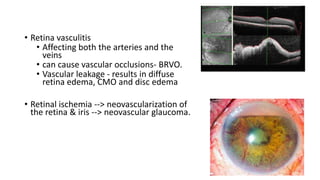
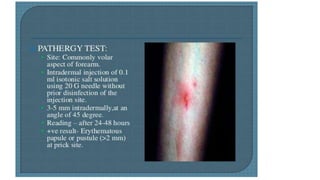
Behçet's disease is an inflammatory disorder characterized by symptoms including aphthous and genital ulcers and uveitis, primarily affecting individuals from the Eastern Mediterranean and Japan. The disease is thought to have an autoimmune etiology triggered by environmental factors in genetically predisposed individuals, leading to various complications including ocular and neurological issues. Management typically involves corticosteroids and immunomodulatory therapies to control acute symptoms and prevent relapses, with the prognosis varying based on several factors, including age and ethnicity.