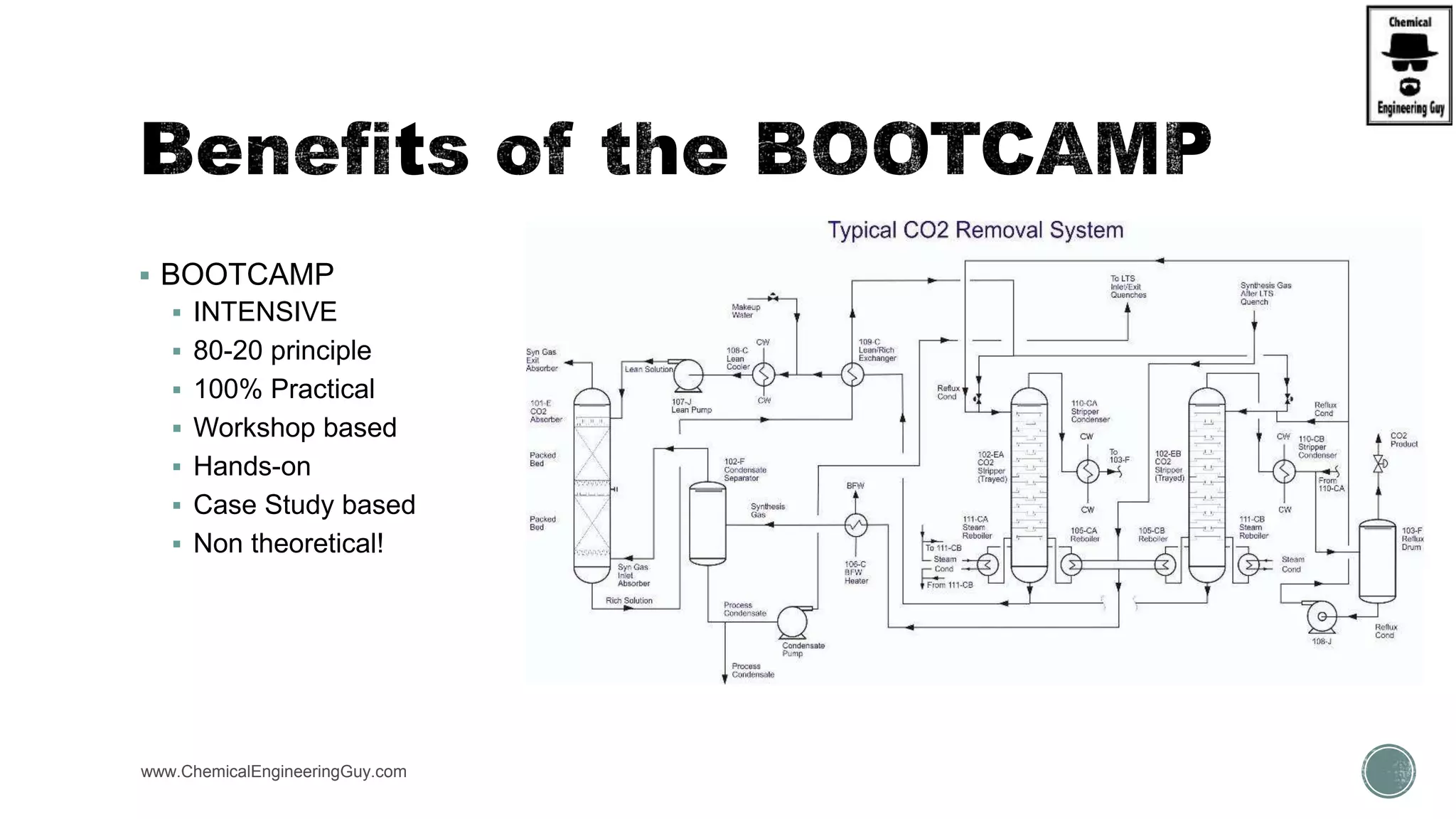
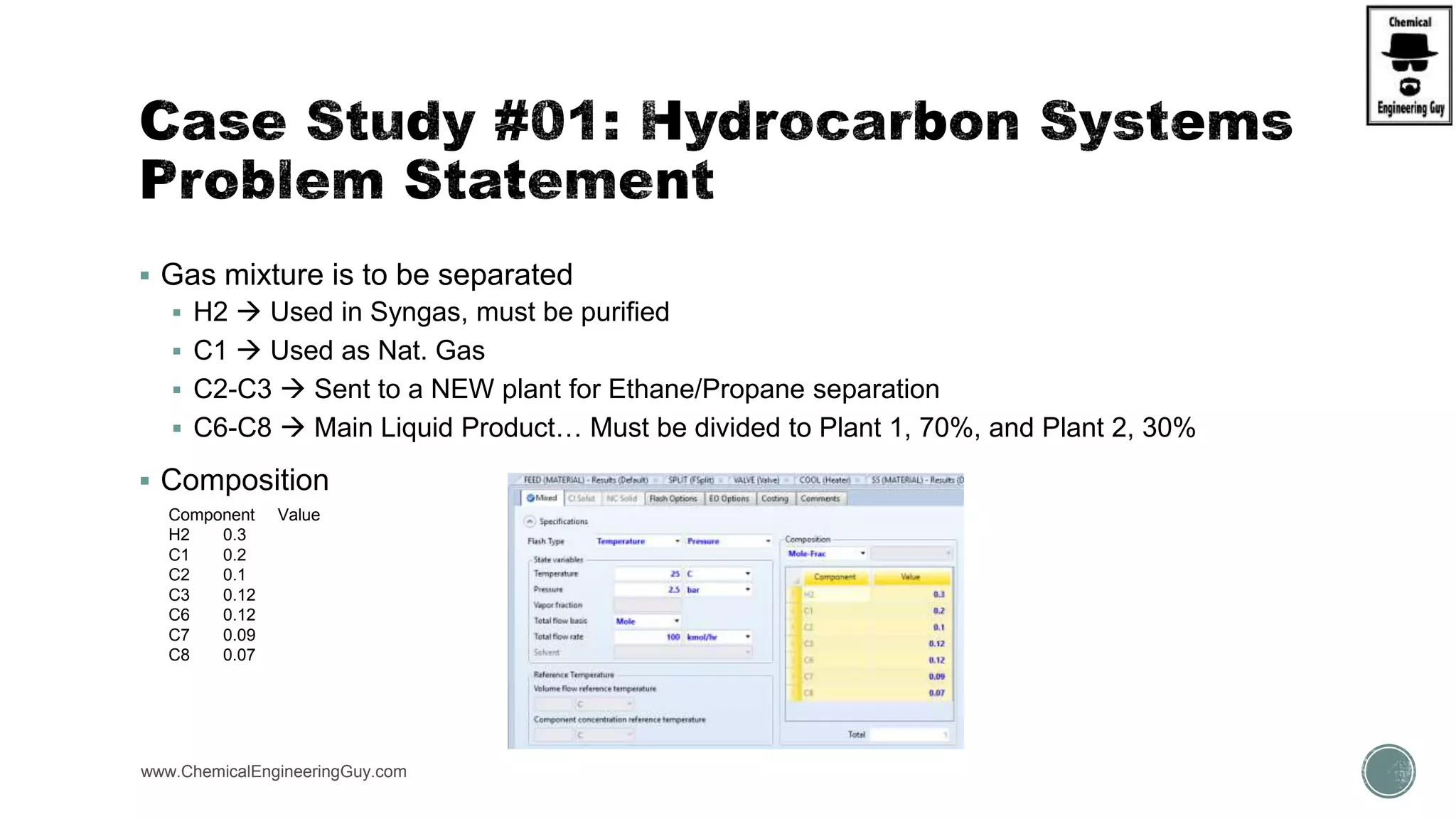
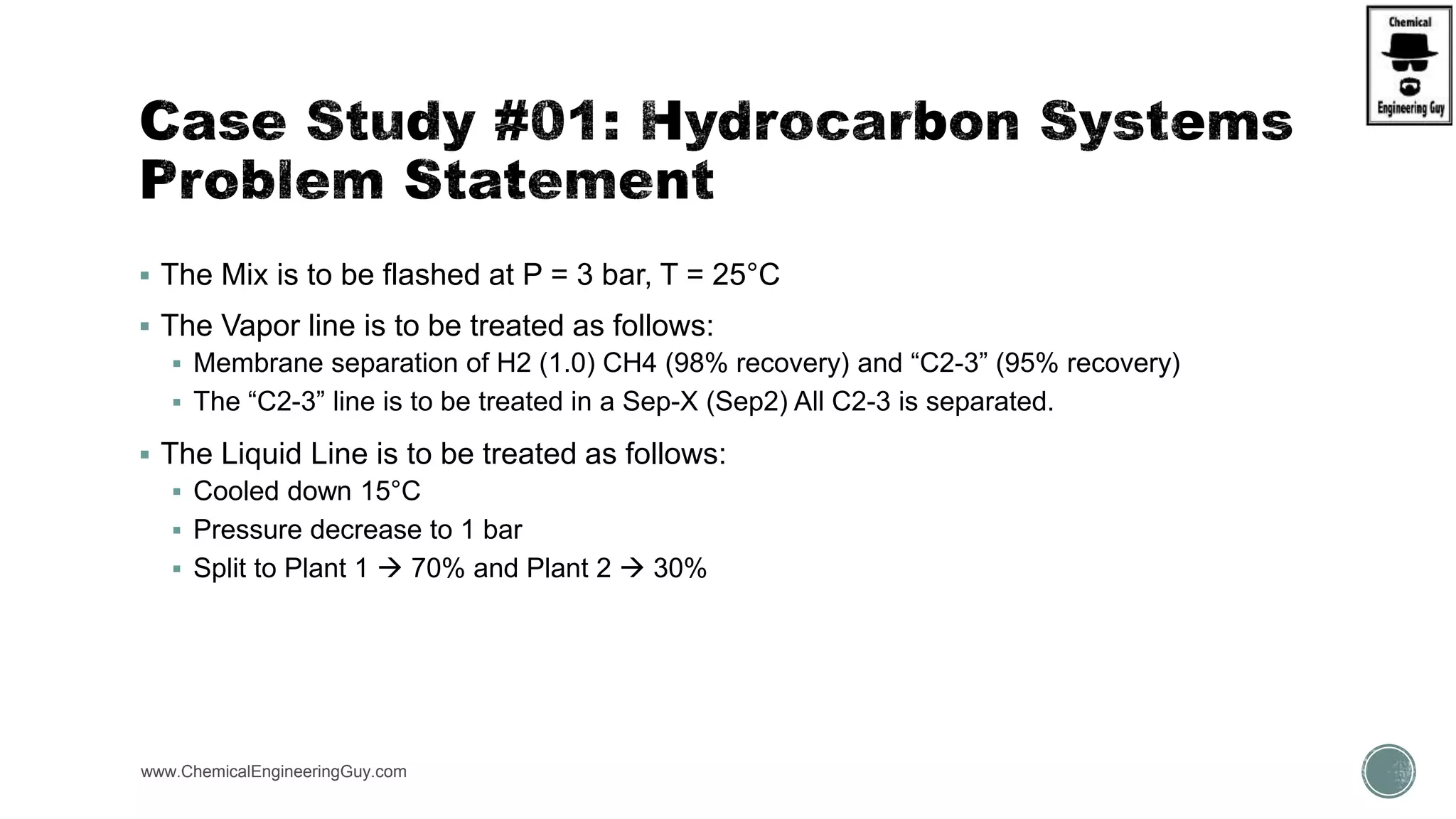
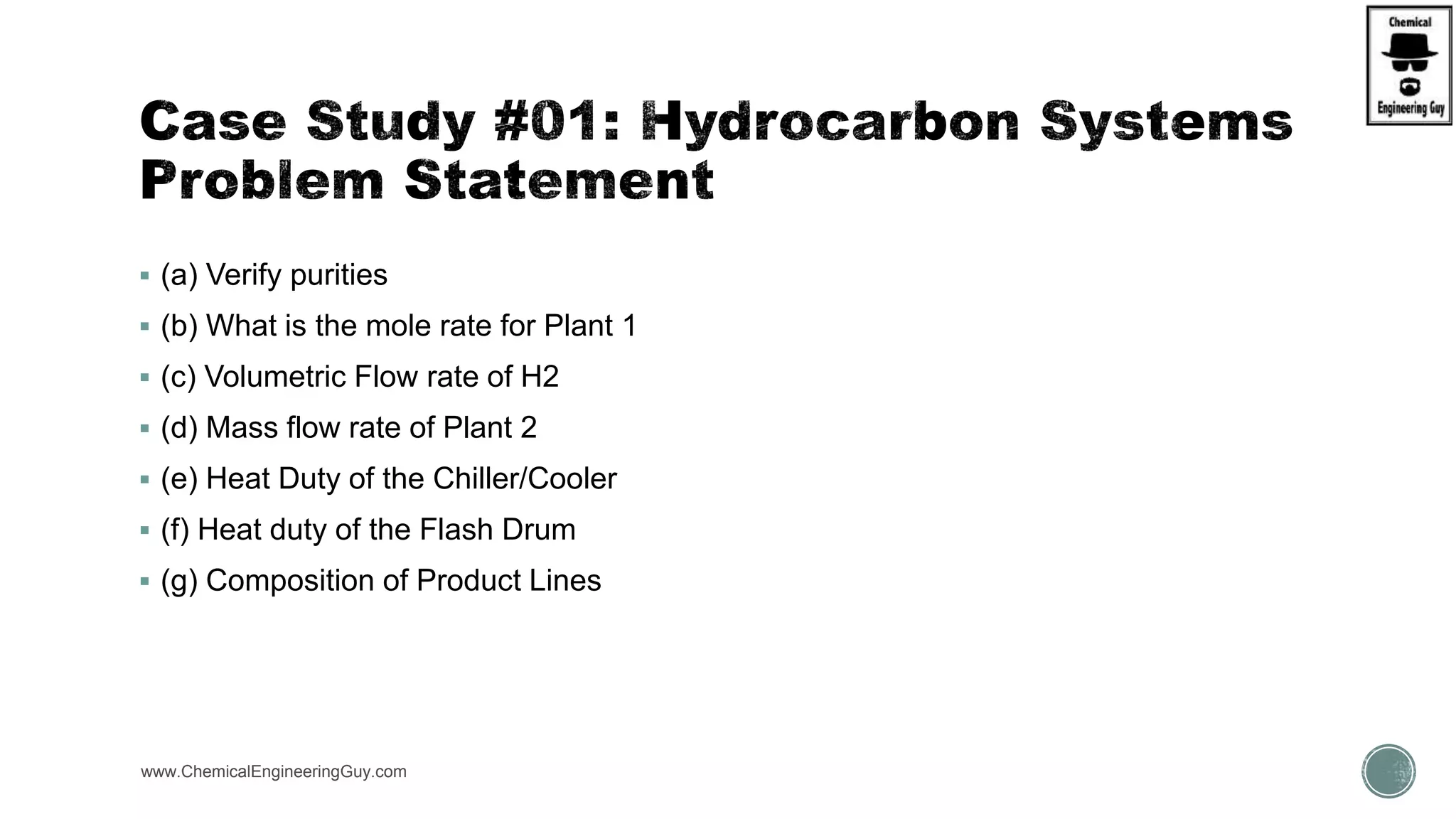
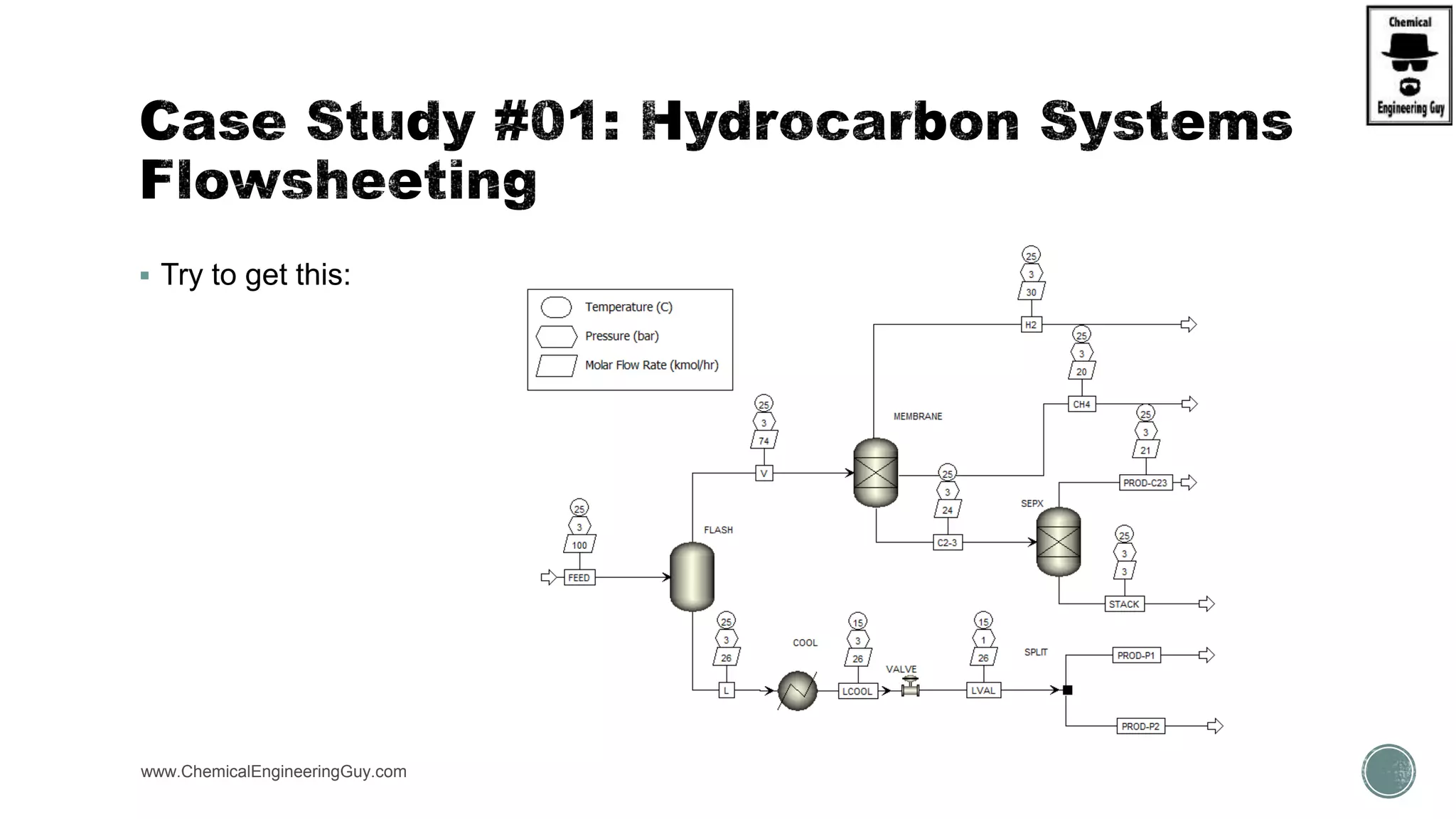
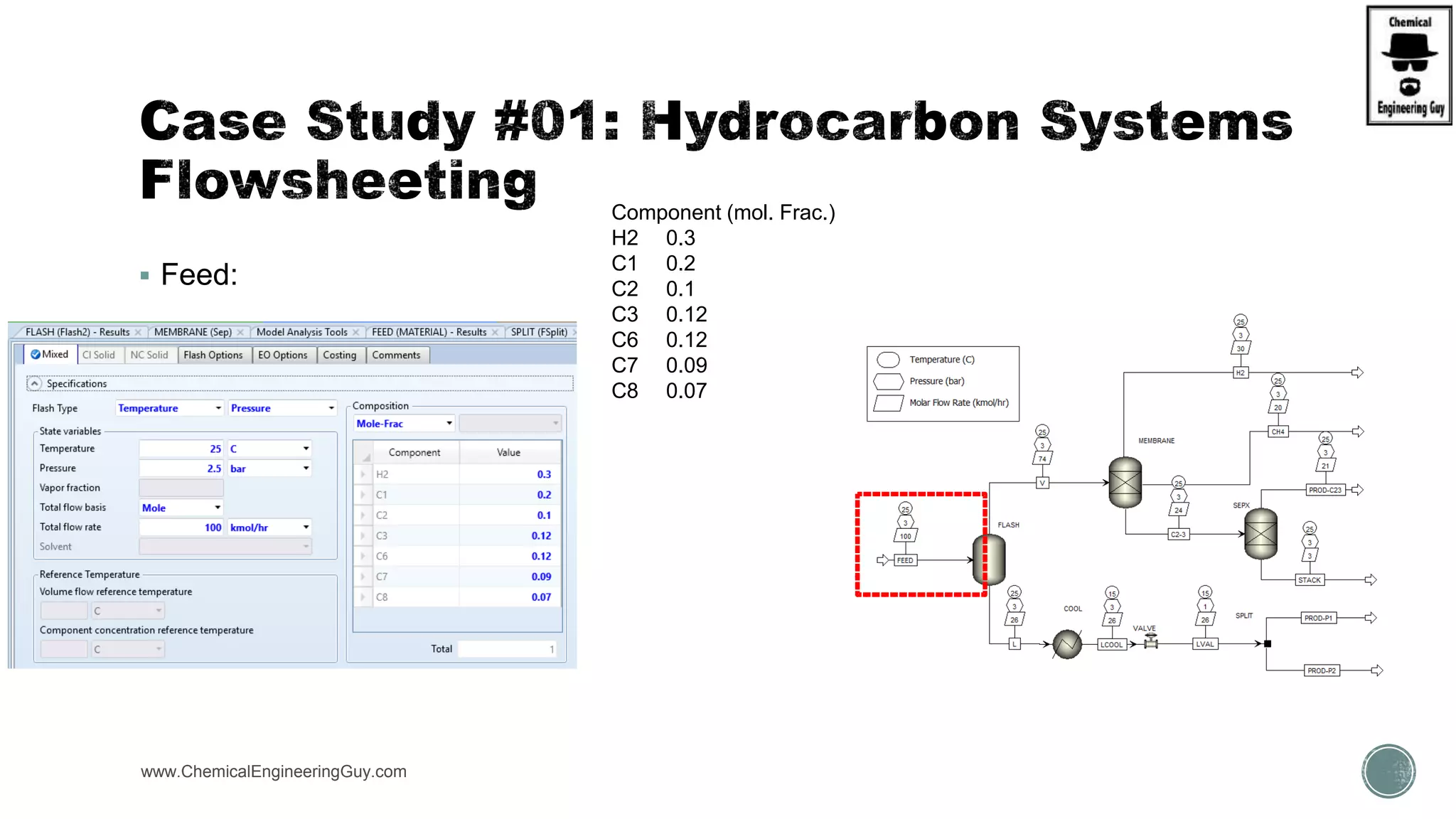
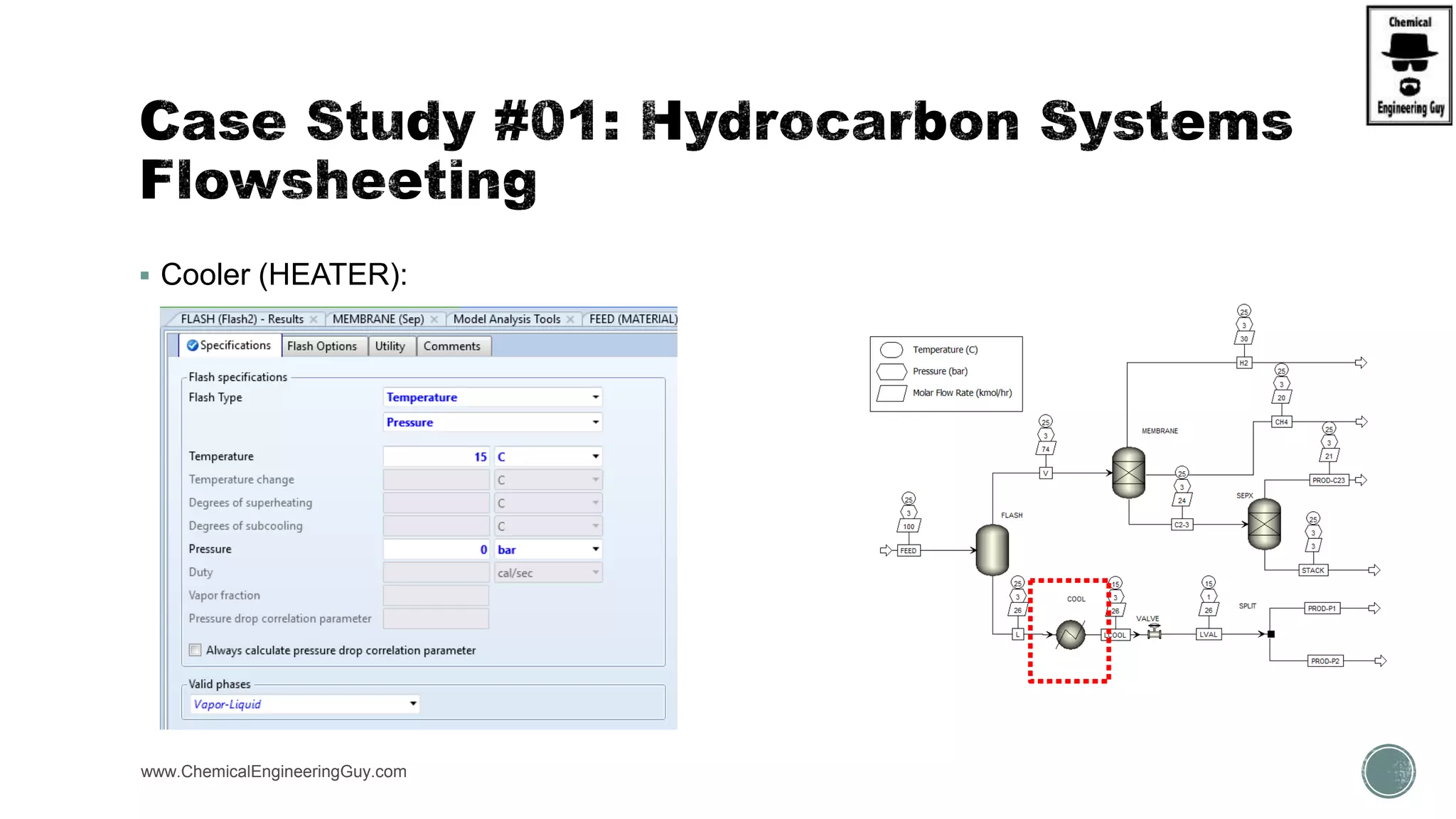
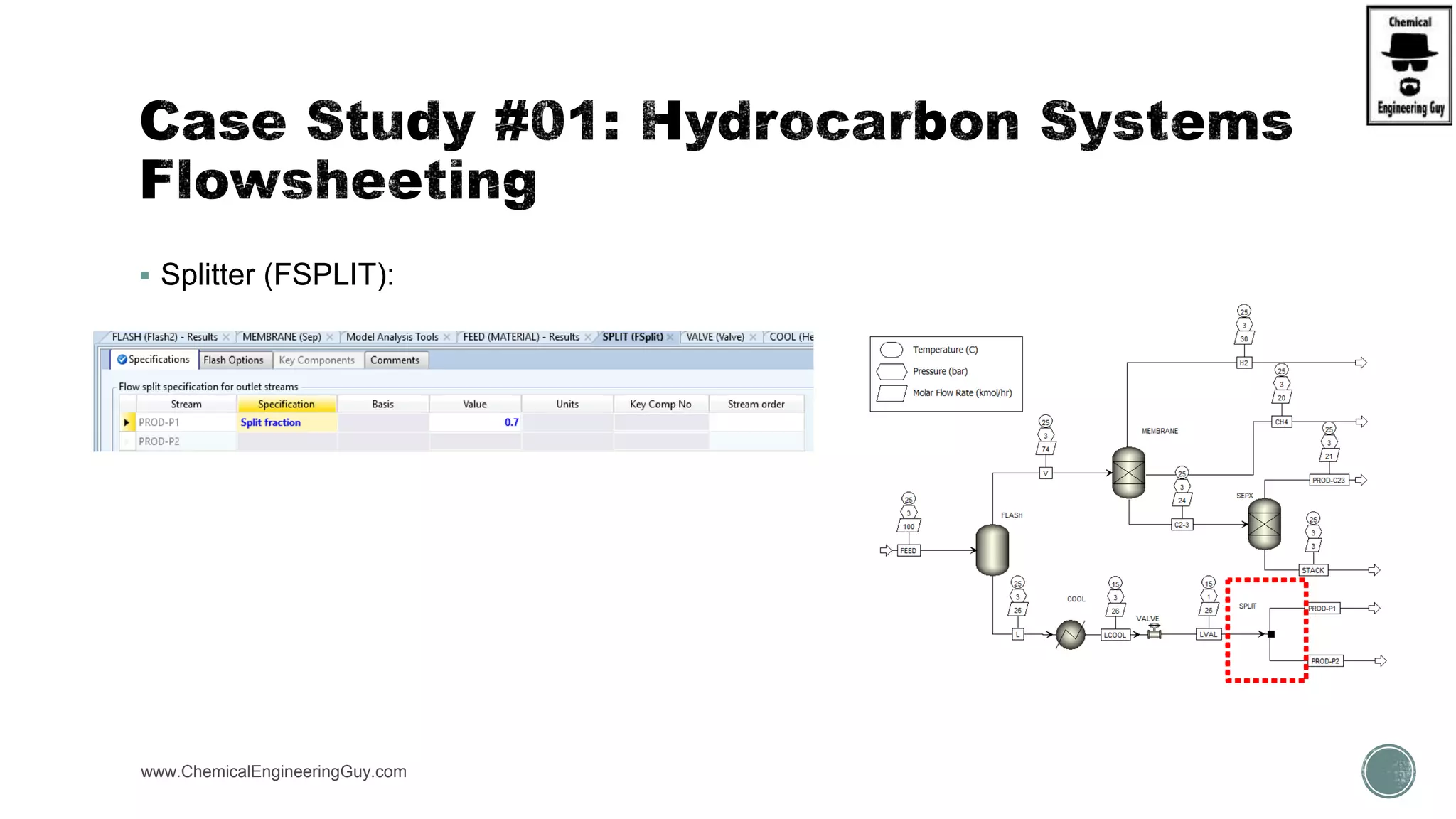
