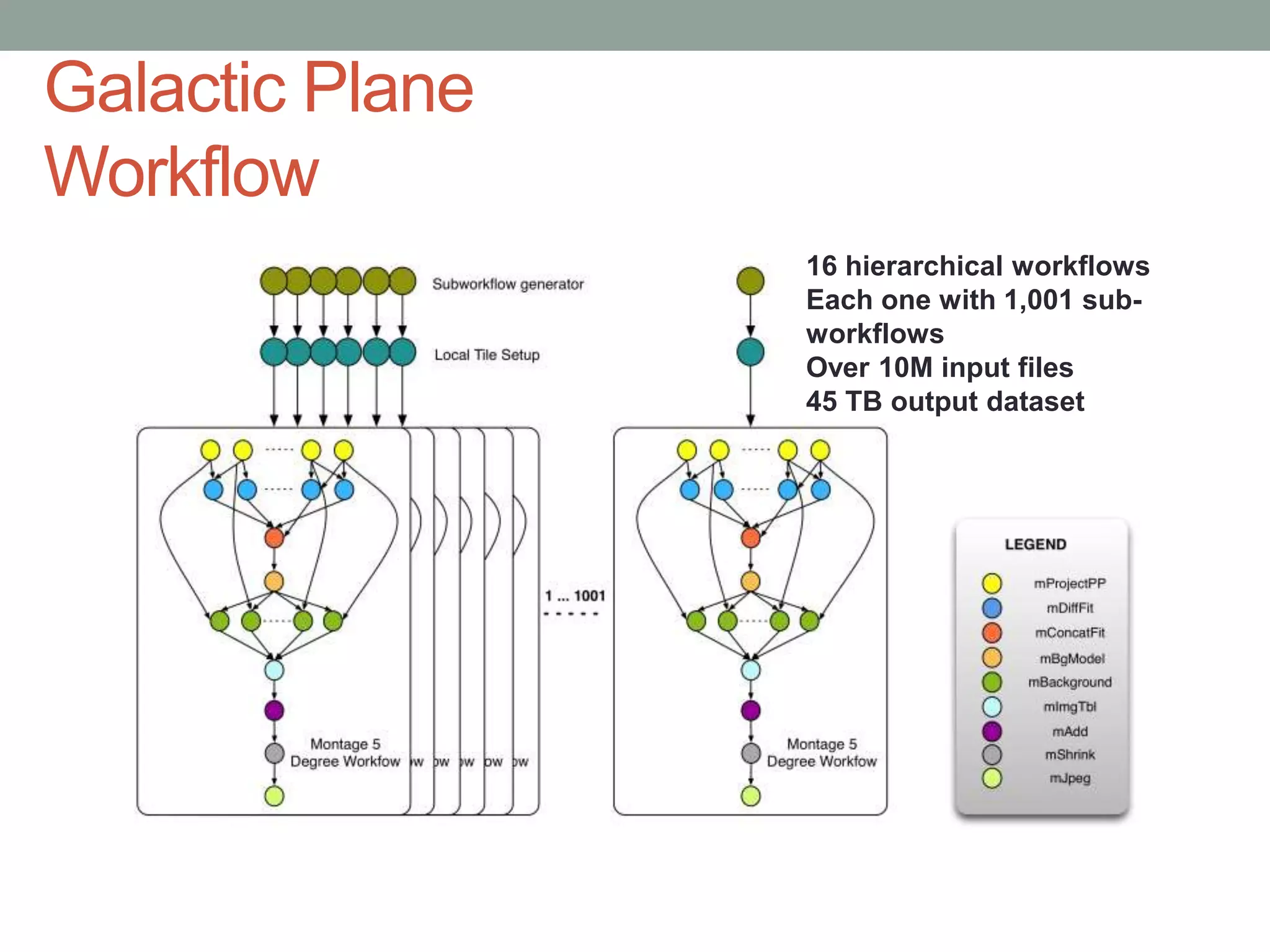
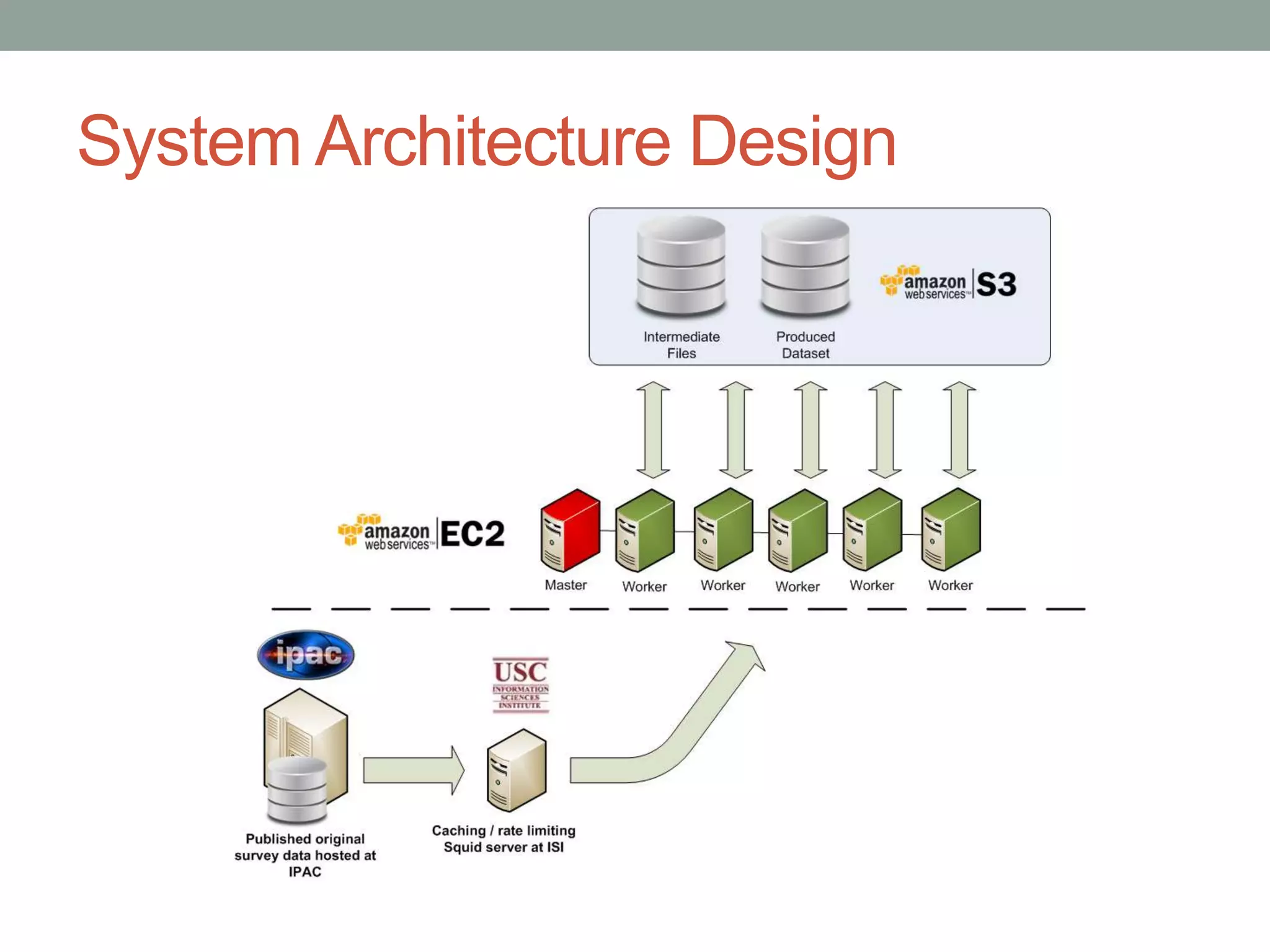
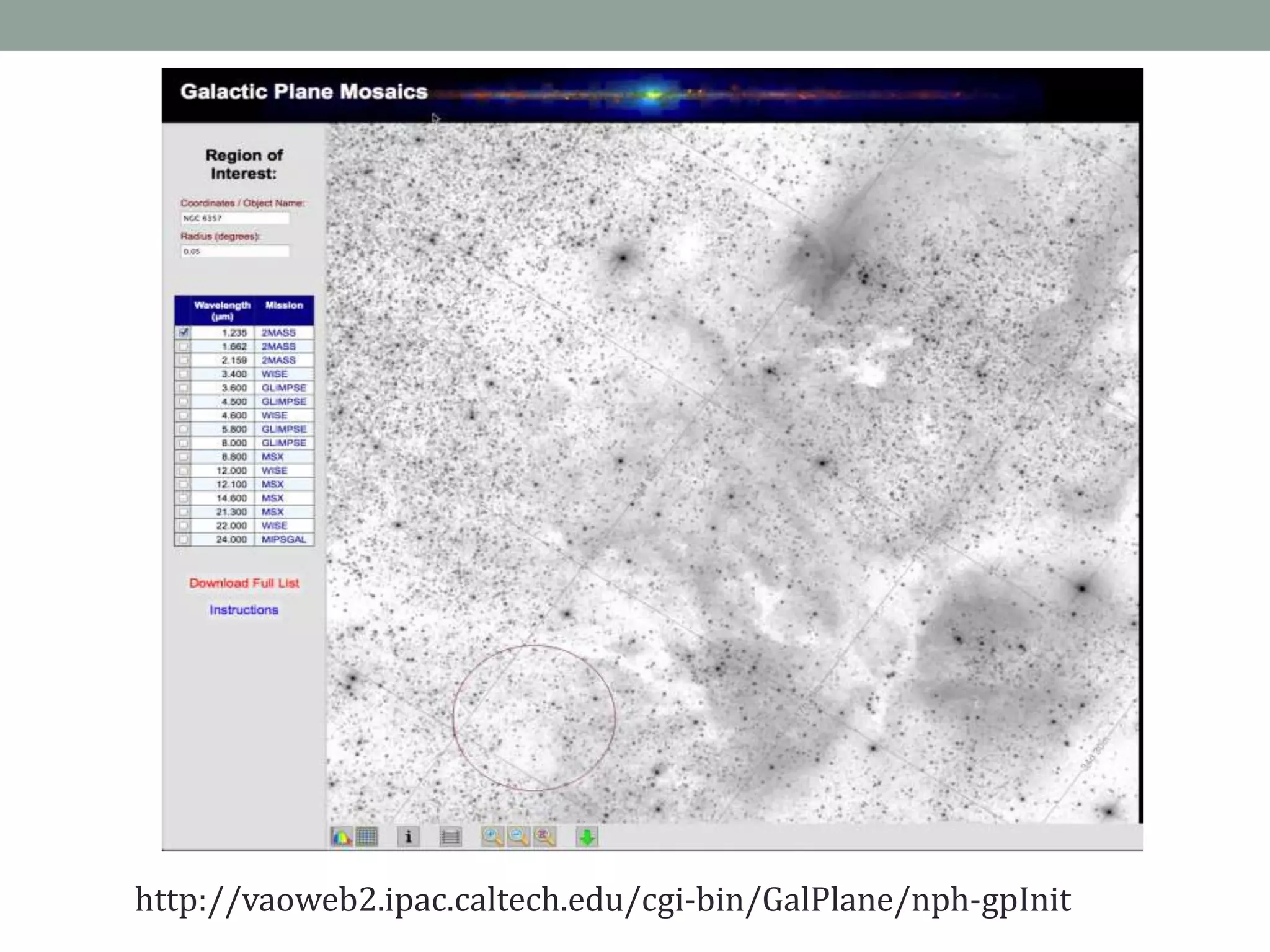
