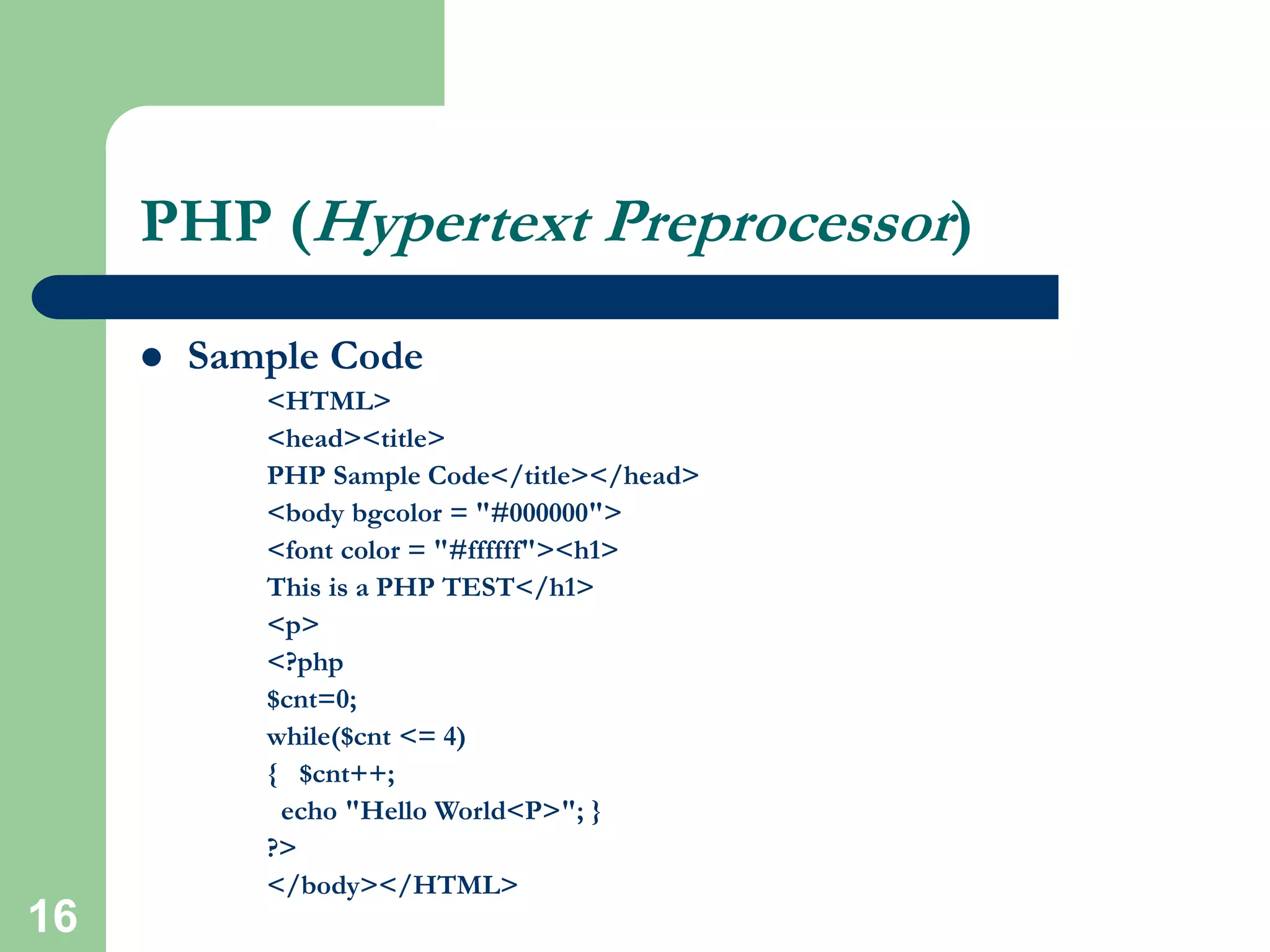
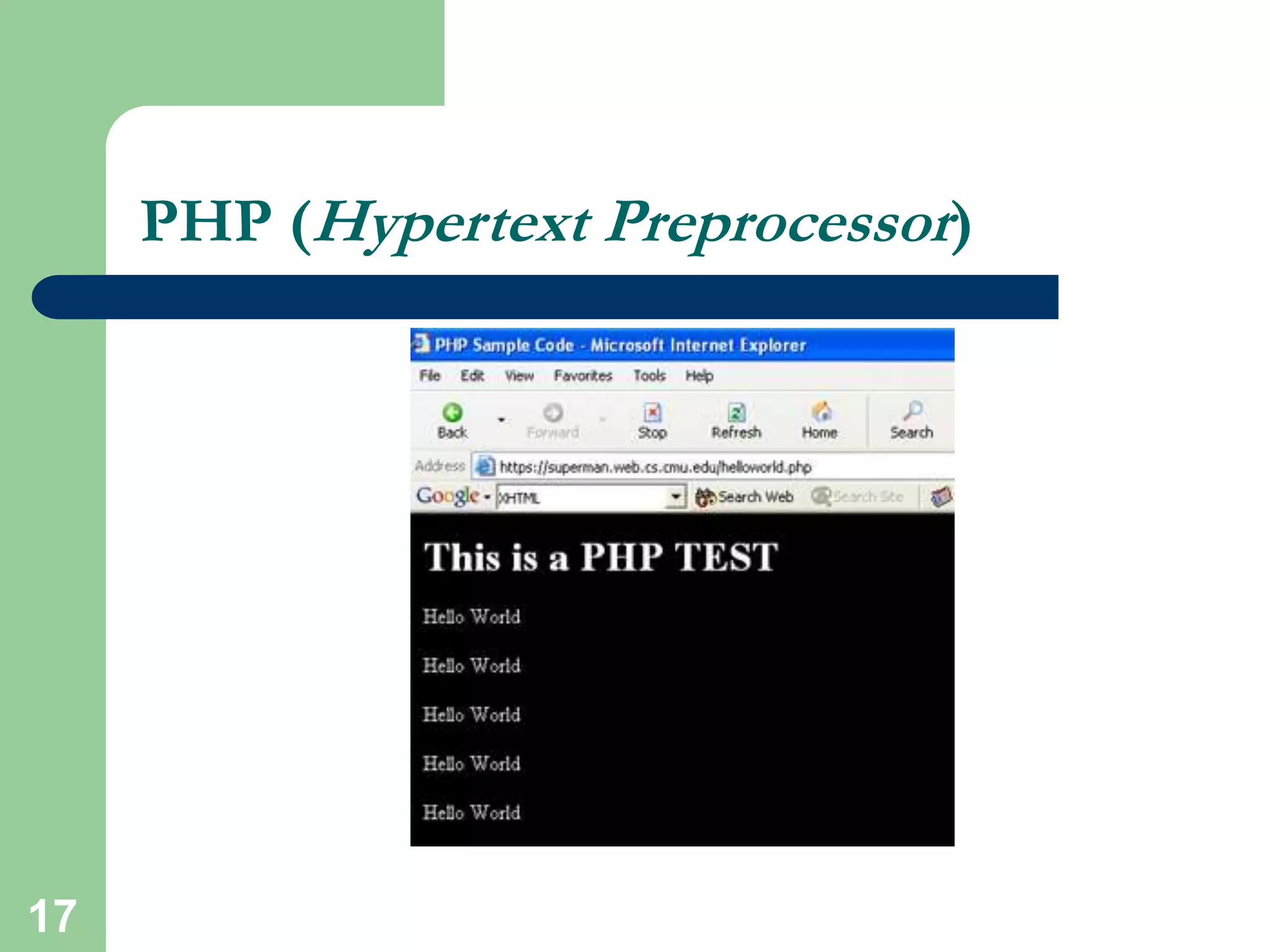
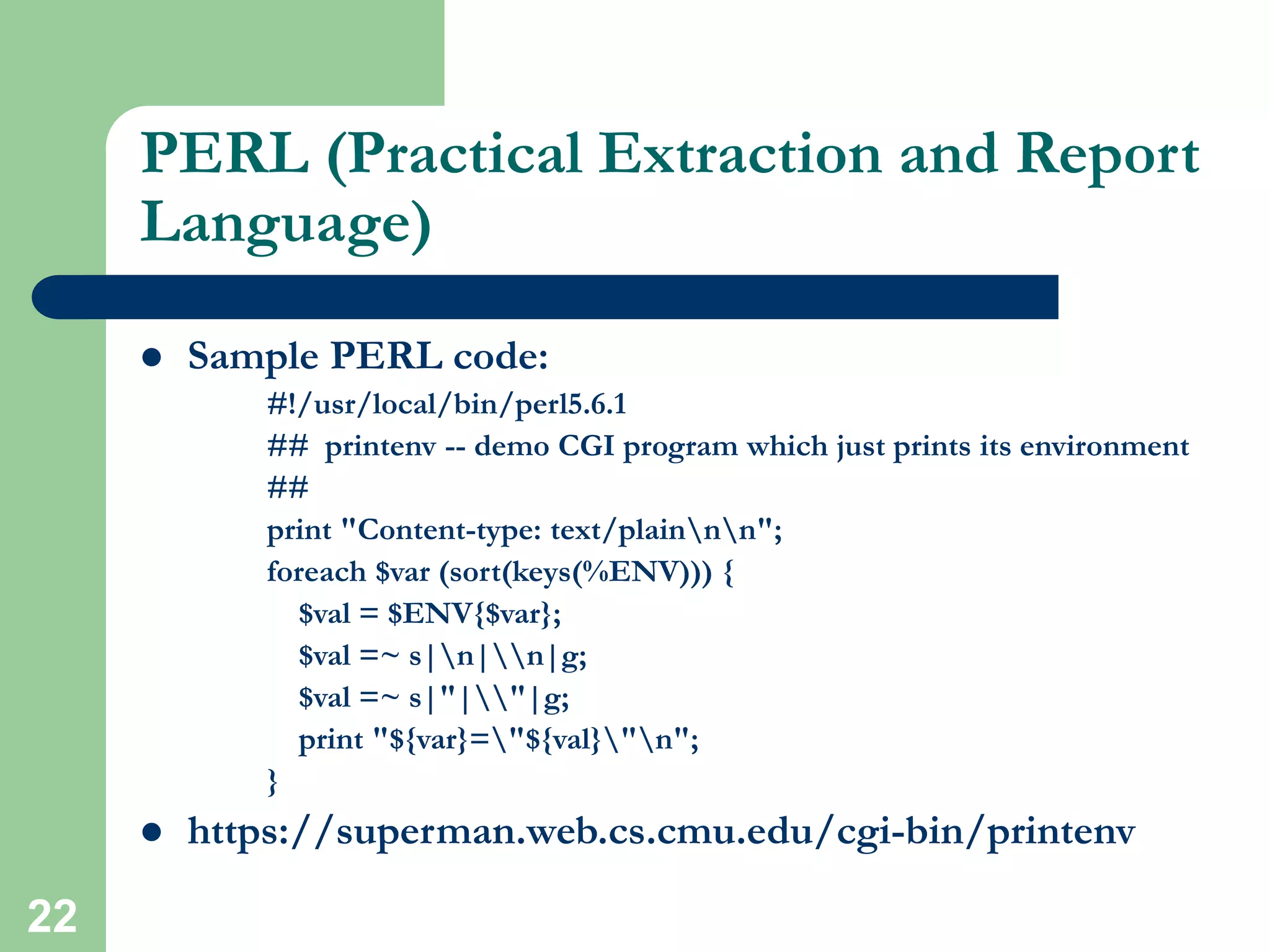
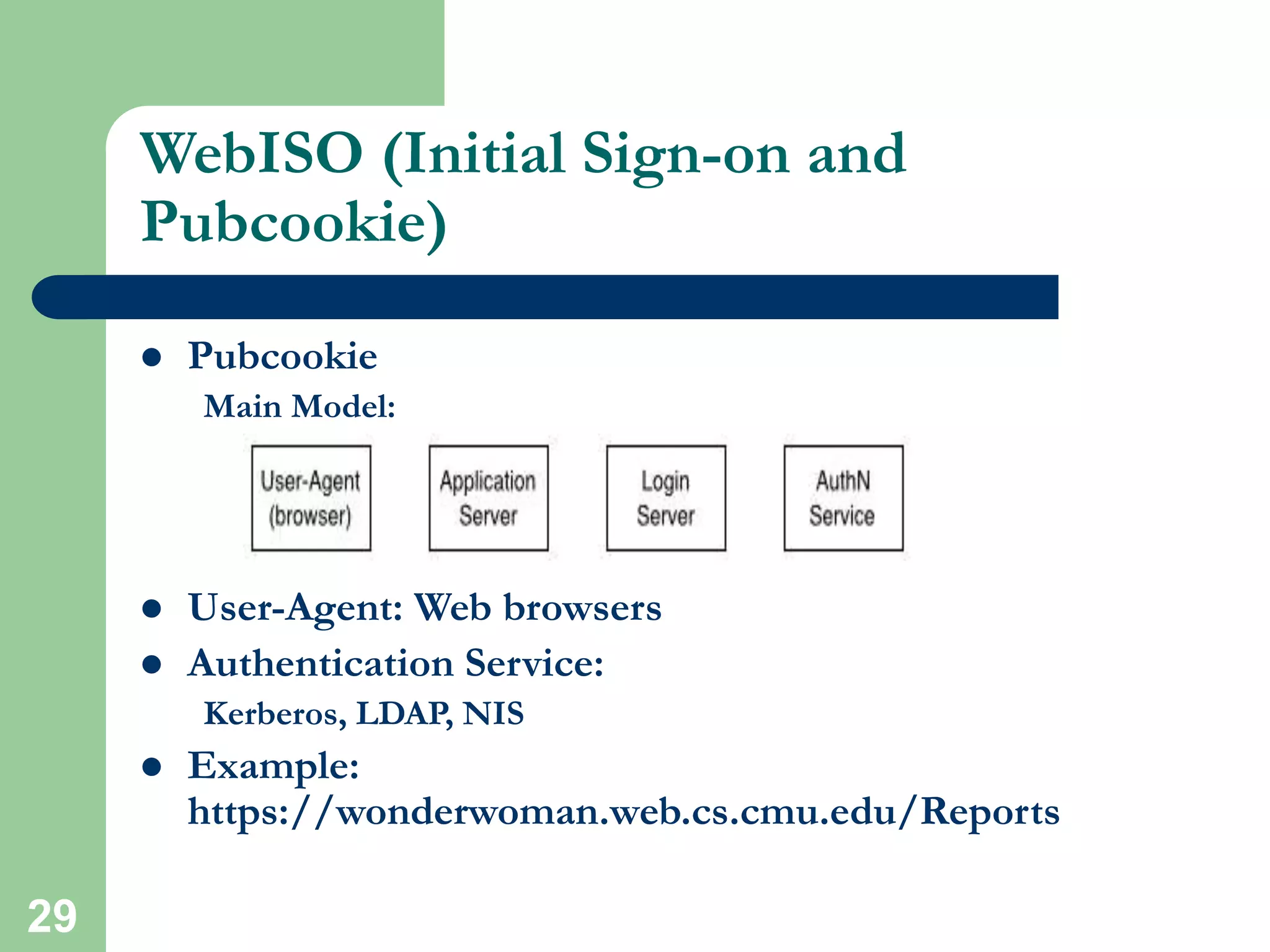