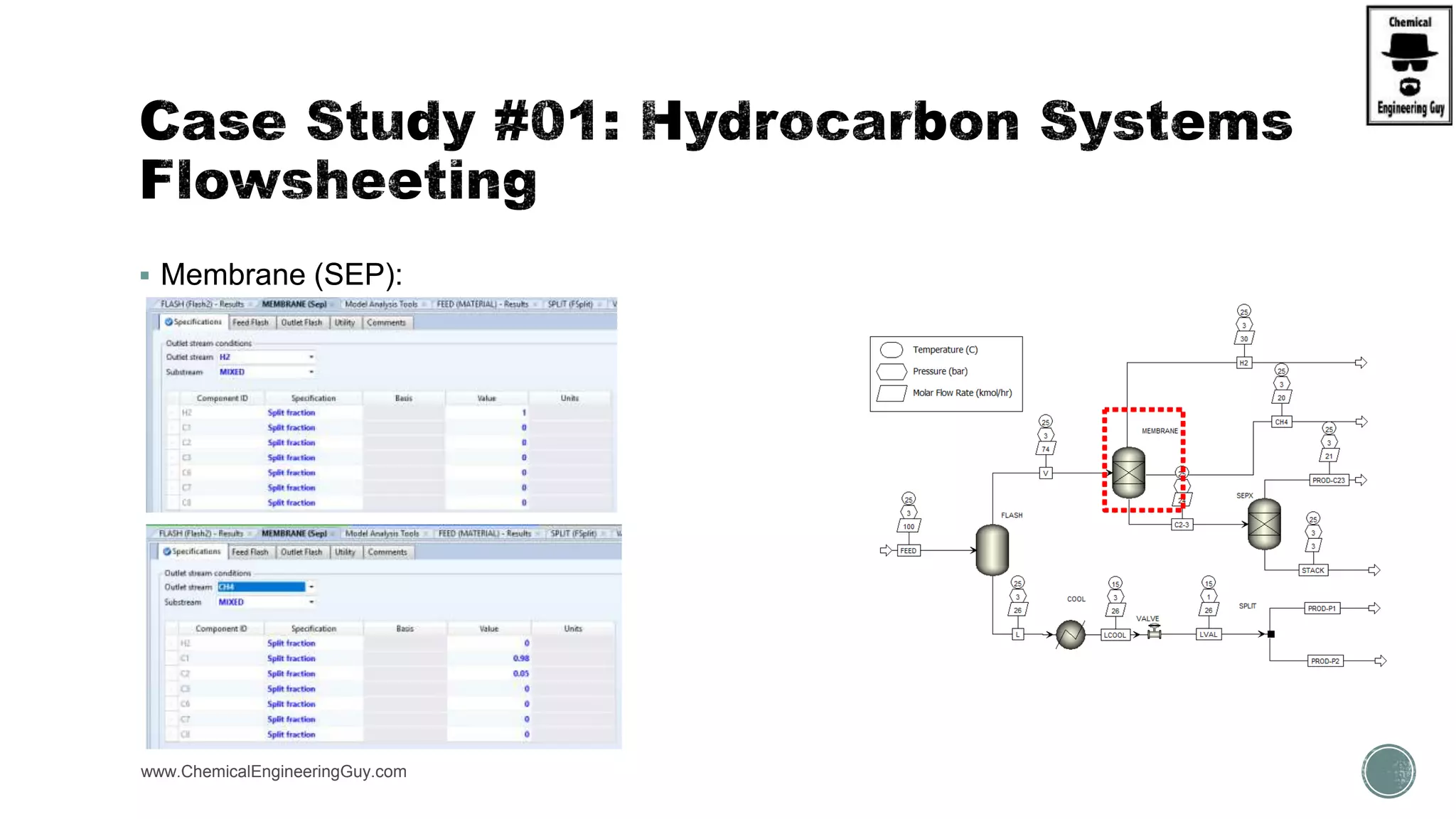
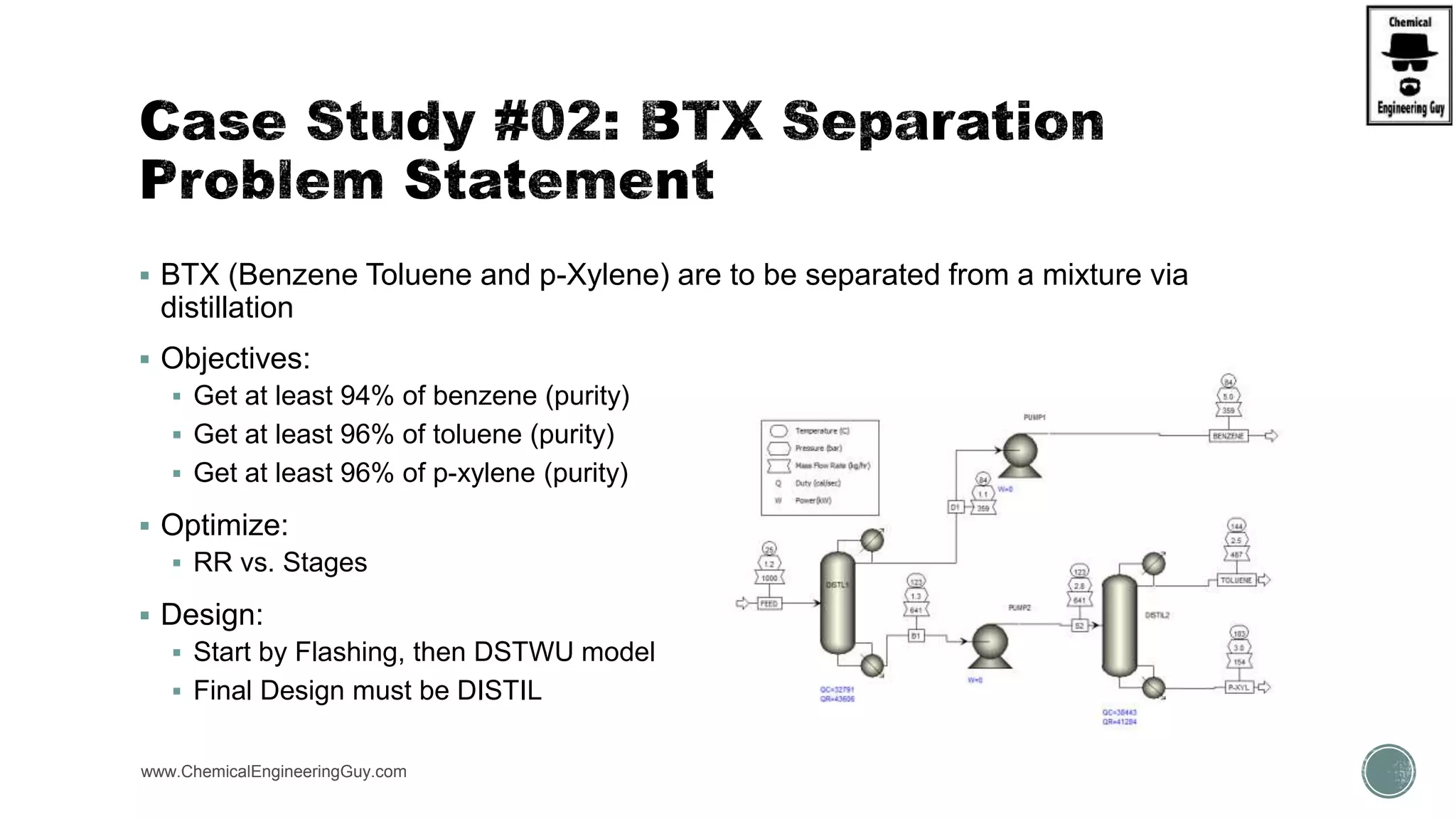
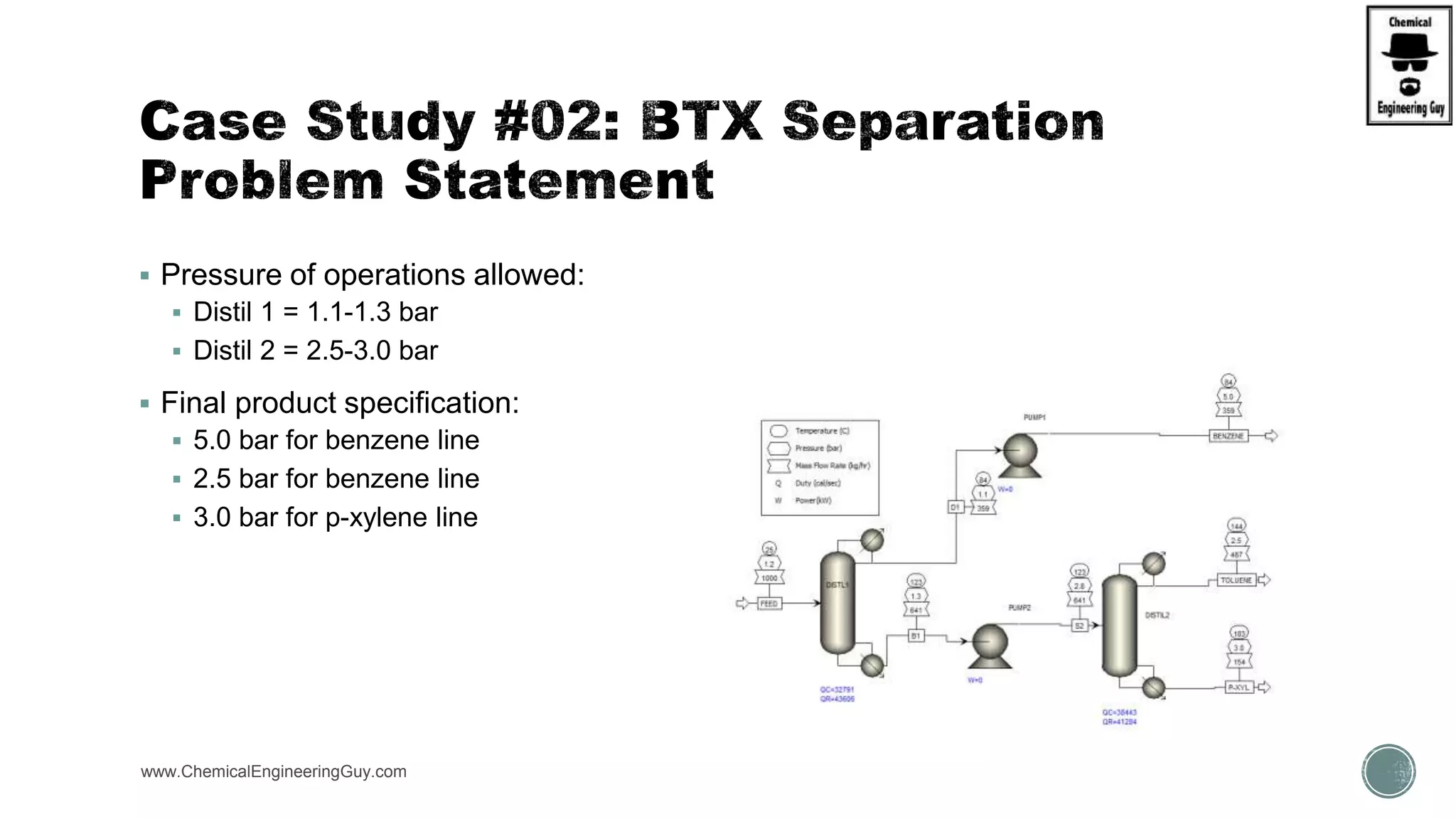
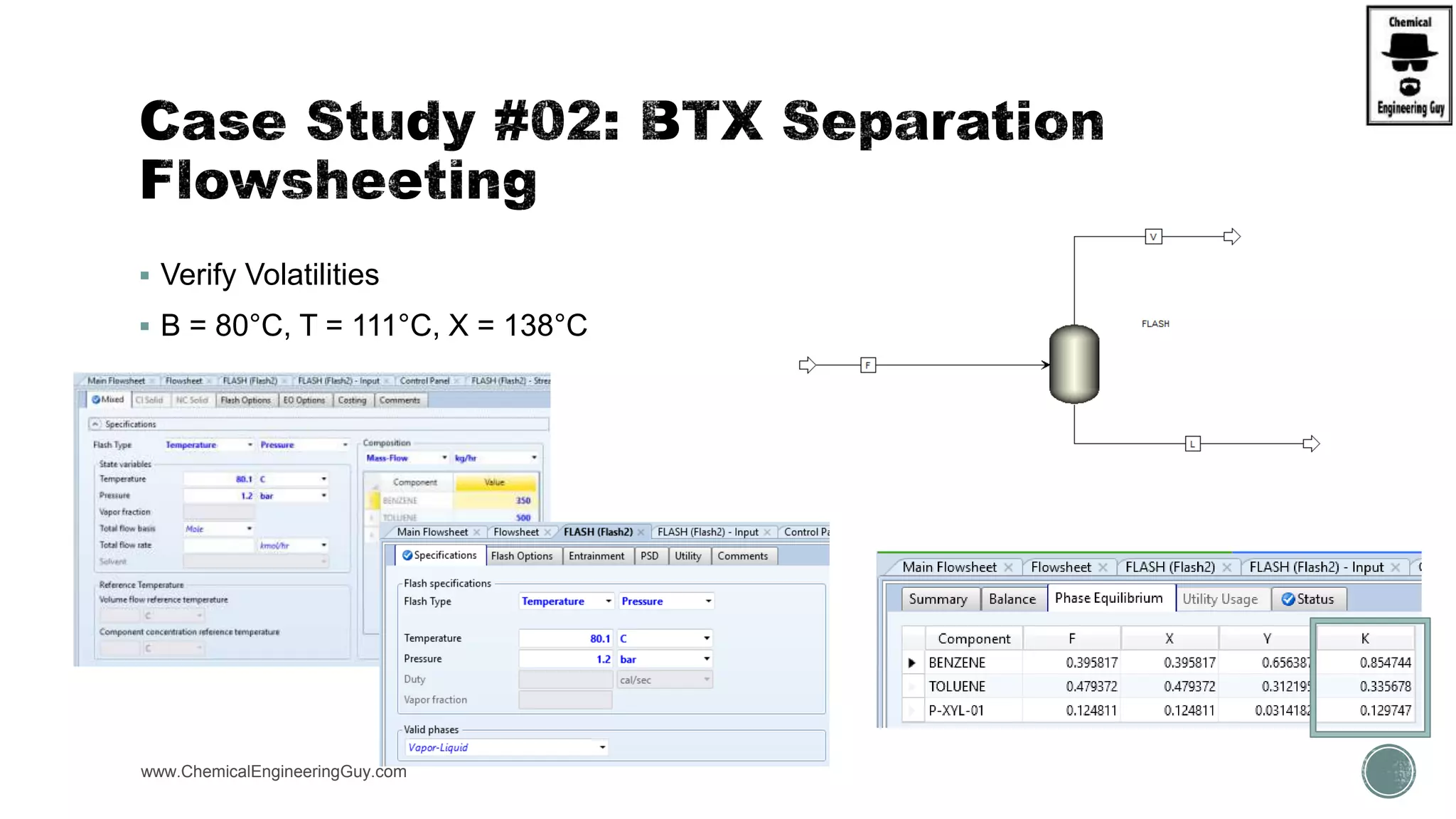
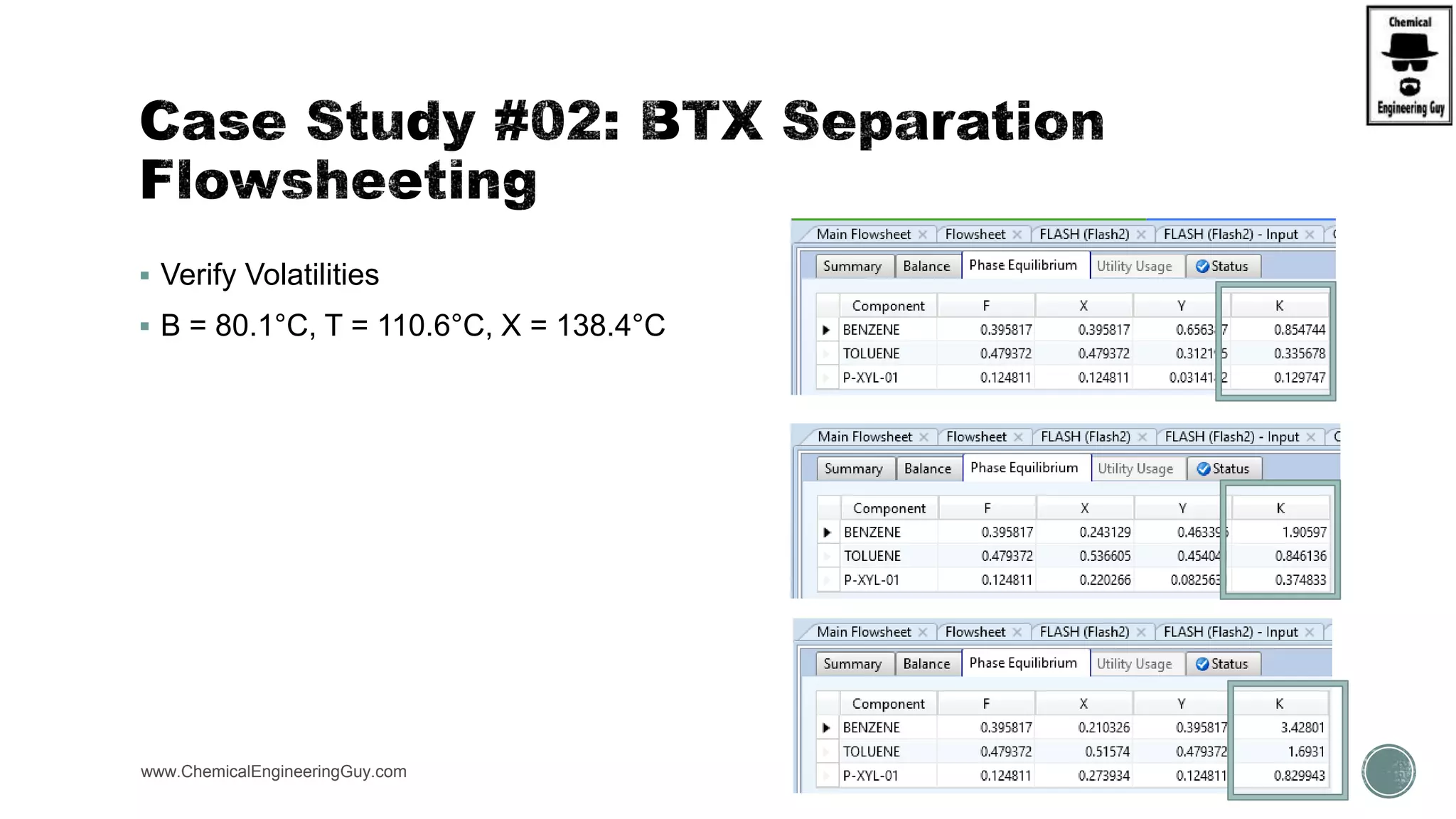
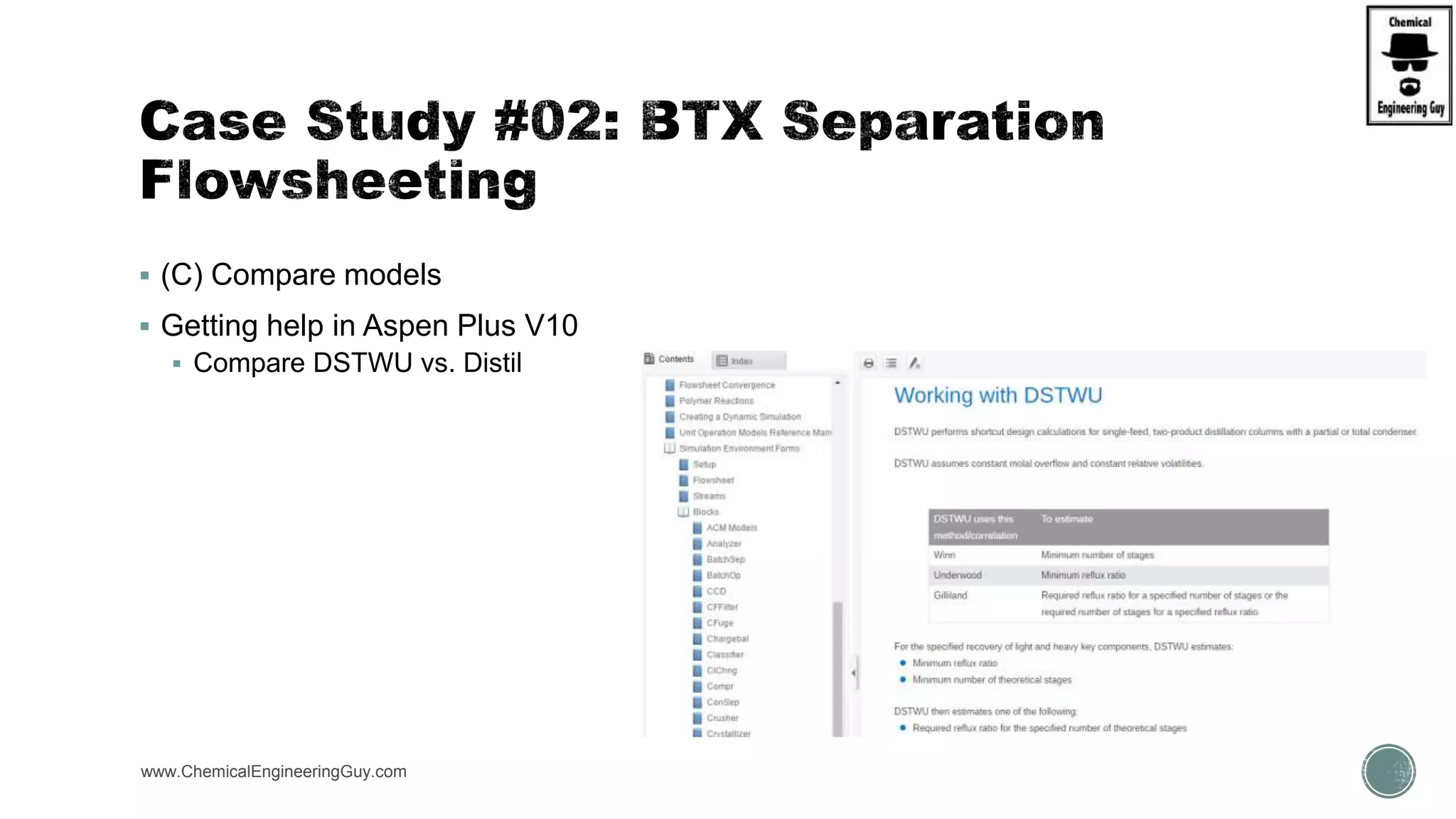
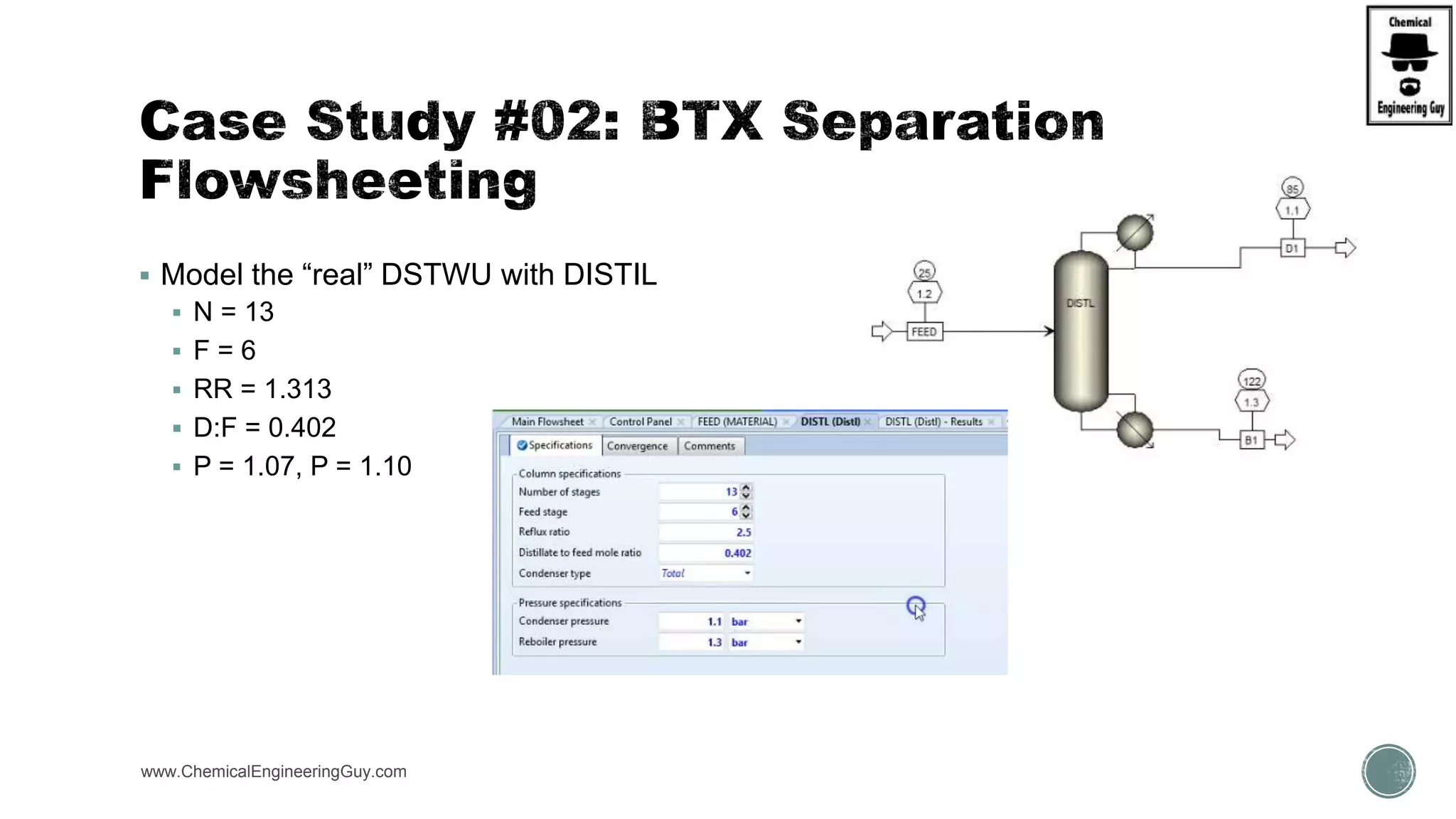
