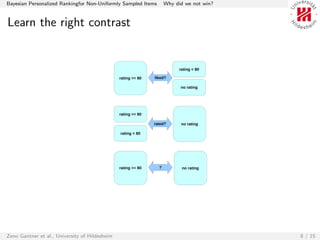
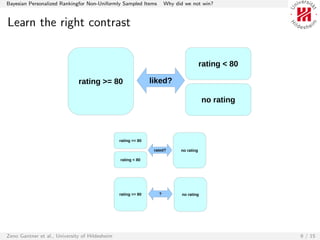
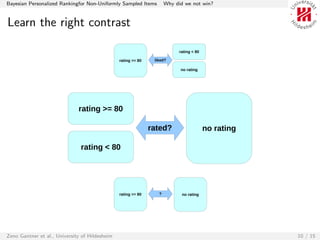
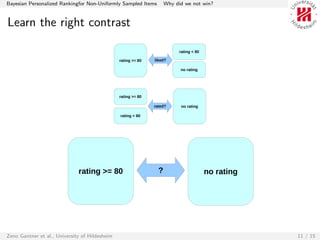
The document discusses Bayesian Personalized Ranking (BPR) for ranking items within the context of a competition. It explains the methodology adopted to tackle the item ranking problem using matrix factorization and introduces Weighted BPR to address issues with sampling bias in negative items. The authors reflect on the competition outcomes, acknowledging their model's effectiveness while also outlining areas for improvement and future exploration.



![Bayesian Personalized Rankingfor Non-Uniformly Sampled Items How did we tackle the problem?
How did we tackle the problem?
Bayesian Personalized Ranking:
2
BPR(DS ) = argmax ln σ(ˆu,i (Θ) − ˆu,j (Θ) )−λ Θ
s s
Θ
(u,i,j)∈DS
DS contains all pairs of positive and negative items for each user,
1
σ(x) = 1+e −x is the logistic function,
Θ represents the model parameters,
ˆu,i (Θ) is the predicted score for user u and item i, and
s
λ Θ 2 is a regularization term to prevent overfitting.
interpretation 1: reduce ranking to pairwise classif. [Balcan et al. 2008]
interpretation 2: optimize for smoothed area under the ROC curve (AUC)
Model: matrix factorization
Learning: stochastic gradient ascent
[Rendle et al., UAI 2009]
Zeno Gantner et al., University of Hildesheim 4 / 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bpr-kddcup-110825120234-phpapp01/85/Bayesian-Personalized-Ranking-for-Non-Uniformly-Sampled-Items-4-320.jpg)