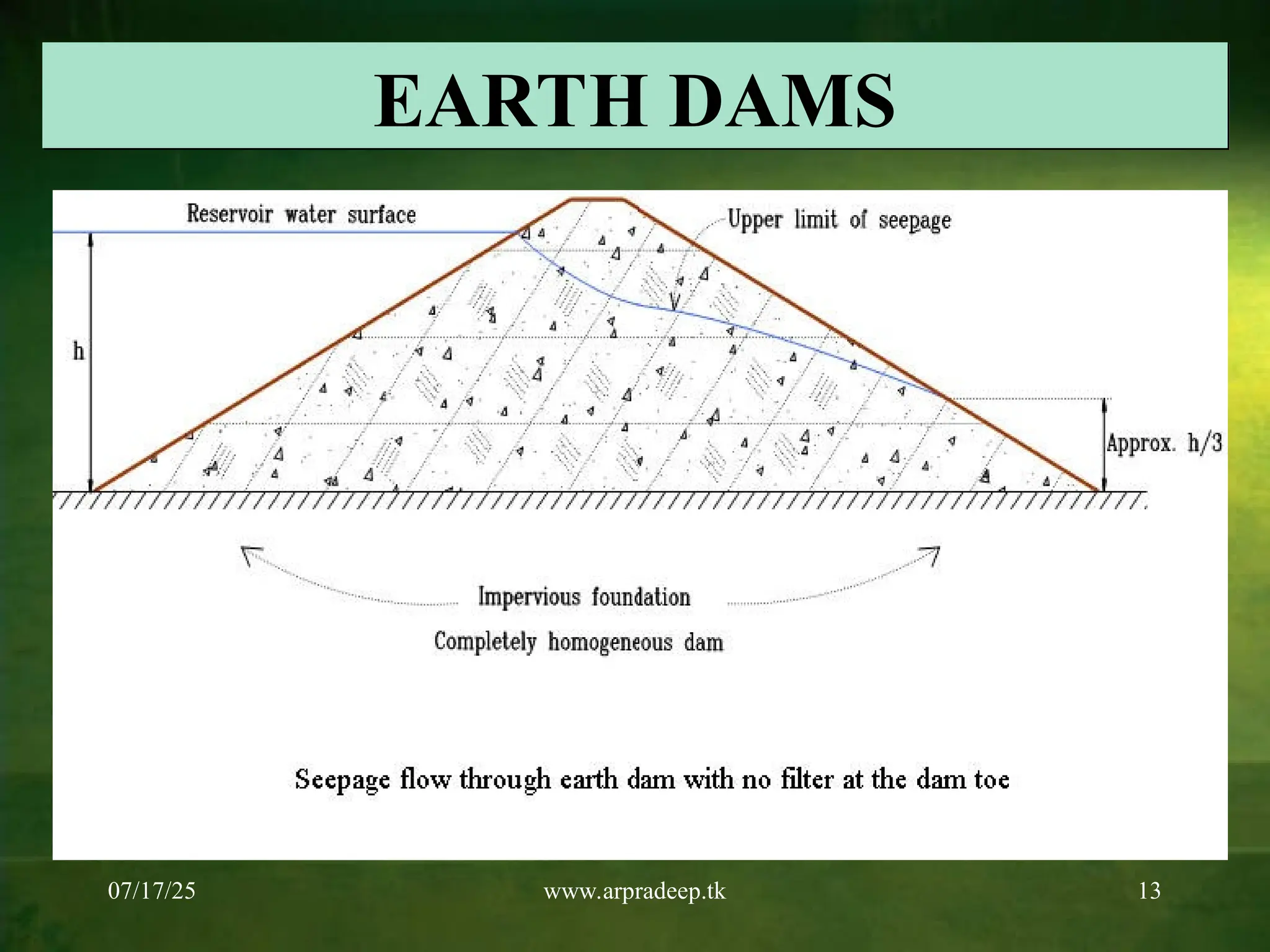
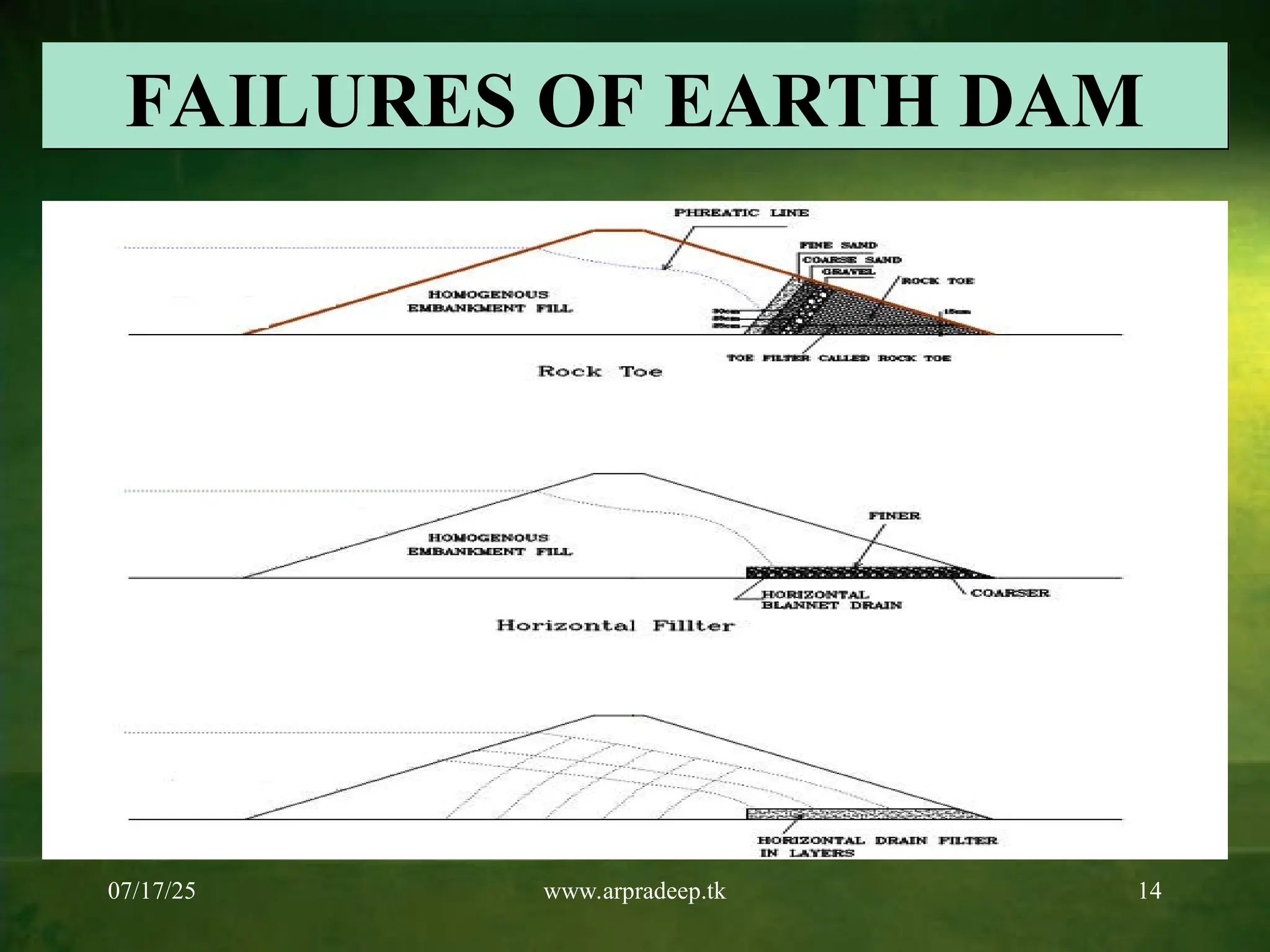
modular robot is becoming a prevalent research object in robots because of its unique configuration advantages and performance characteristics. It is possible to form robot configurations with different functions by reconfiguring functional modules. This paper focuses on studying the modular robot’s configuration design and self-reconfiguration process and hopes to realize the industrial application of the modular self-reconfiguration robot to a certain extent. We design robotic configurations with different DOF based on the cellular module of the hexahedron and perform the kinematic analysis of