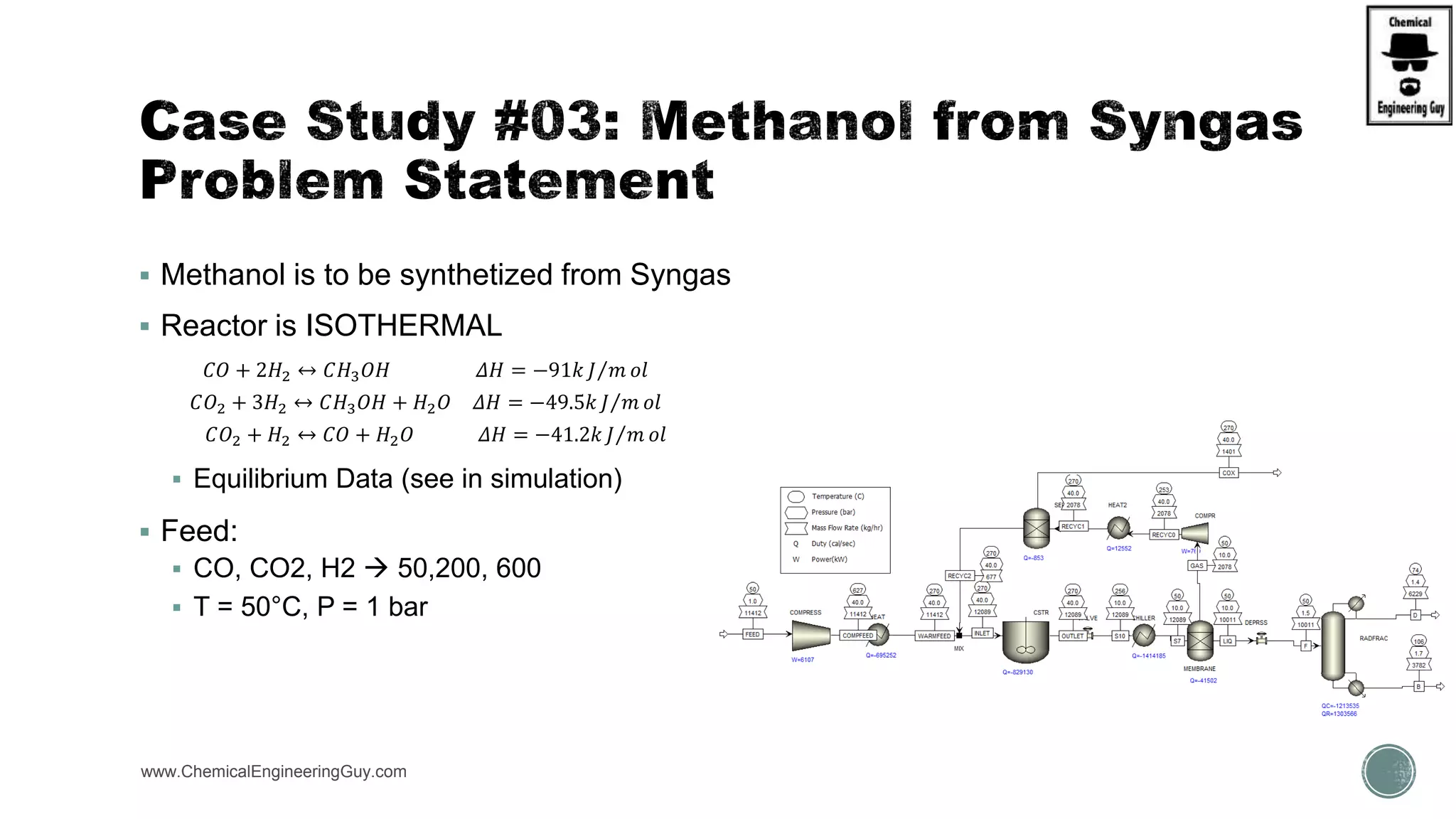
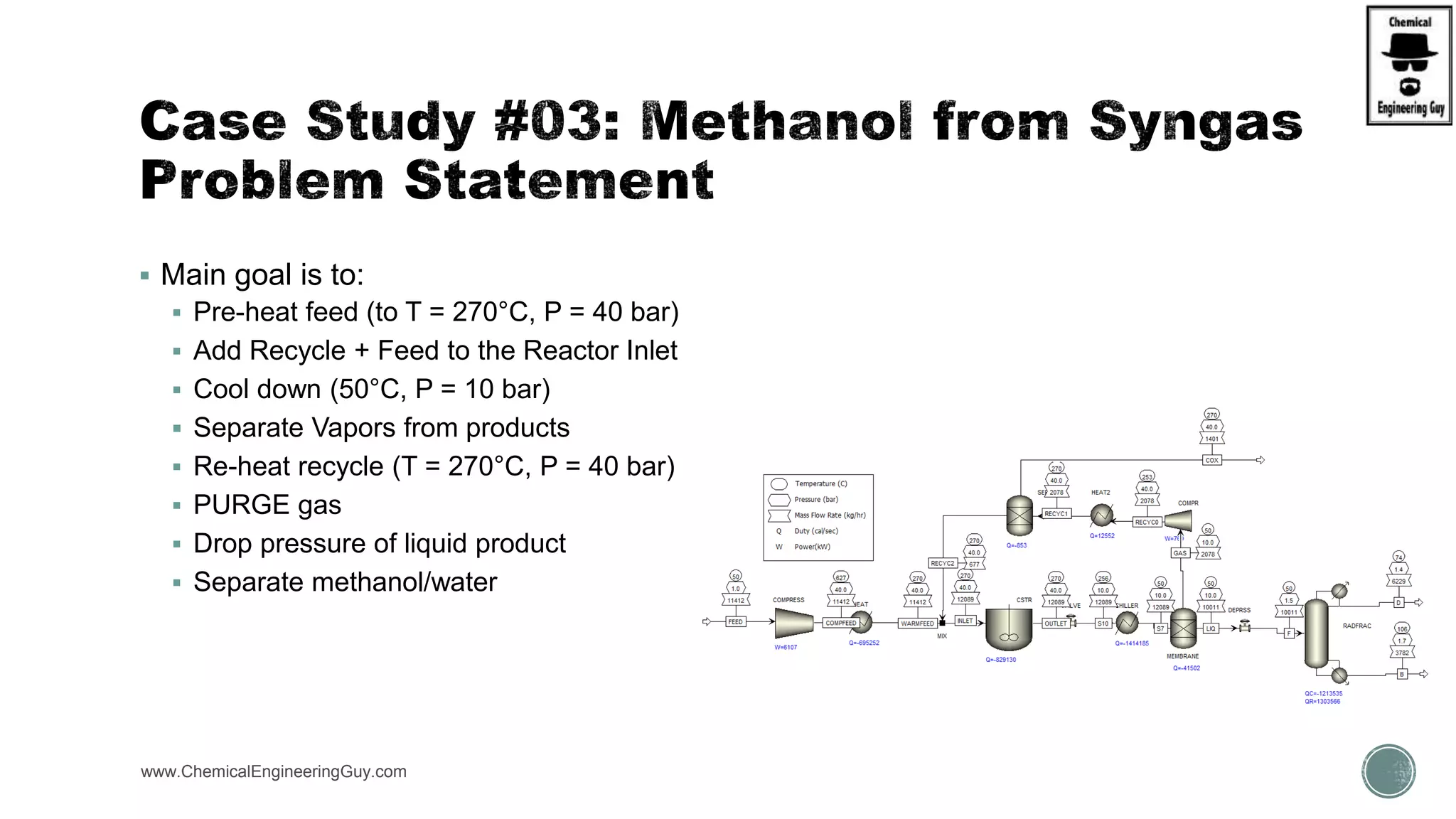
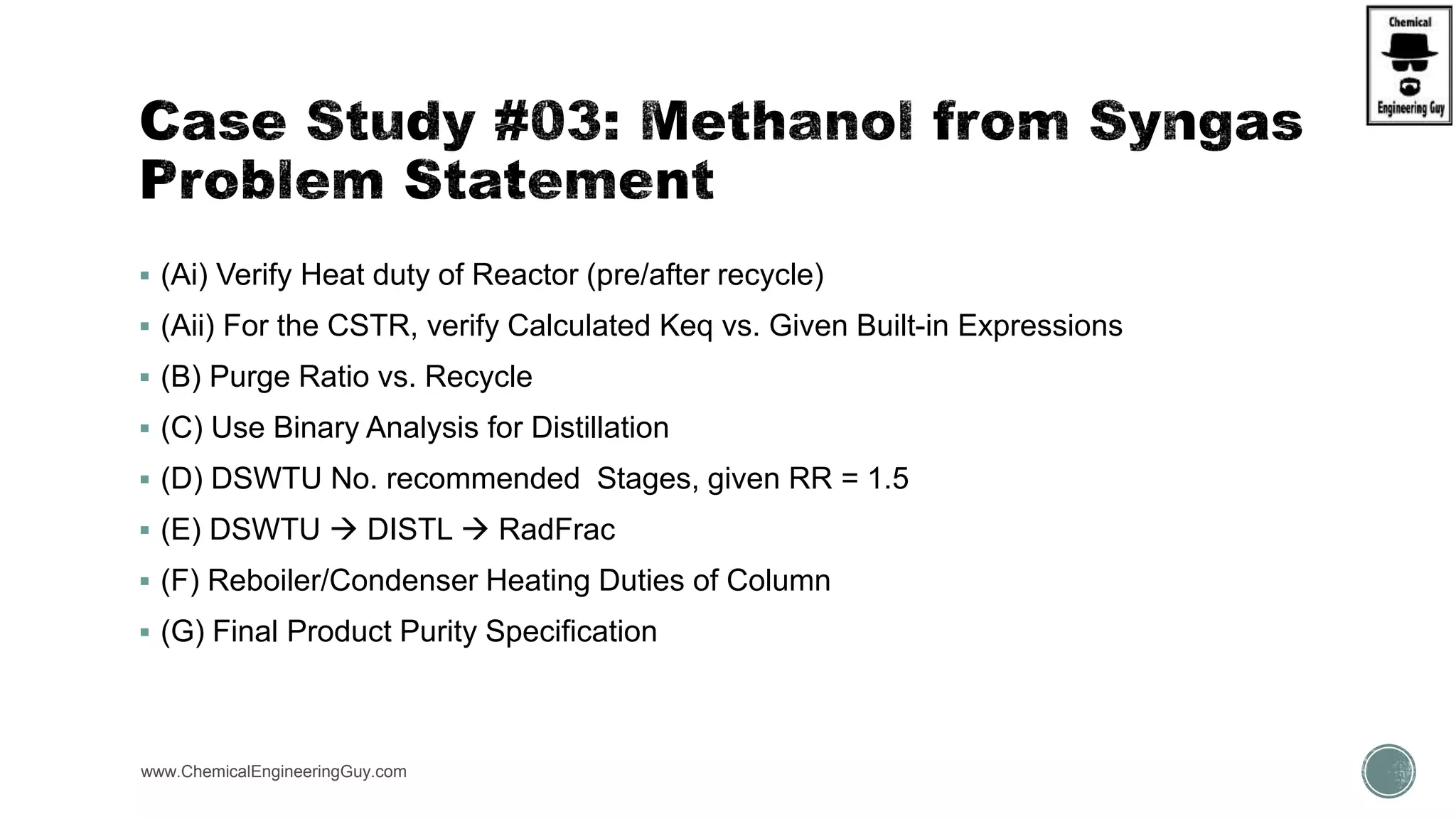
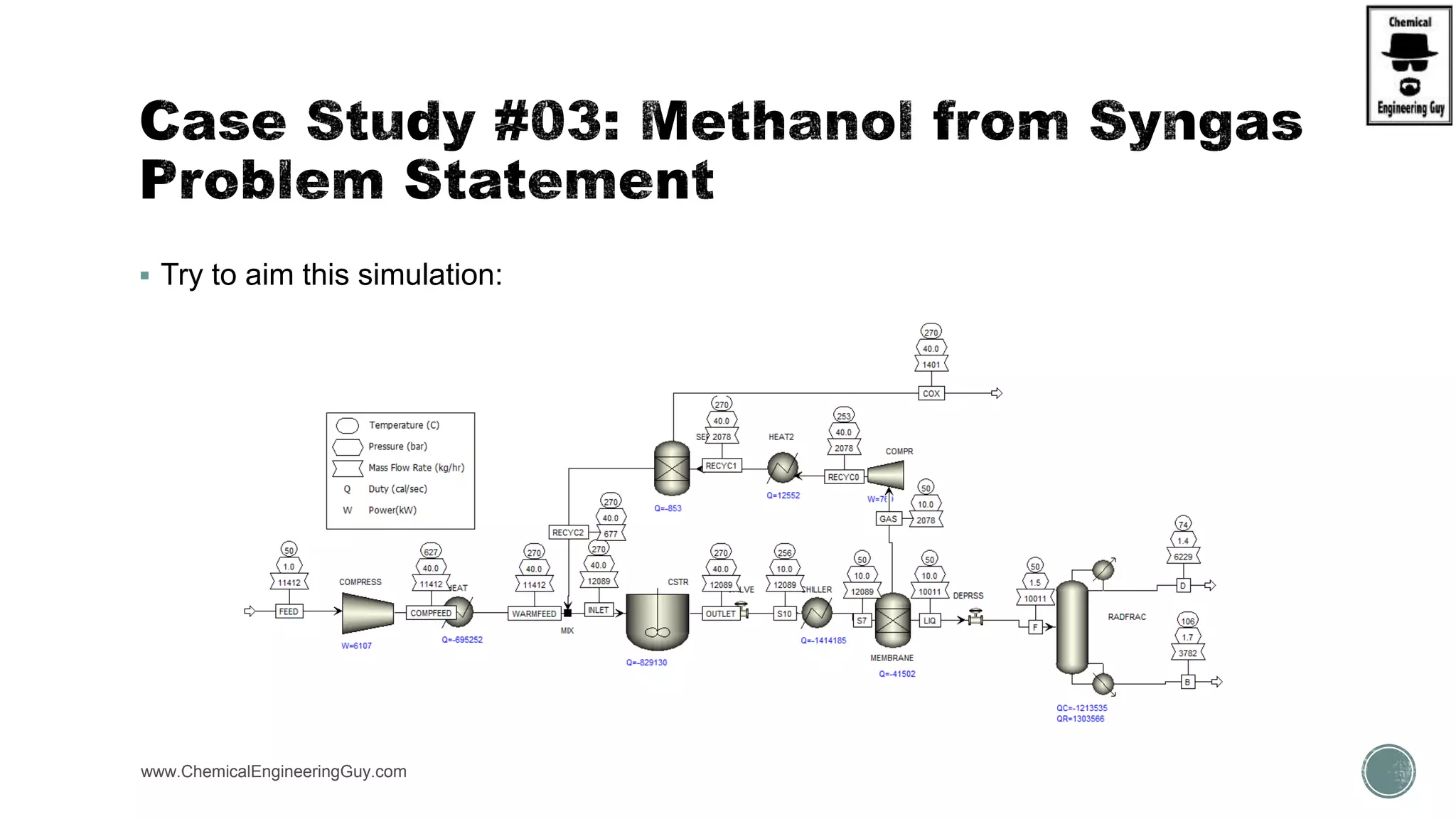
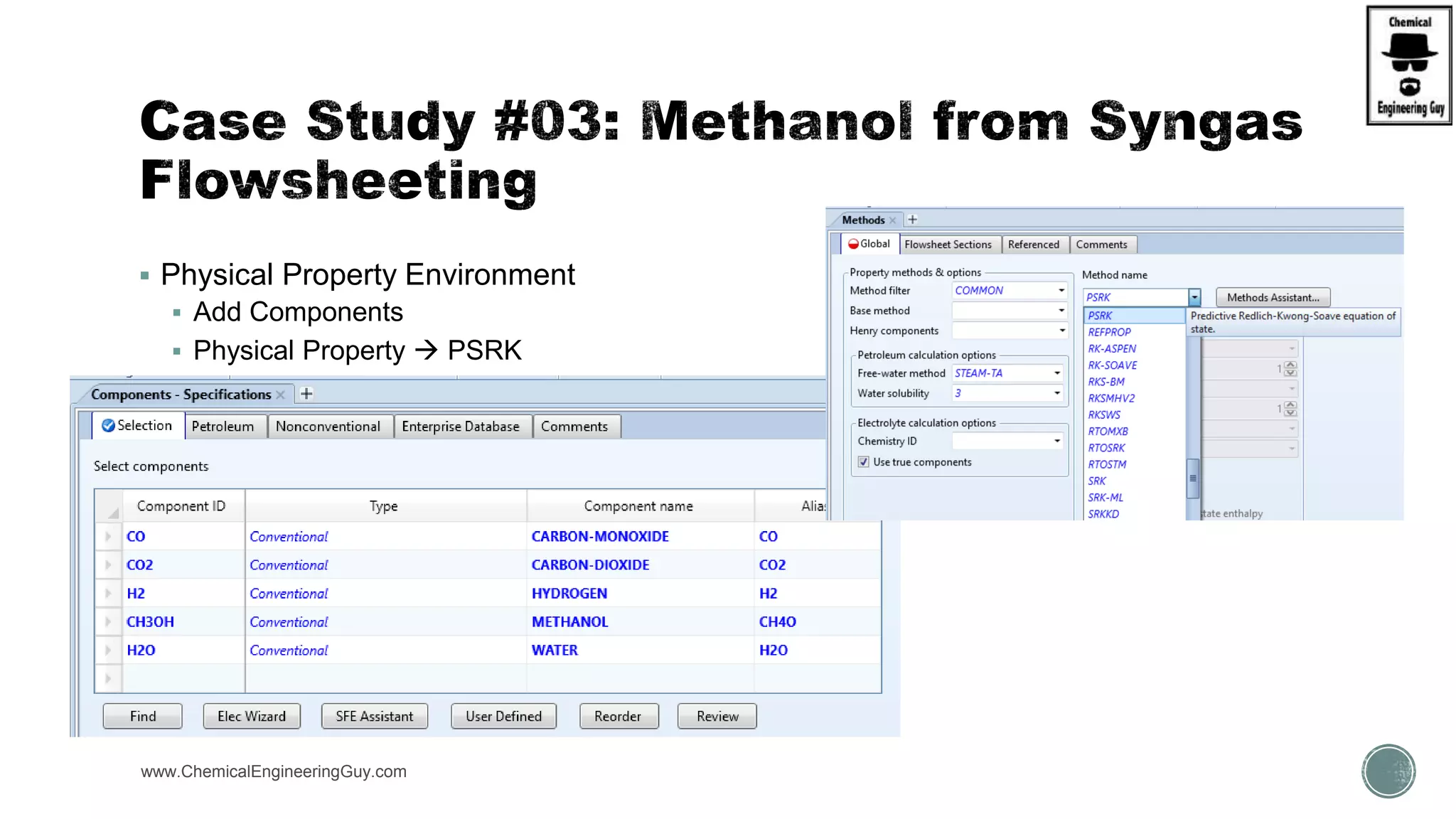
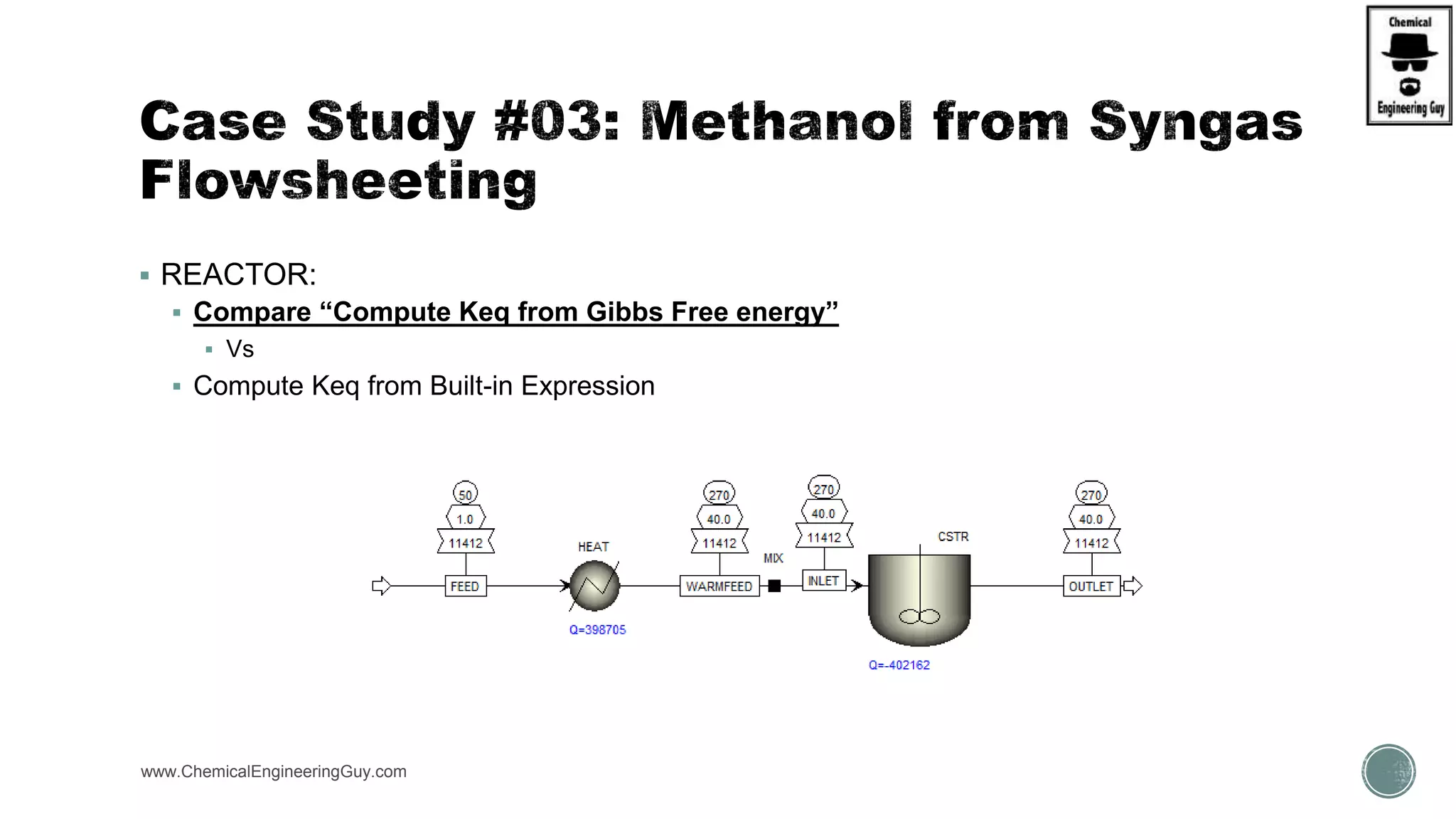
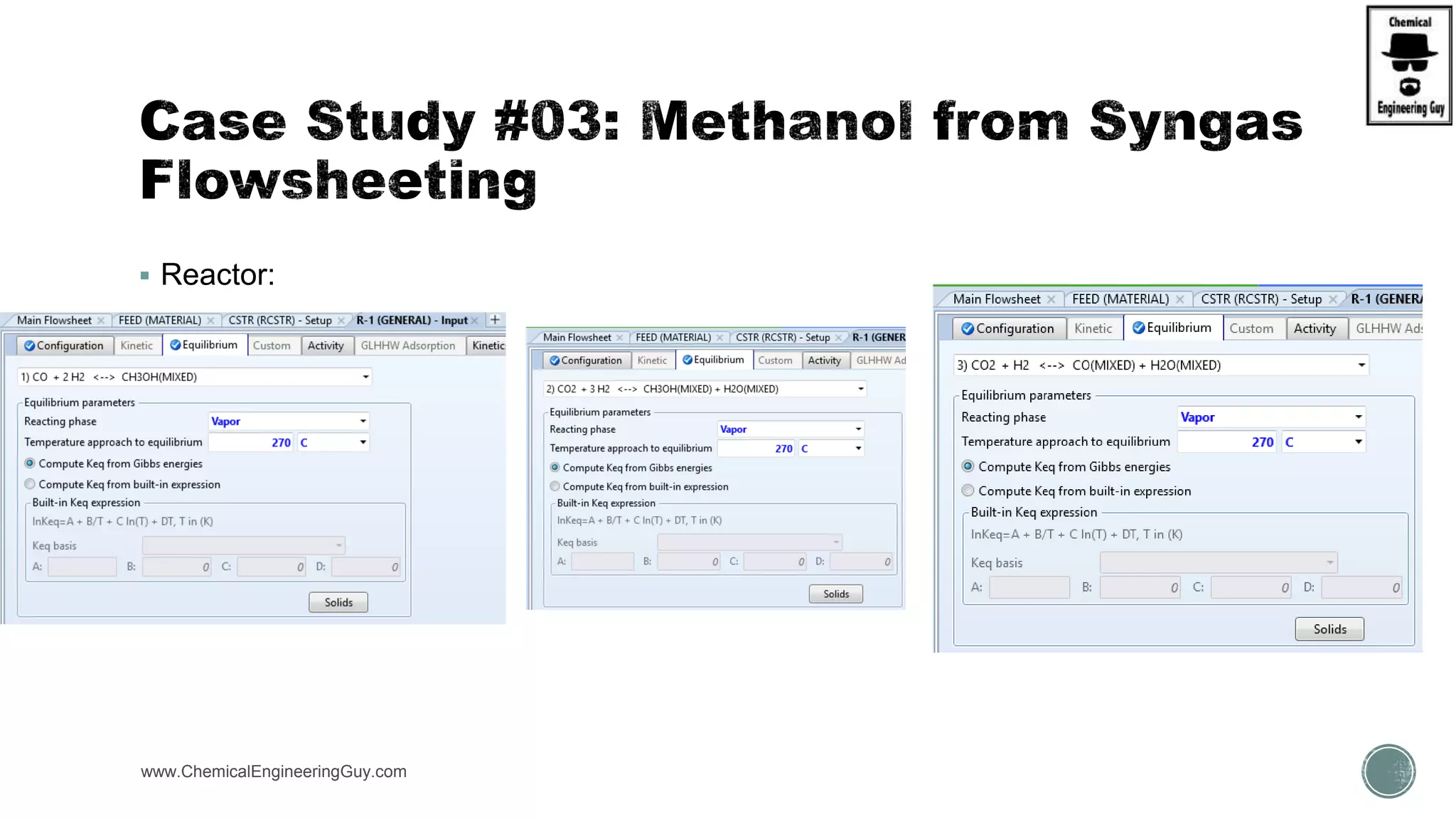
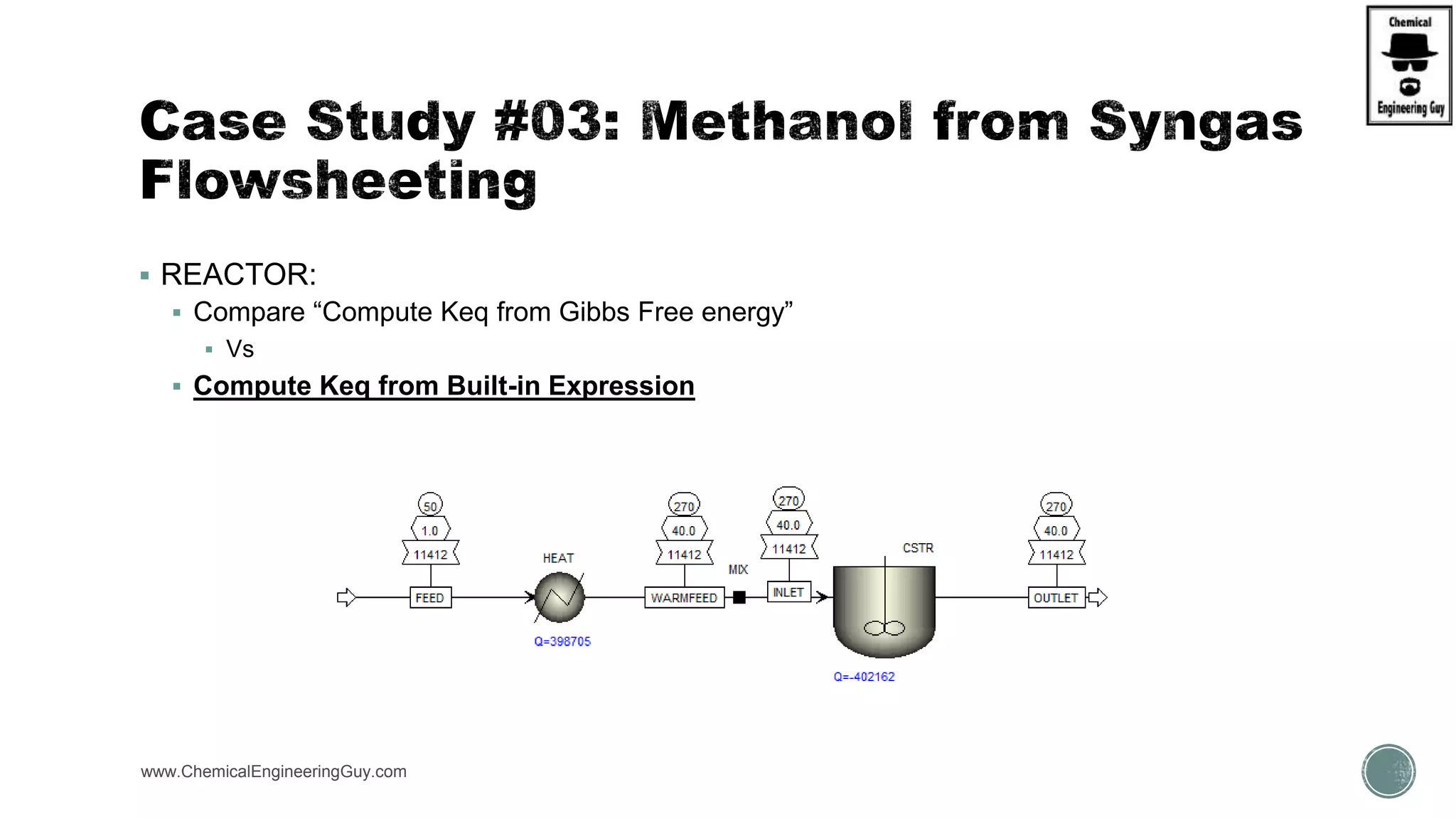
