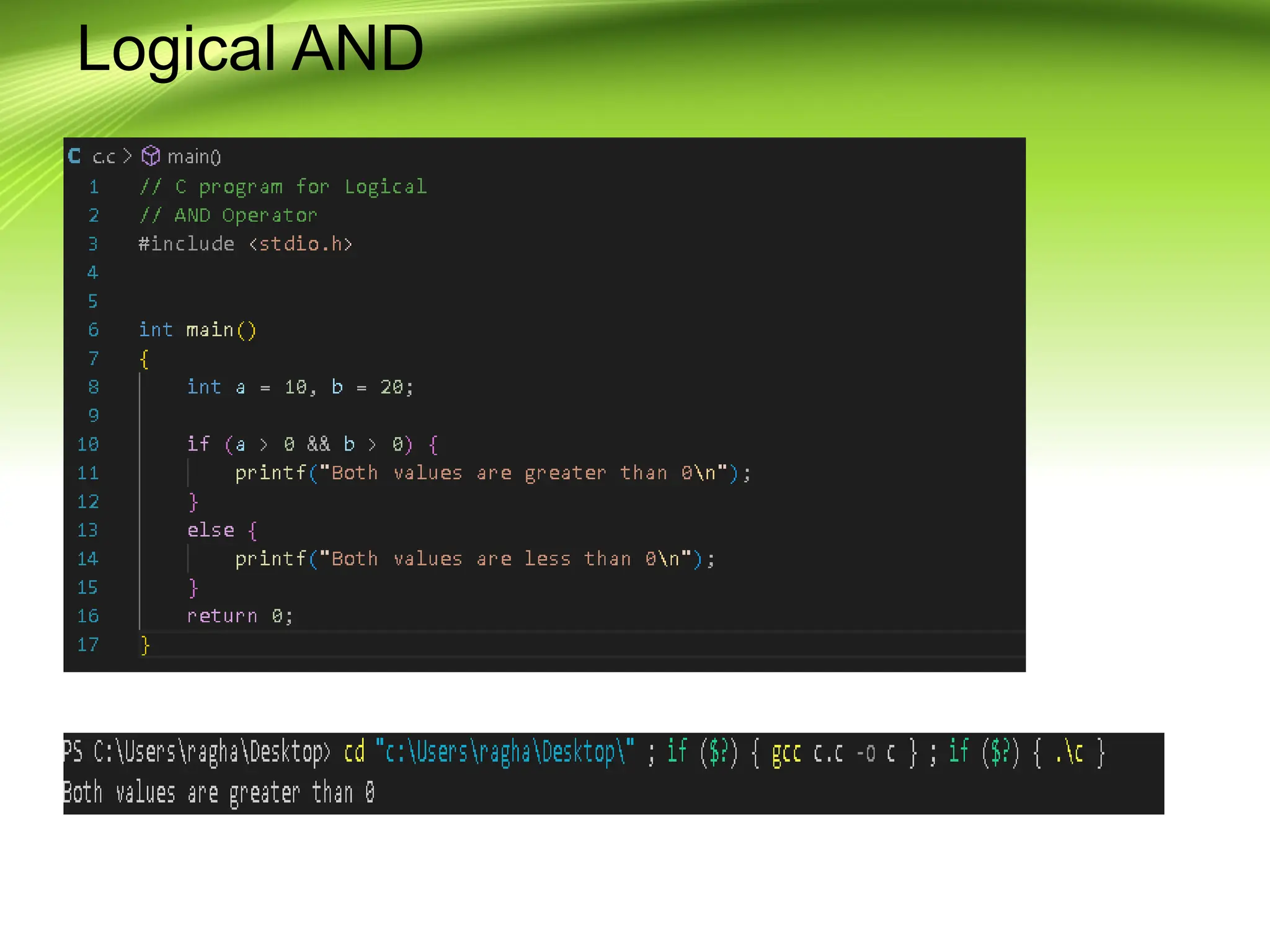
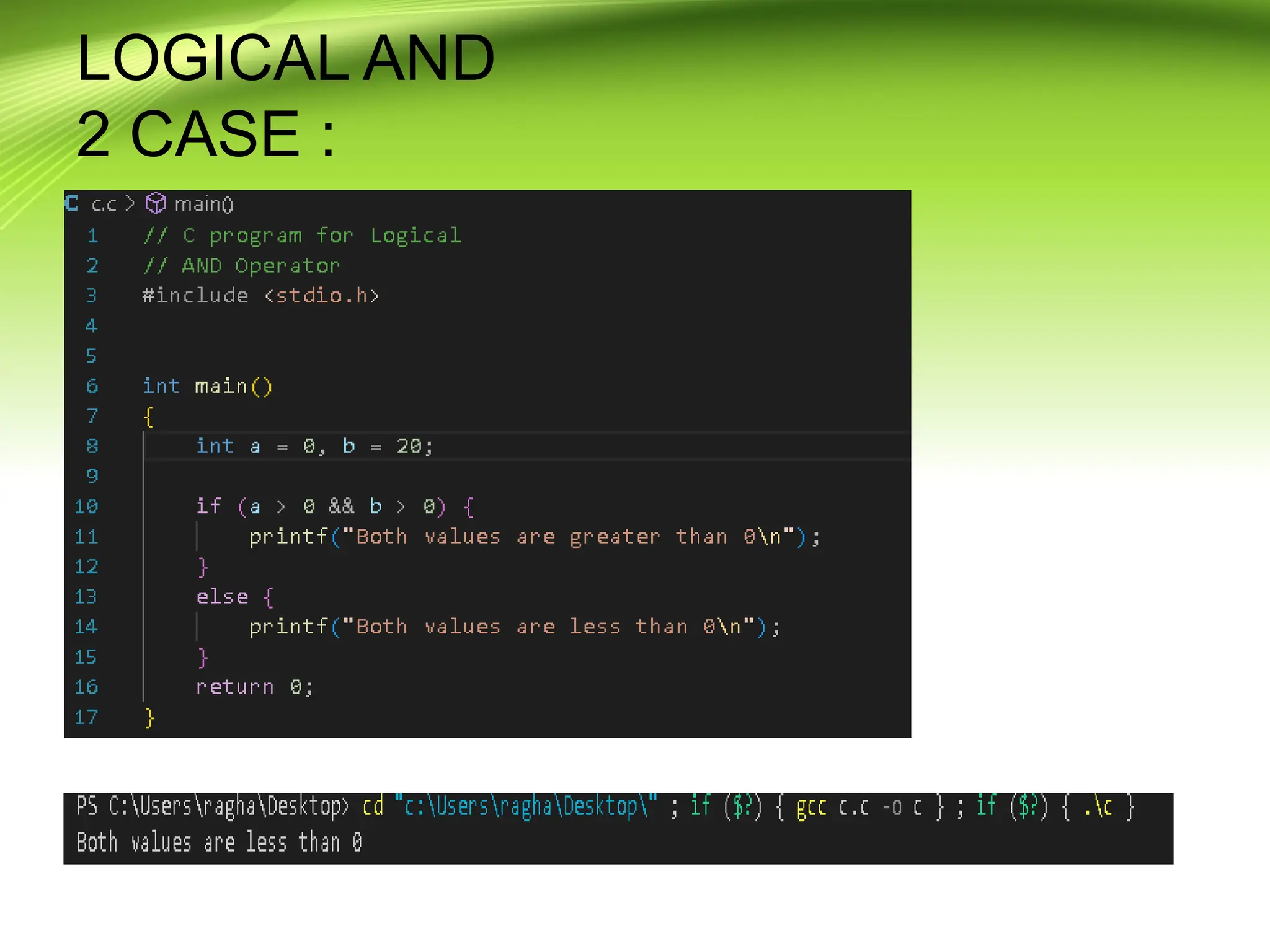
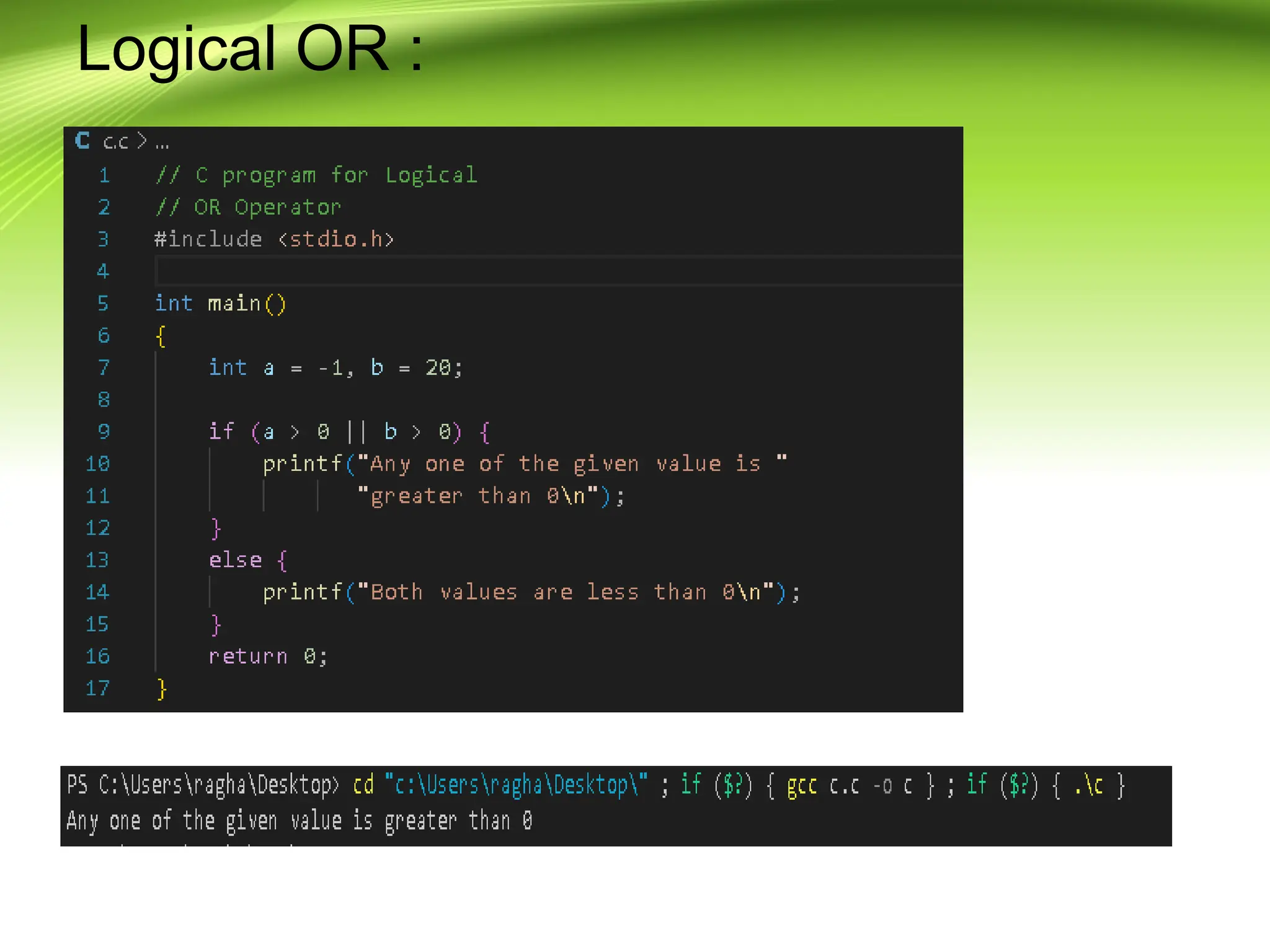
