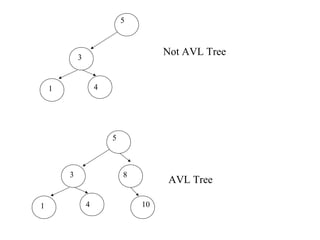
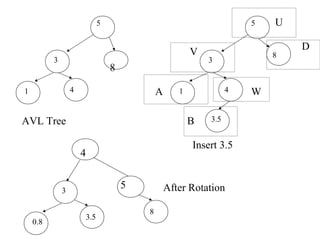
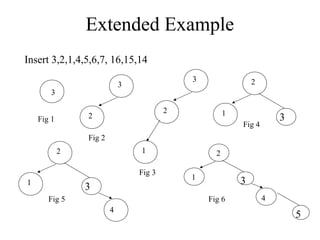
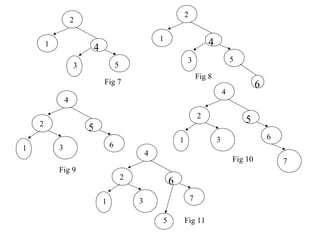
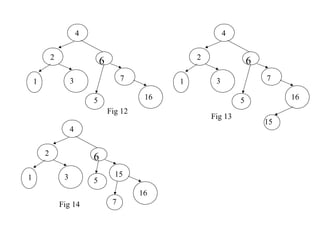
- AVL trees are binary search trees where the heights of the two subtrees of every node differ by at most one. This balances the tree and ensures search, insertion, and deletion operations take O(log N) time.
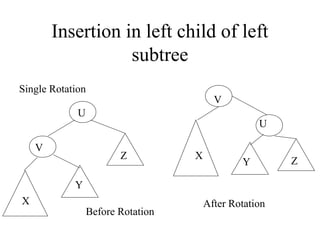
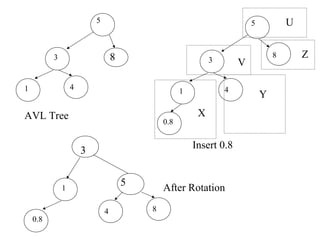
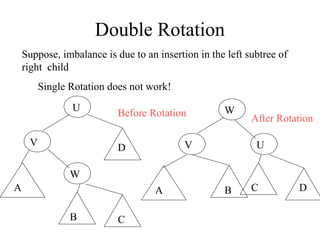
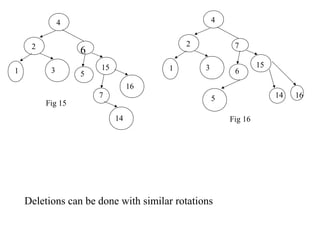
- Insertions can cause imbalance, requiring rotations to restore balance. The node nearest to the inserted node that becomes imbalanced is rotated. Single and double rotations are used depending on insertion location.
- The number of nodes in an AVL tree of height h is approximately equal to the hth Fibonacci number. Since the Fibonacci numbers grow exponentially with h, h must be O(log N) to contain N nodes.