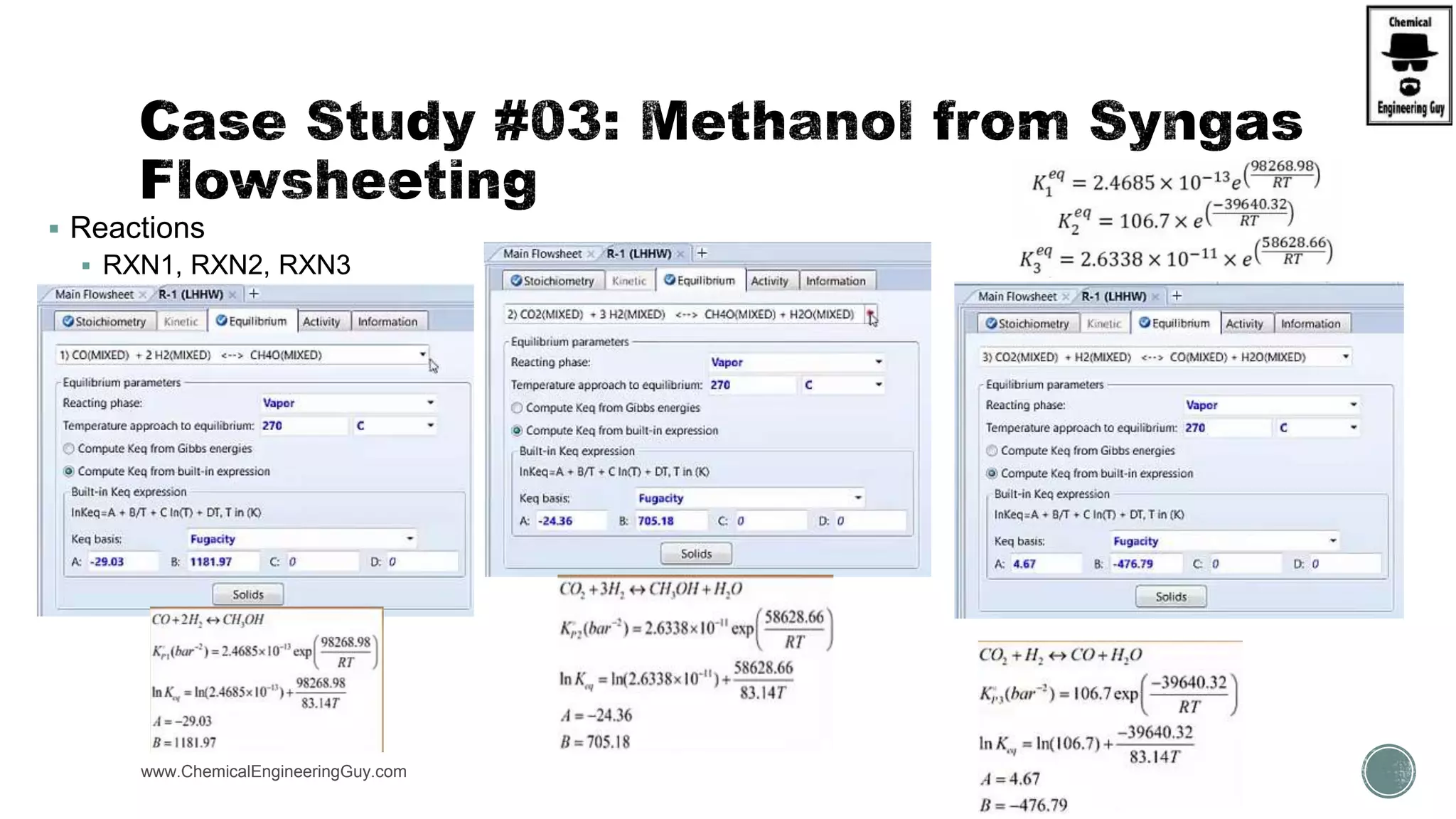
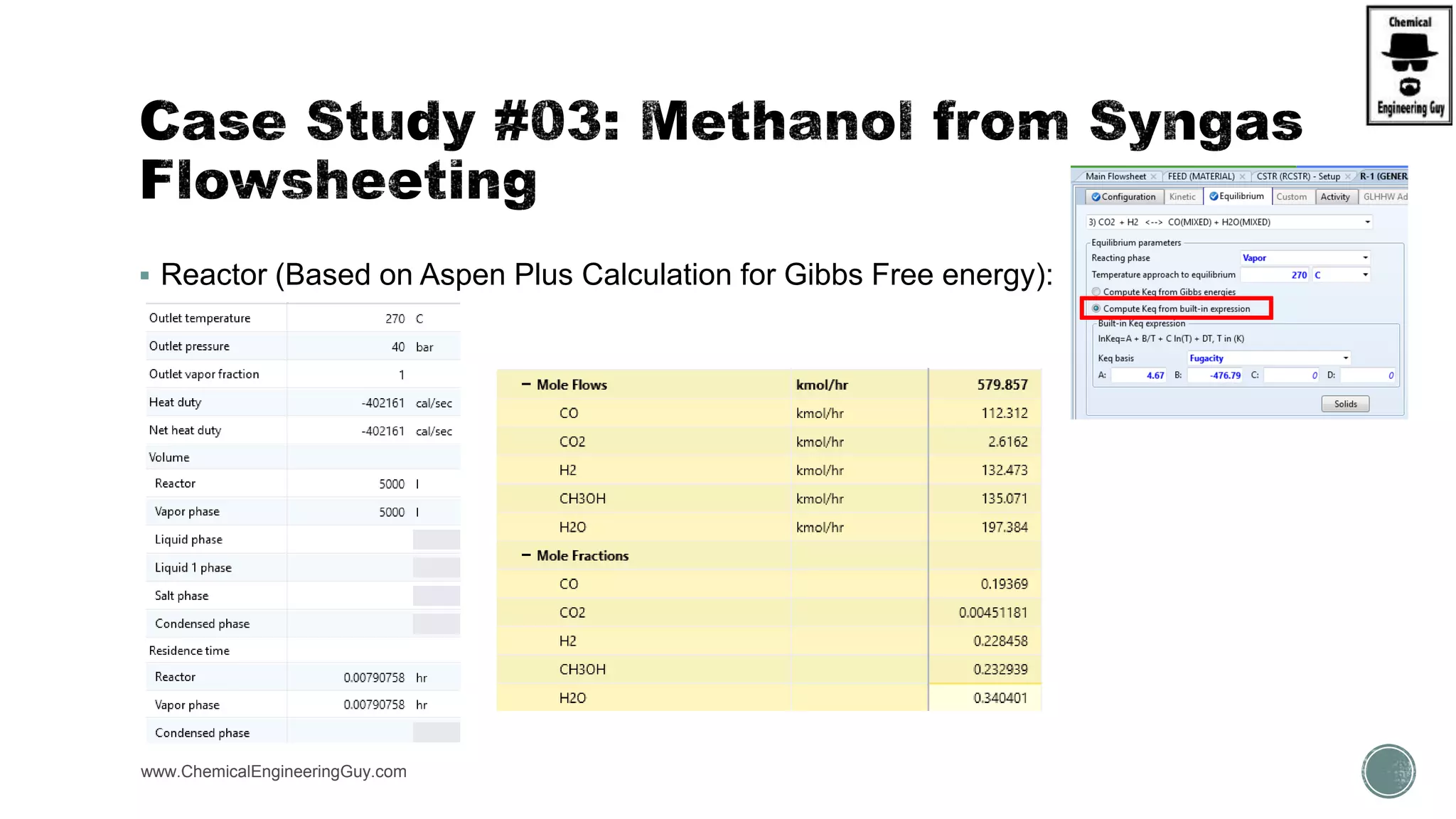
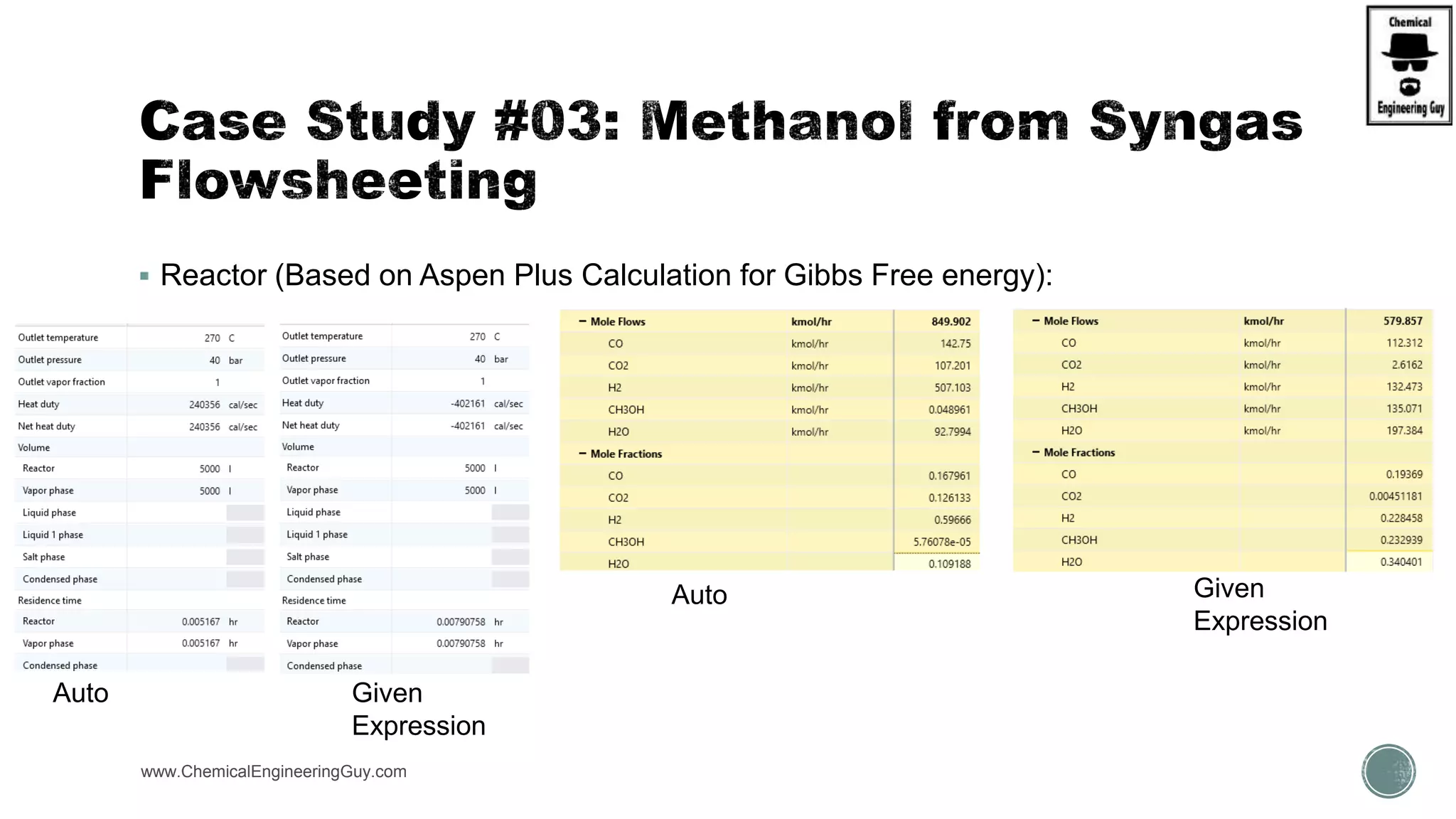
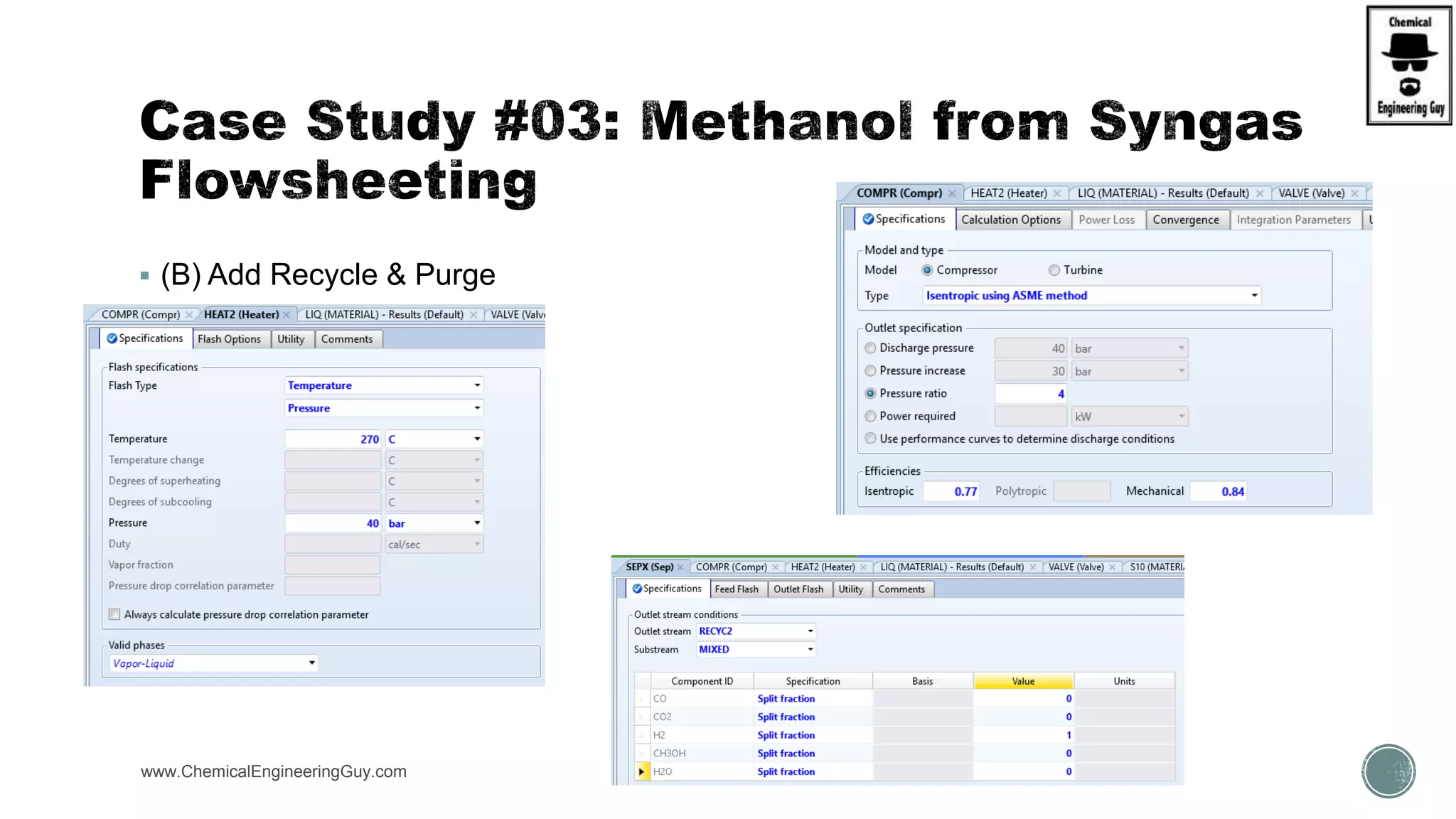
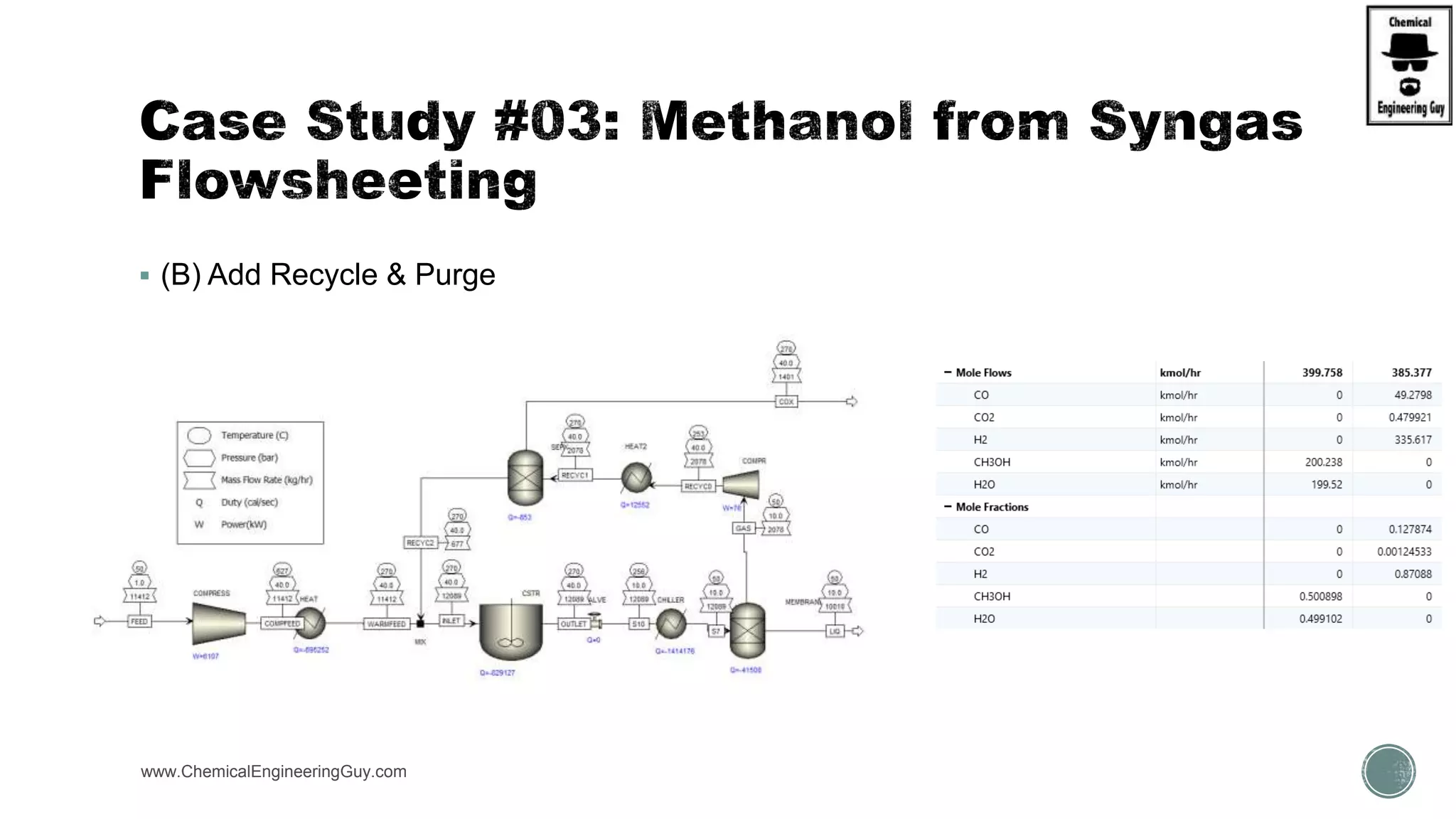
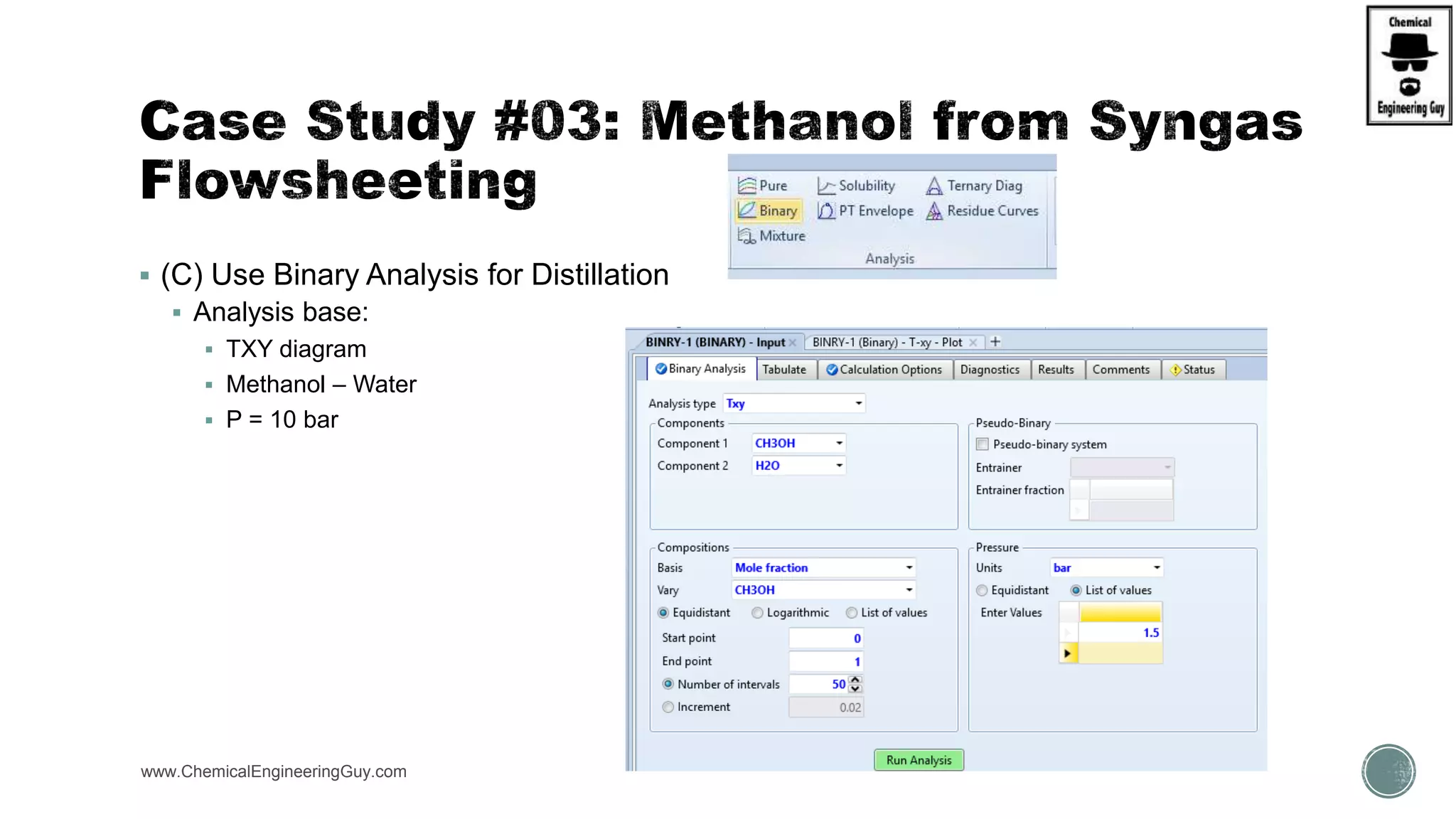
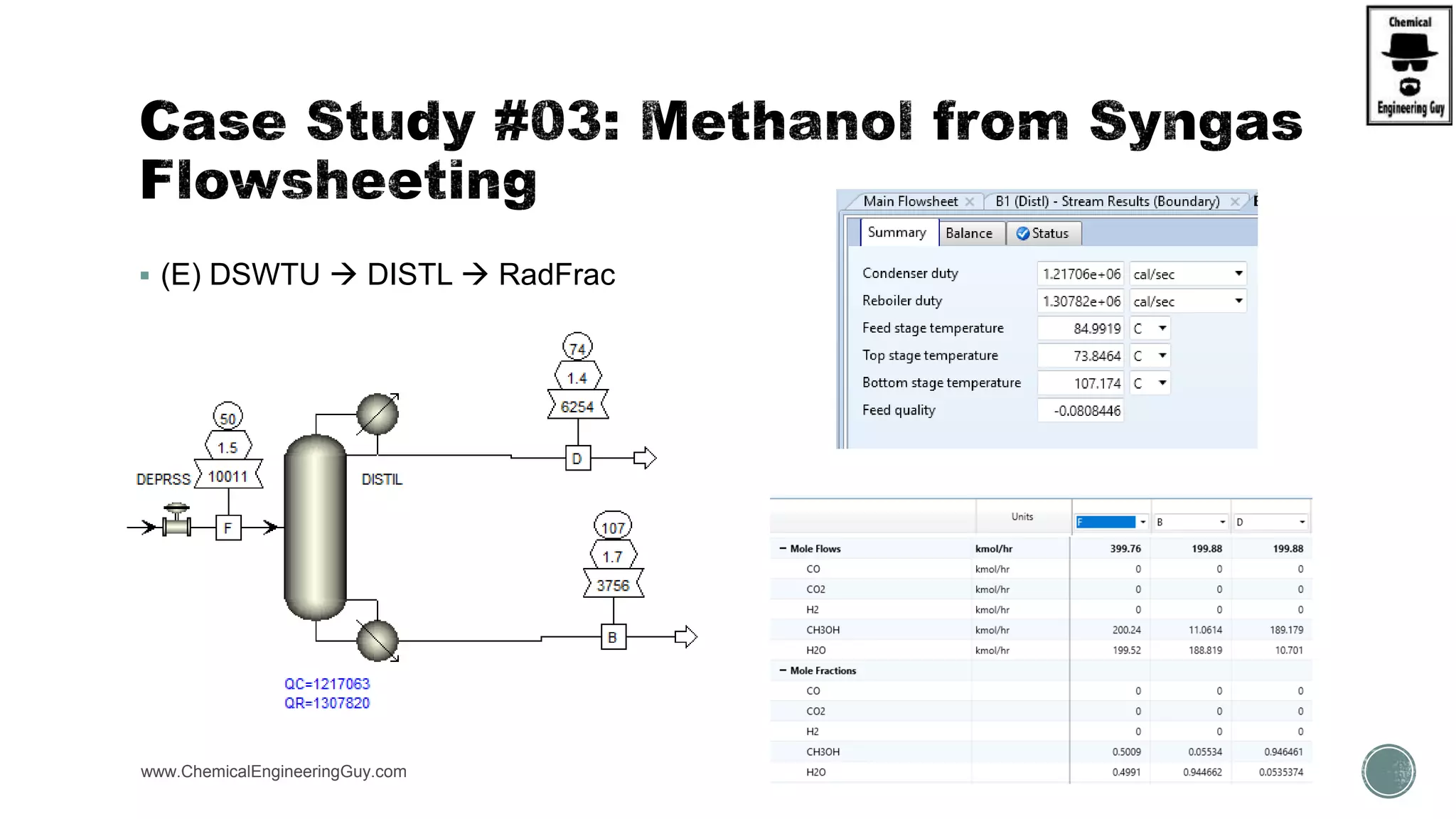
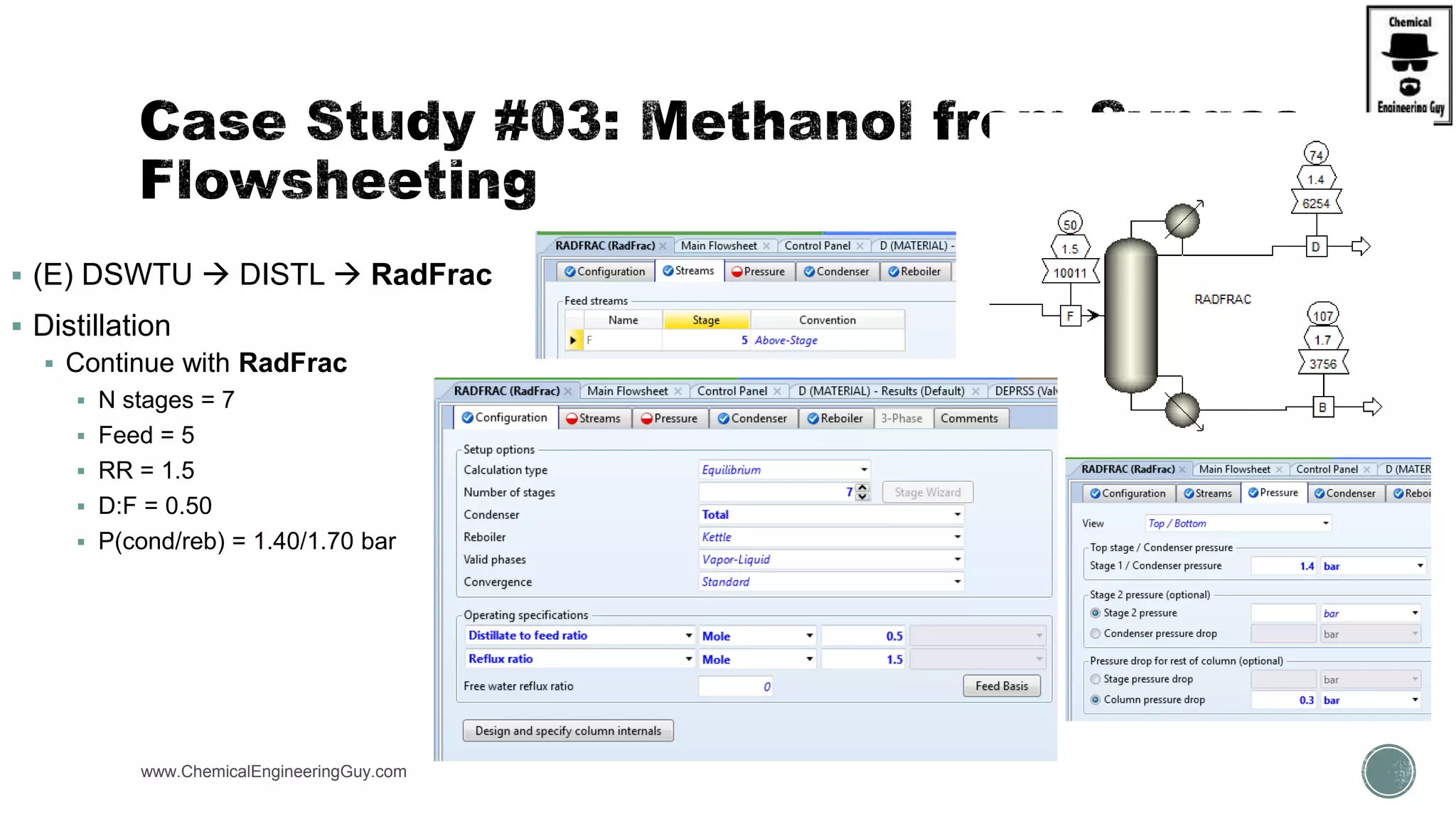
