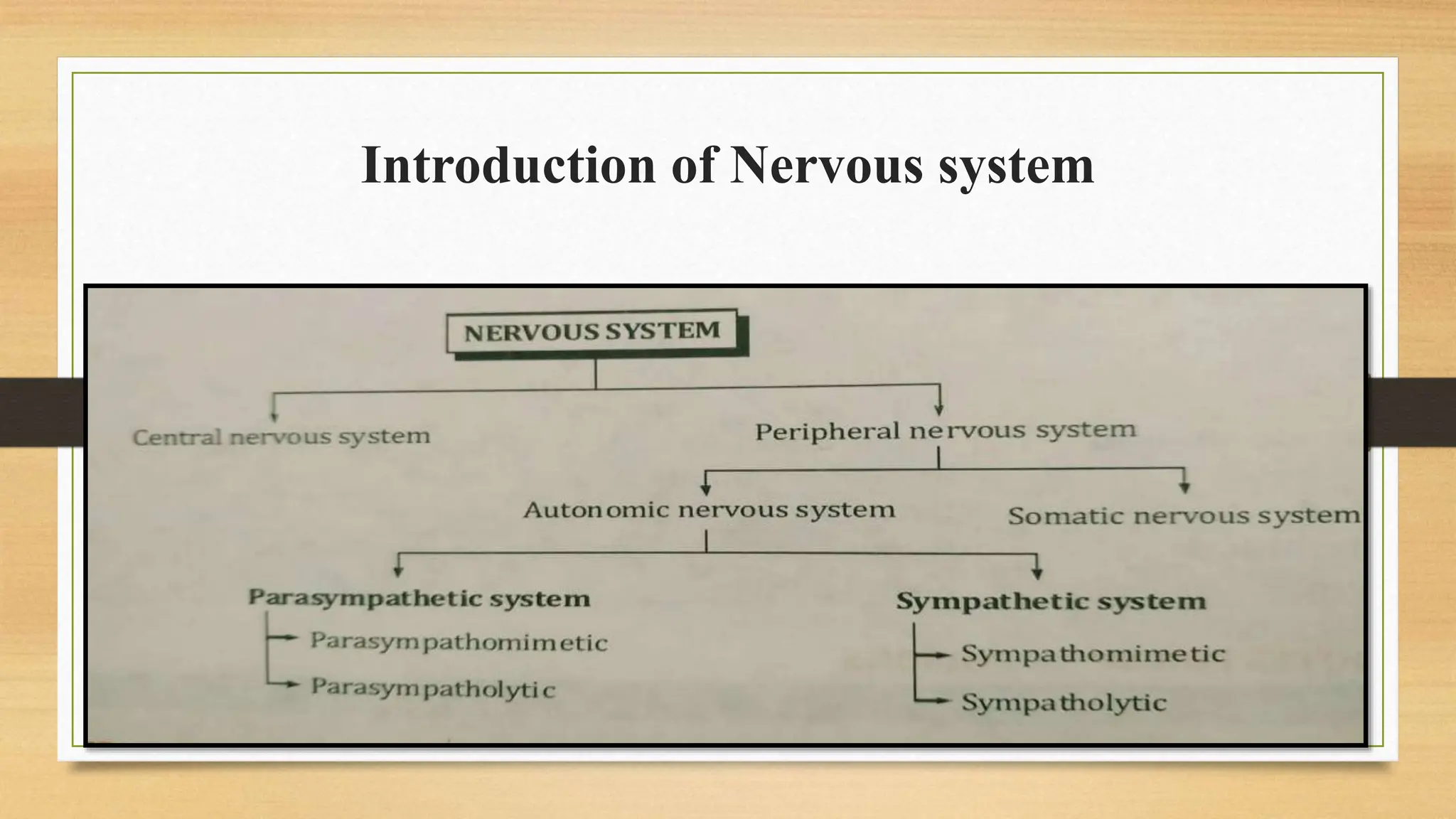
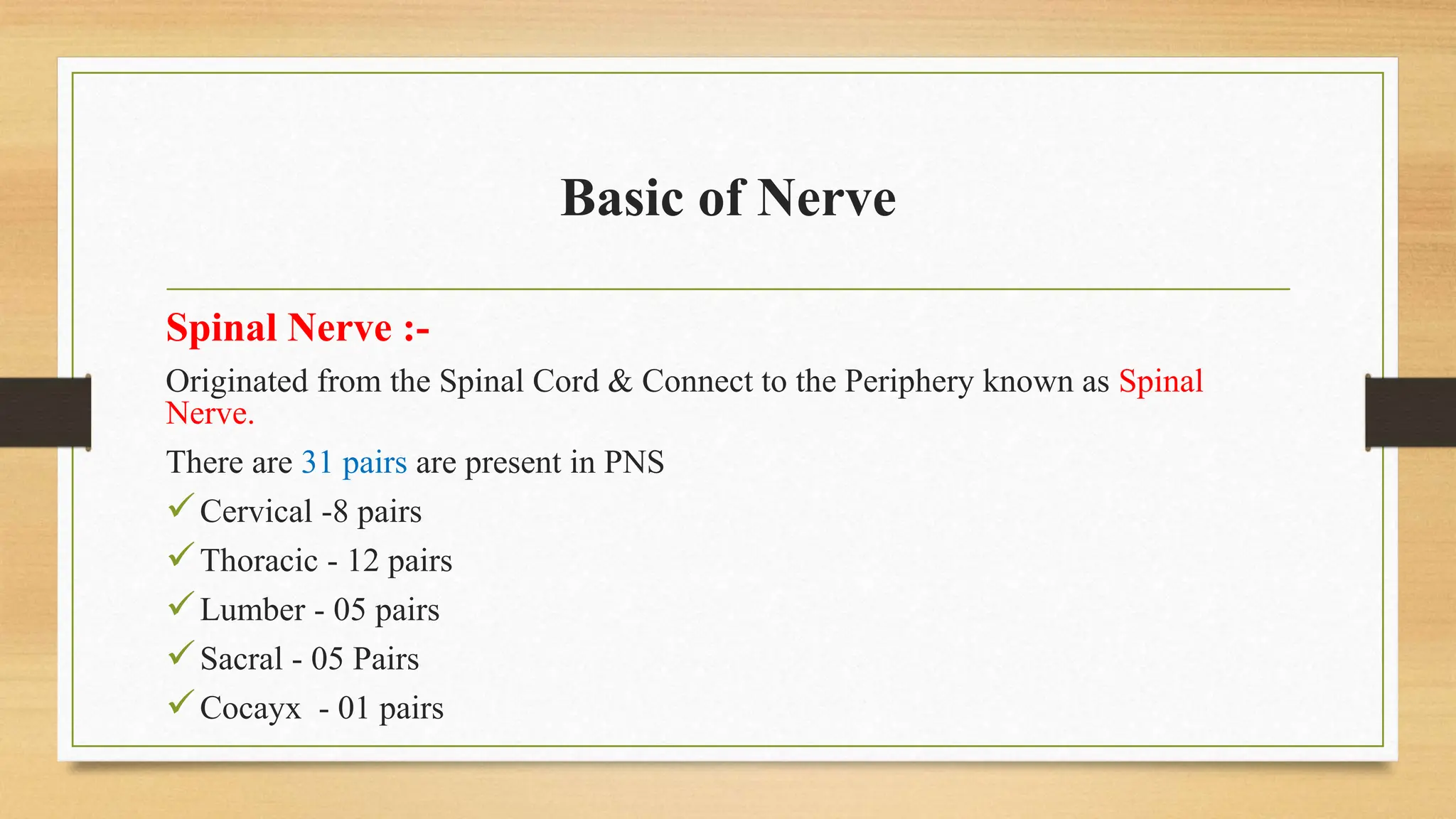
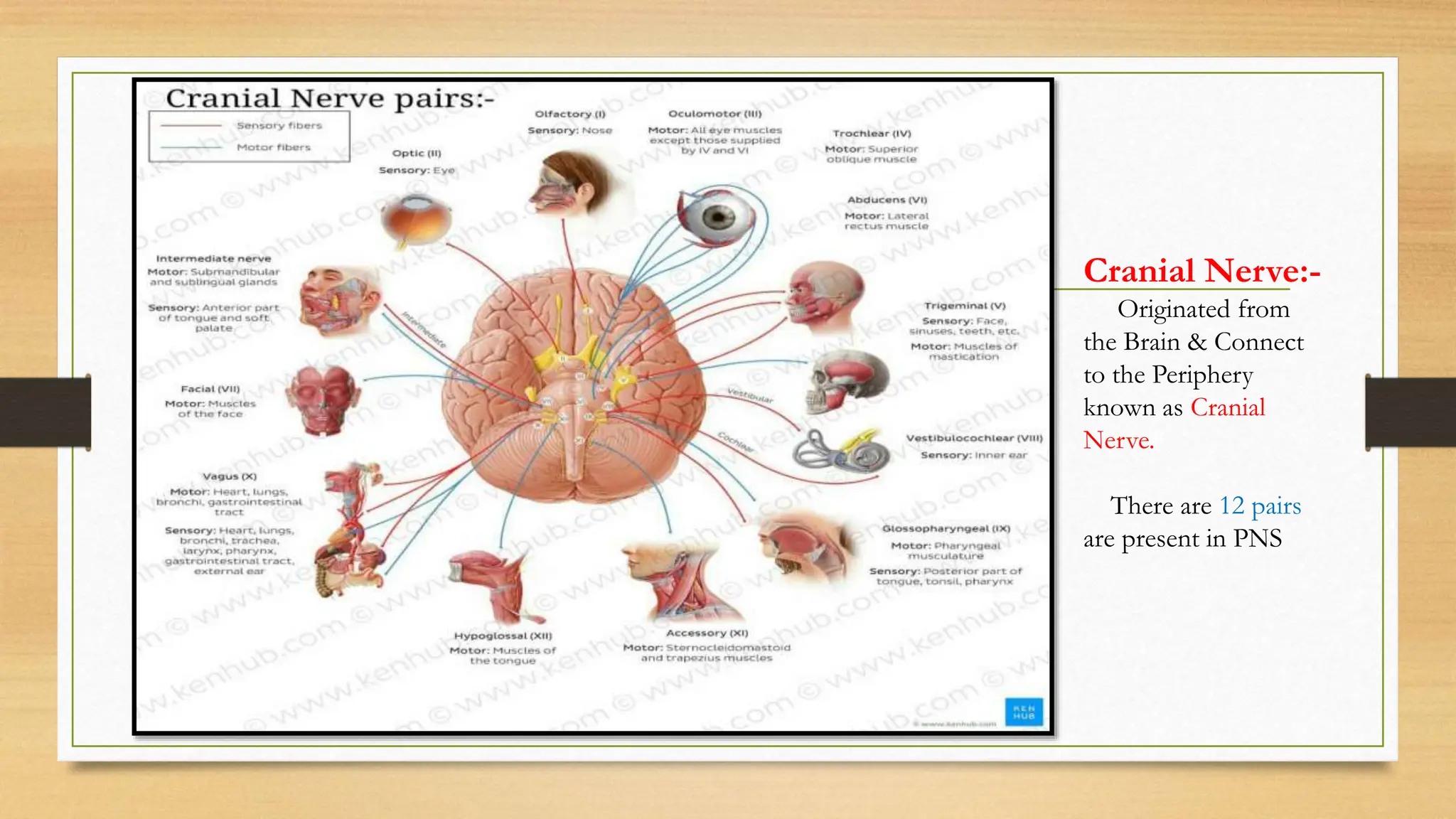
