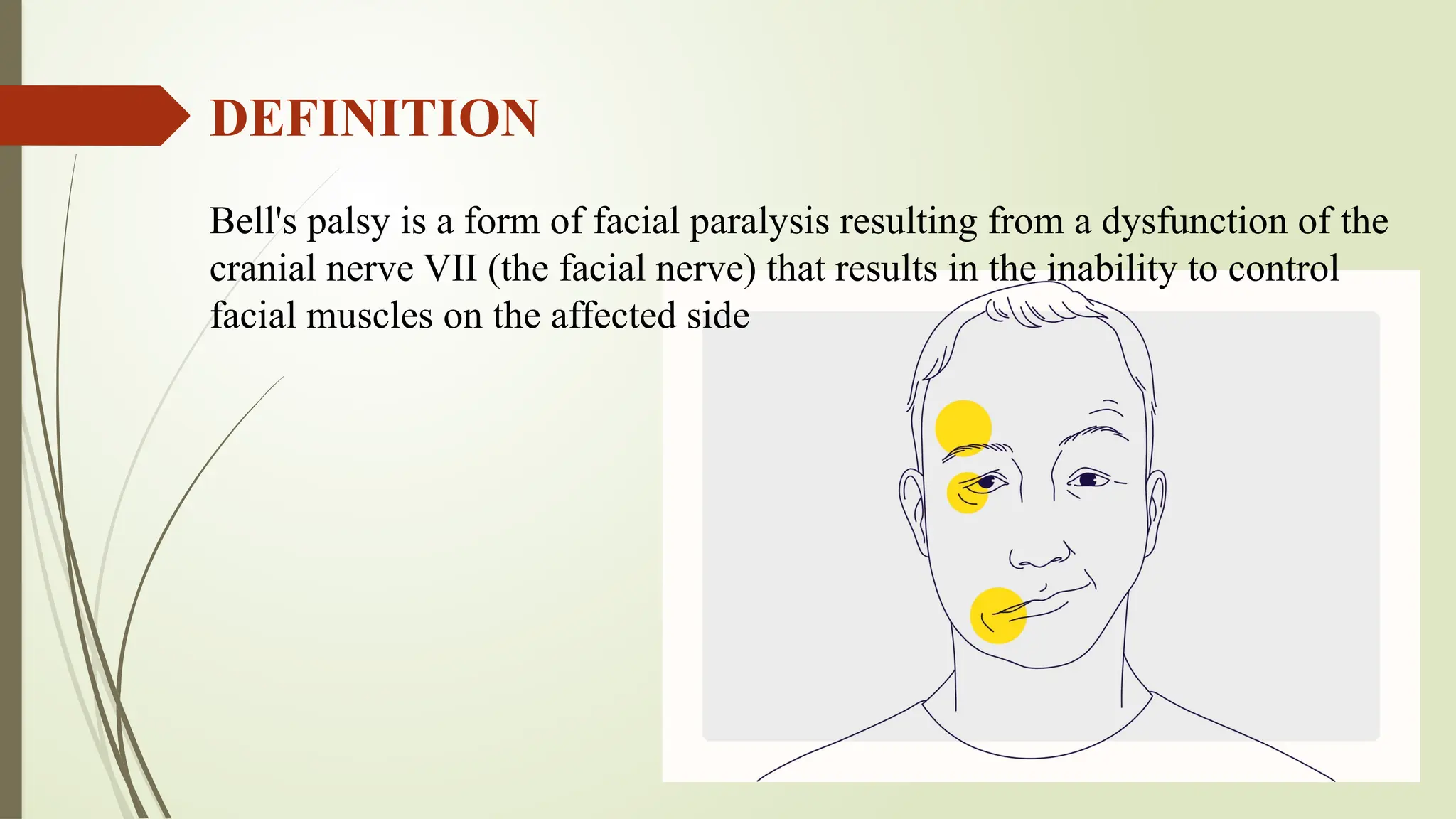
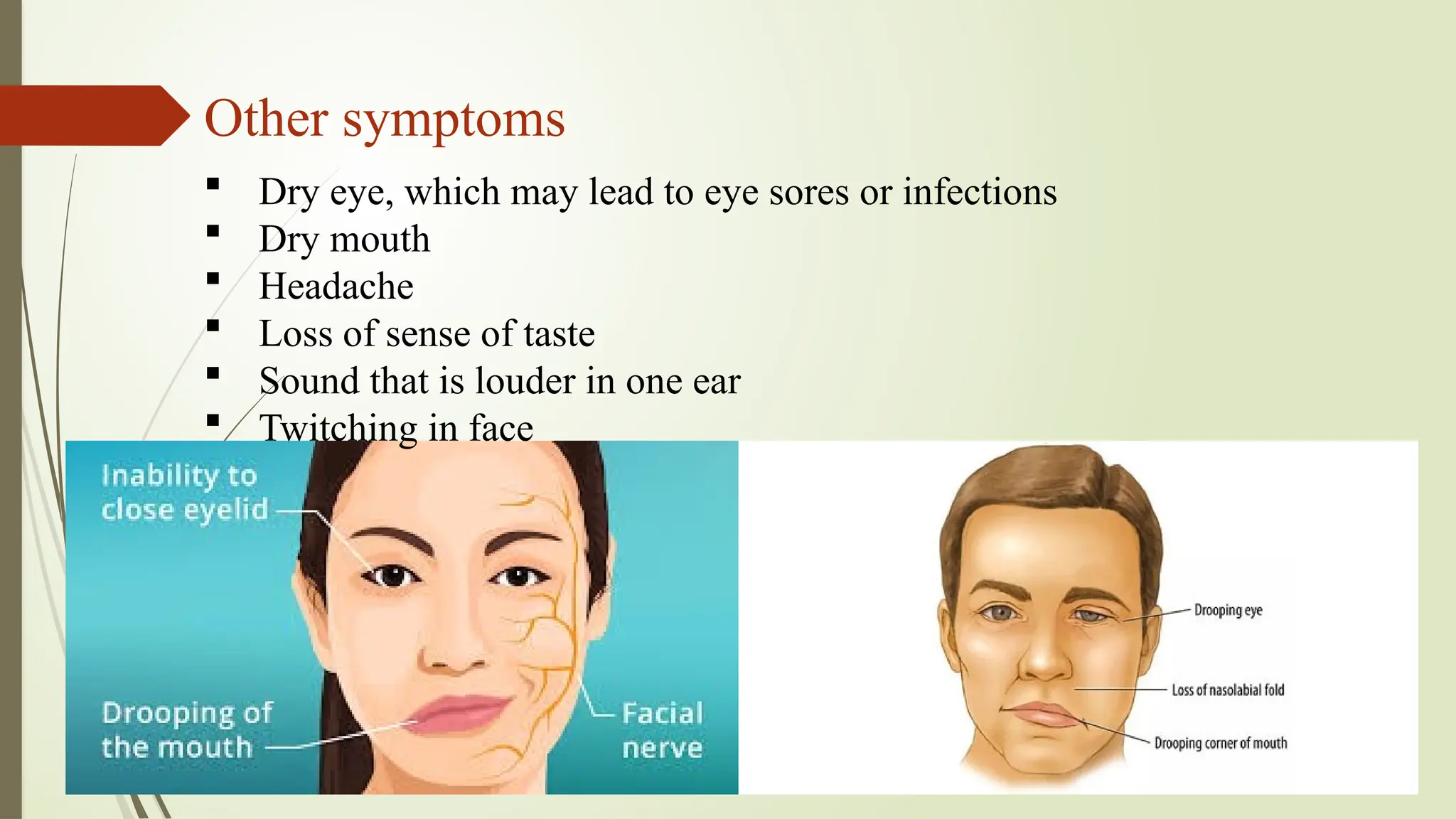
Bell's palsy is a type of facial paralysis caused by dysfunction of the facial nerve, leading to symptoms such as facial stiffness, drooping, and difficulty with facial expressions, usually affecting one side of the face. Diagnosis is primarily through health history and physical examination, with possible imaging tests if a brain tumor is suspected. Treatment may include eye lubricants, corticosteroids, antivirals, and physiotherapy, although there is no known prevention for the condition.