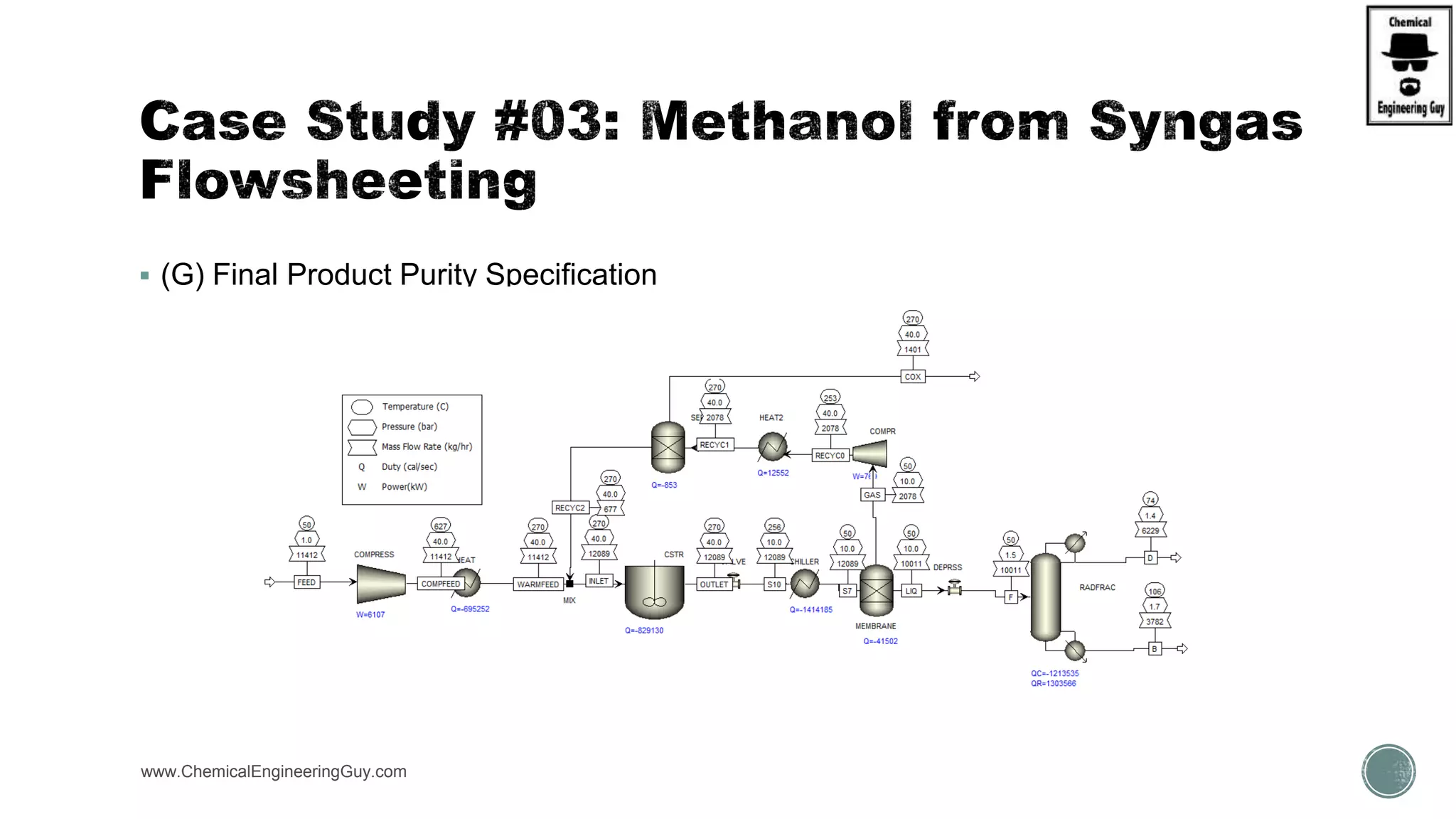
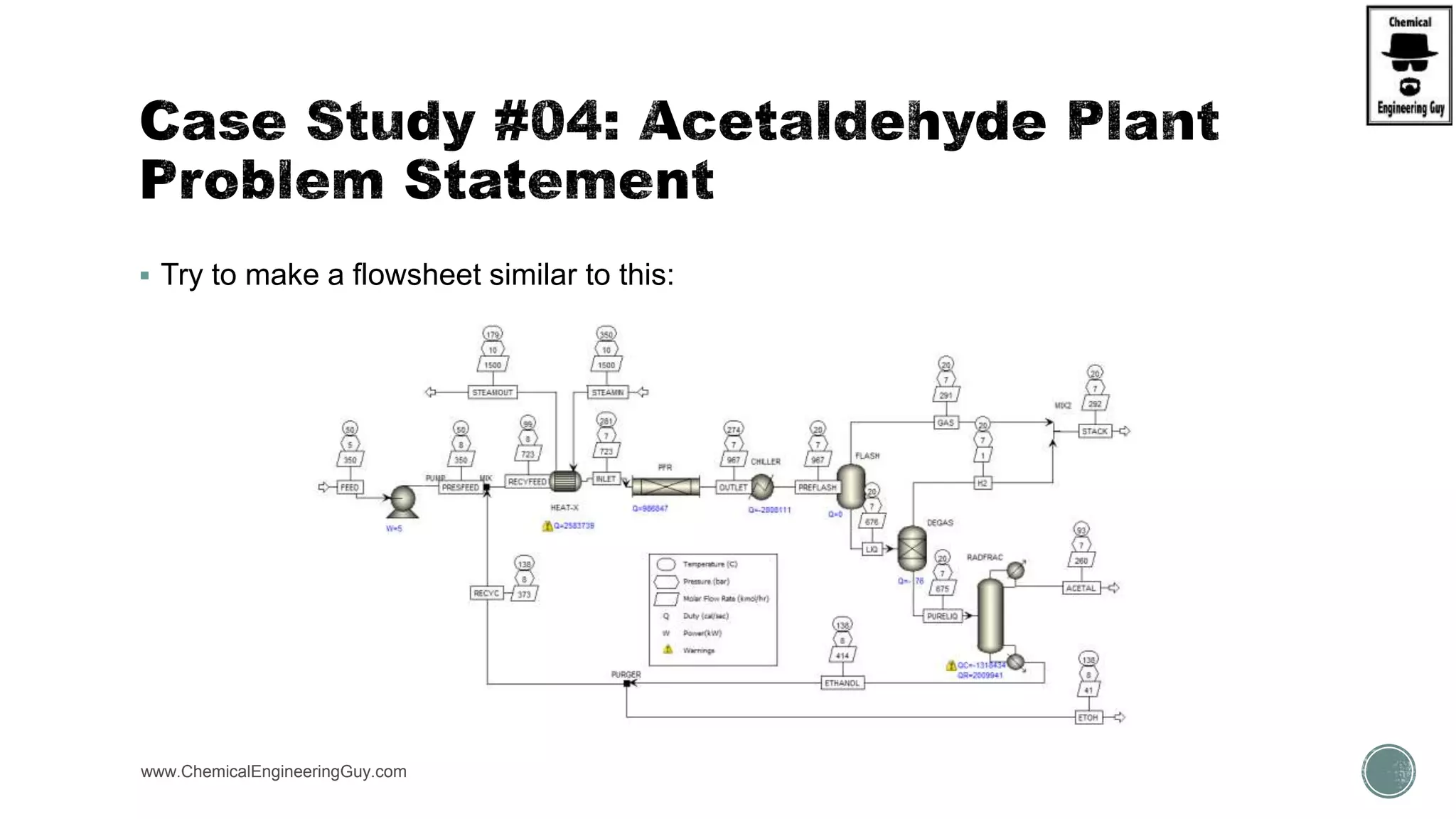
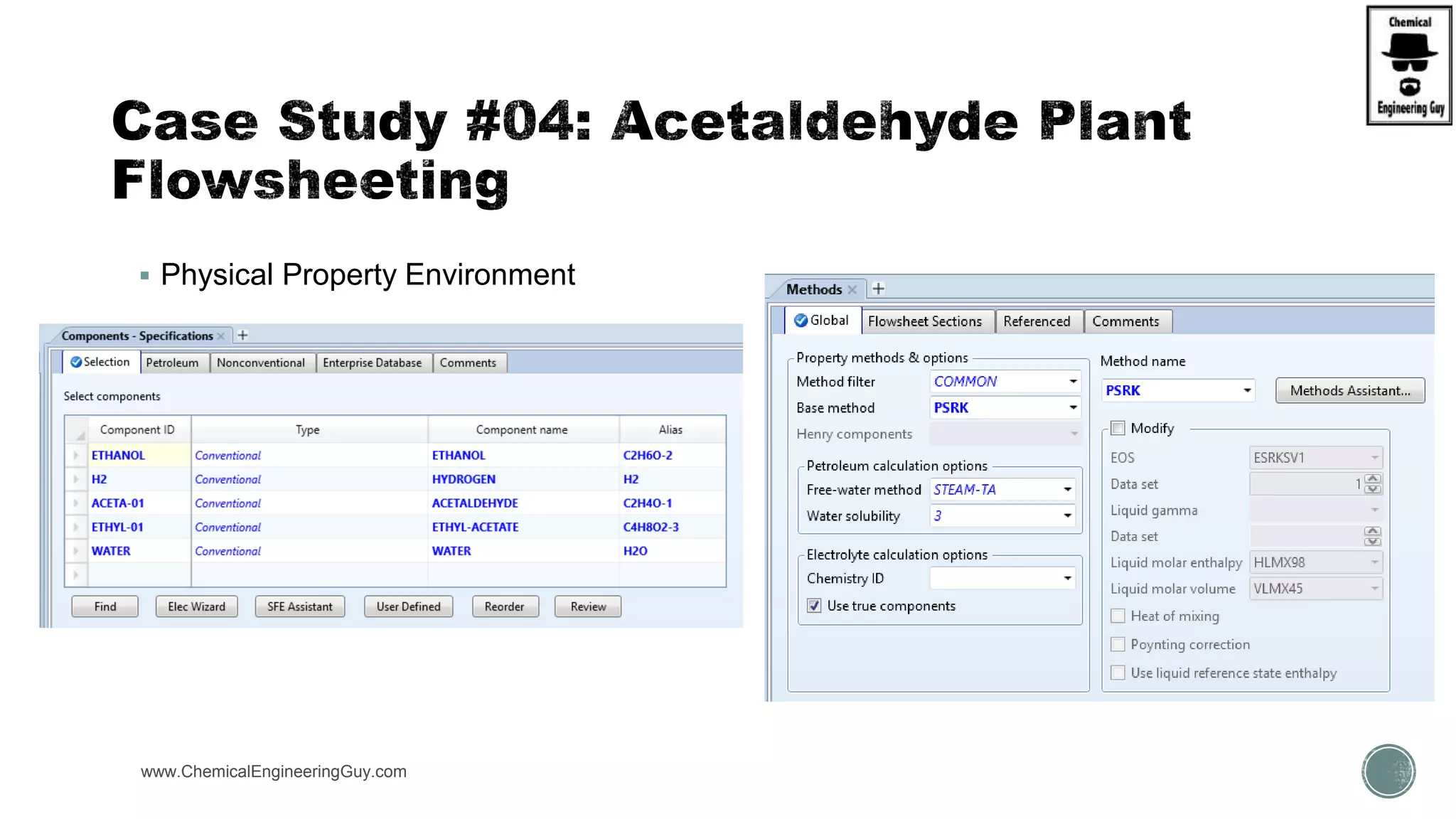
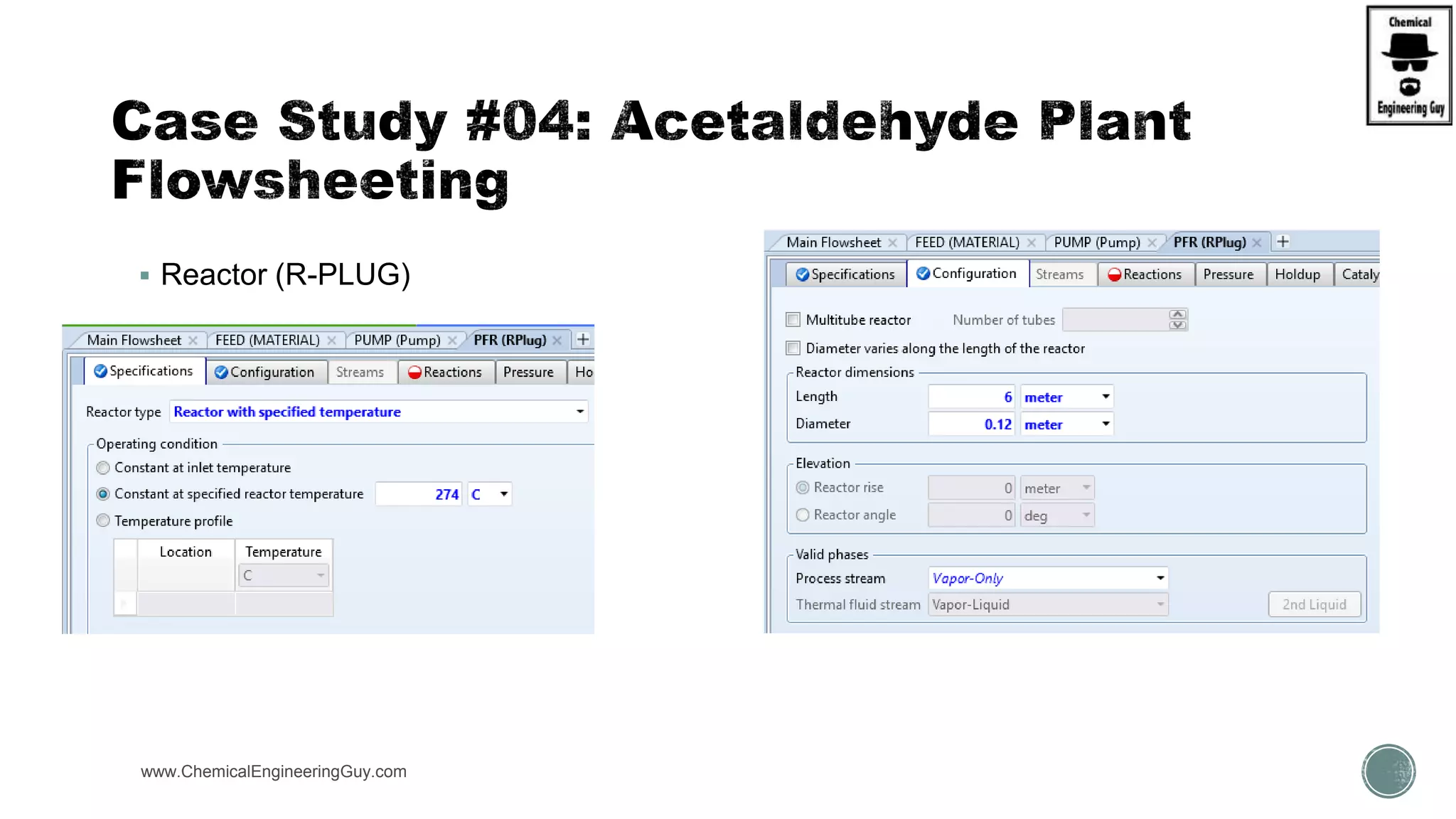
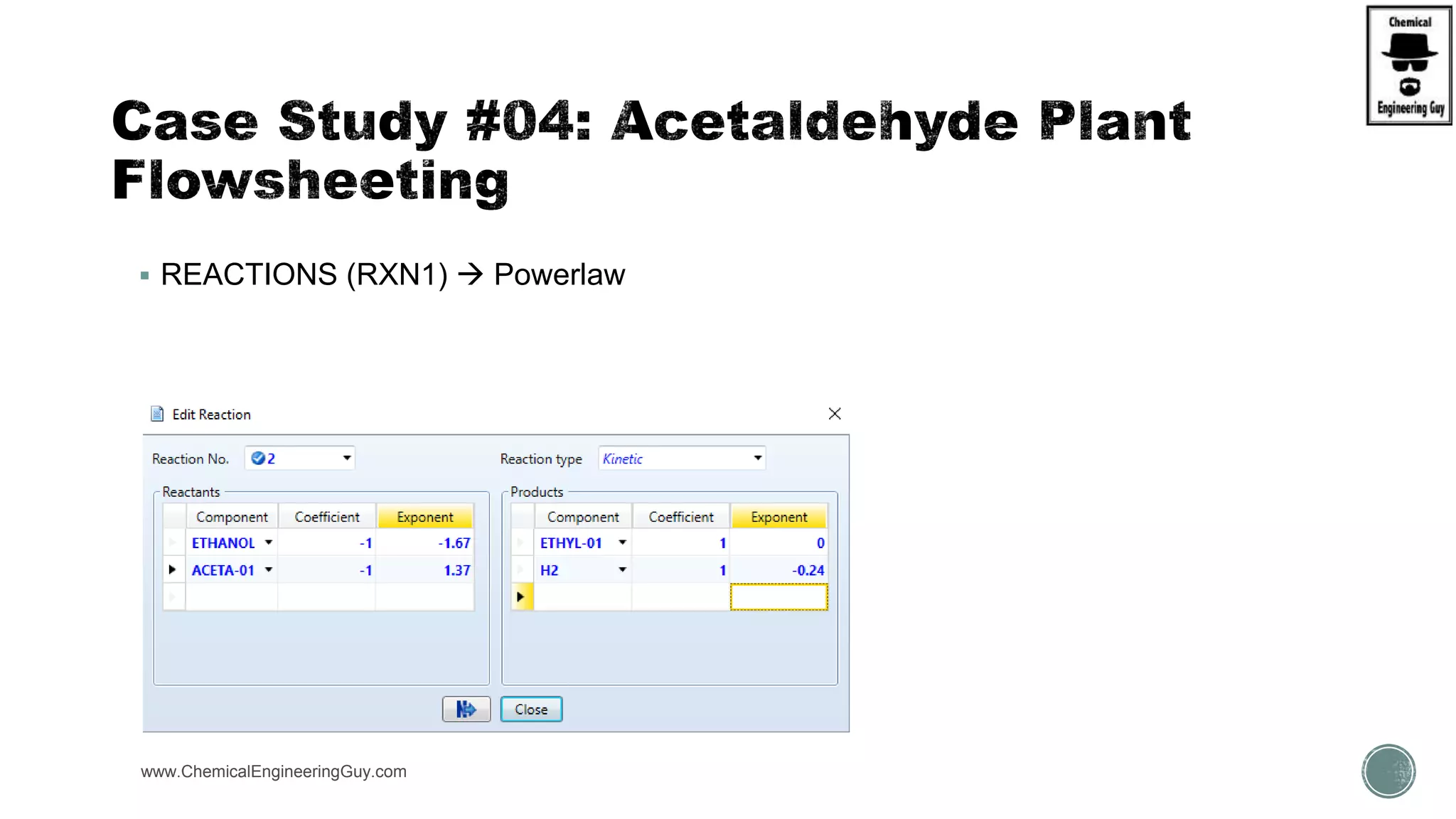
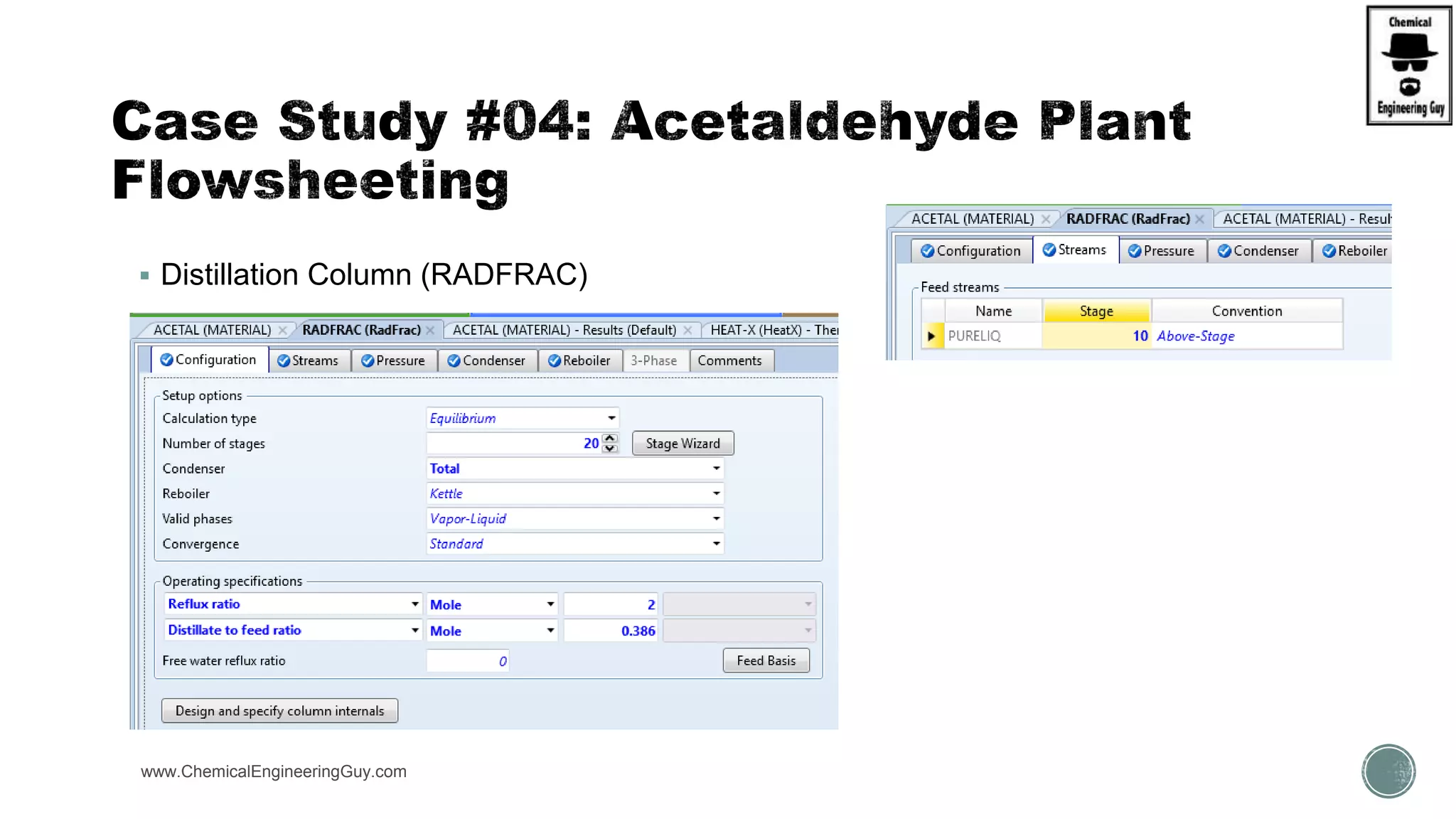
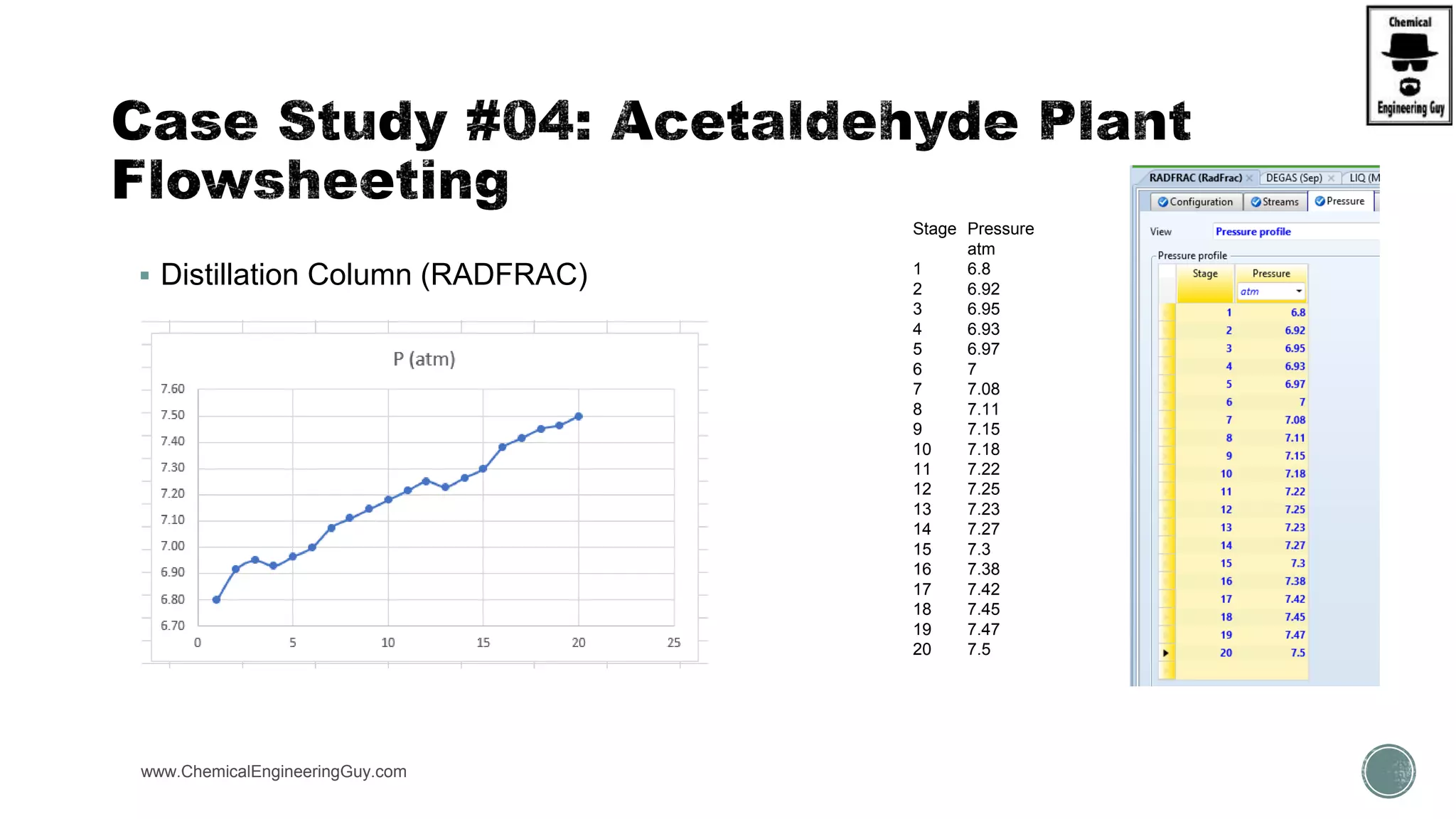
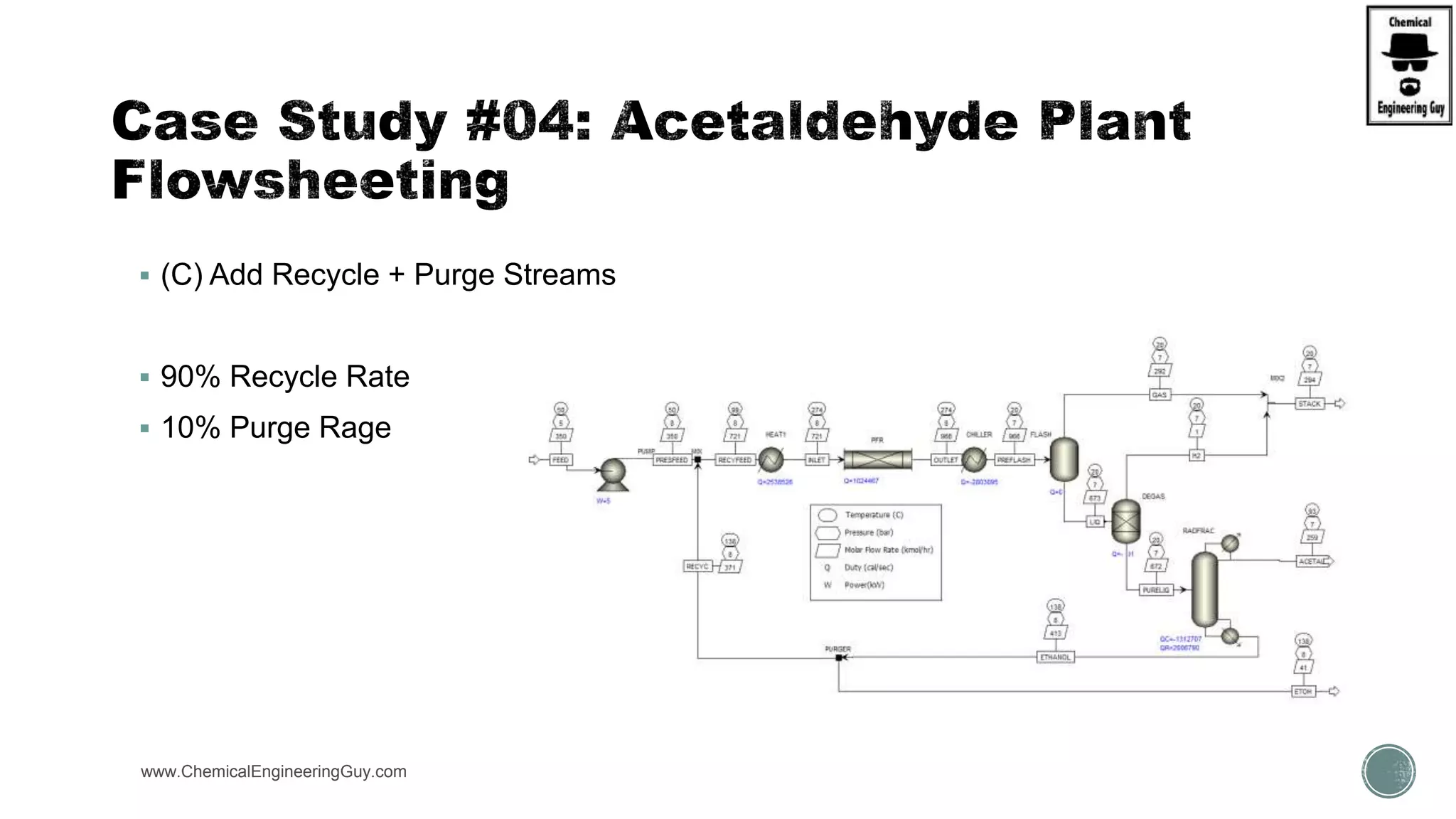