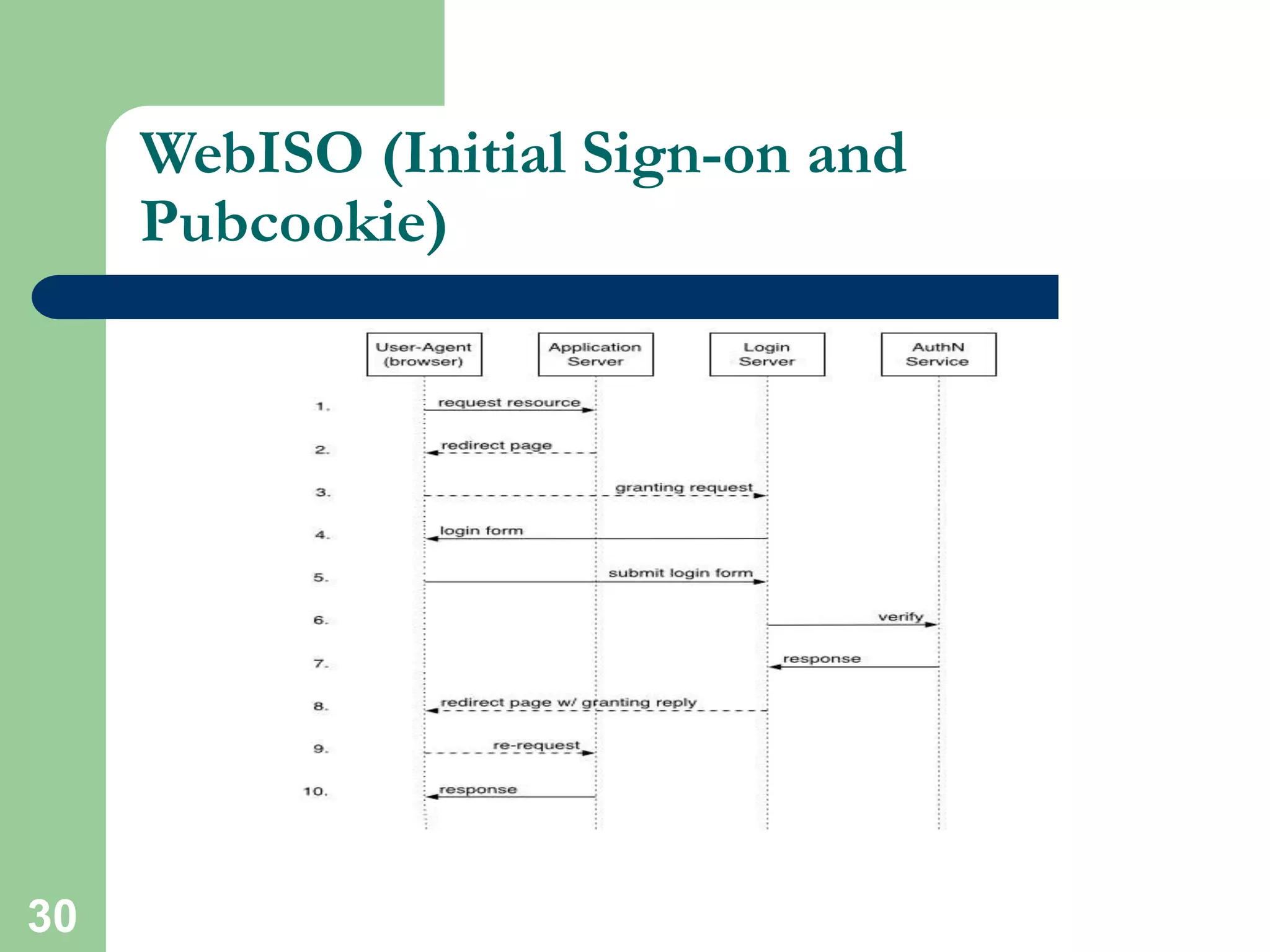
HTML is the standard markup language used to create web pages and defines tags like <html> and <body> to structure documents. CSS can be used to style and lay out HTML elements. JavaScript and other scripting languages can be embedded to add interactive functionality. Server-side languages like PHP and Perl are commonly used via CGI to dynamically generate webpage content. Security is important and HTTPS, SSL, and mod_ssl can encrypt server connections. Technologies like databases, XML, Java applets, and Flash add further capabilities to websites.