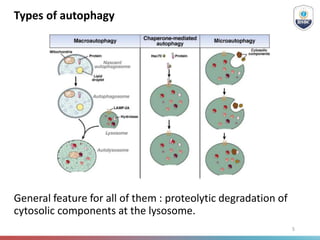
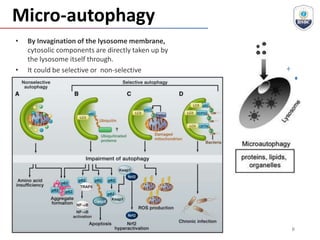
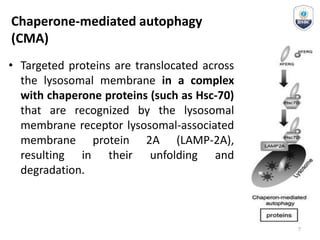
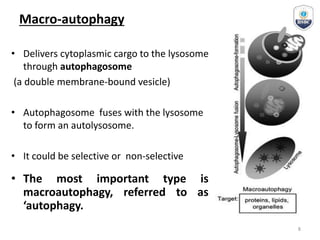
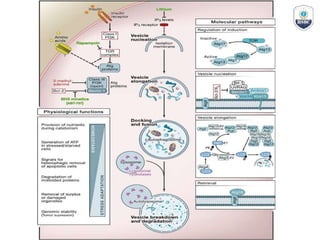
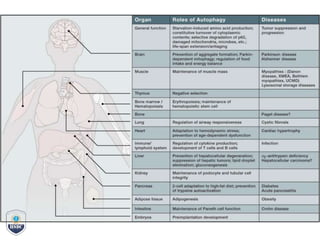
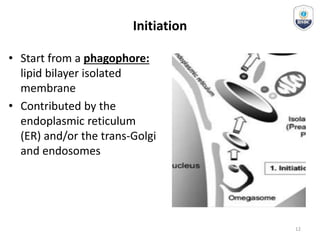
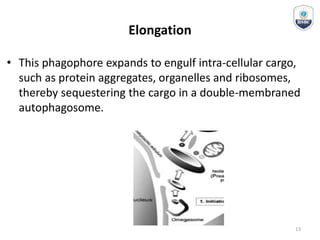
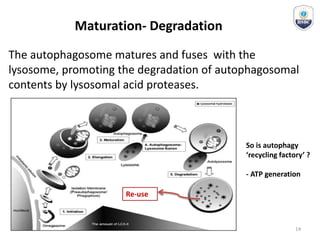
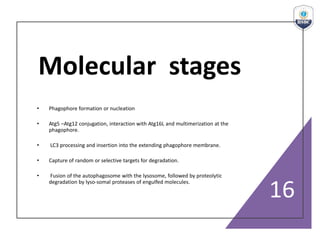
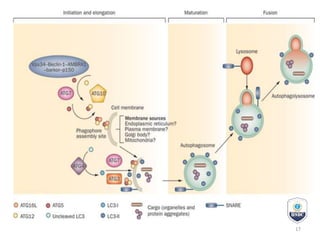
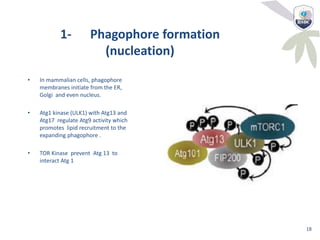
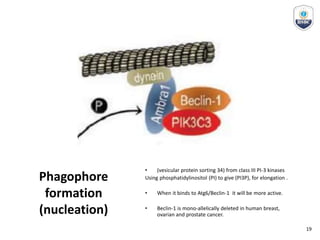
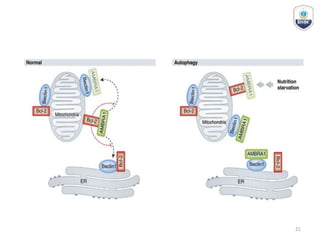
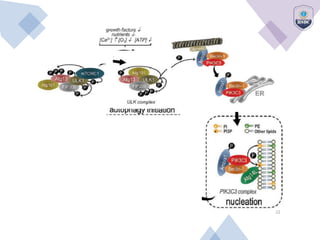
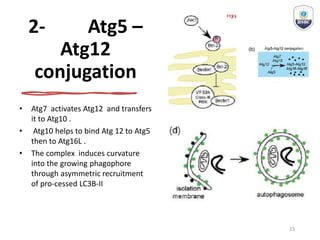
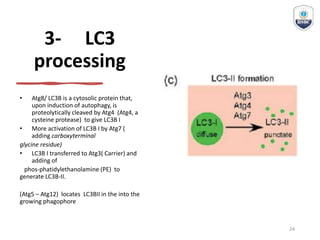
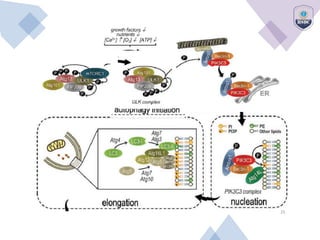
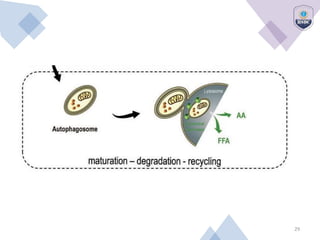
Autophagy is a critical cellular process that involves the lysosomal degradation of cytoplasmic components, crucial for maintaining homeostasis and protecting against various diseases. It encompasses several types, primarily macroautophagy, and involves a complex molecular machinery including autophagy-related genes (atg) that regulate its initiation, elongation, and degradation stages. Key mechanisms include the formation of phagophores, the processing of LC3 proteins, and the fusion of autophagosomes with lysosomes for effective cellular recycling.