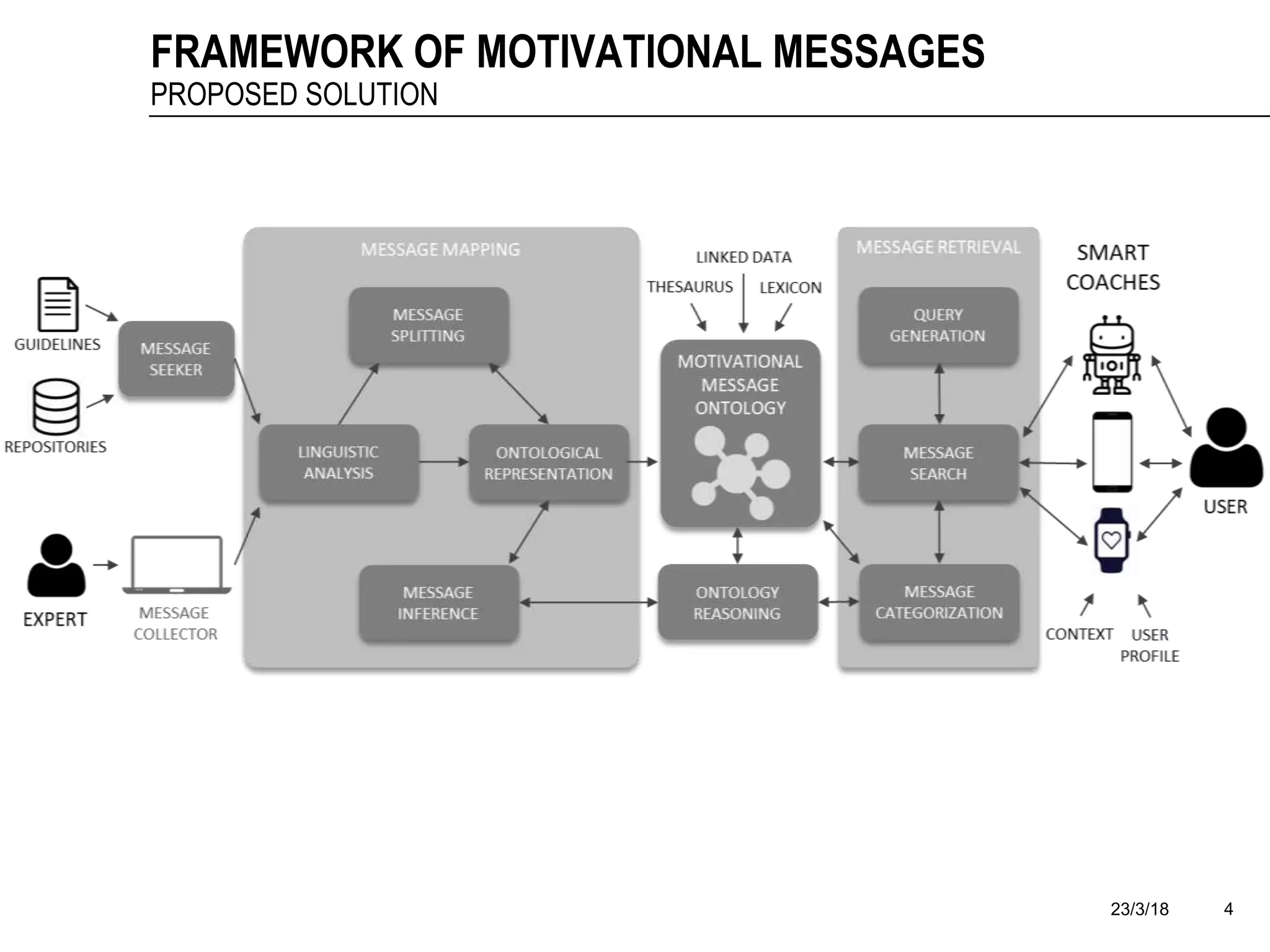
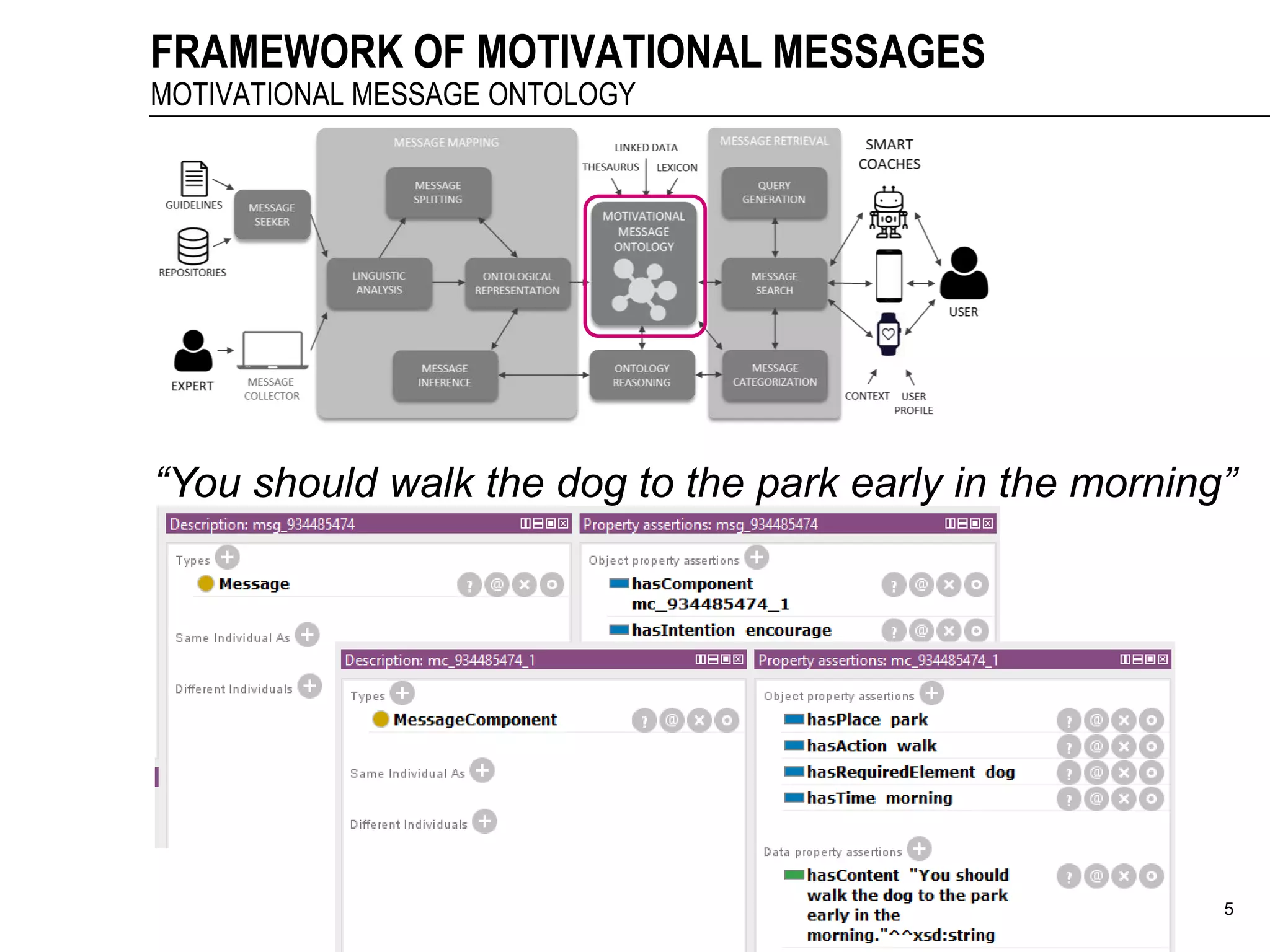
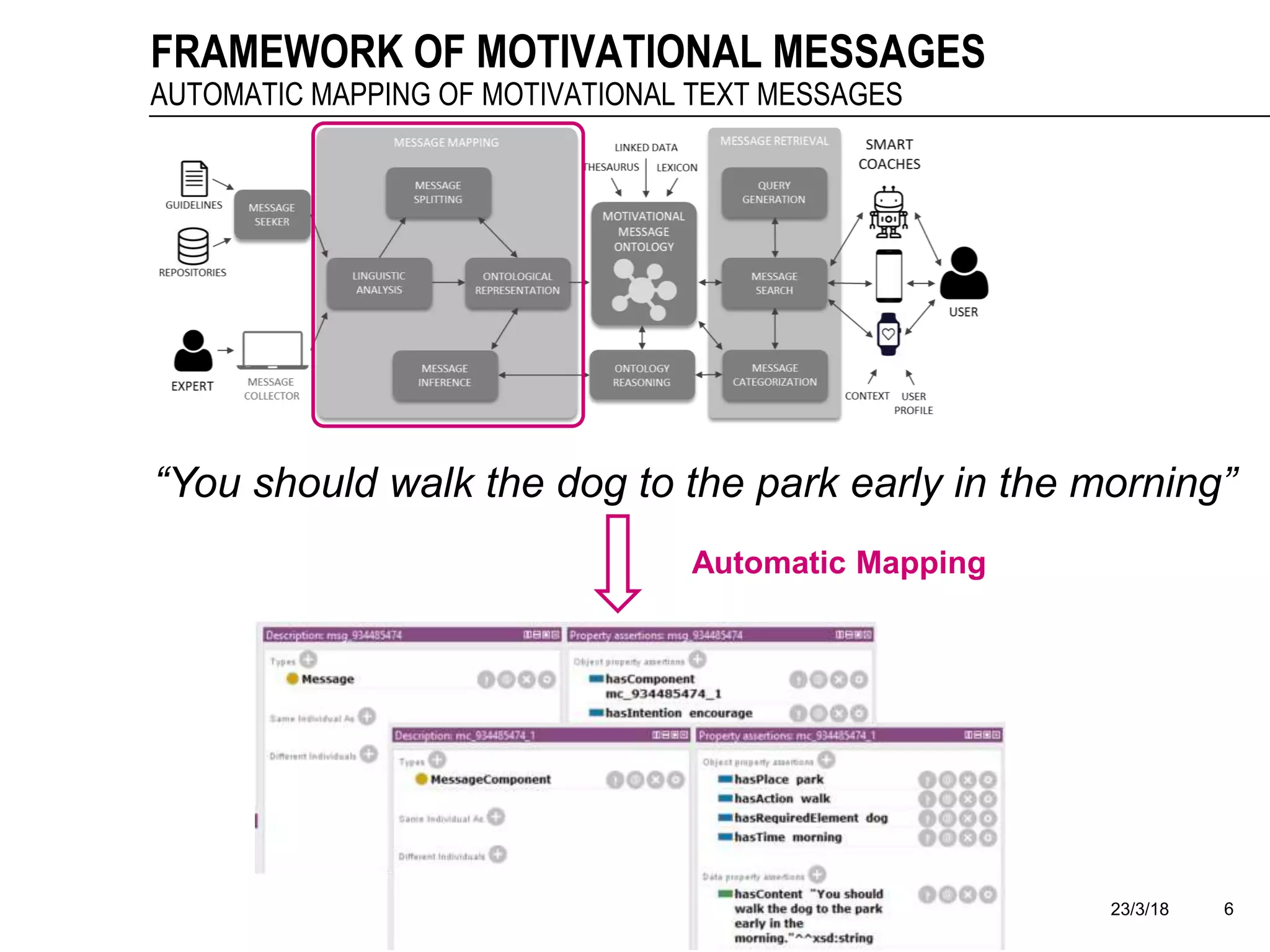
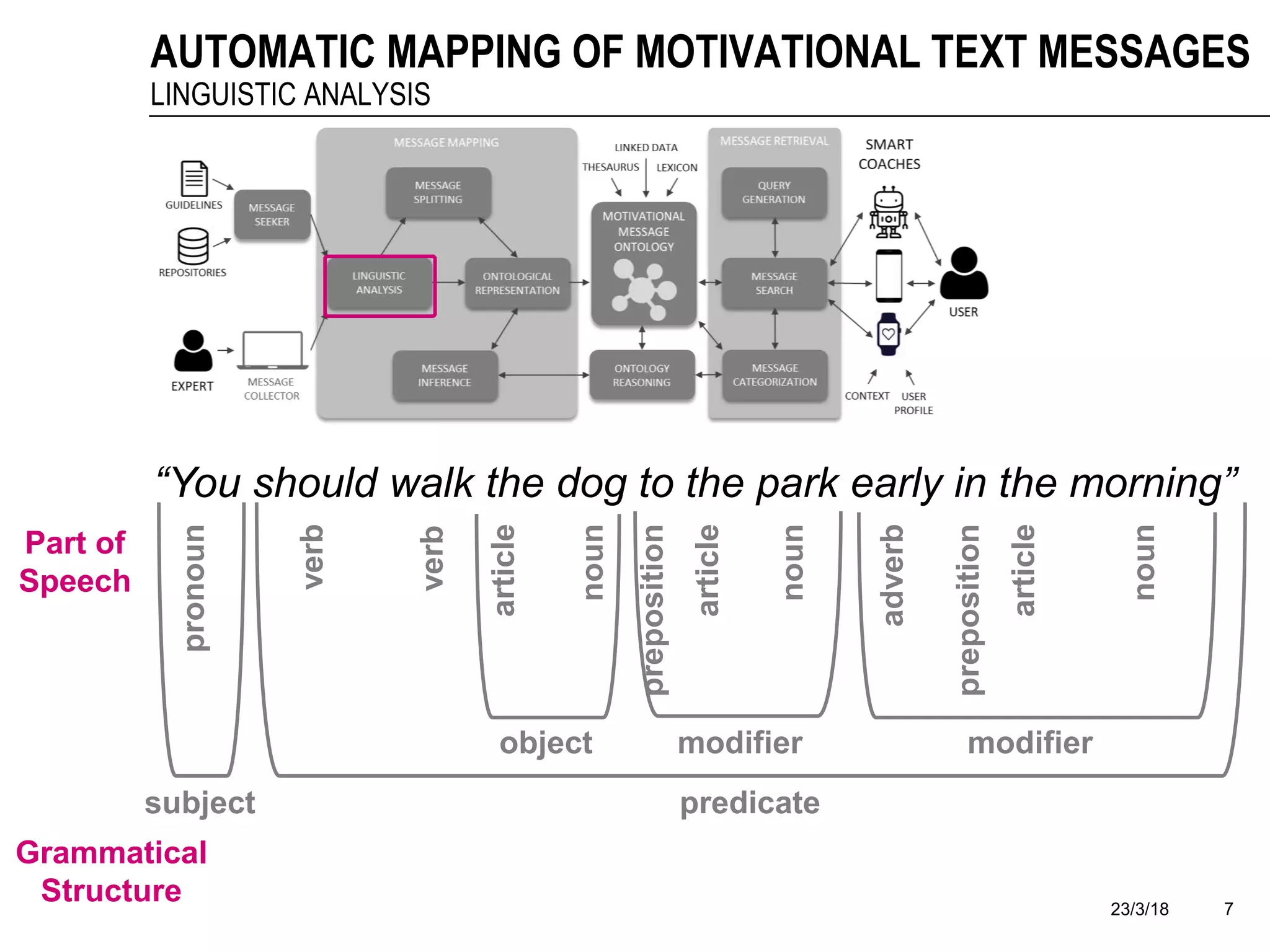
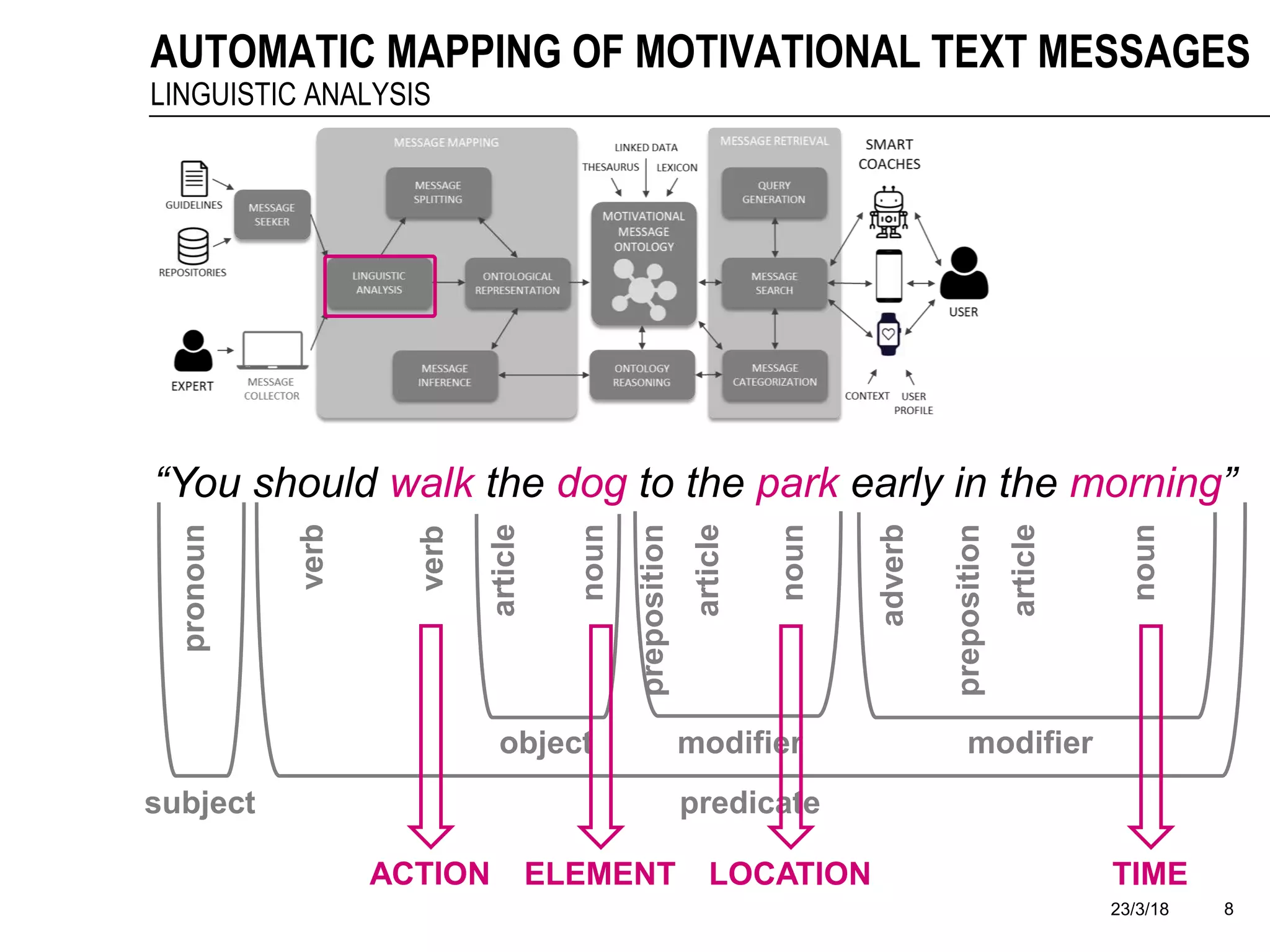
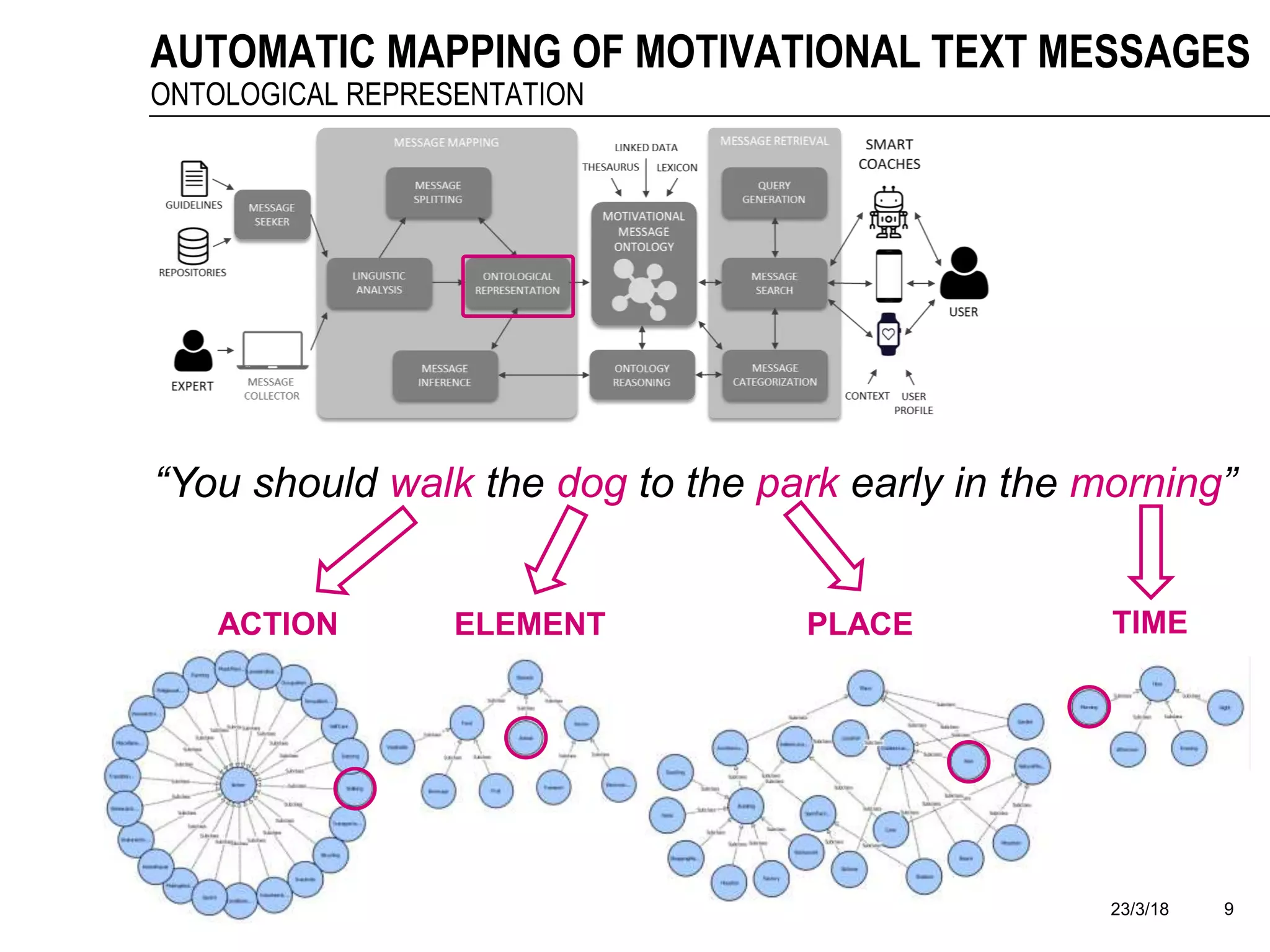
