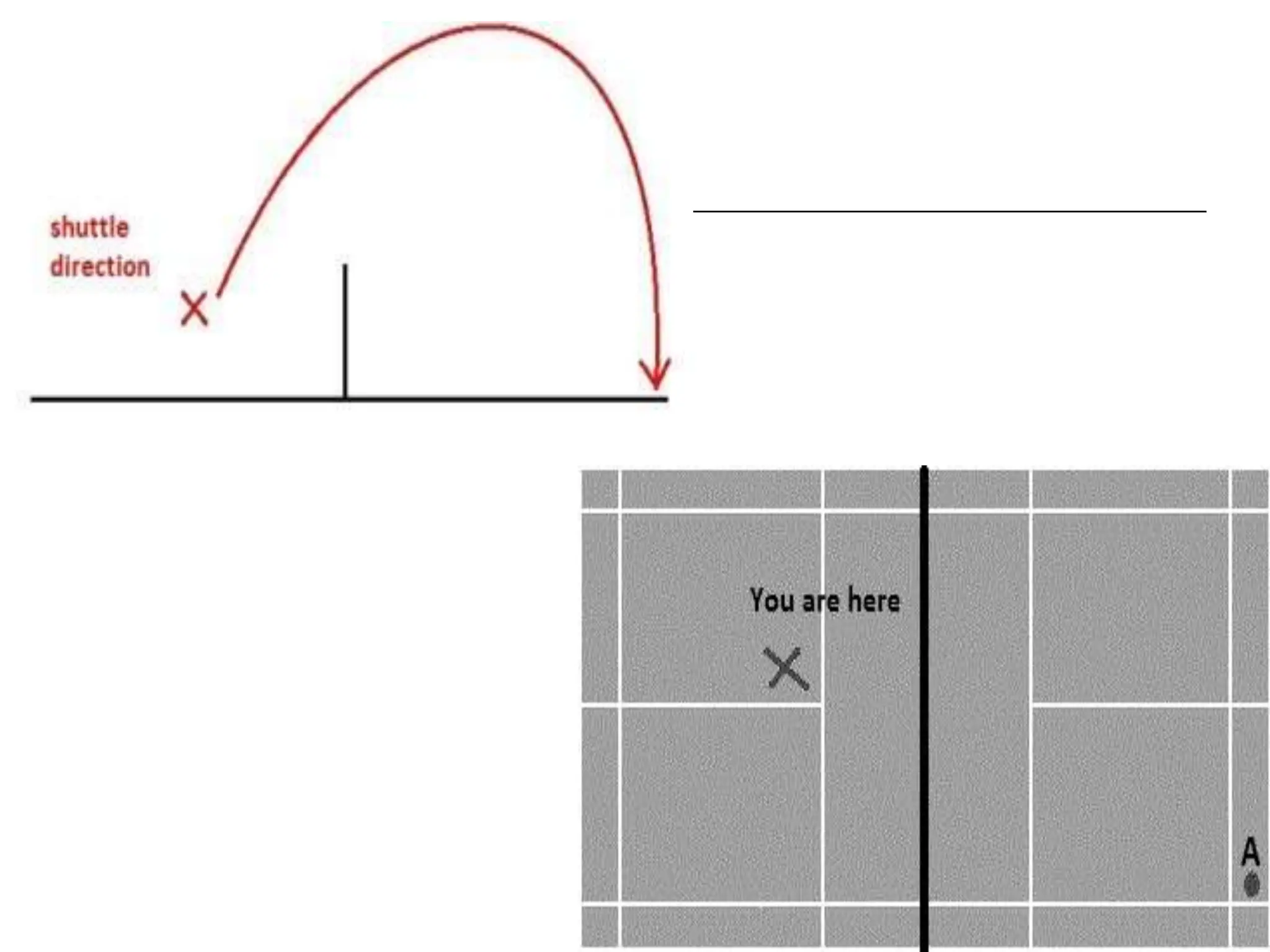
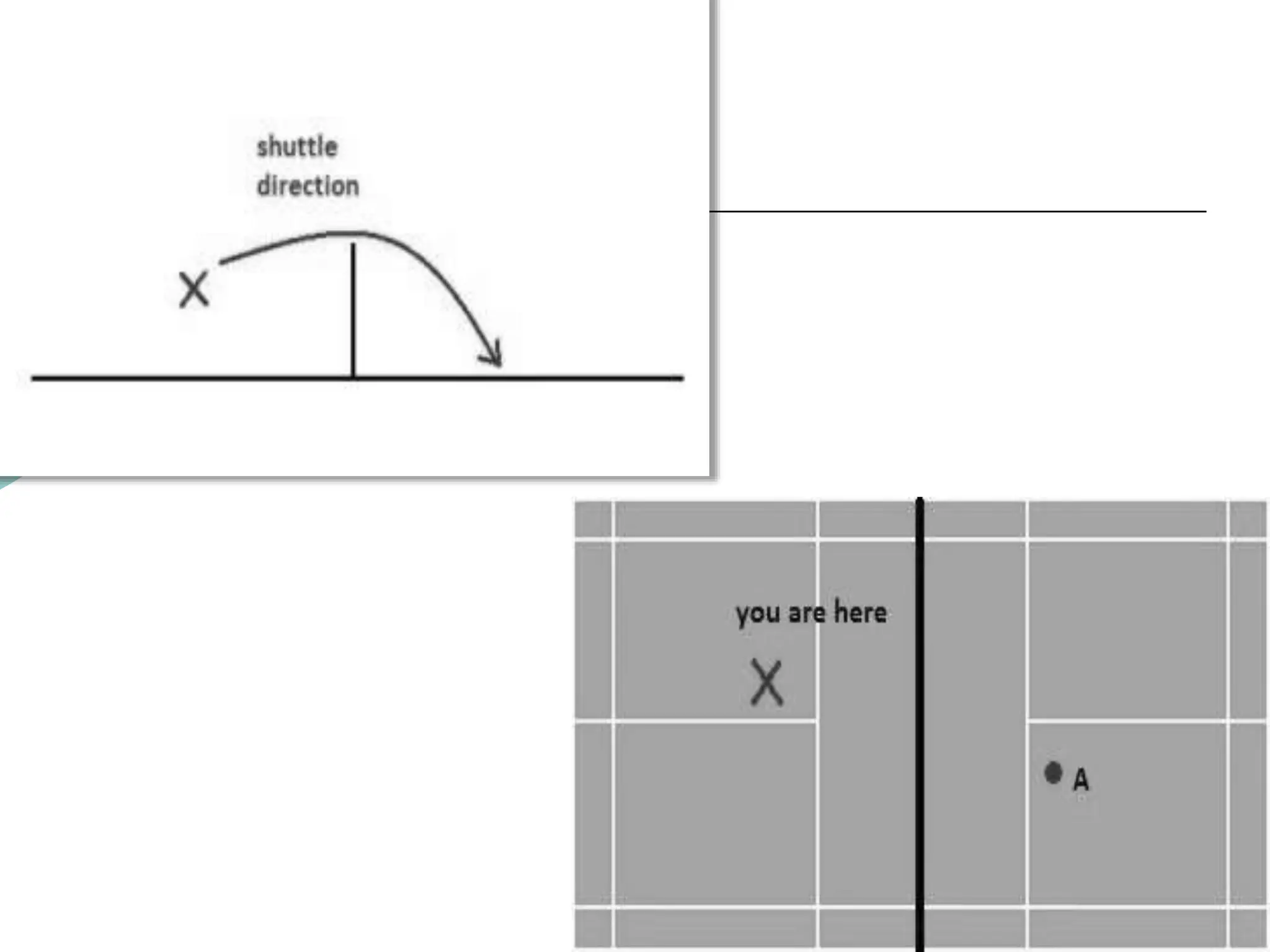
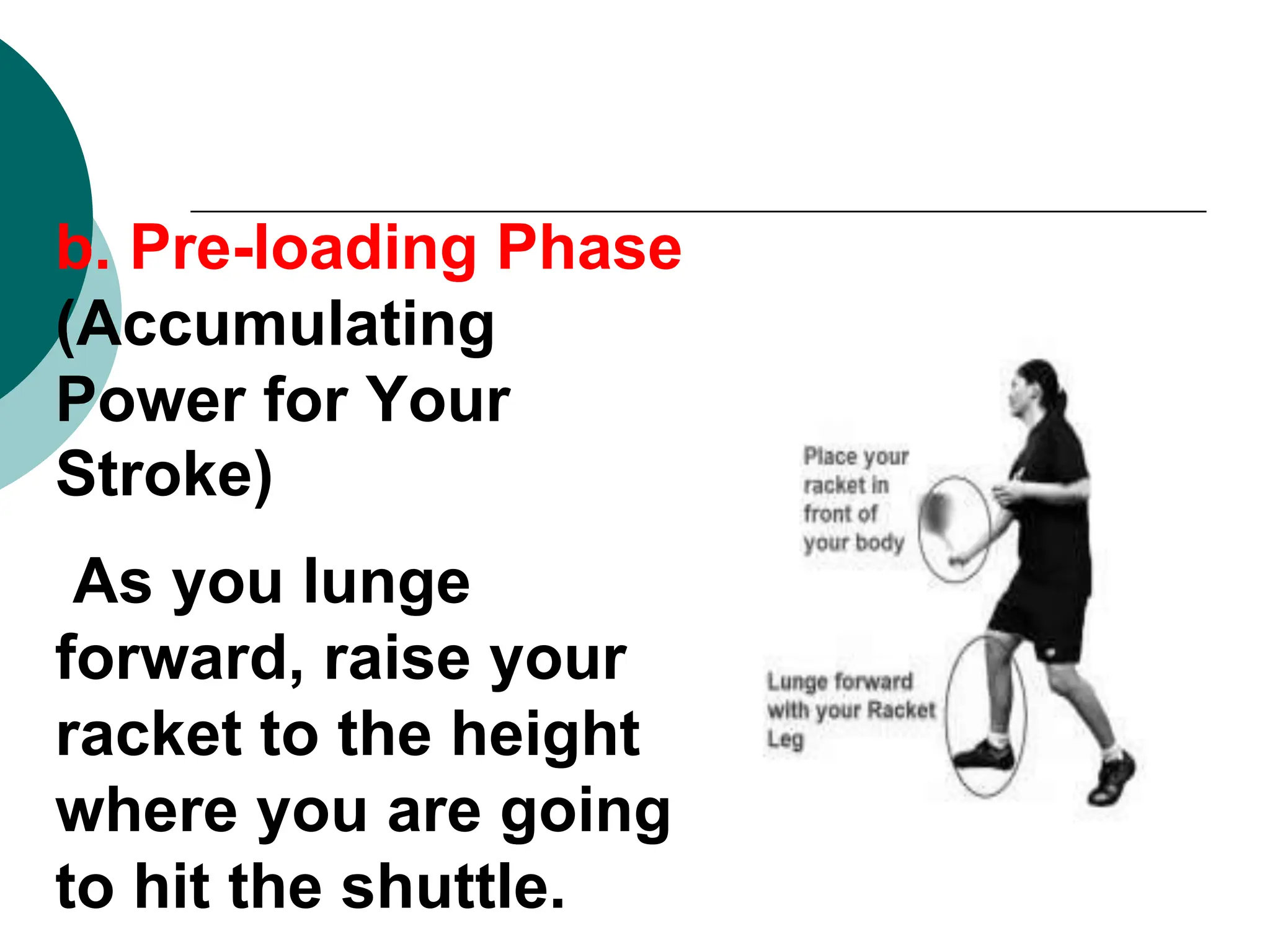
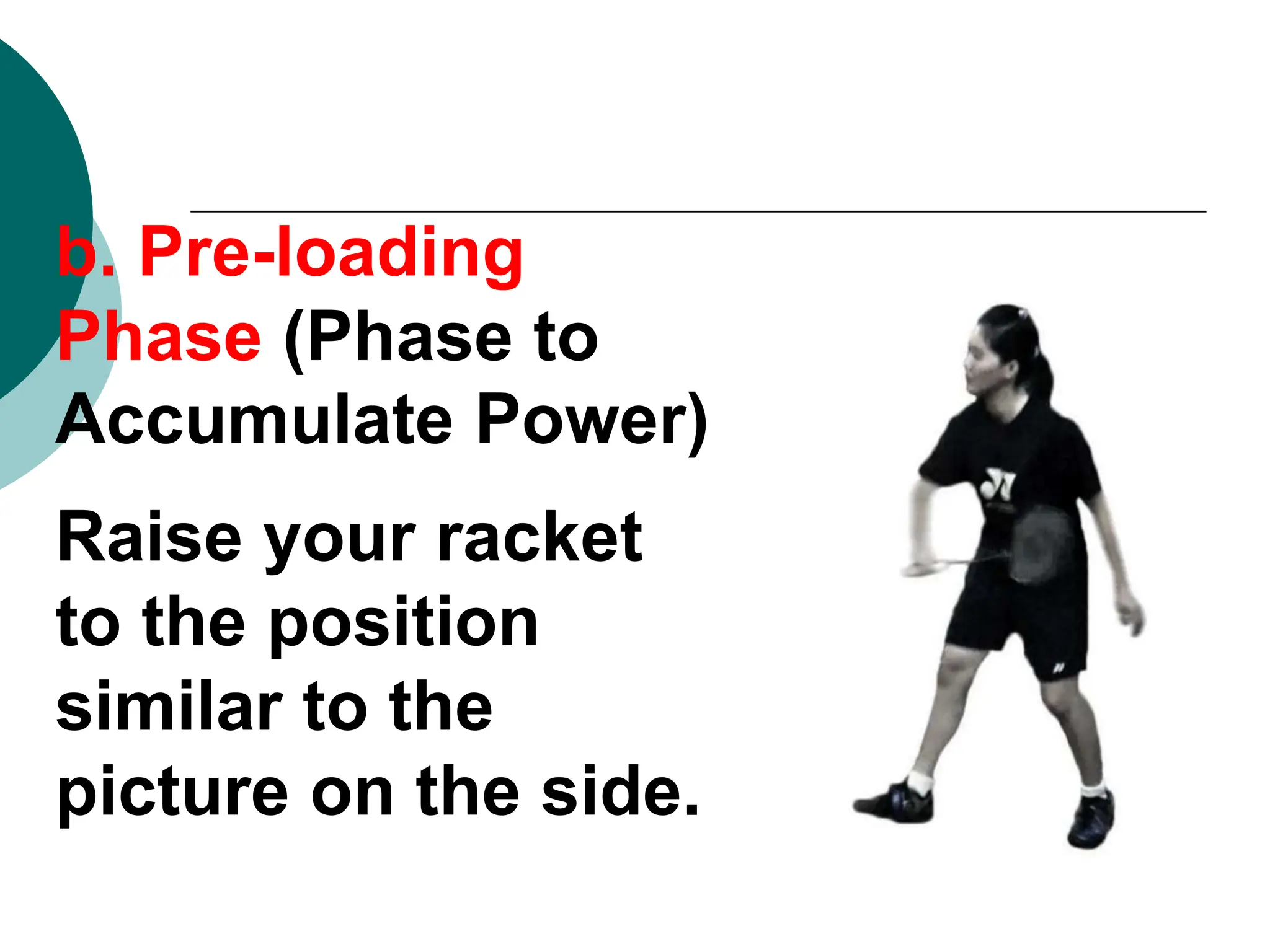
The document provides information about basic skills and techniques for playing badminton, including different types of serves, strokes, grips, scoring, faults, lets, equipment needed, and court dimensions. It describes high, low, and fake serves. It explains the forehand, backhand, and underarm strokes in terms of preparation, pre-loading, and execution phases. It also outlines the rules for scoring, serving, and common faults in badminton.