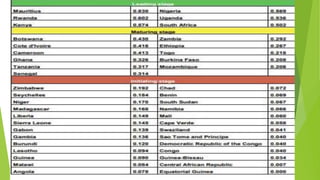
Cyber security is important to protect networks, computers, programs and data from unauthorized access. The document discusses the costs of cyber security to businesses and the global economy. Larger businesses and those with more sensitive data require more spending on security products, services, audits and personnel. Cyber attacks globally cost over $3.5 billion annually in the US alone. The Cyber Security Index ranks African countries' cyber security commitments and readiness. Tanzania has improved to the 5th position in the "maturing stage" category due to strengthened legal frameworks.