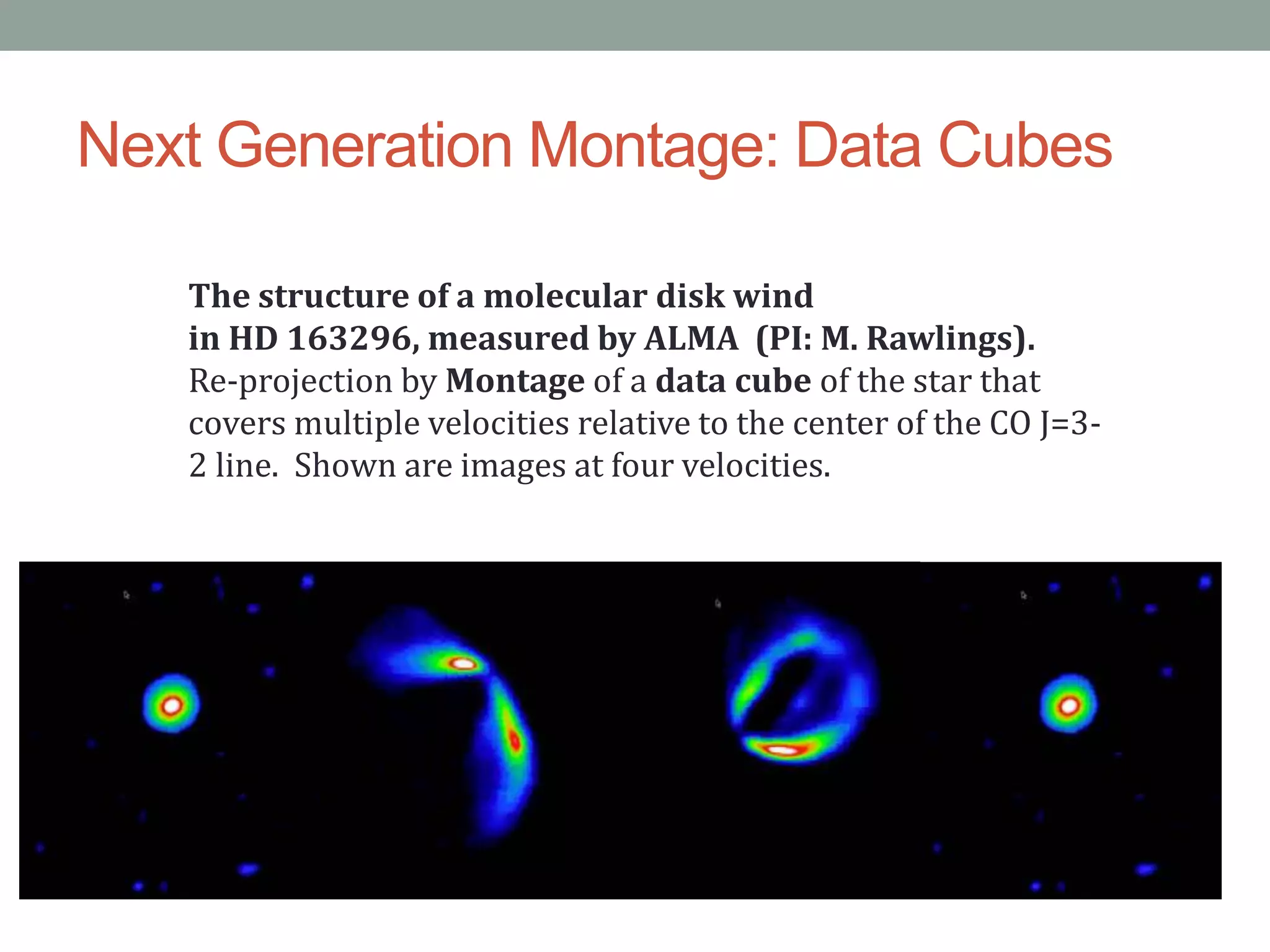
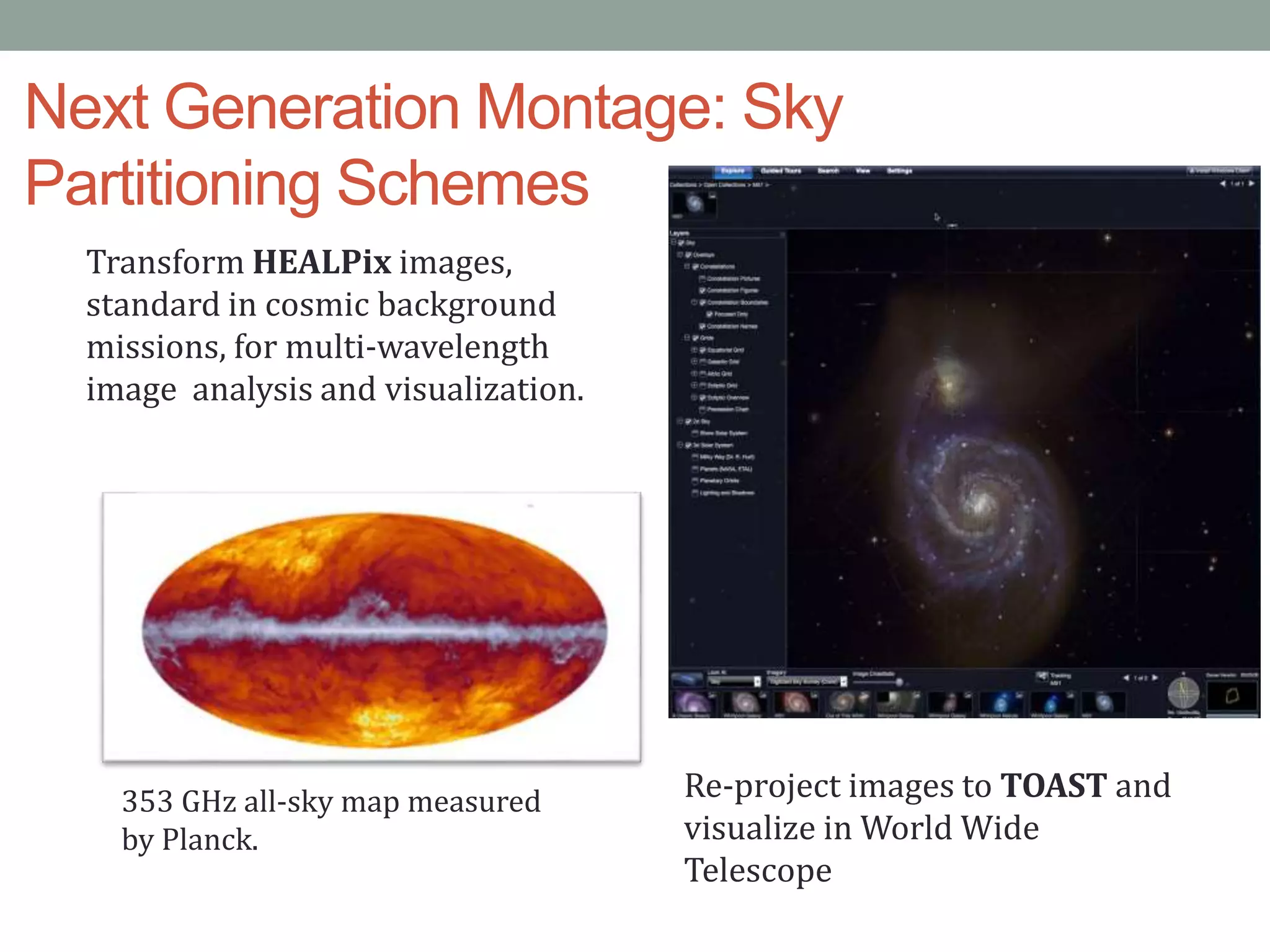
The document outlines the development of a multi-wavelength galactic plane atlas using Amazon Web Services, detailing tools like Montage for image processing and Pegasus for workflow management. It emphasizes the importance of cost optimization and careful instance selection when utilizing cloud services for astronomical computing. Key lessons include the value of open-source tools, the need for human oversight in operations, and challenges related to storage latency.