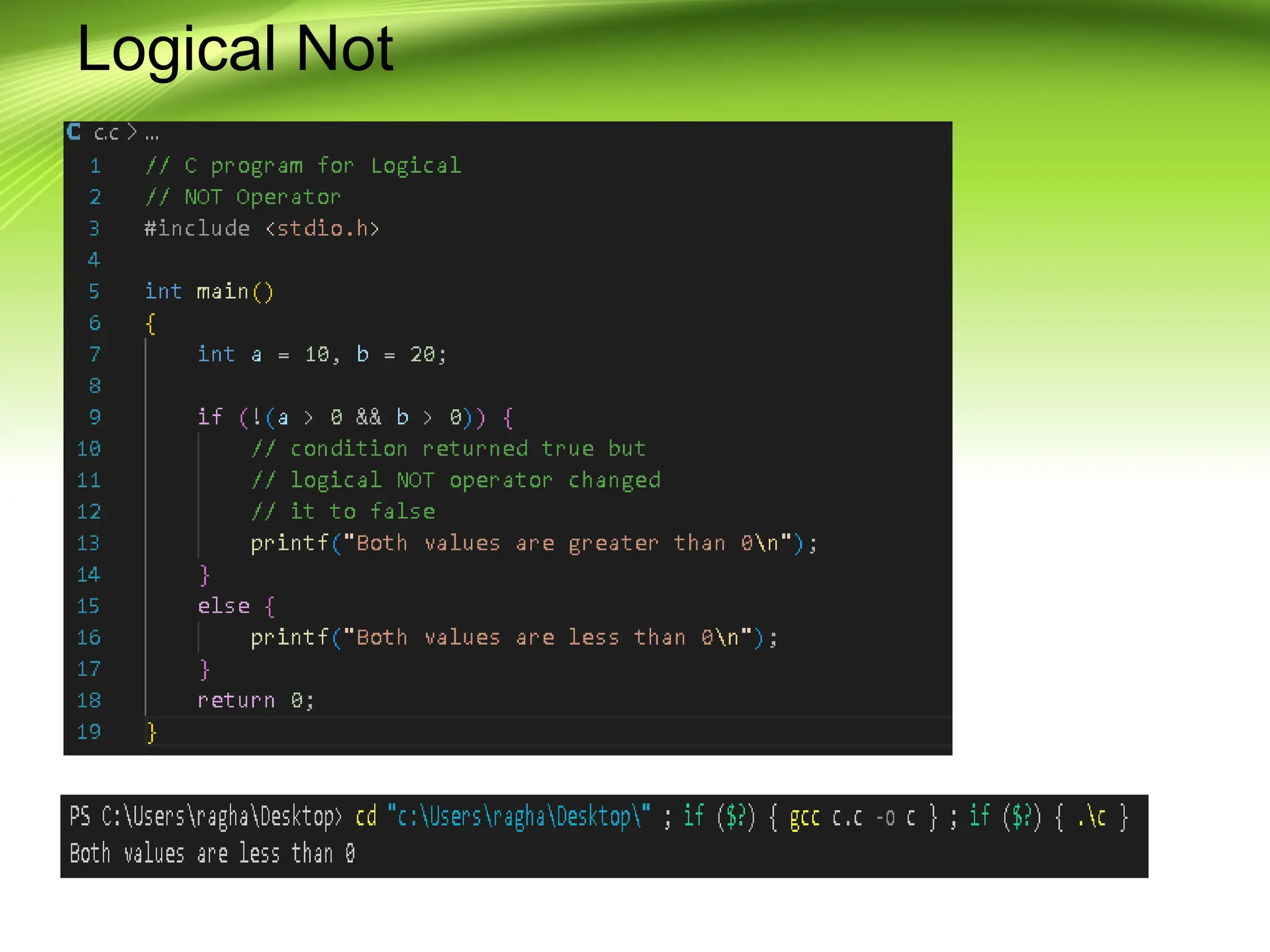
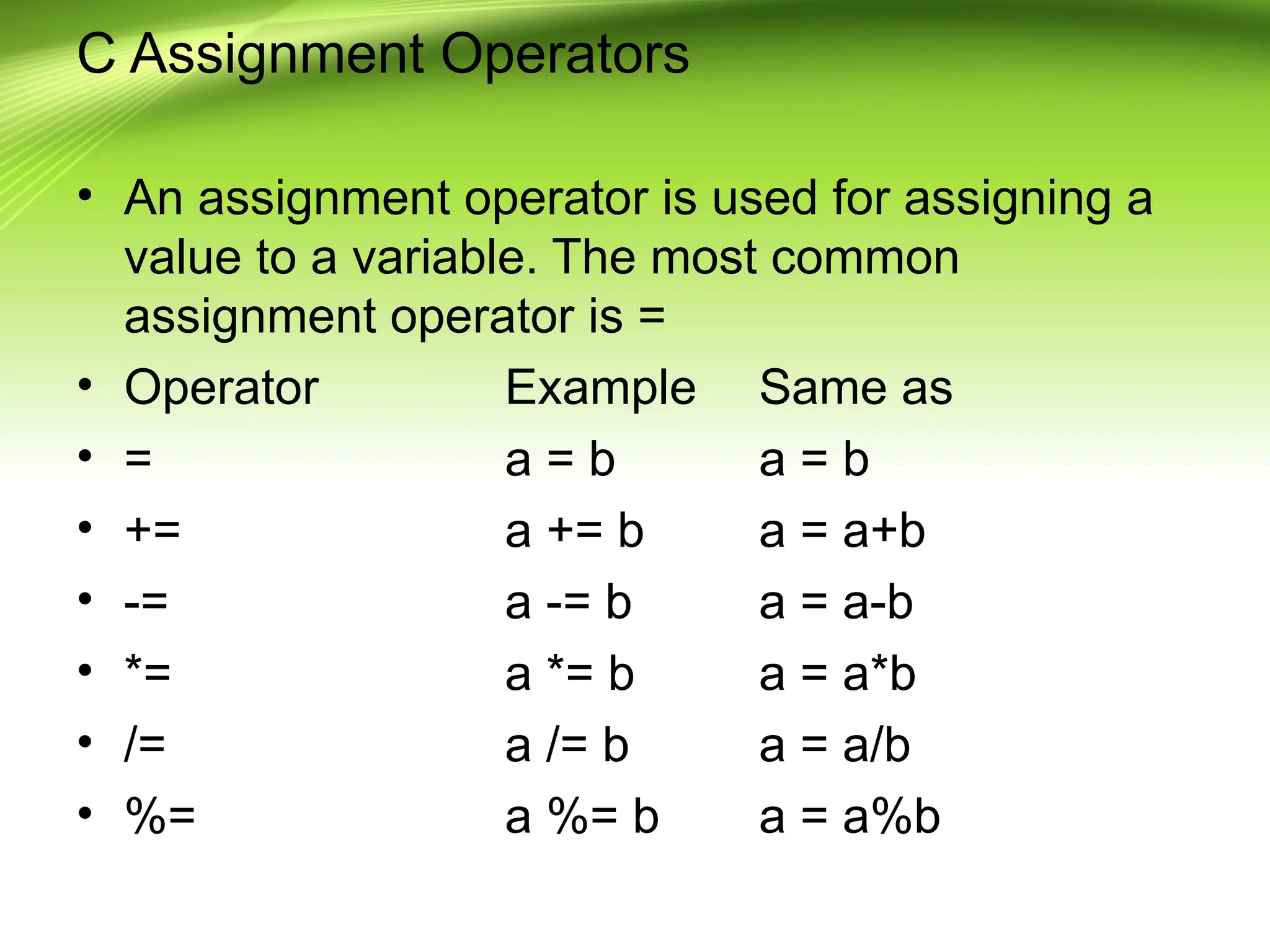