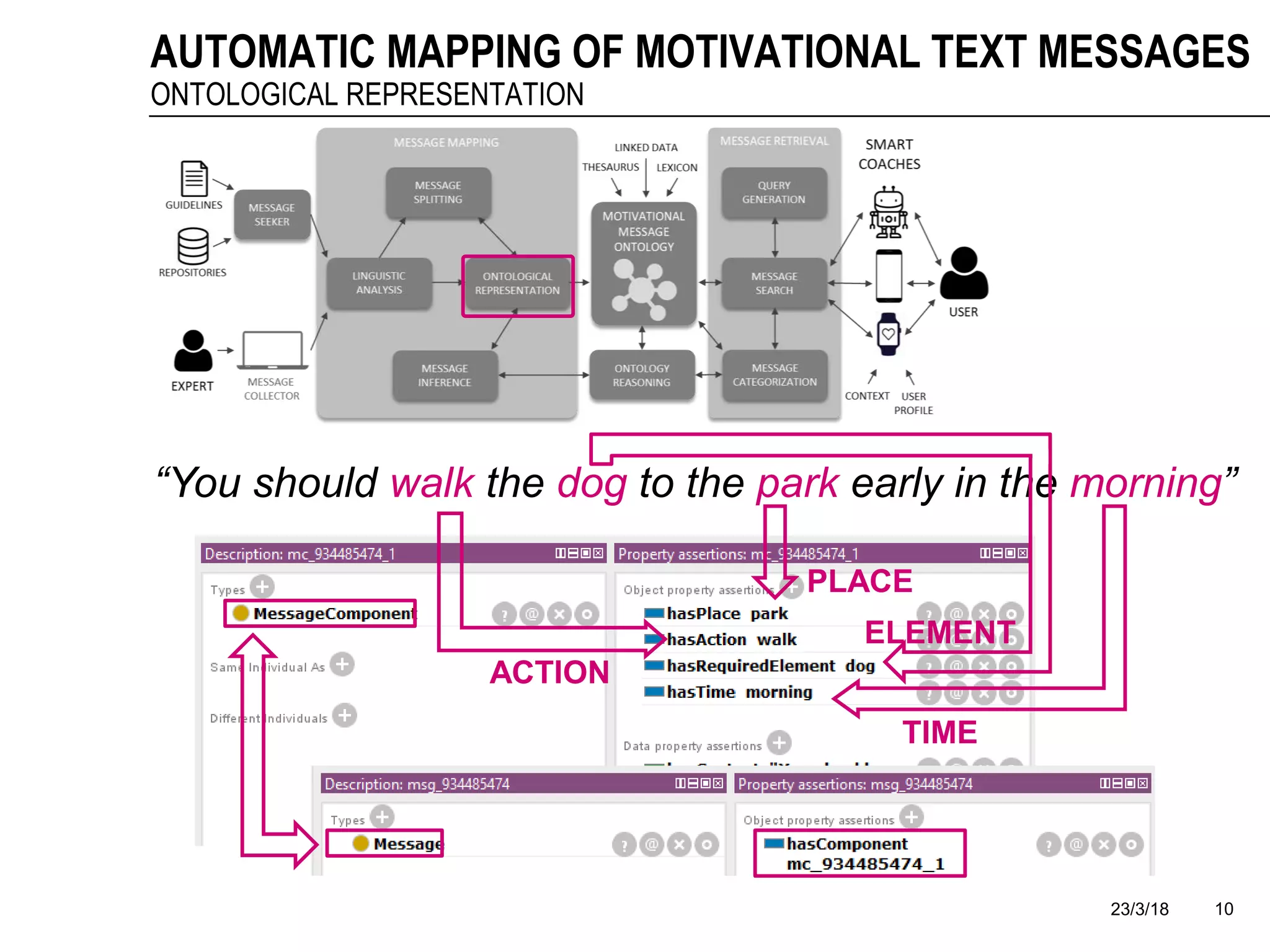
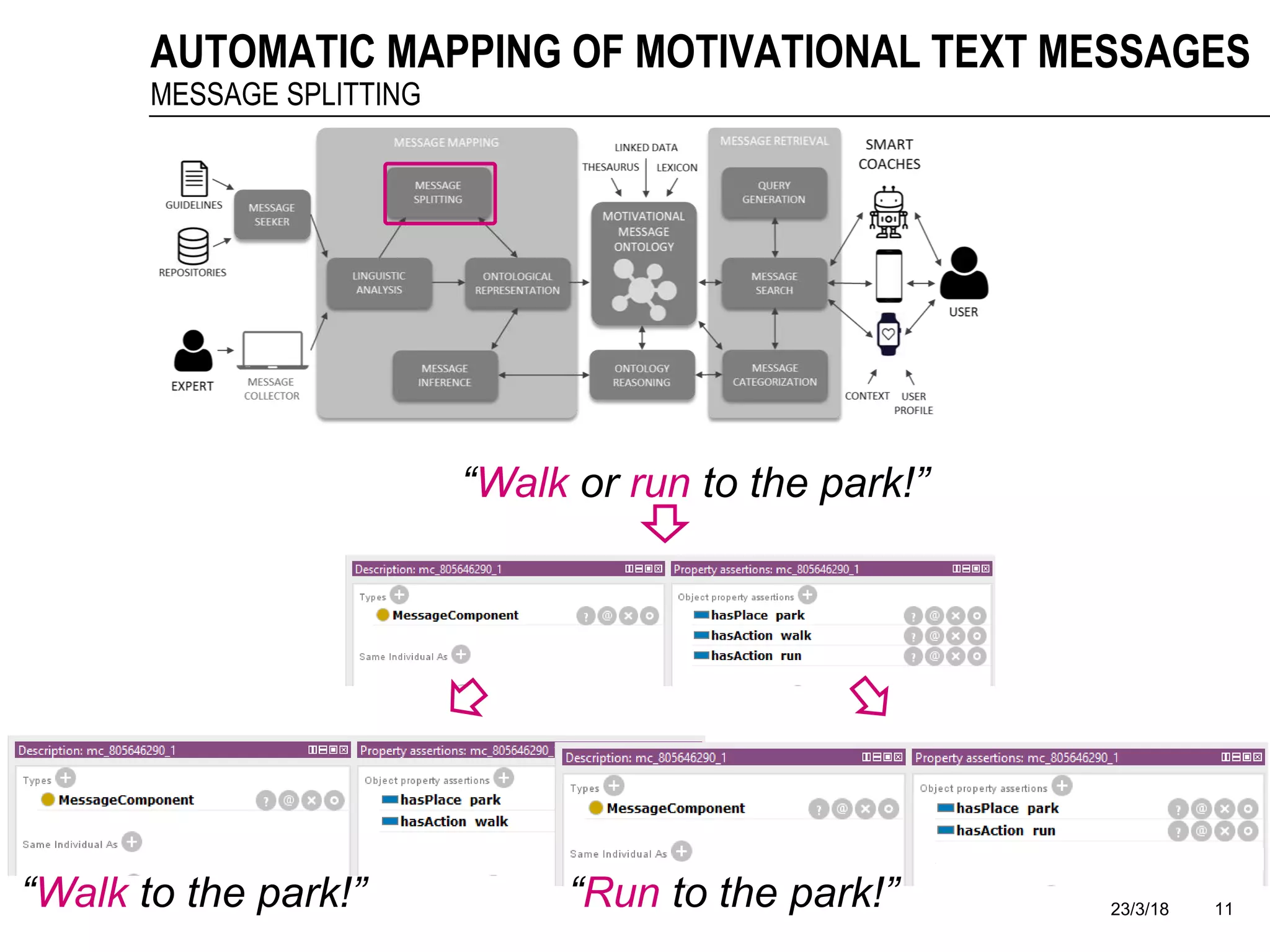
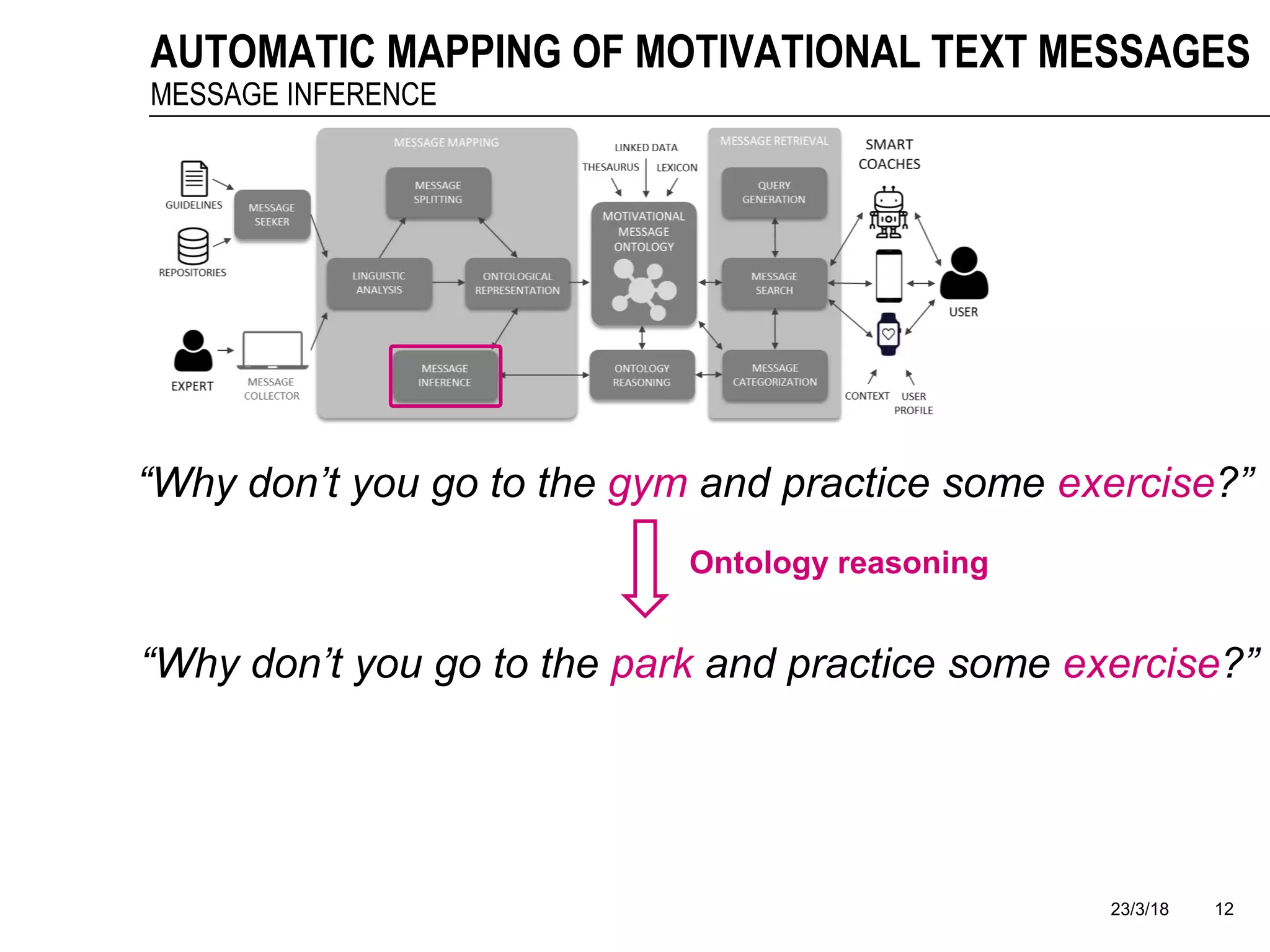
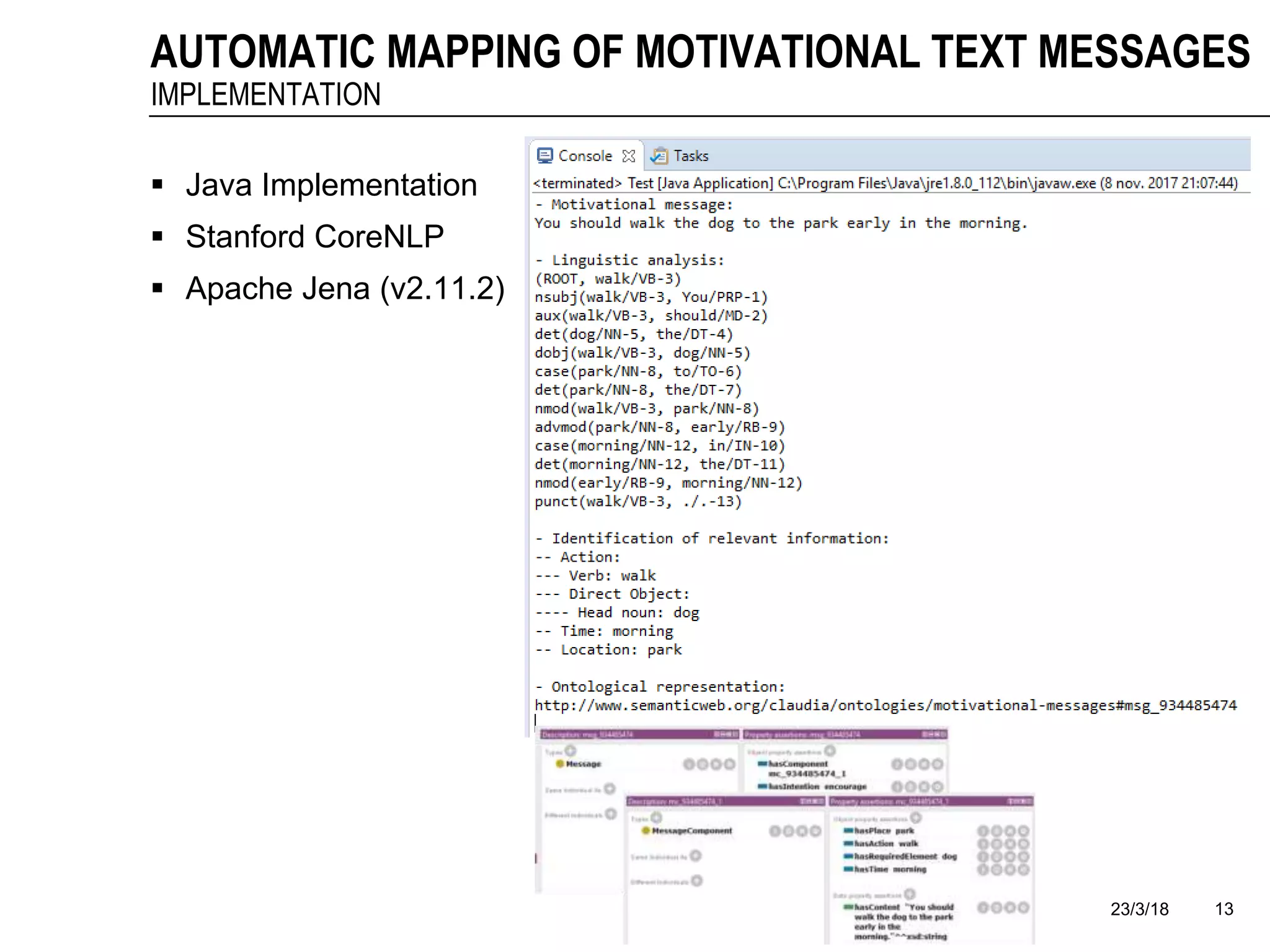
The document discusses a framework for the automatic mapping of motivational text messages into