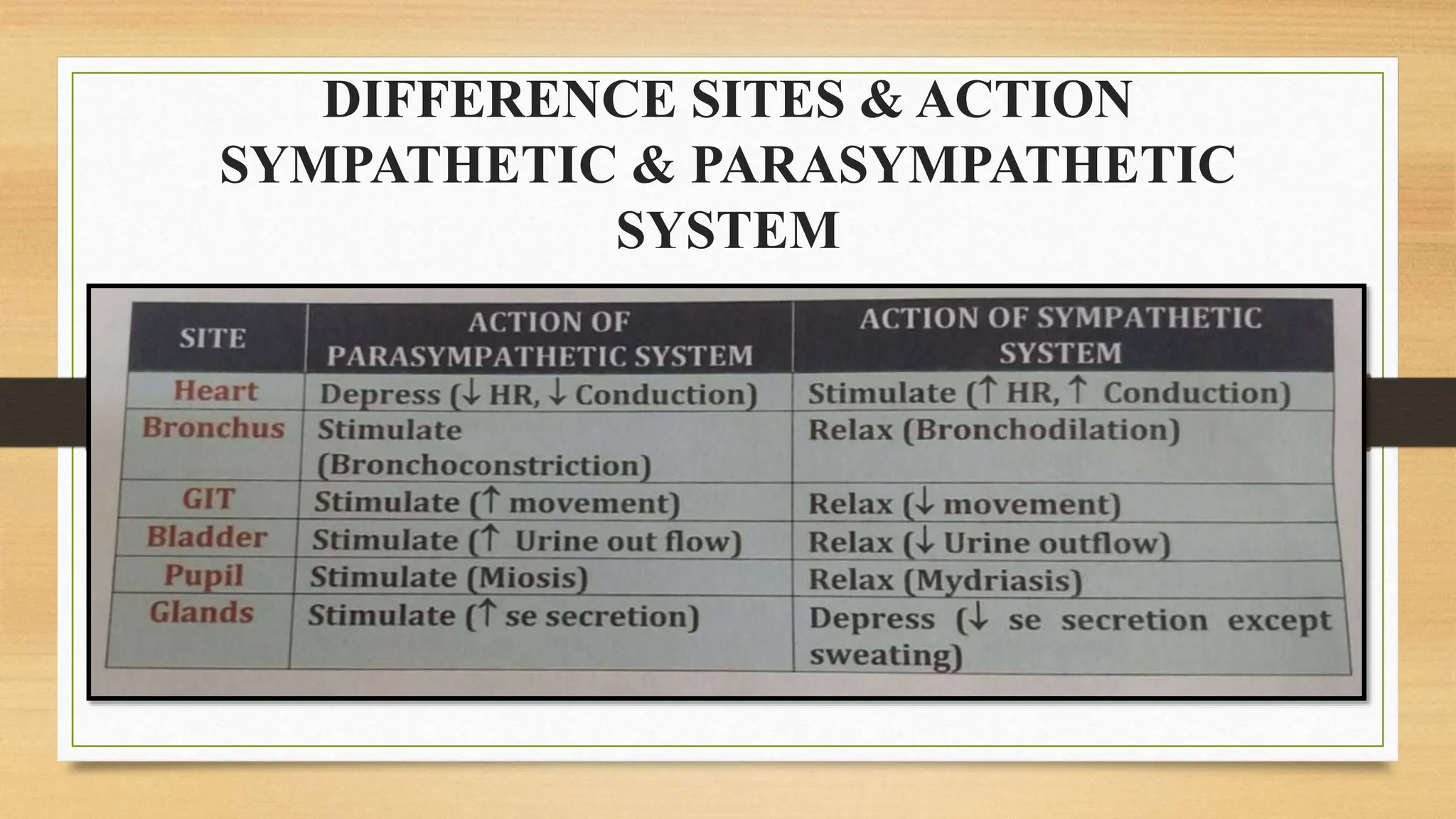
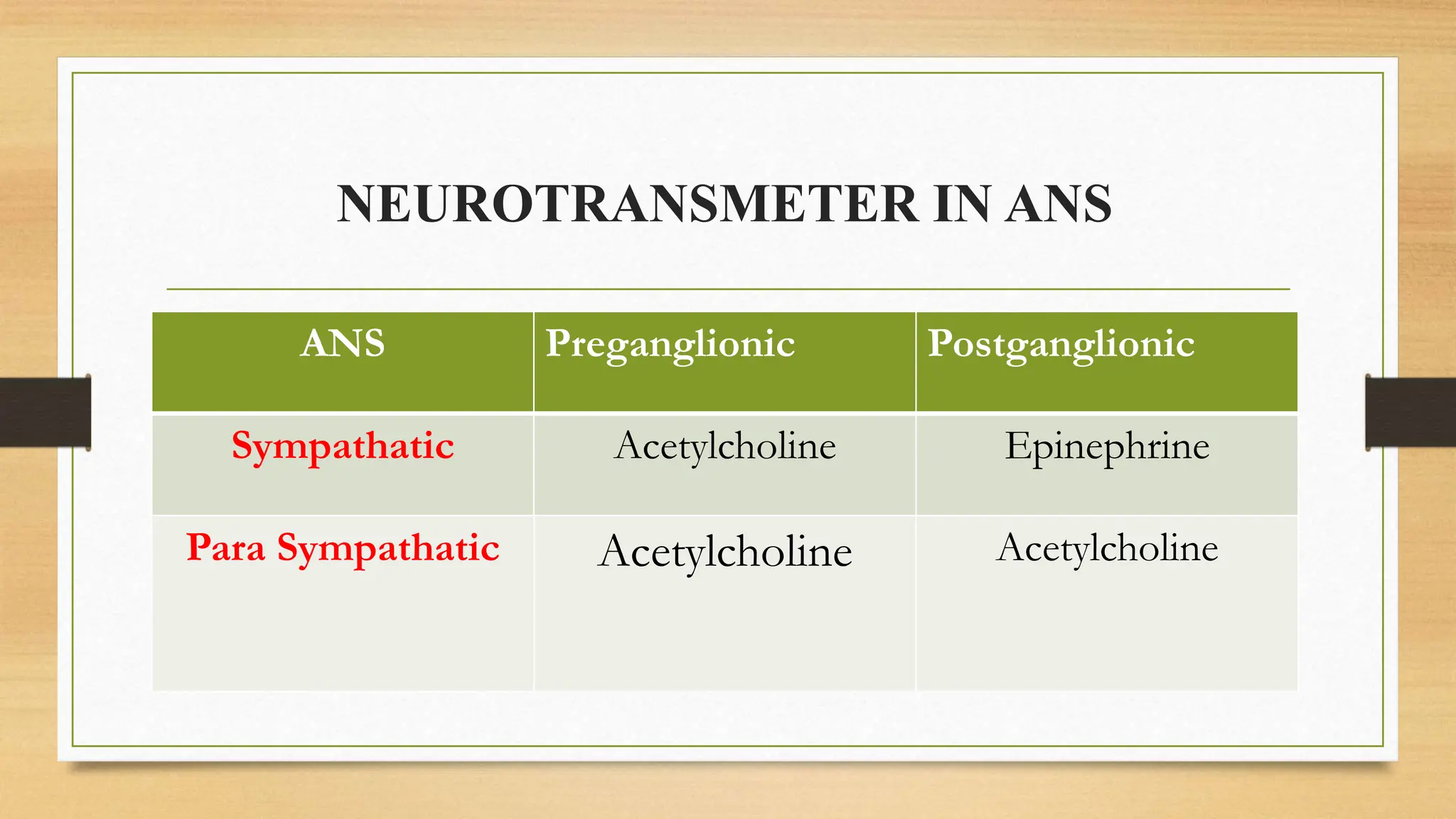
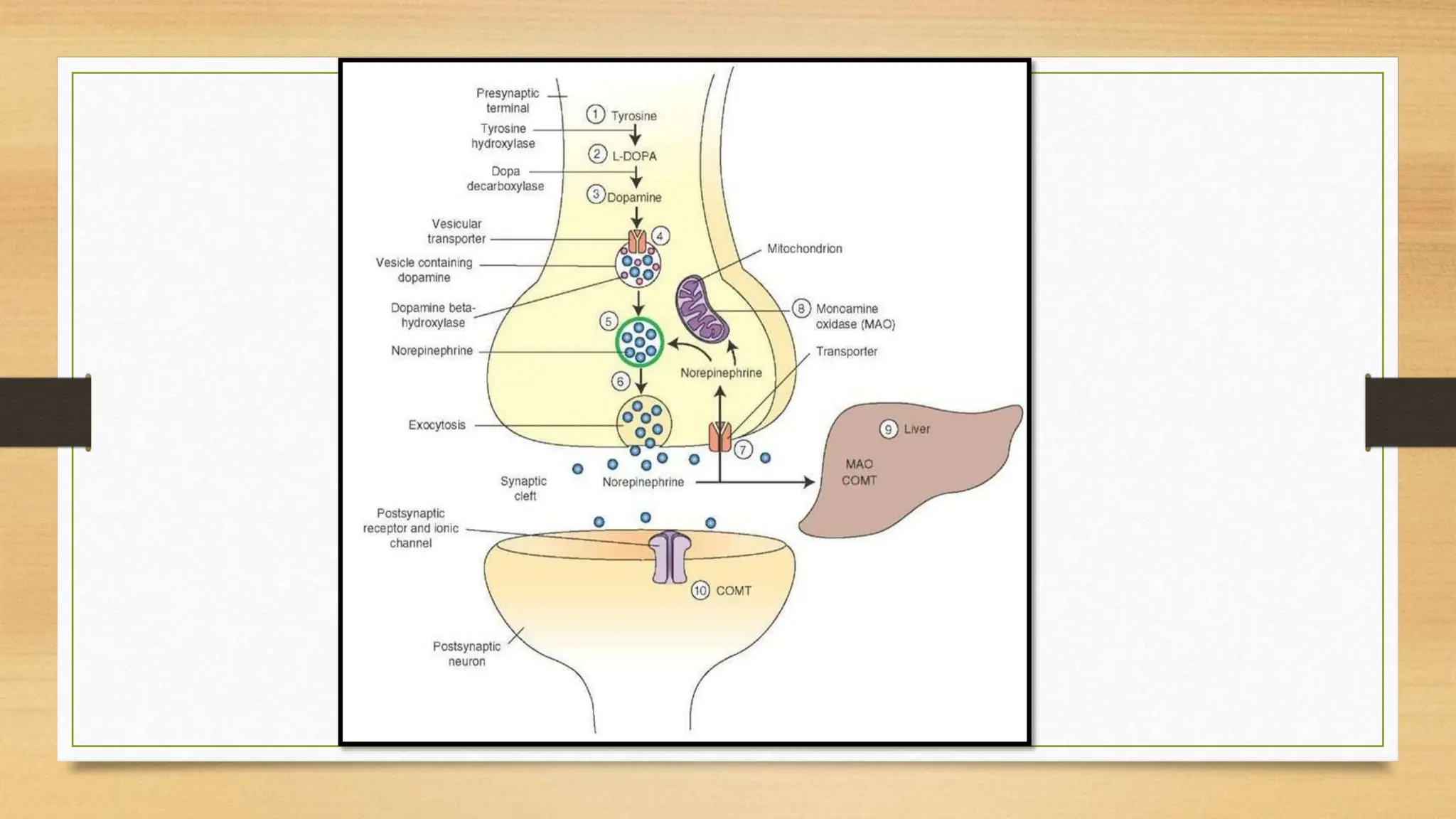
