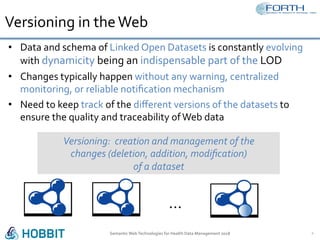
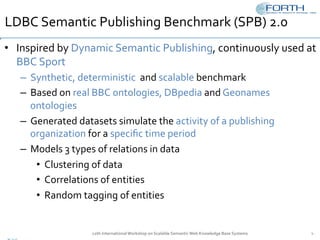
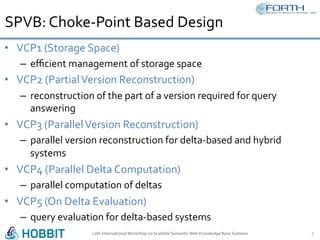
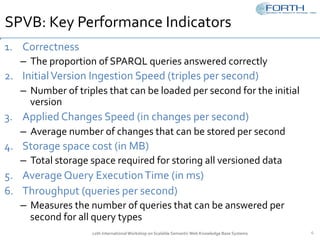
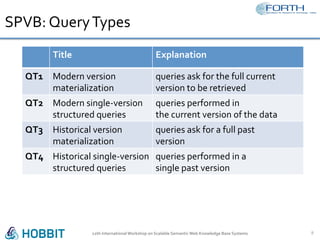
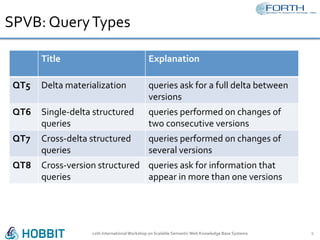
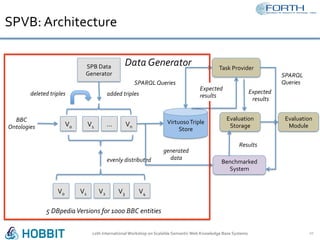
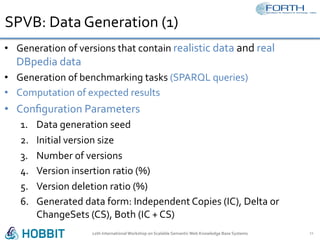
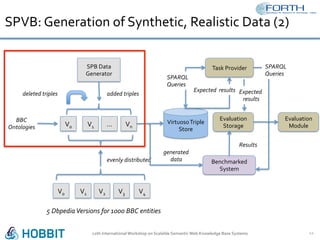
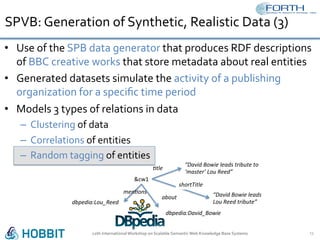
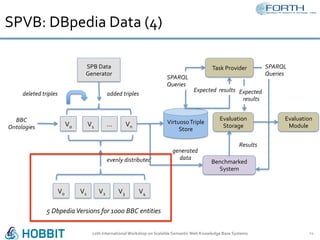
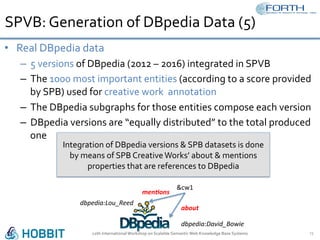
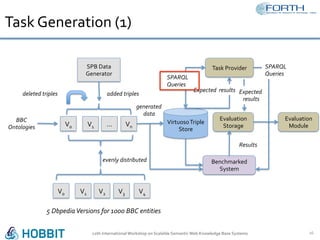
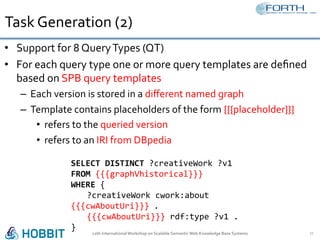
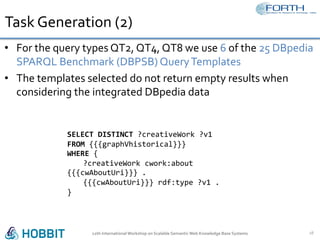
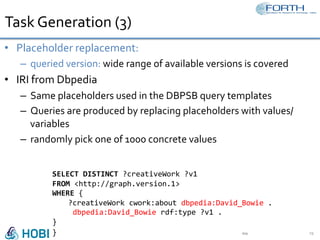
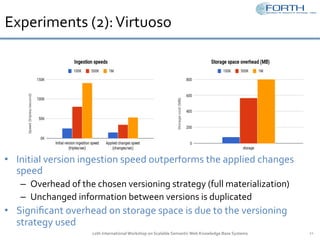
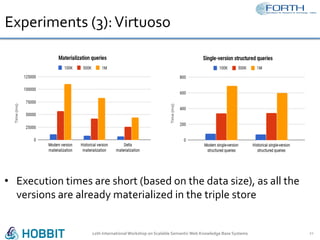
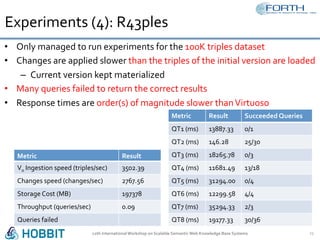
The document discusses the development of the Semantic Publishing Versioning Benchmark (SPVB) designed to assess the performance of various linked data versioning systems. It highlights the importance of tracking dataset versions for quality and traceability, detailing key performance indicators and types of versioning queries. Additionally, it describes a comparative analysis of benchmarked systems, showcasing their operational efficiencies and challenges in a high-volume data context.