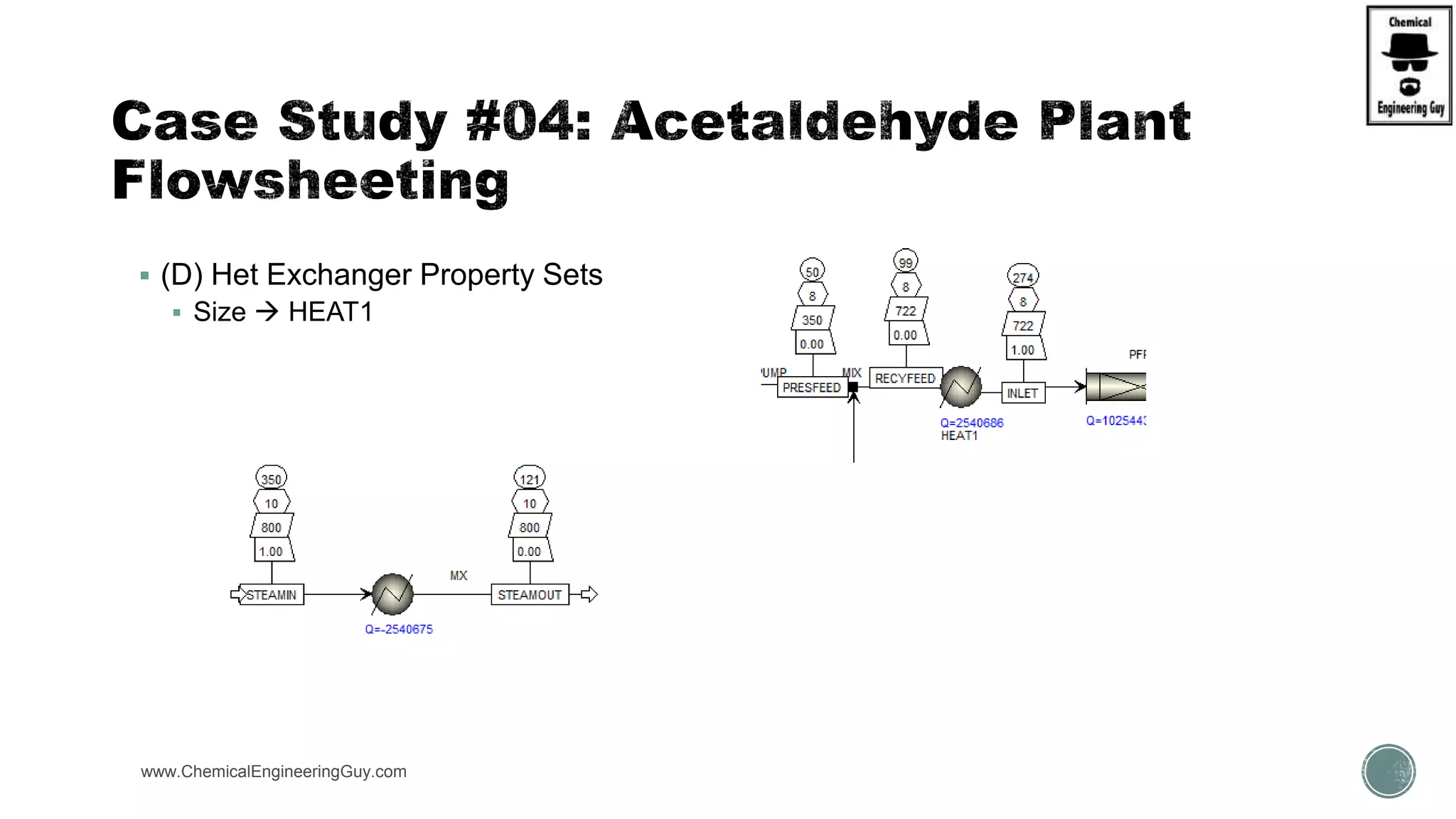
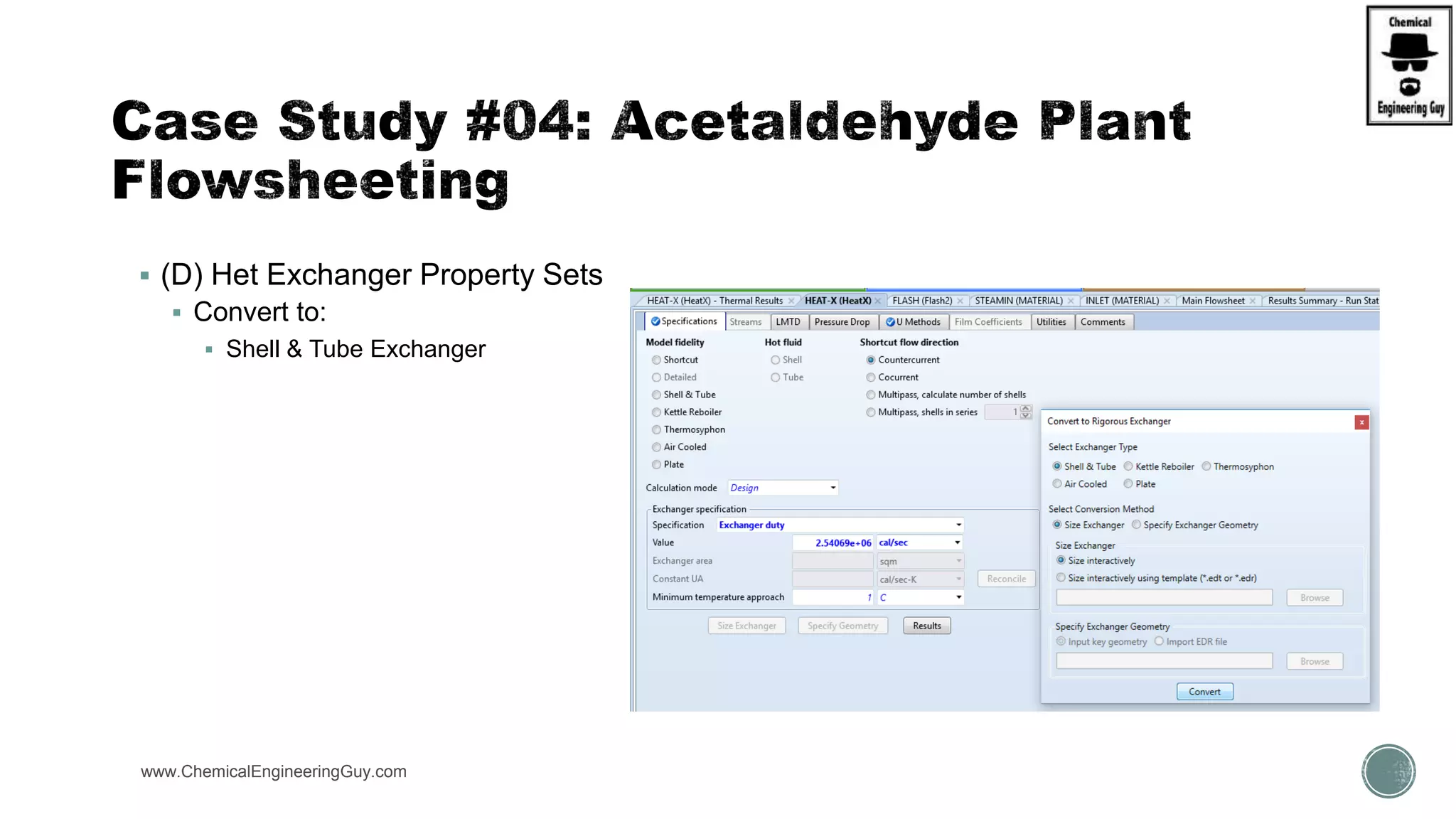
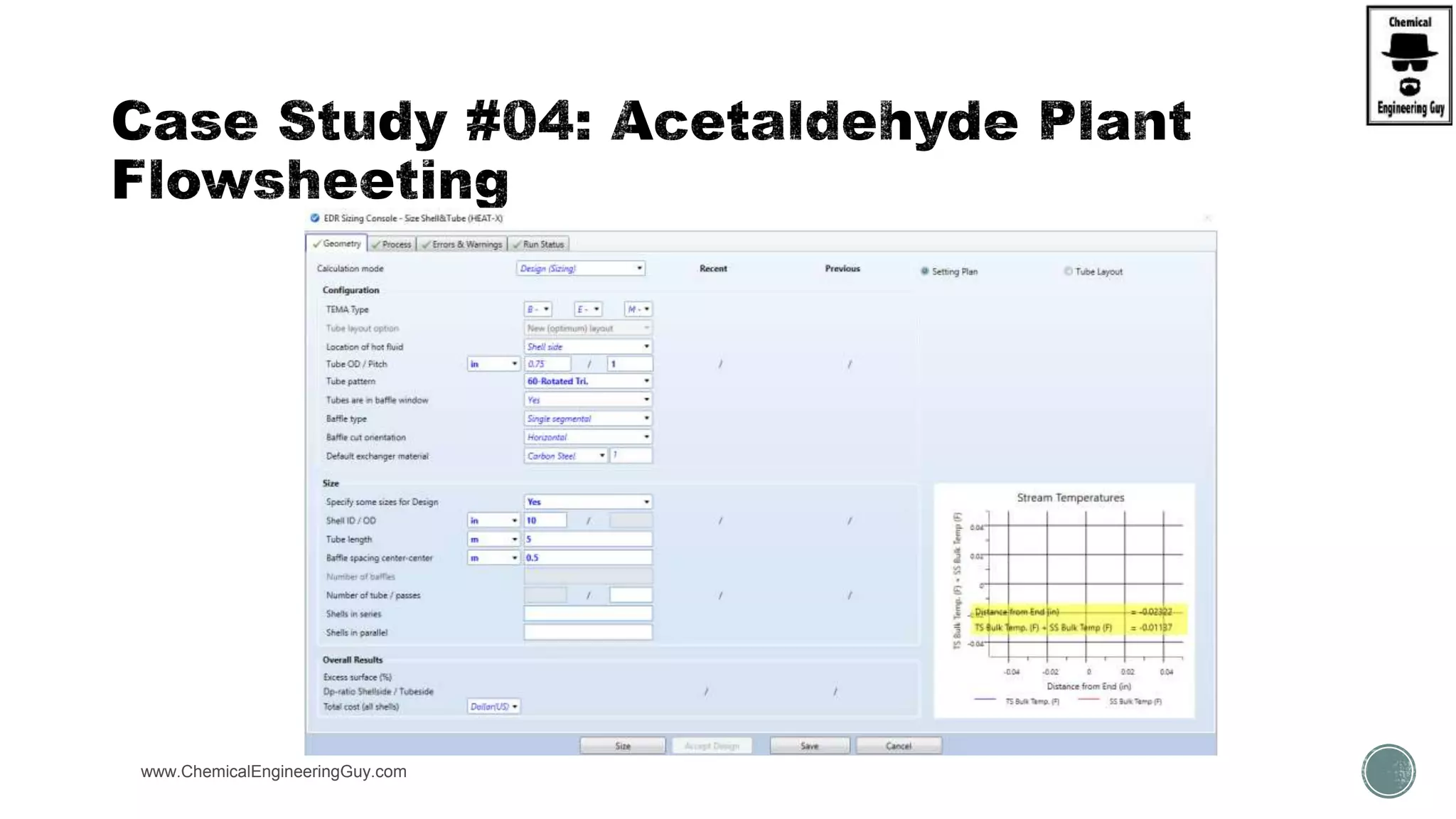
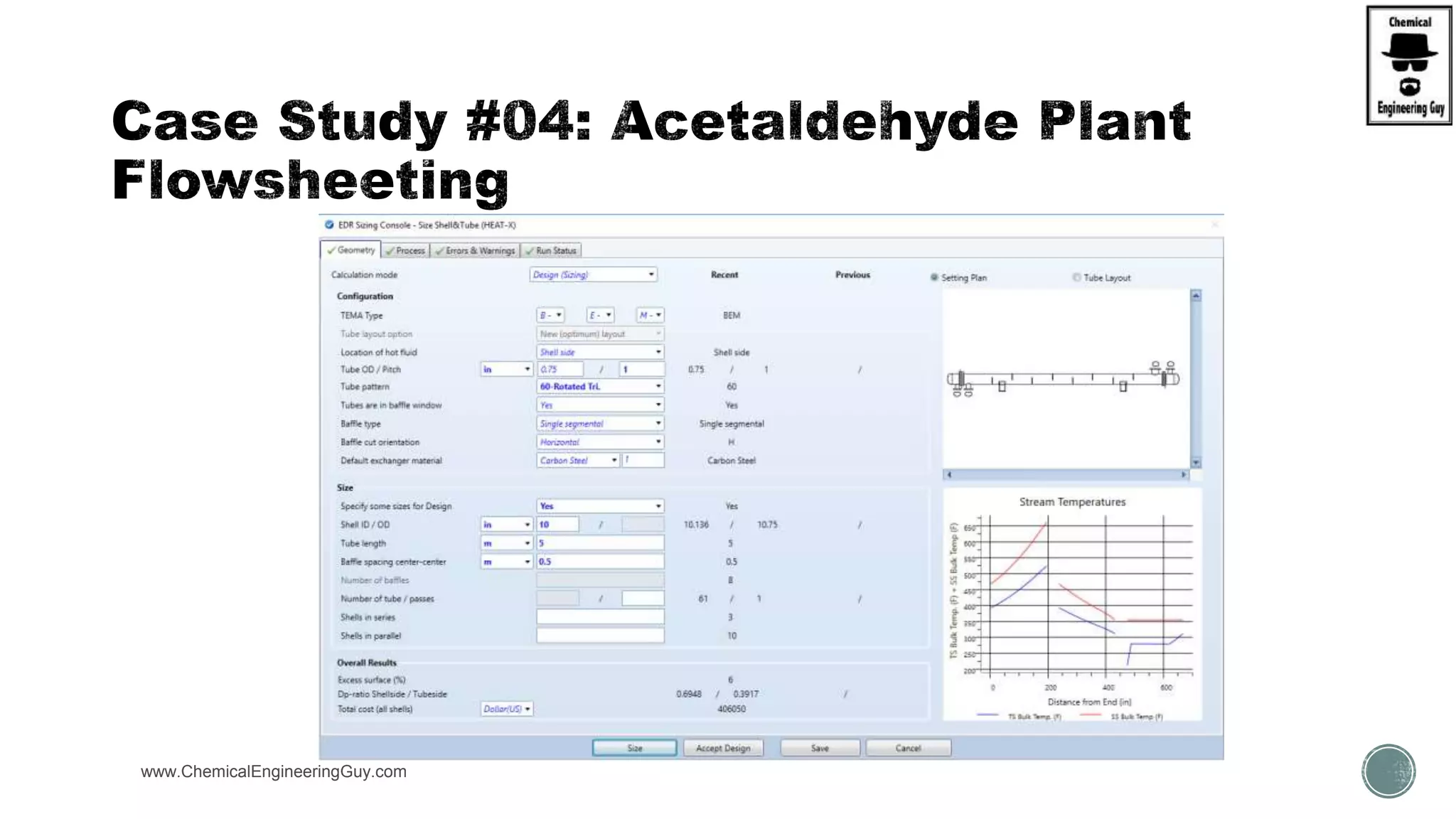
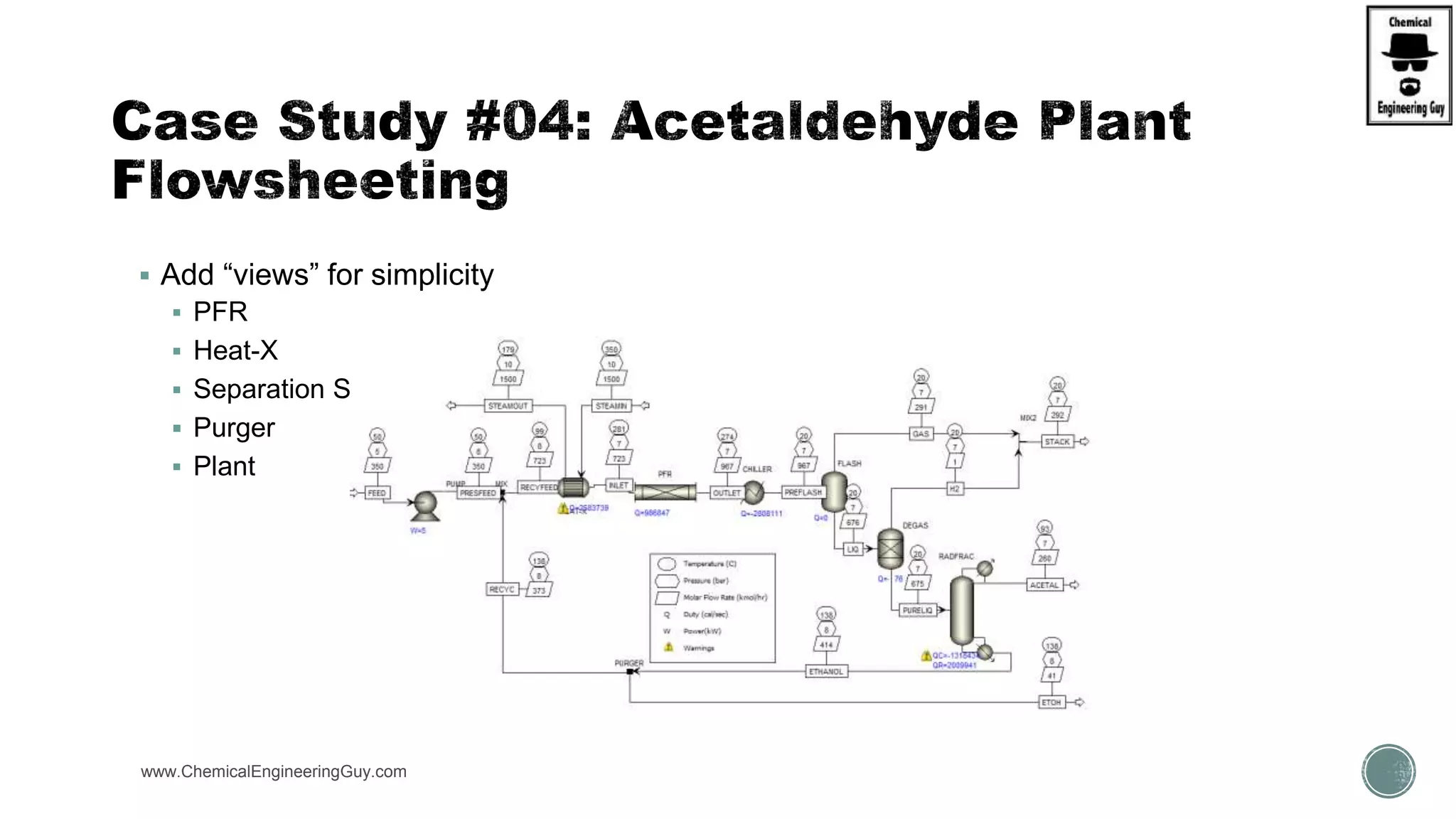
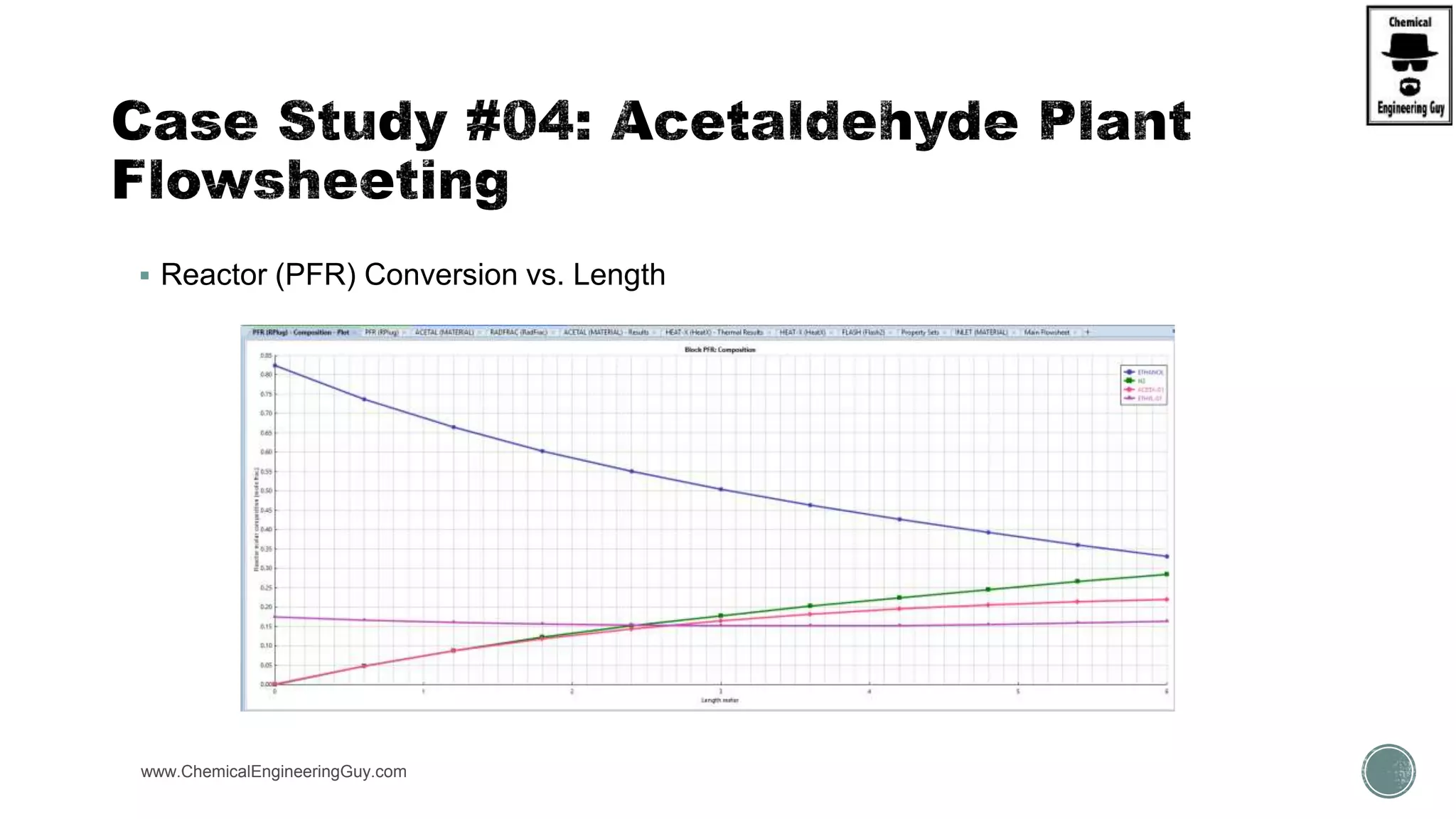
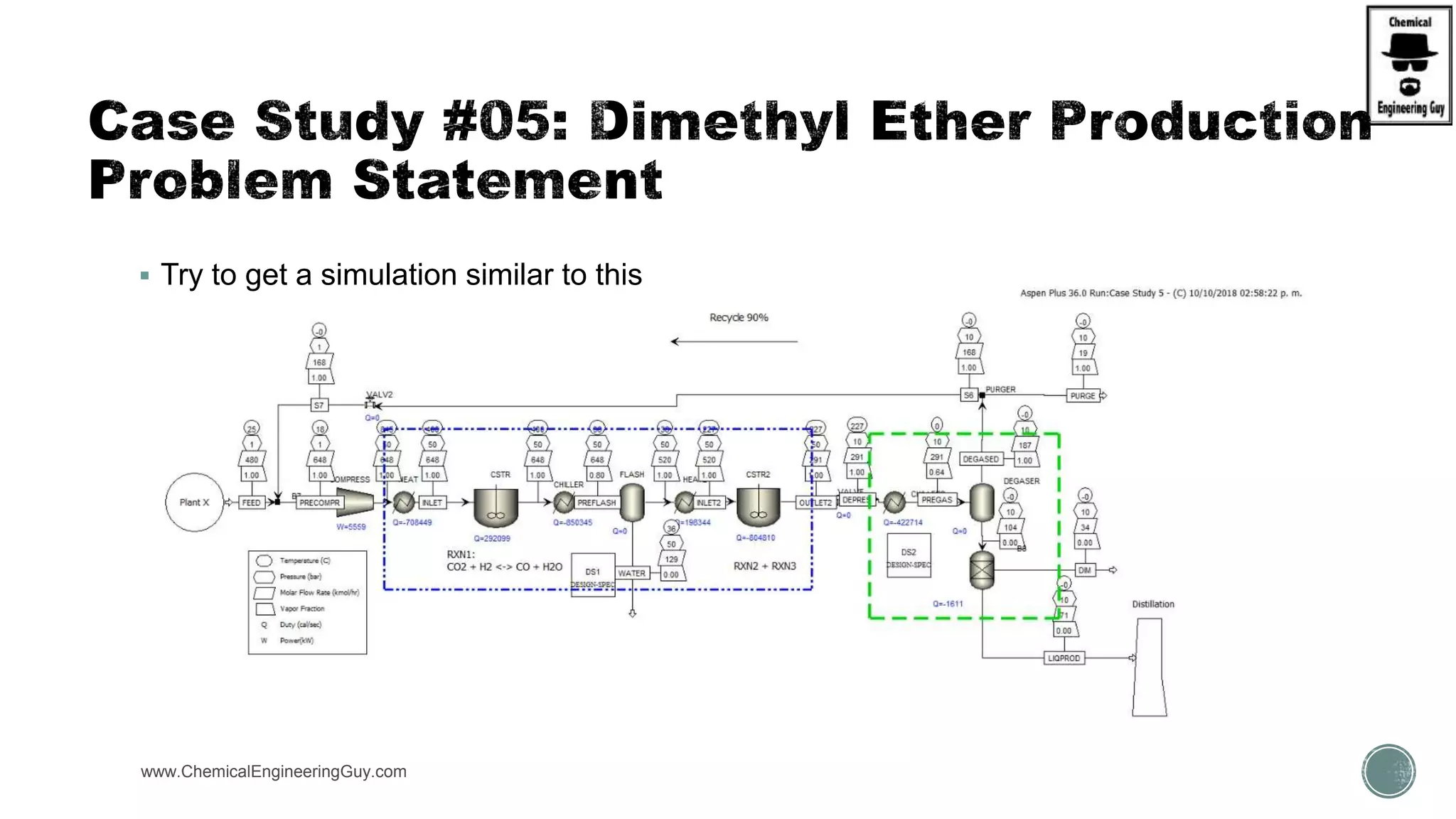