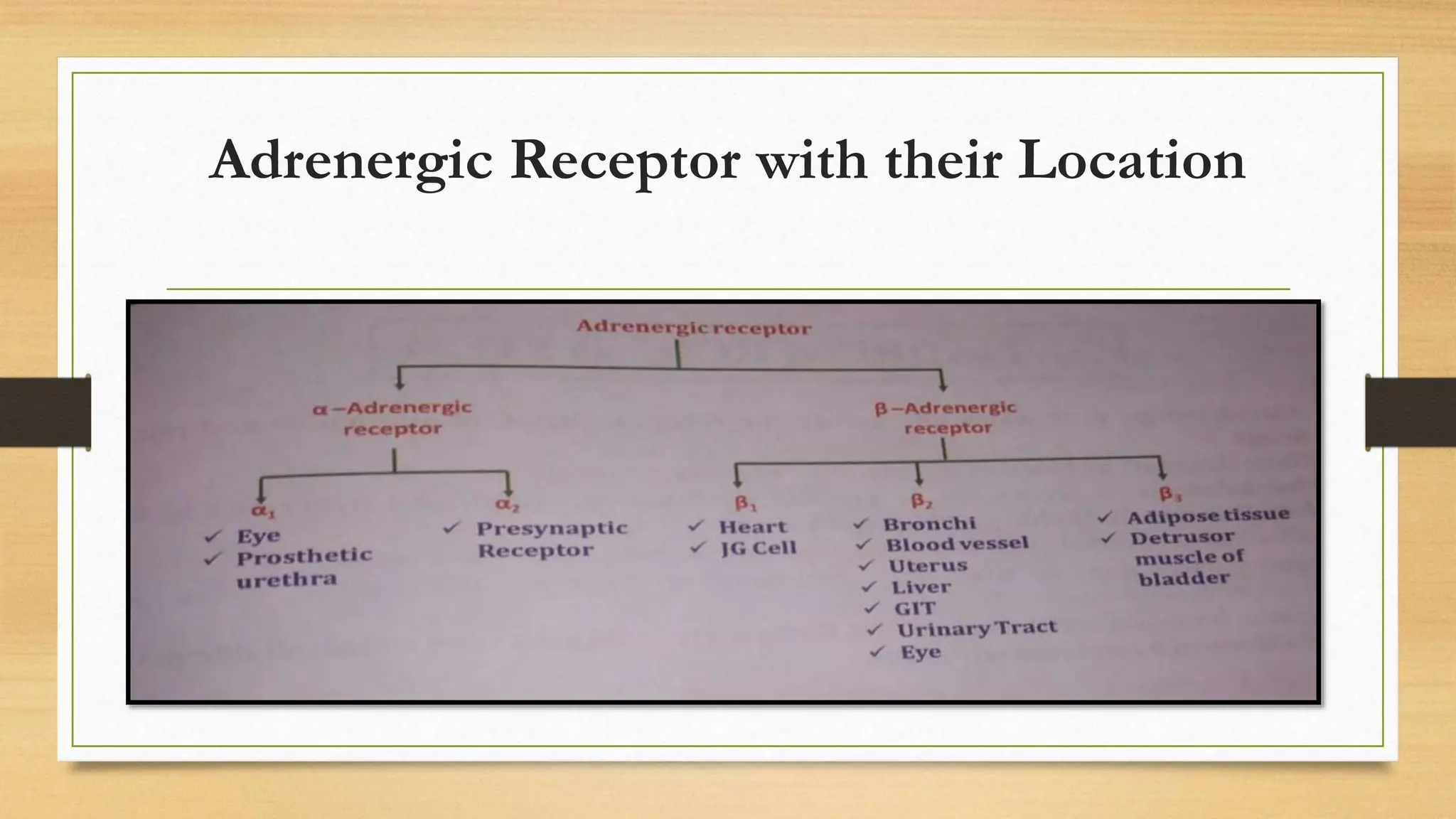
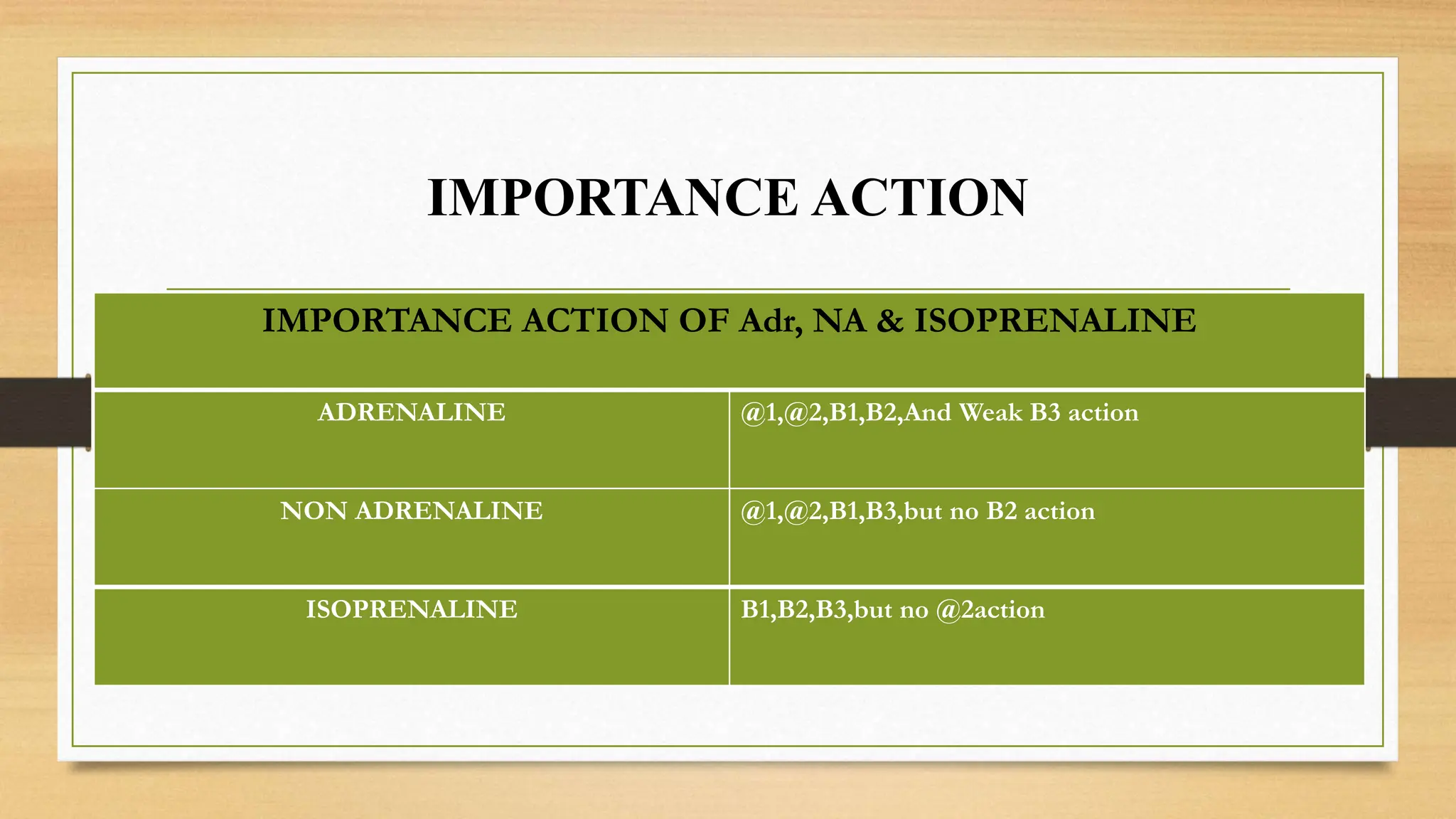
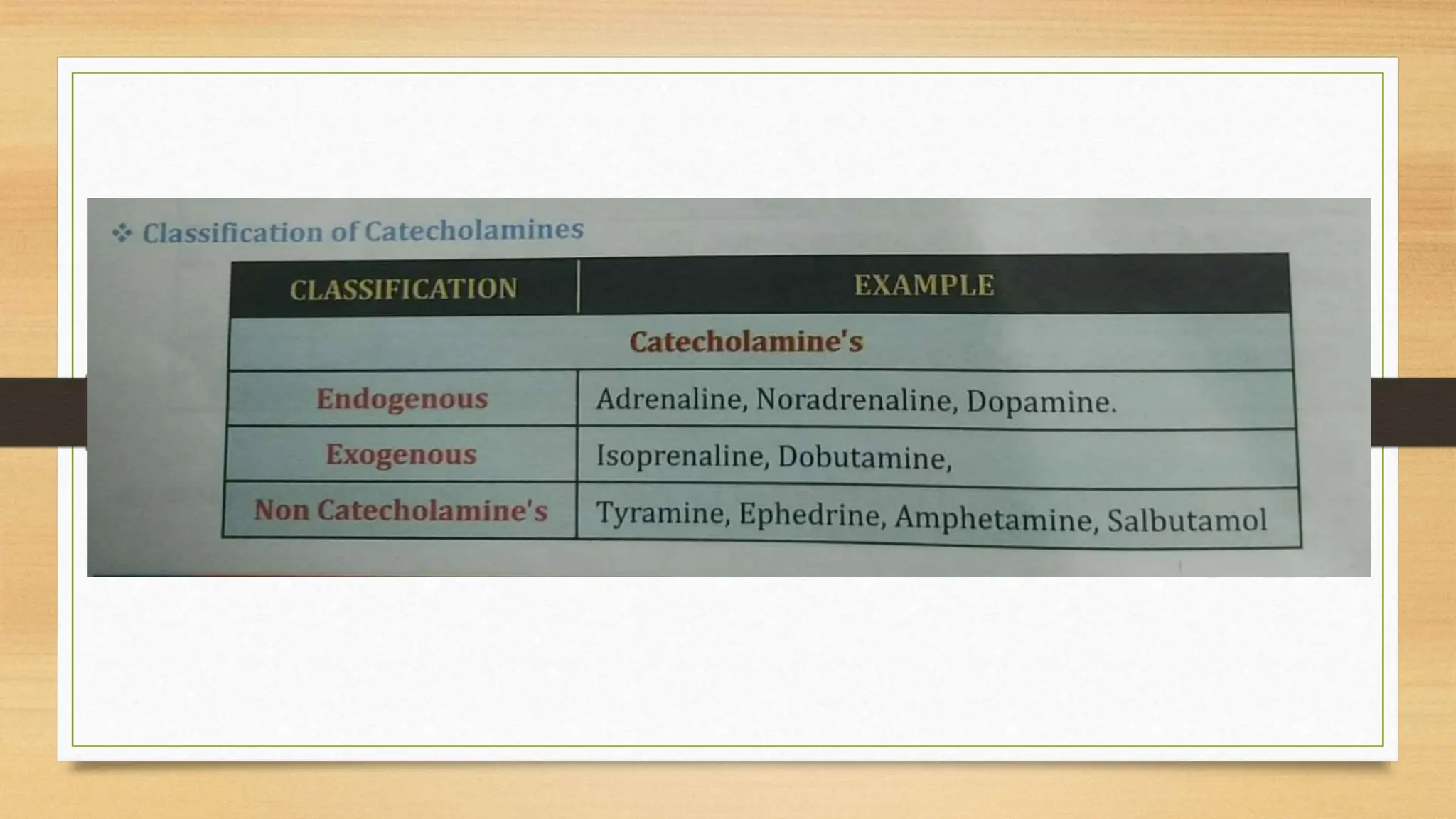
