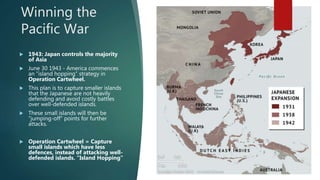
The document discusses the ending phases of World War II in both Europe and the Pacific. It describes the Allied strategy of "island hopping" to defeat Japan, involving taking less defended islands and using them to launch further attacks. It then details the Manhattan Project to develop atomic weapons and the bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945. While the U.S. argued this ended the war sooner than an invasion would have, others debate whether the atomic bombings were justified given the massive loss of civilian life.