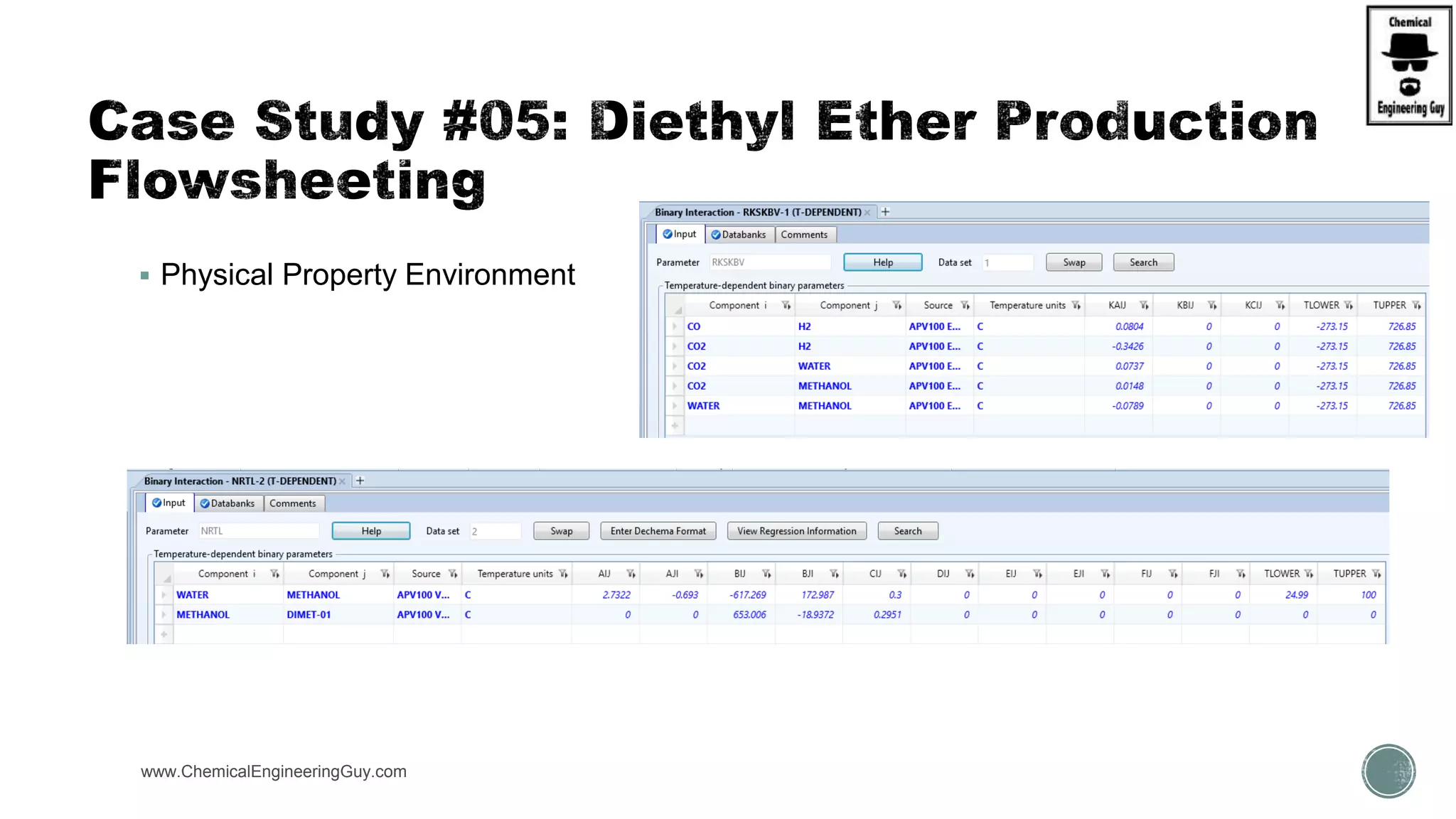
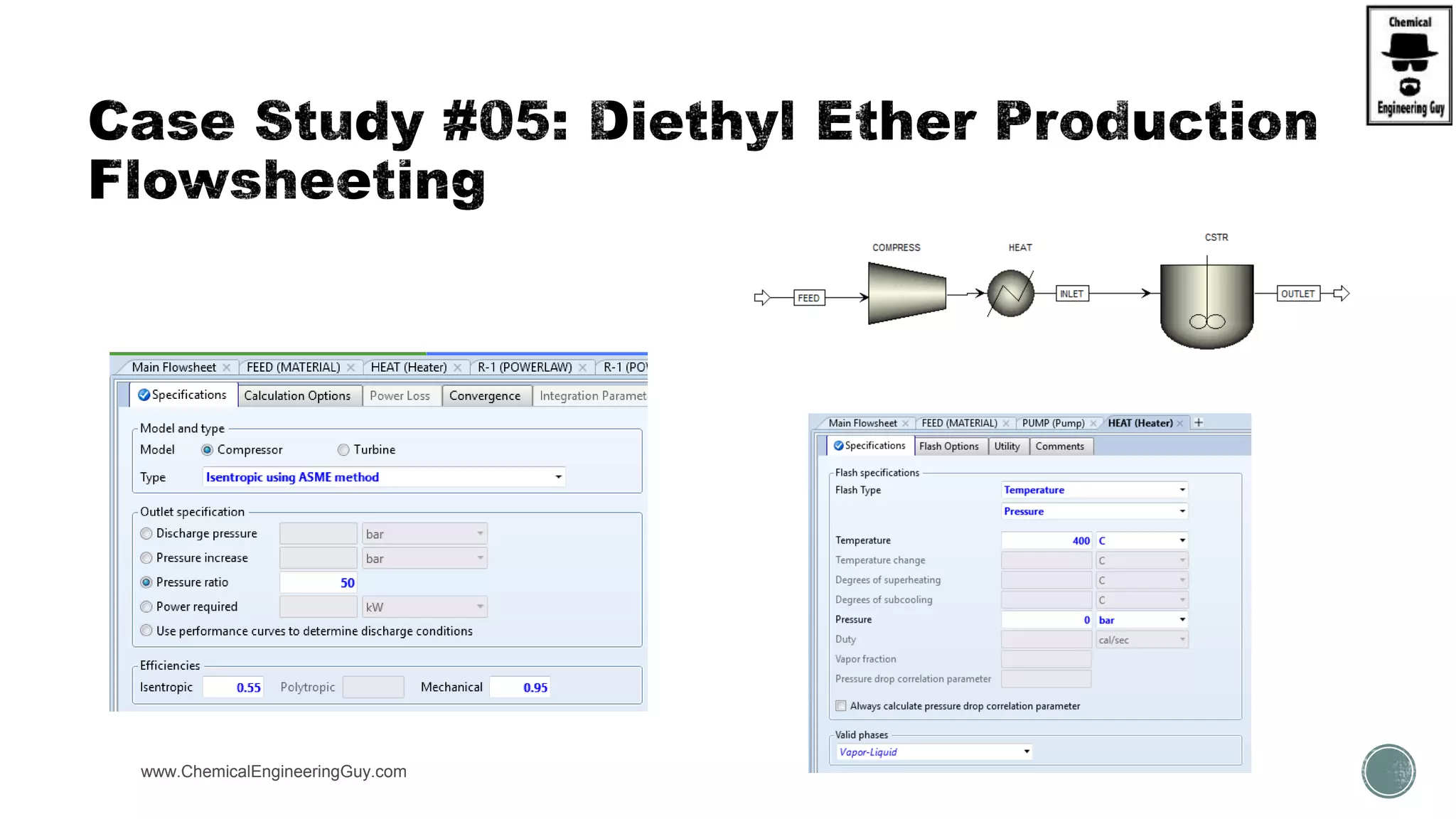
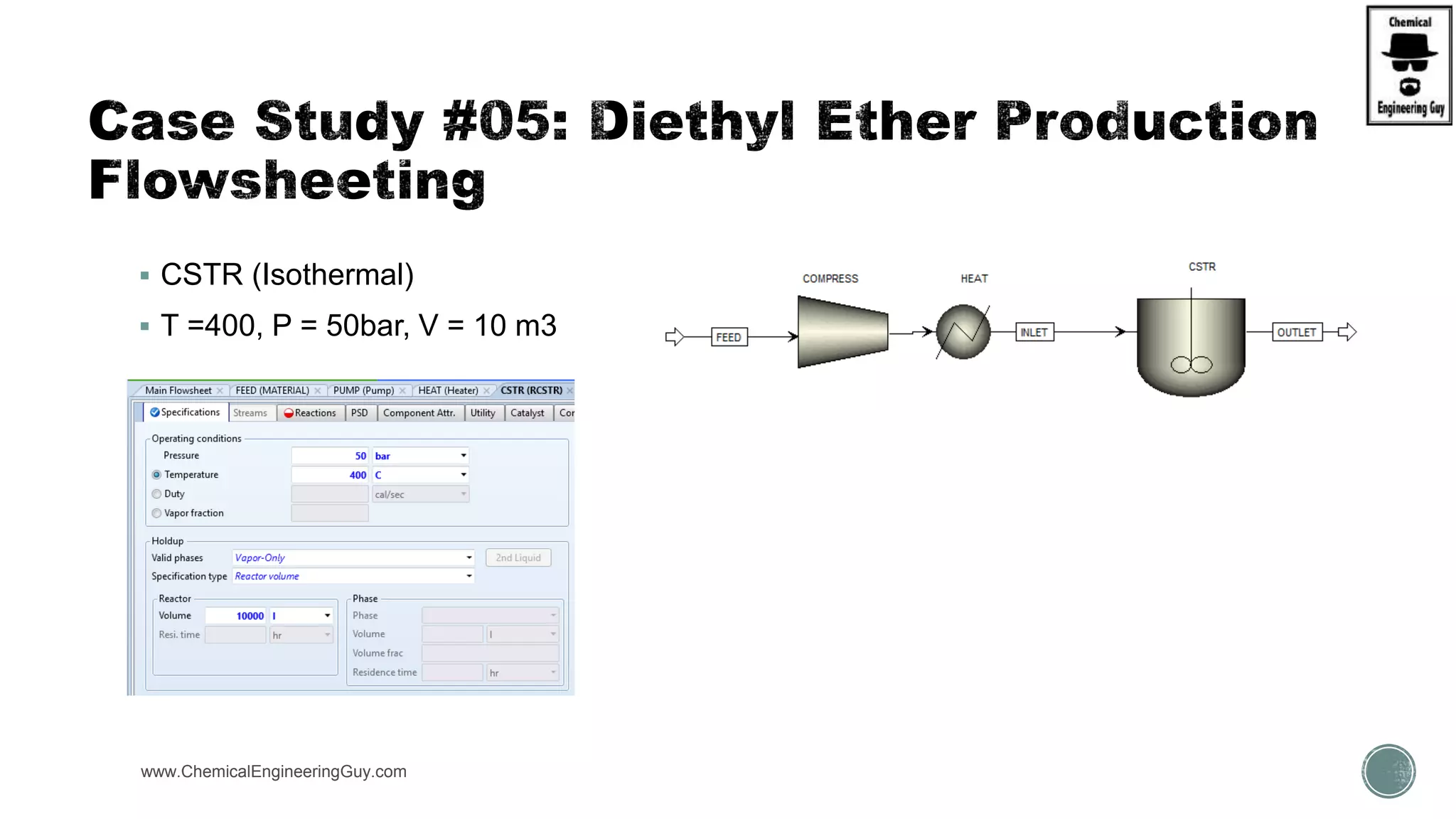
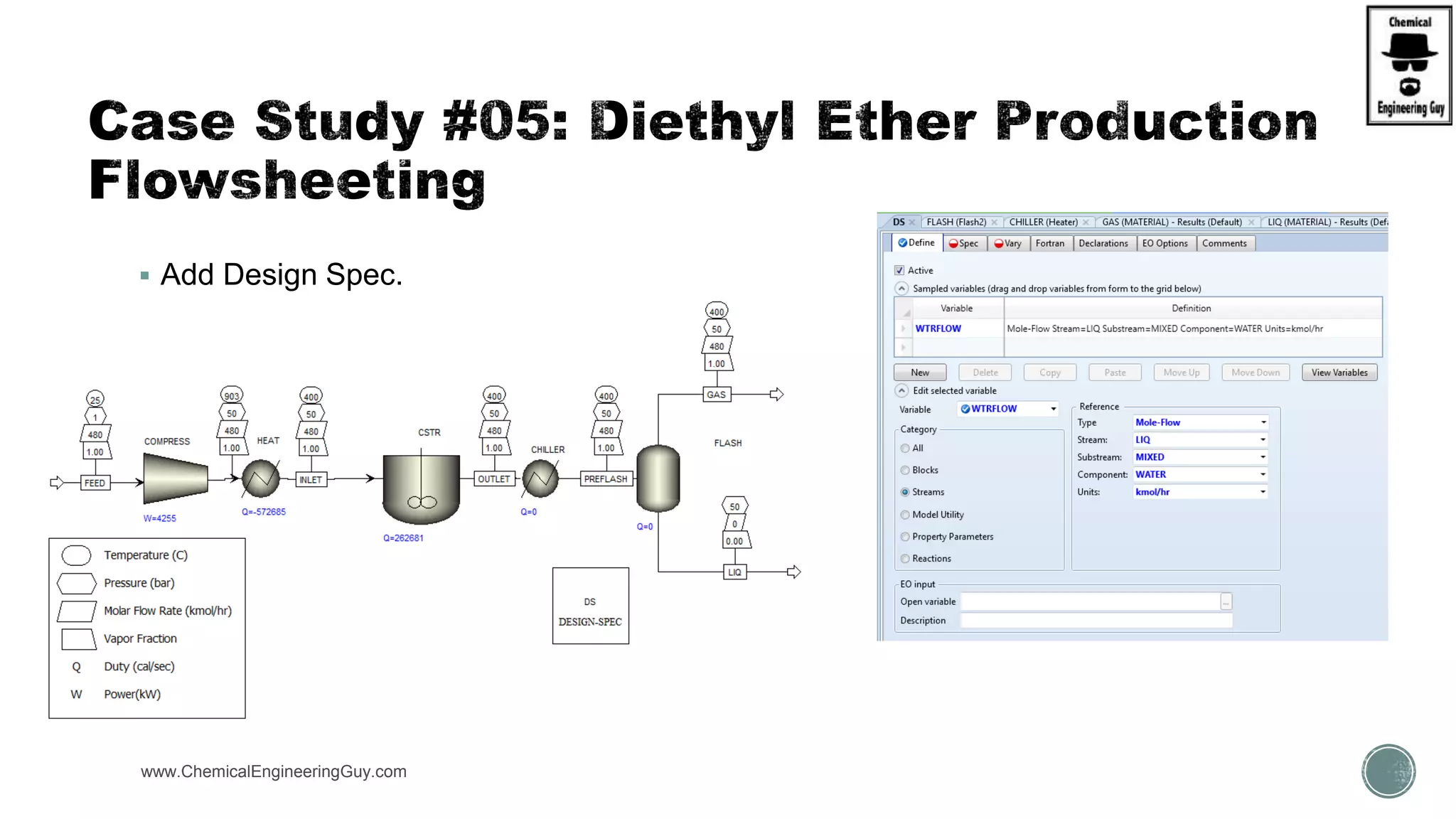
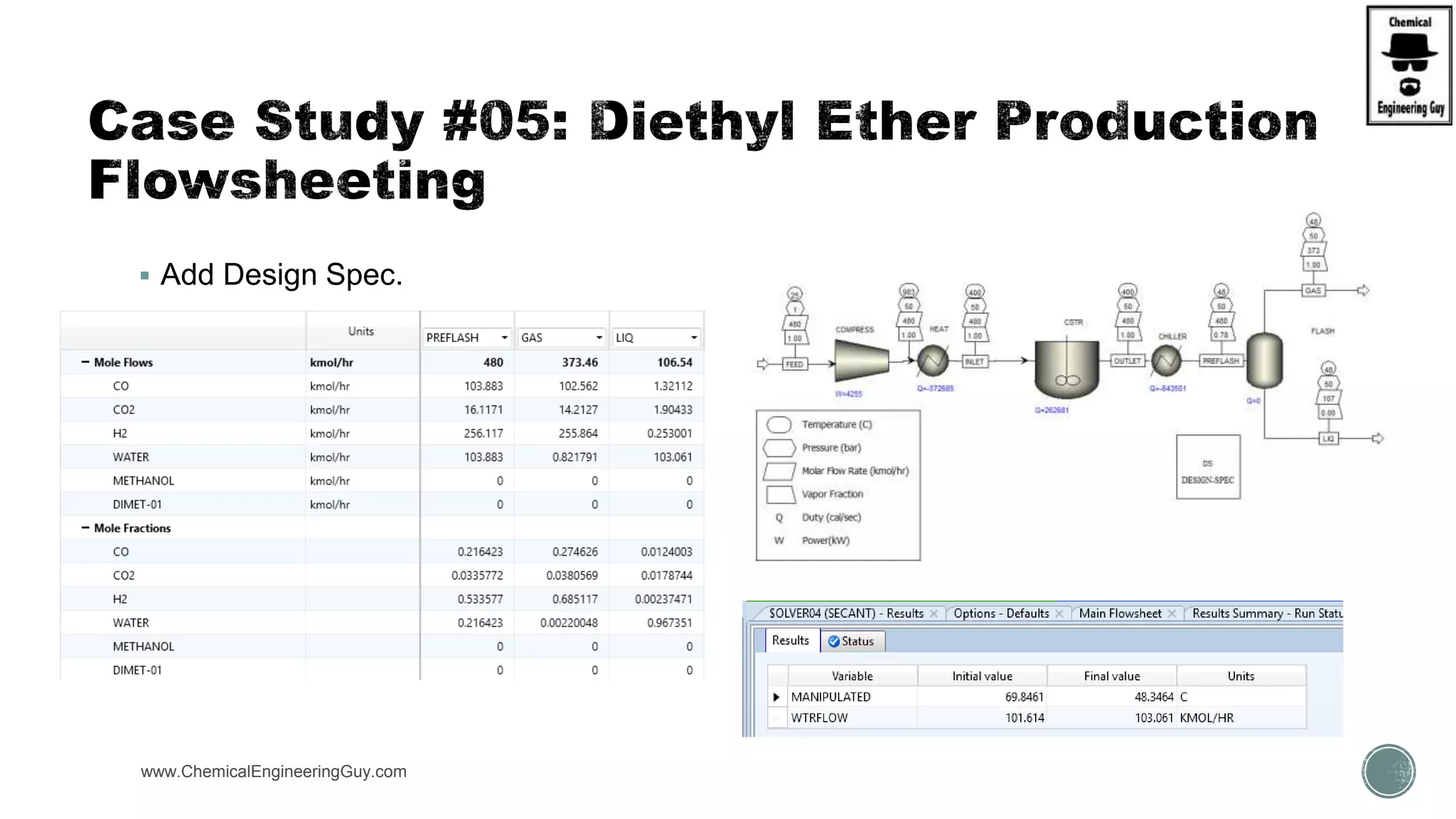
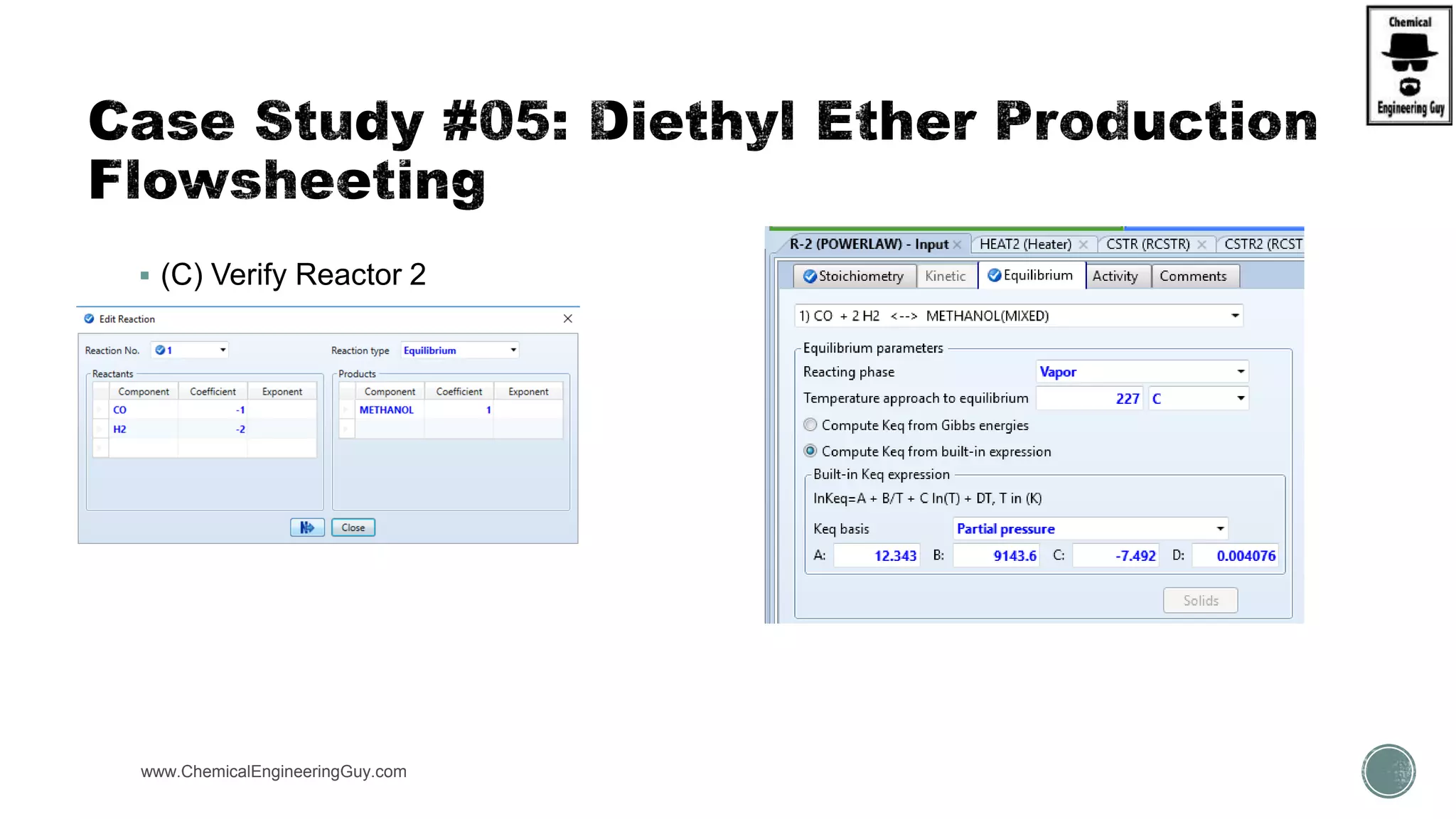
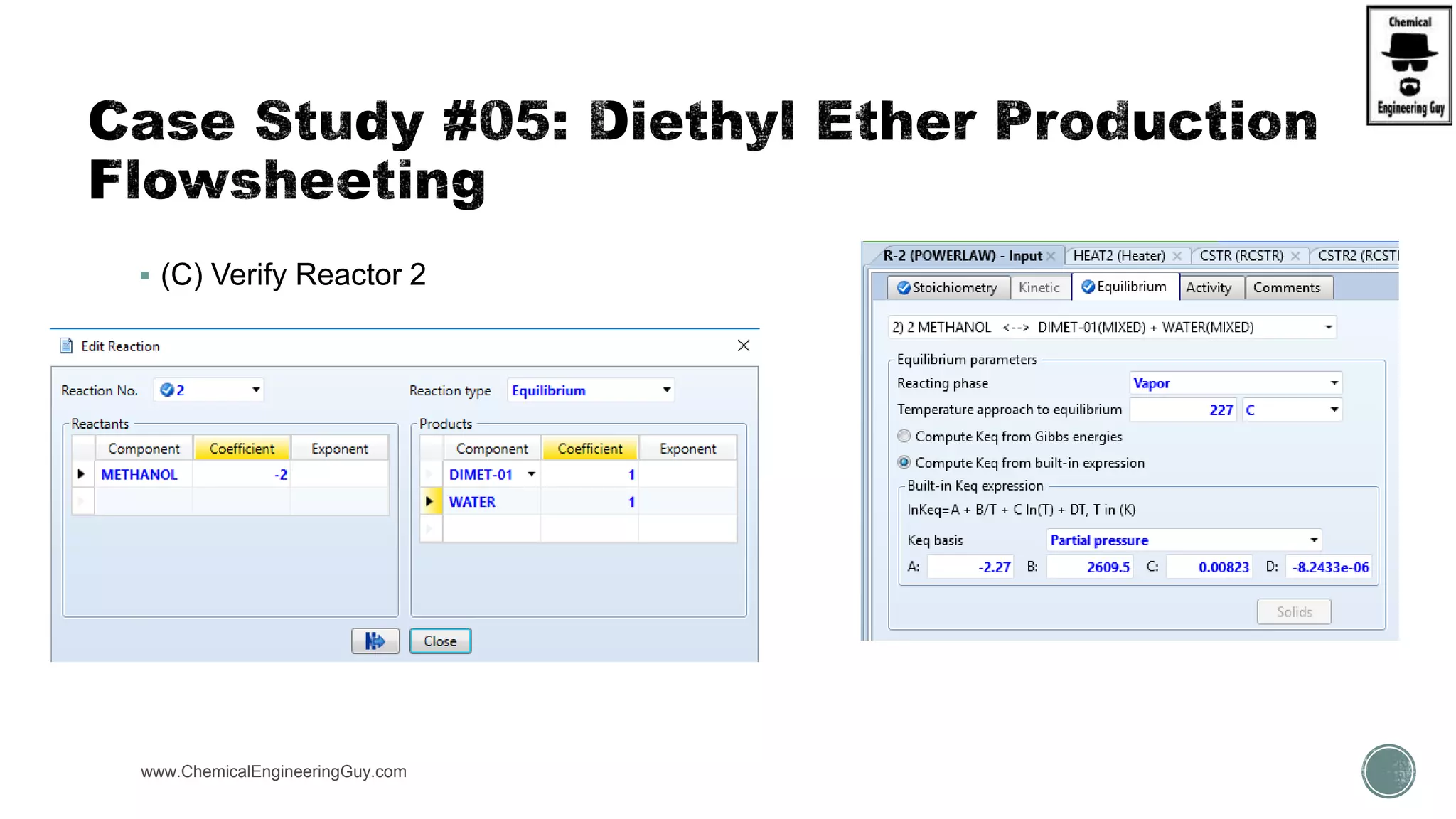
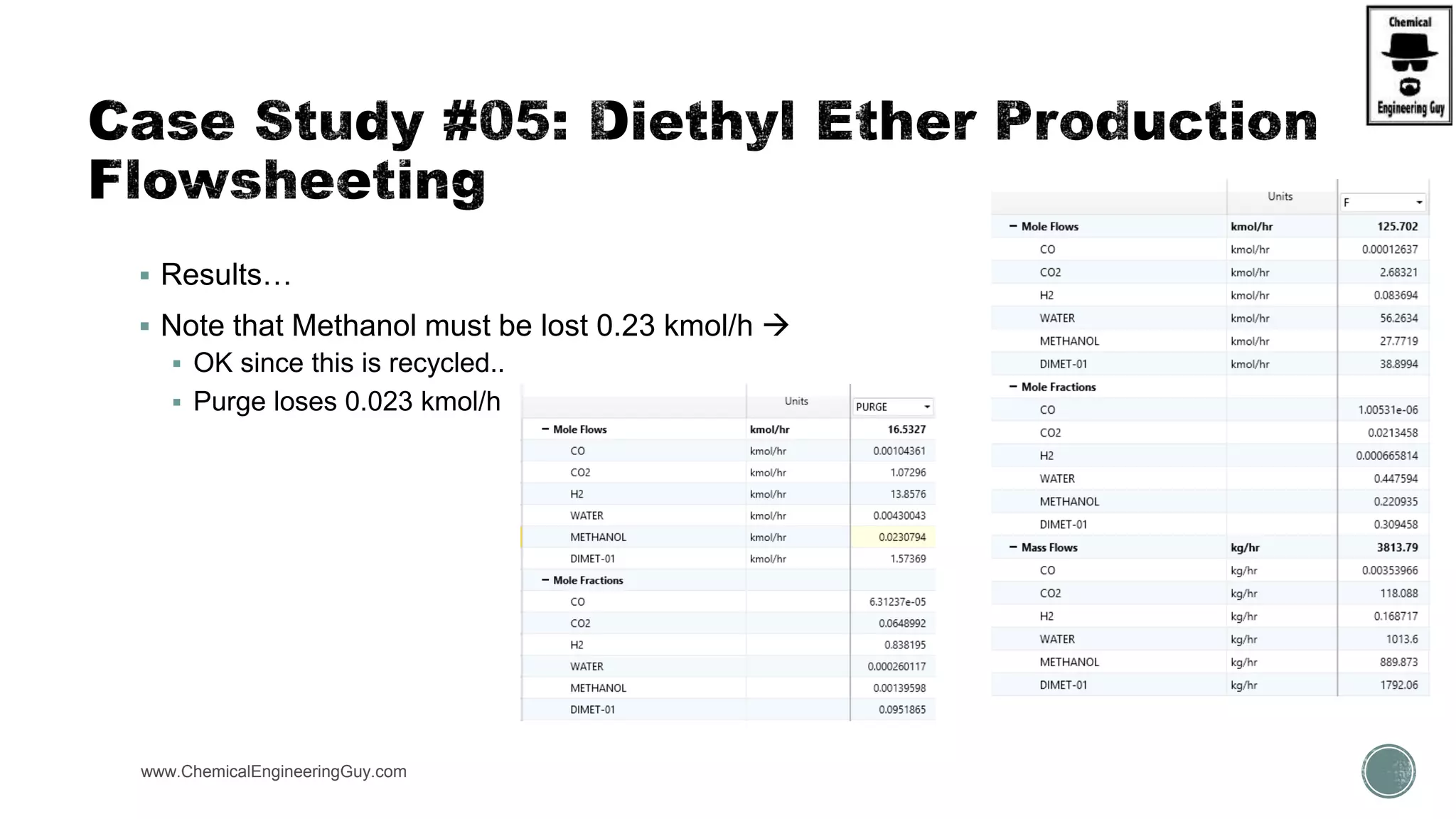
