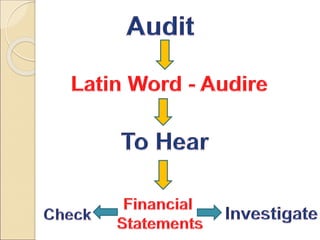
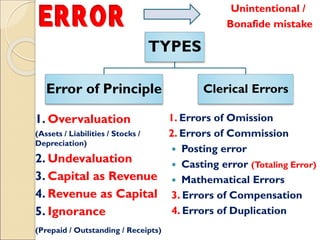
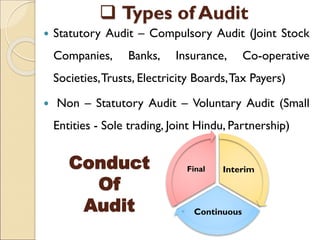
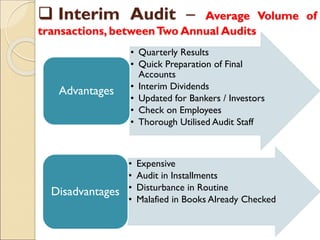
The document provides an introduction to auditing, focusing on its objectives, definitions, types of errors and fraud, and the principles guiding the audit process. It discusses the importance of true and fair views in financial statements, detailing advantages and limitations of auditing, as well as various audit types, including statutory and non-statutory. Key qualities of auditors and the concept of materiality in relation to auditing are also emphasized throughout the content.