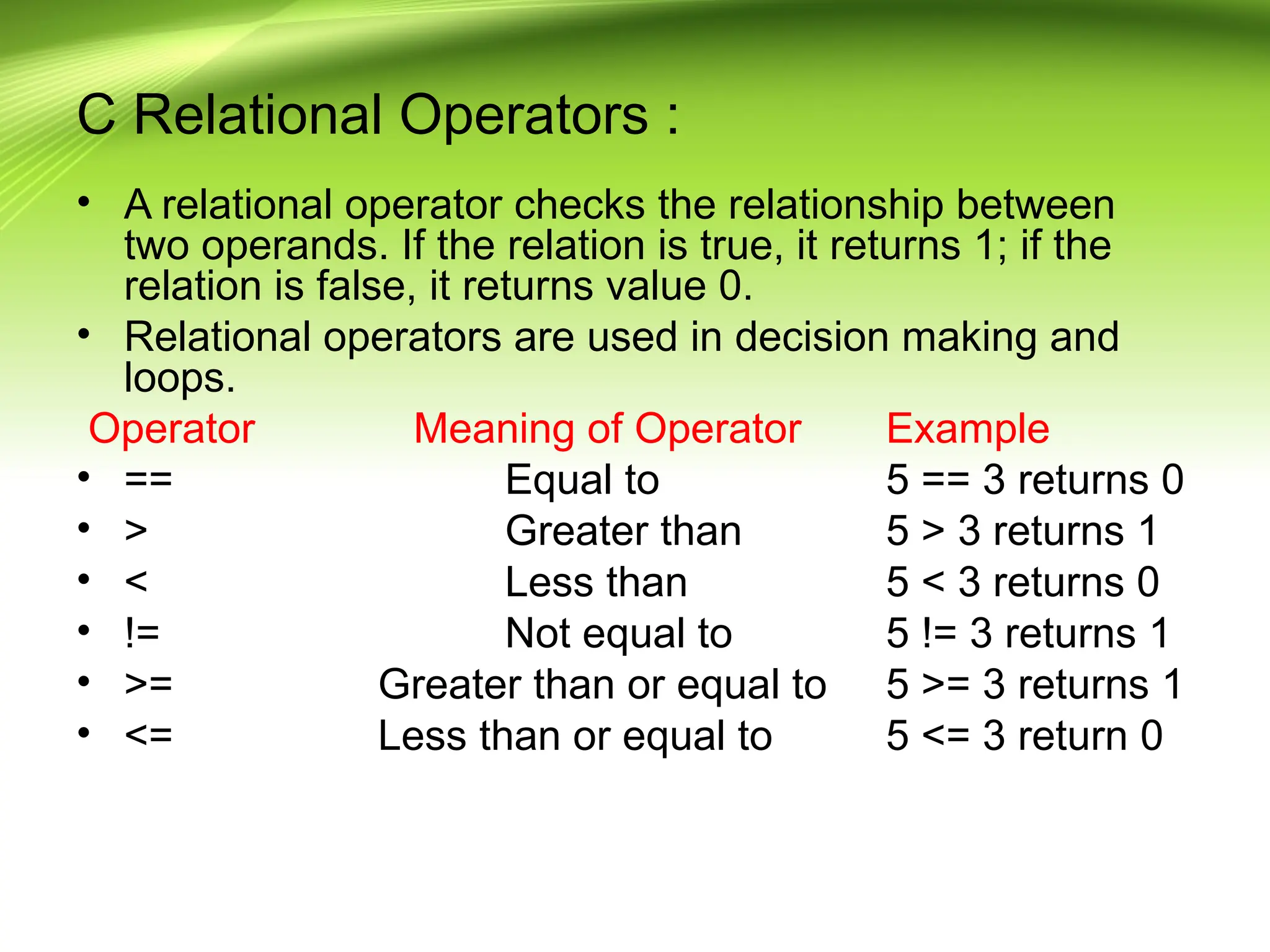
The document provides an overview of the C programming language, developed by Dennis Ritchie in the 1970s, emphasizing its structured and general-purpose nature. It details various operators in C, including arithmetic, assignment, relational, logical, and increment/decrement operators, explaining their functions and usage. The discussion includes examples of how these operators work in practice.