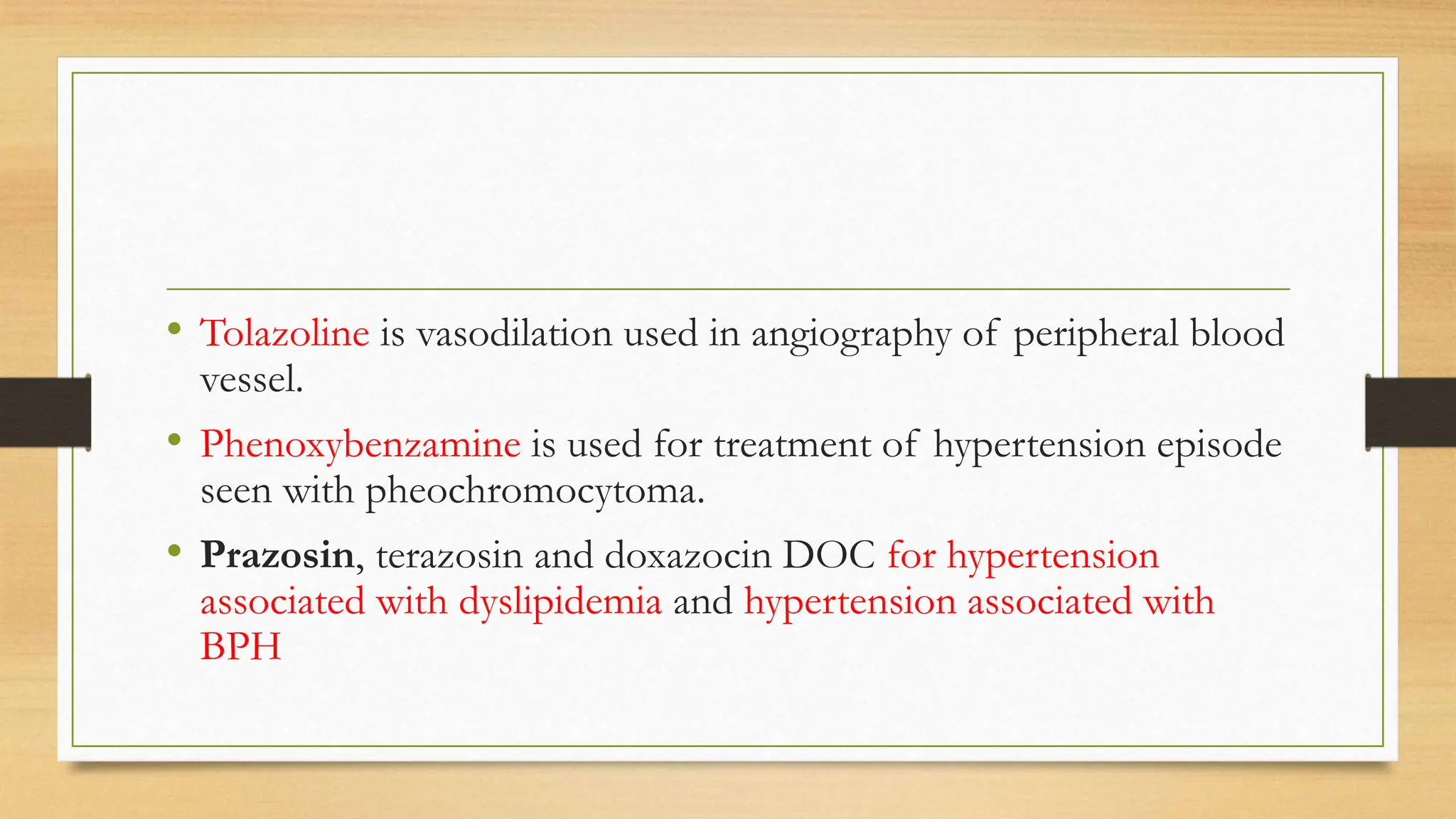
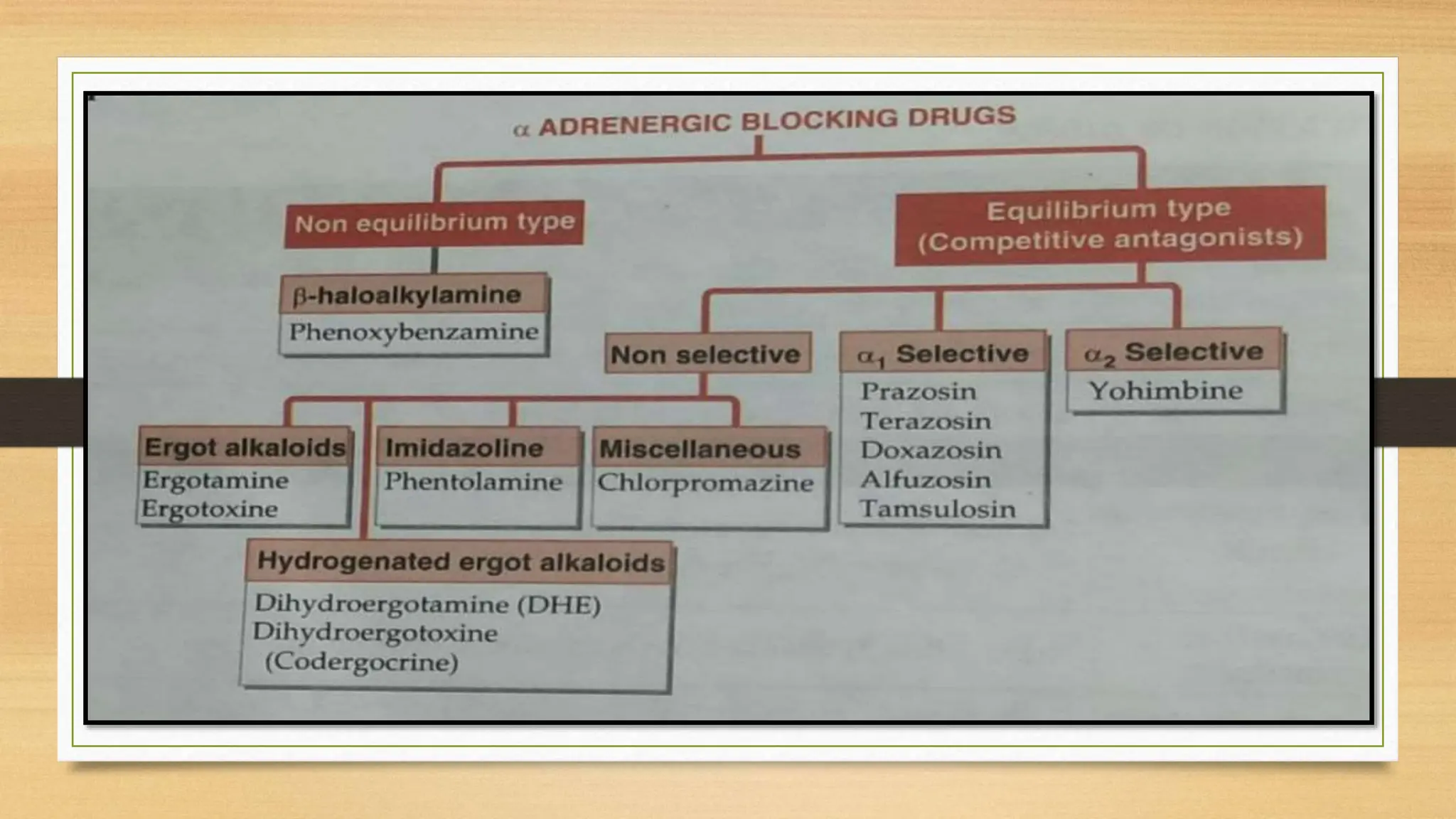
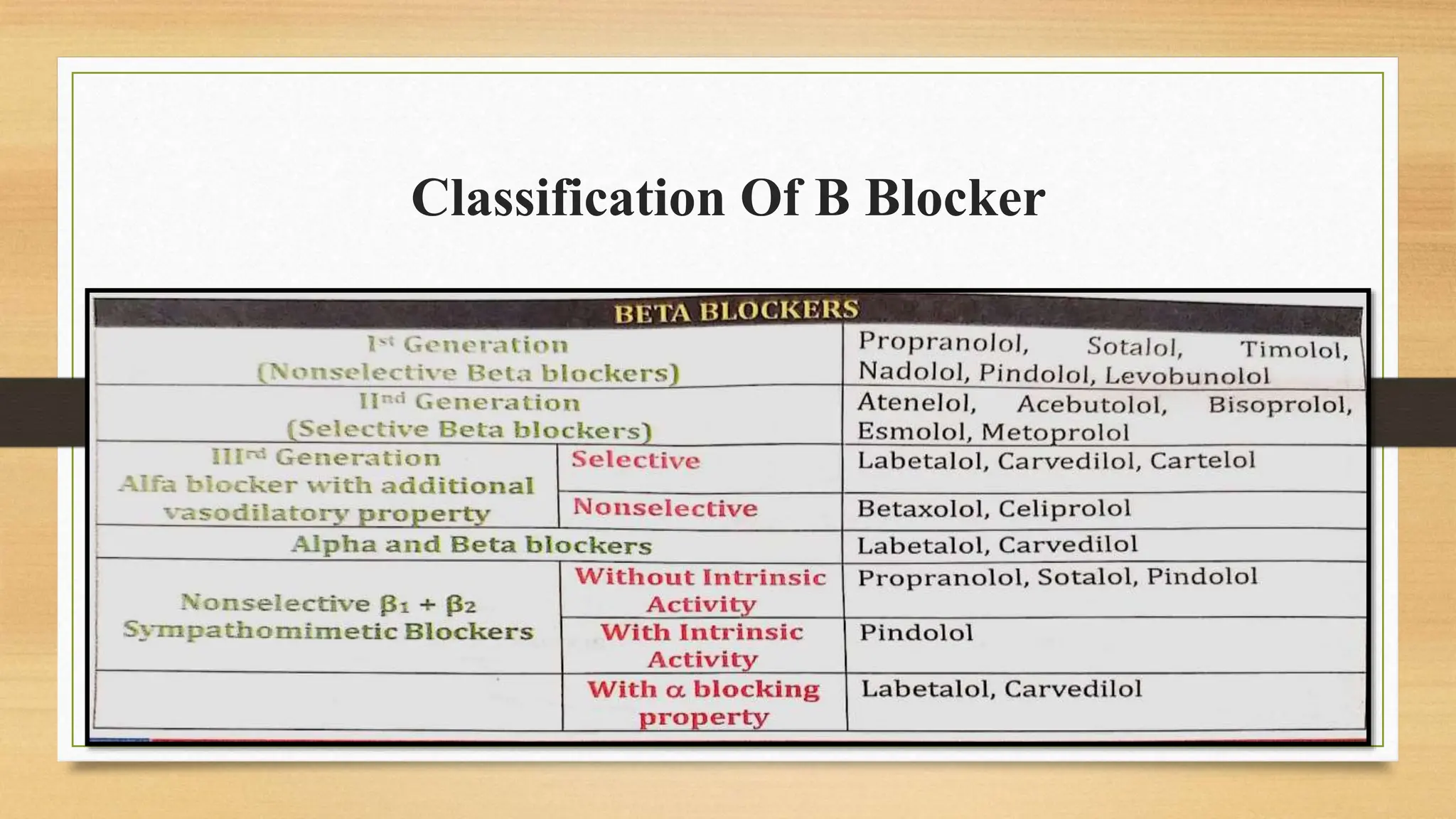
The document covers the autonomic nervous system, detailing the differences between the sympathetic (adrenergic) and parasympathetic (cholinergic) systems, as well as the functions of various adrenergic and anti-adrenergic drugs. It explains the role of the nervous system in regulating bodily functions and the synthesis of neurotransmitters like adrenaline from tyrosine. Additionally, it discusses several adrenergic drugs and their applications in medical treatments such as hypertension and erectile dysfunction.