ontological entities for smart coaching applications, addressing the challenges of generating relevant and tailored messages. It outlines a linguistic analysis approach for breaking down and inferring the semantics of motivational messages, ultimately contributing to a new method for creating personalized coaching recommendations. Future work includes evaluating and improving the mapping method, as well as expanding the ontology to enhance message generation capabilities.


![23/3/18 3
MOTIVATIONAL MESSAGES FOR E-COACHING
MAIN CHALLENGES
Represent the principal, and perhaps more natural,
means for translating behavioral findings into easy-to-
follow and realizable recommendations (actions)
KEY challenges:
Generation of relevant messages tailored to the
performance, needs and characteristics of each
specific user [Noar2007]
Fostering the diversity of the messages to
increase adherence and make the coaching system
more realistic and trustworthy [opdenAkker2015]
Noar et al. Does tailoring matter? Meta-analytic review of tailored print health behavior change interventions. Psychological bulletin 133, 4 (2007),
673.
op den Akker et al.Tailored motivational message generation: A model and practical framework for real-time physical activity coaching. Journal of
Biomedical Informatics 55 (2015), 104-115.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/villalongaucami2017slides-180323134135/75/Automatic-mapping-of-motivational-text-messages-into-ontological-entities-for-smart-coaching-applications-3-2048.jpg)