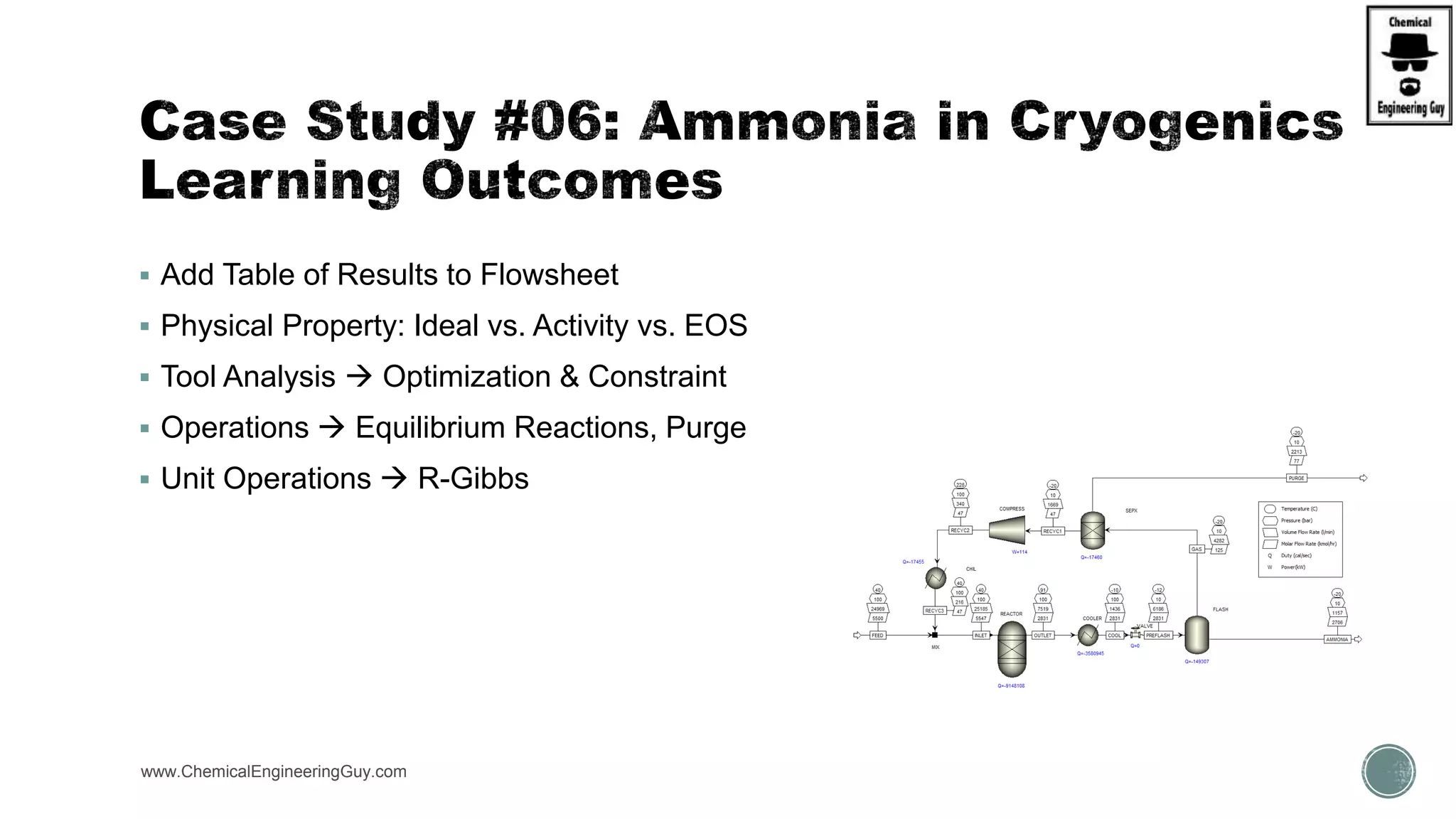
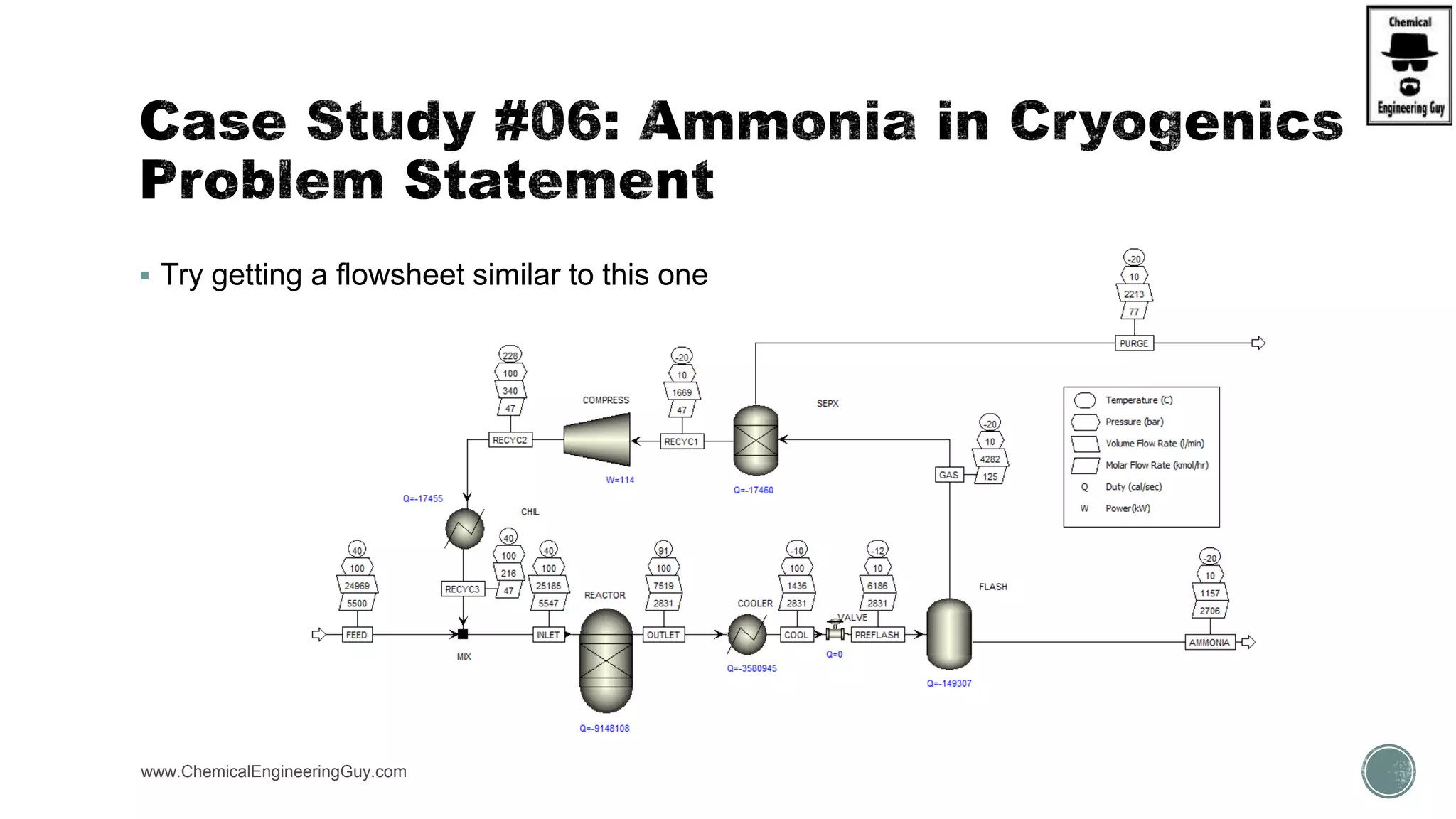
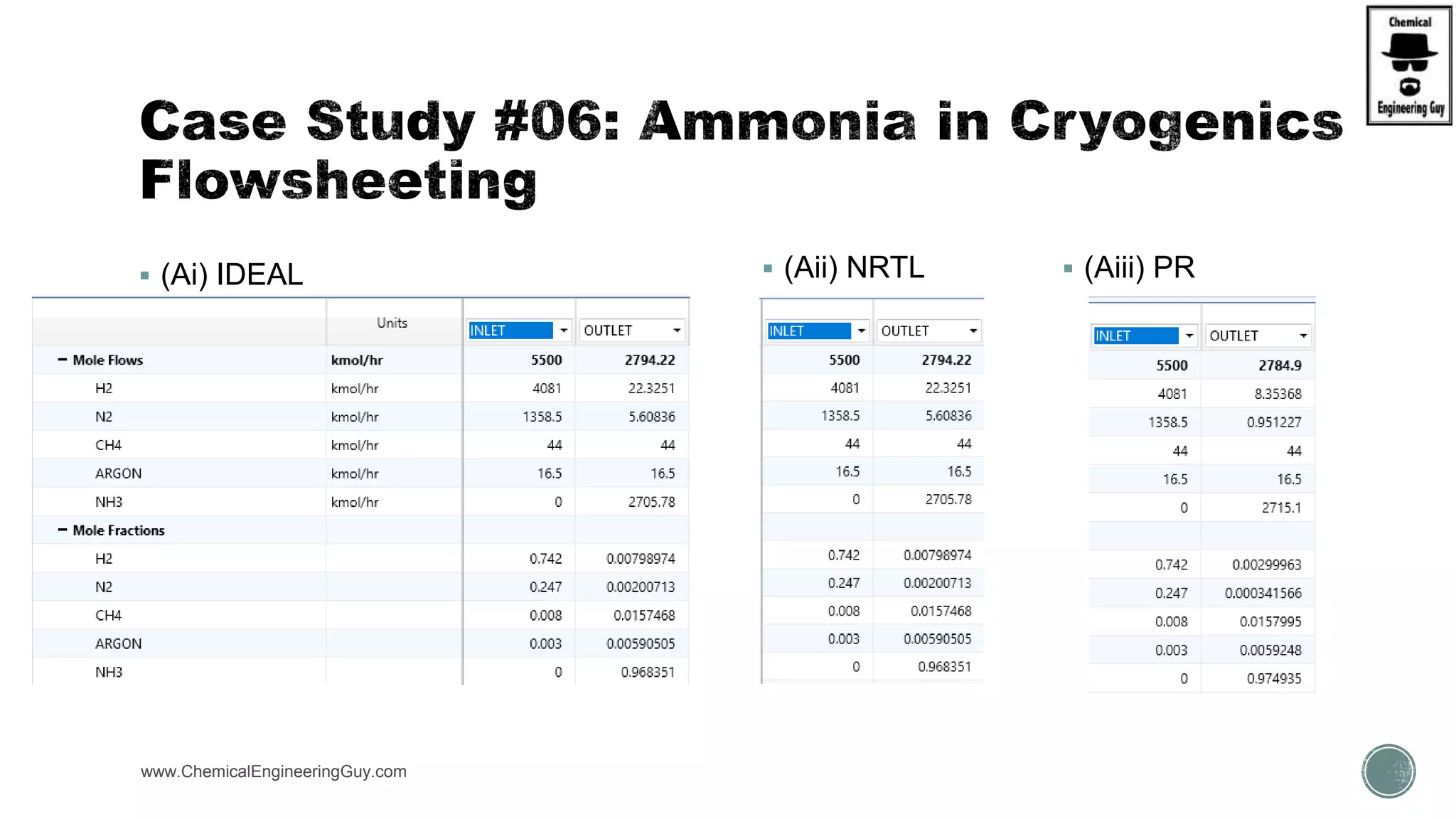
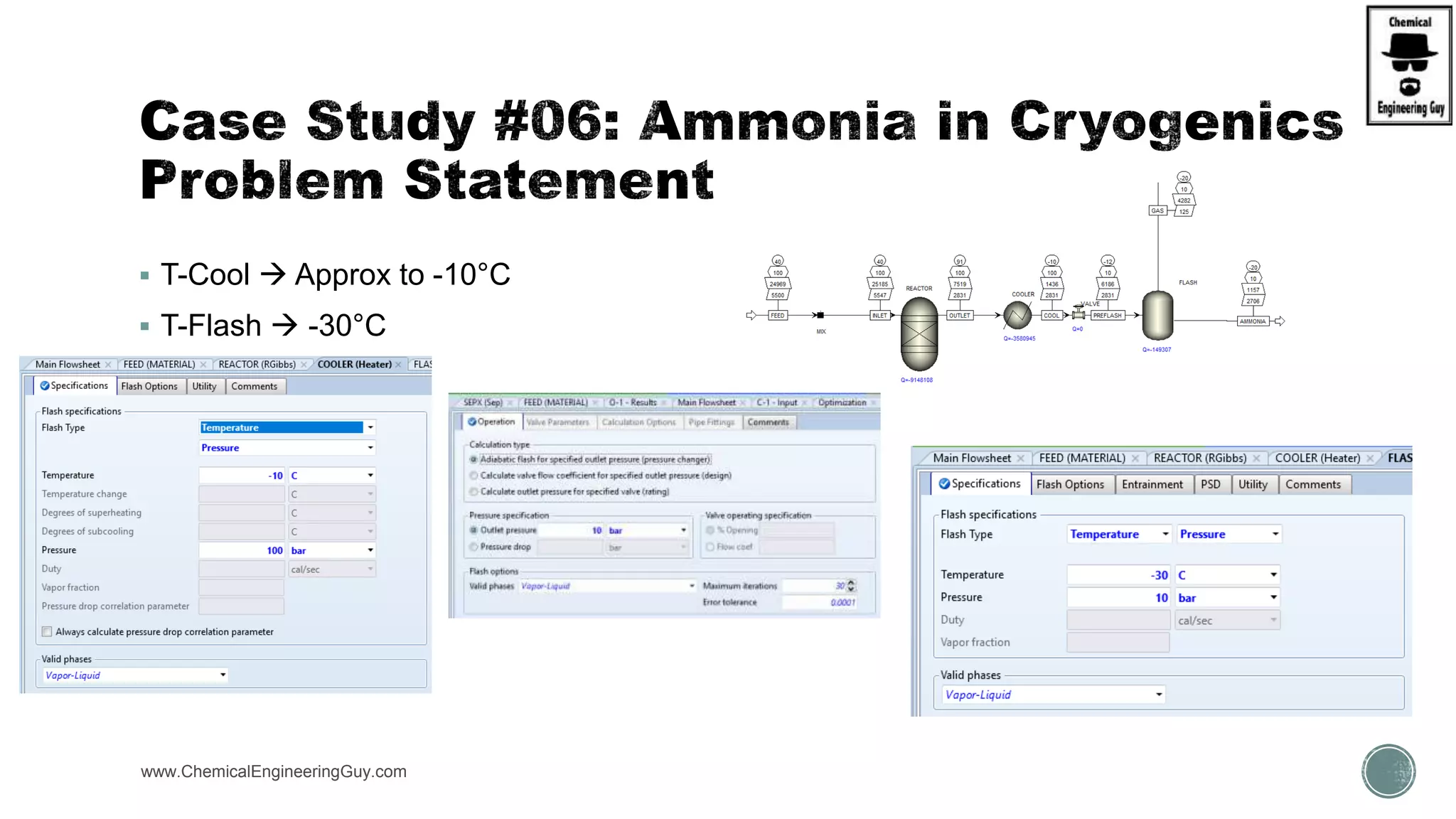
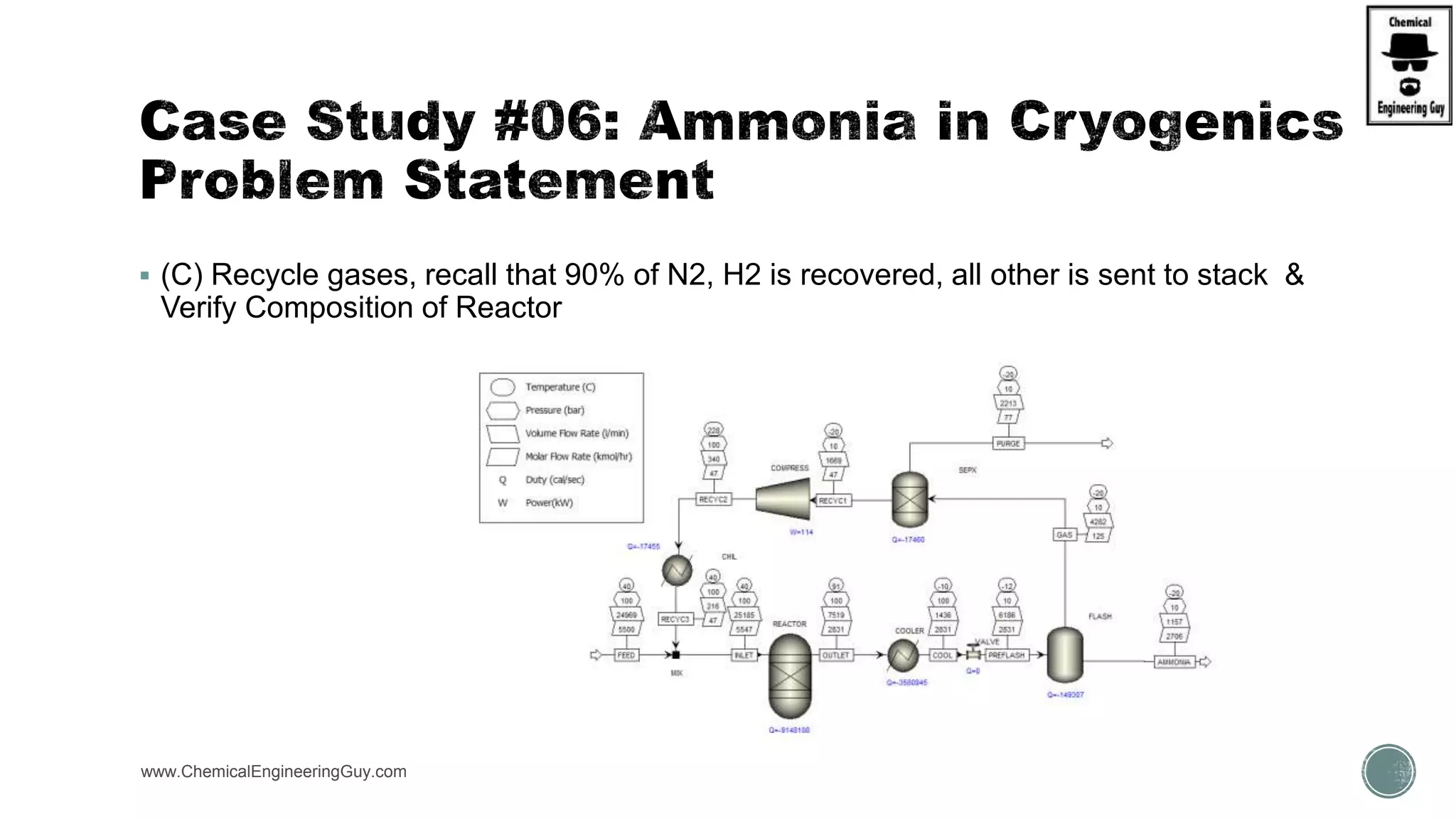
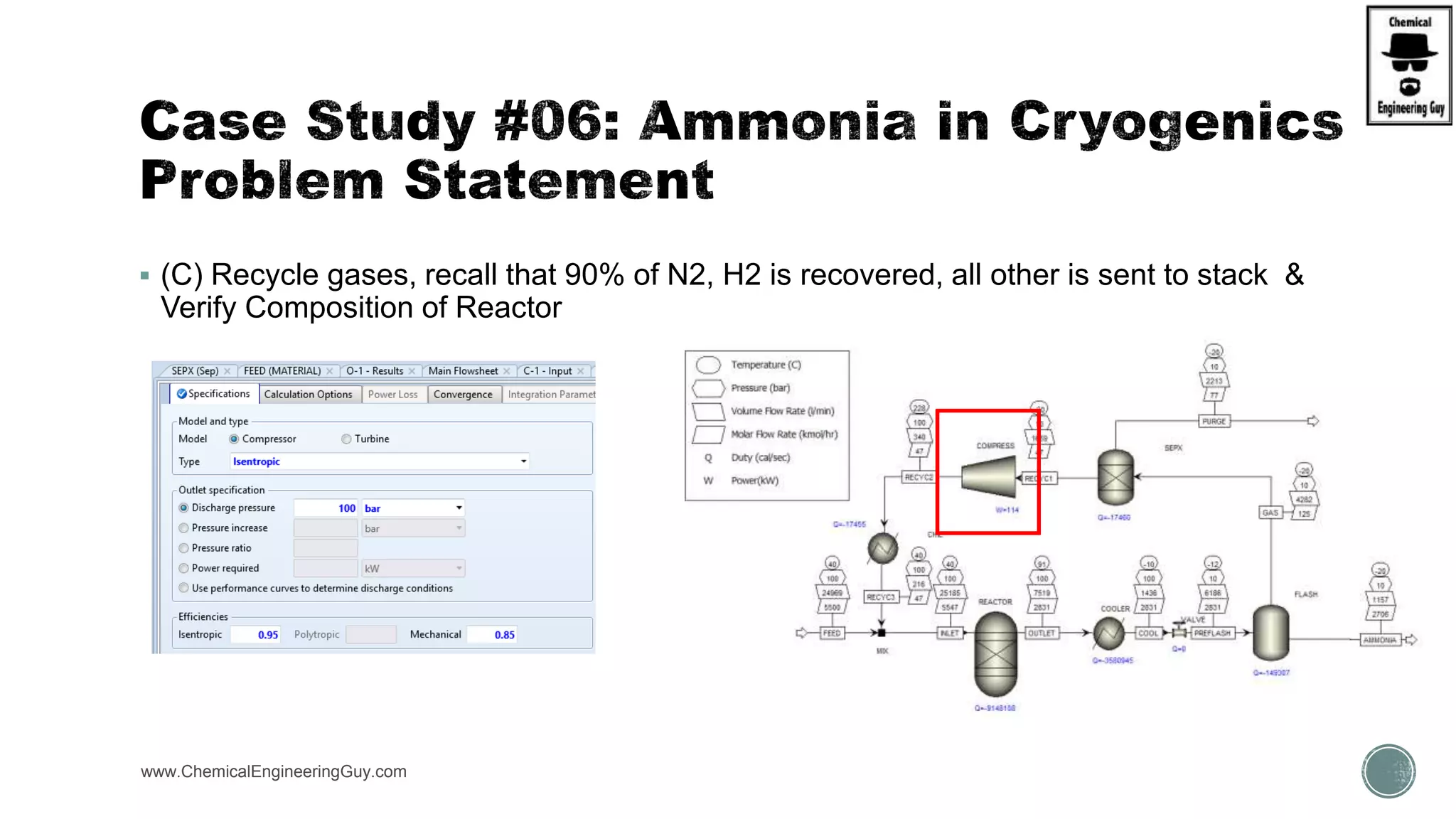
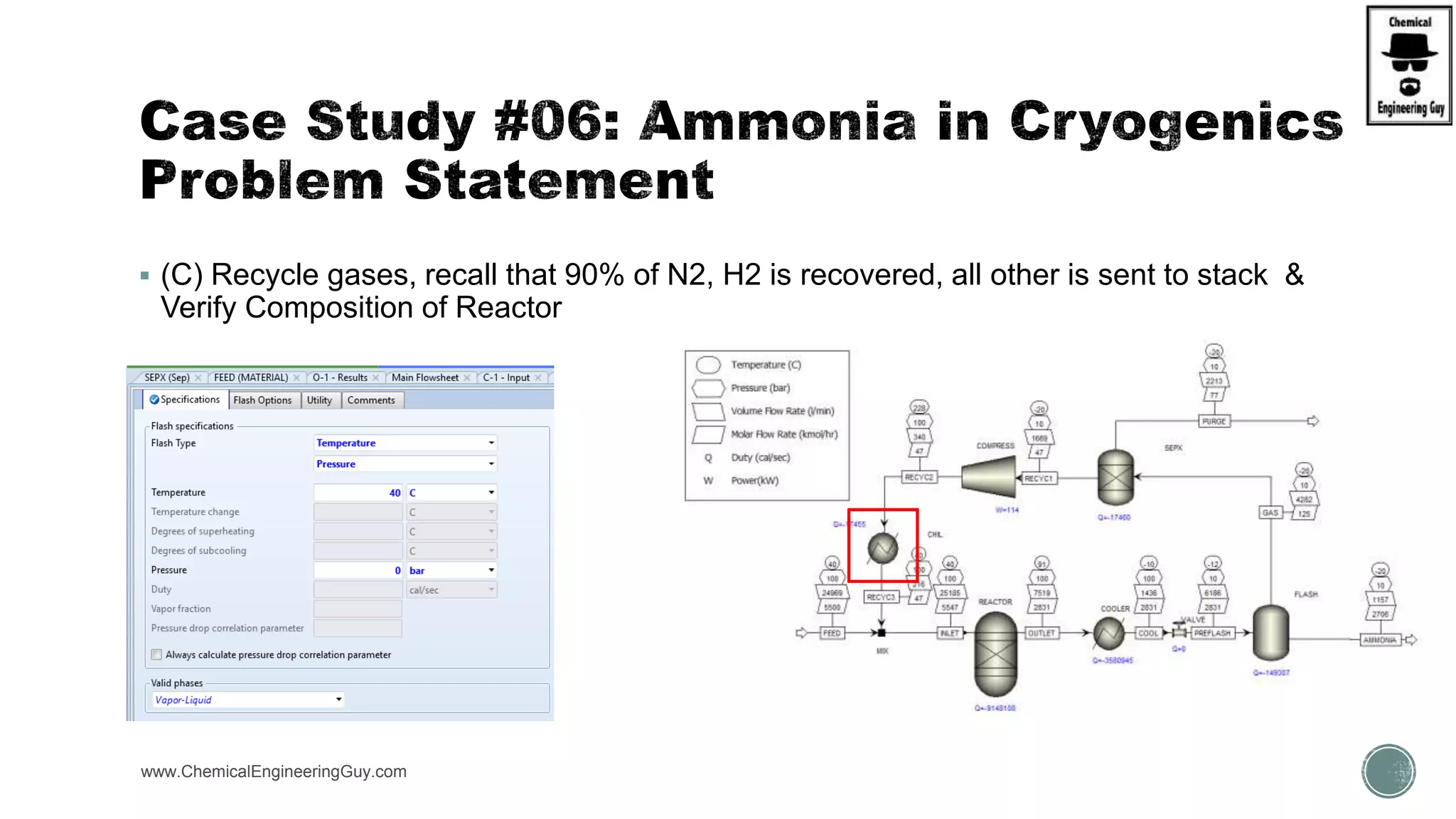
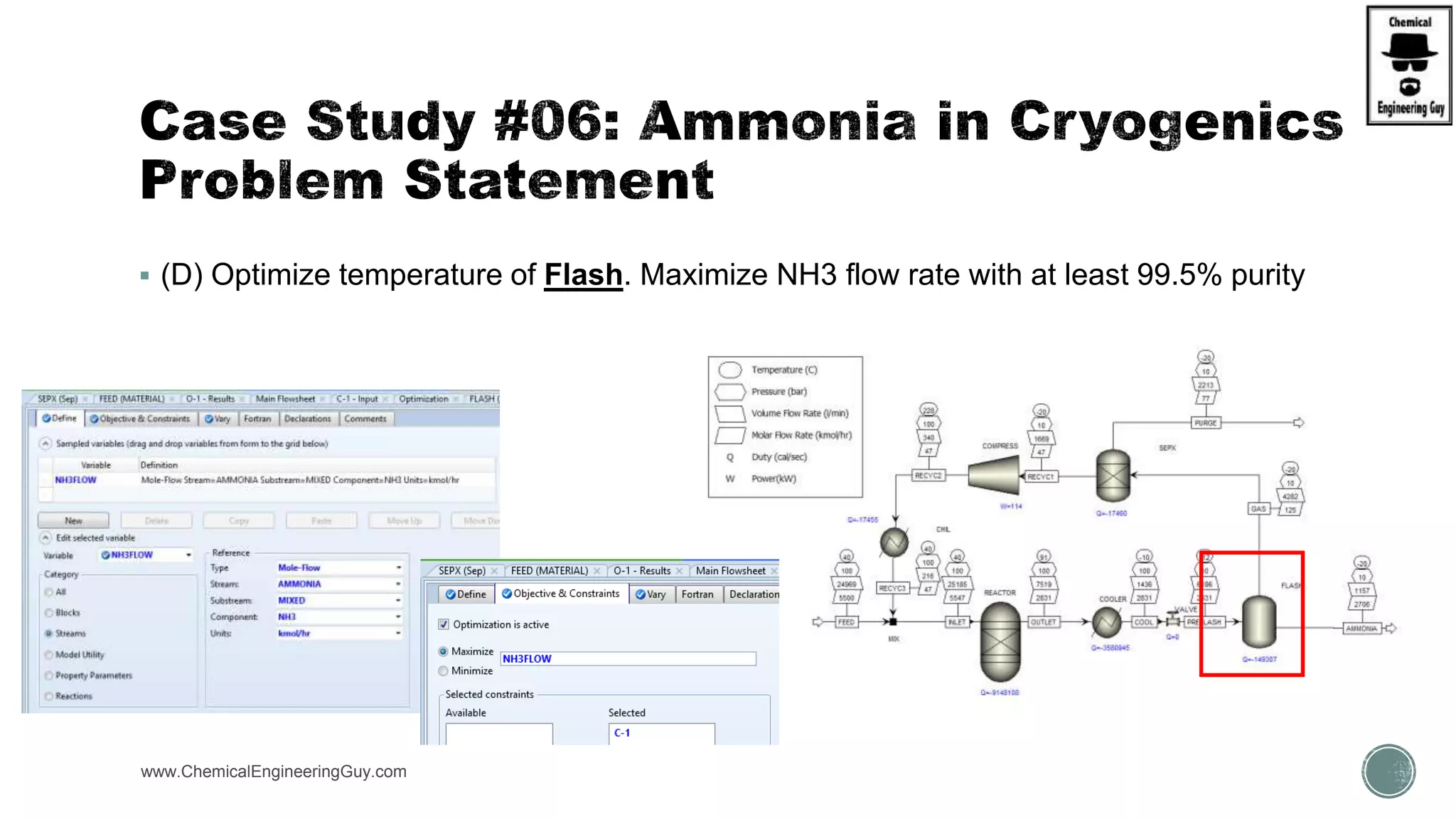
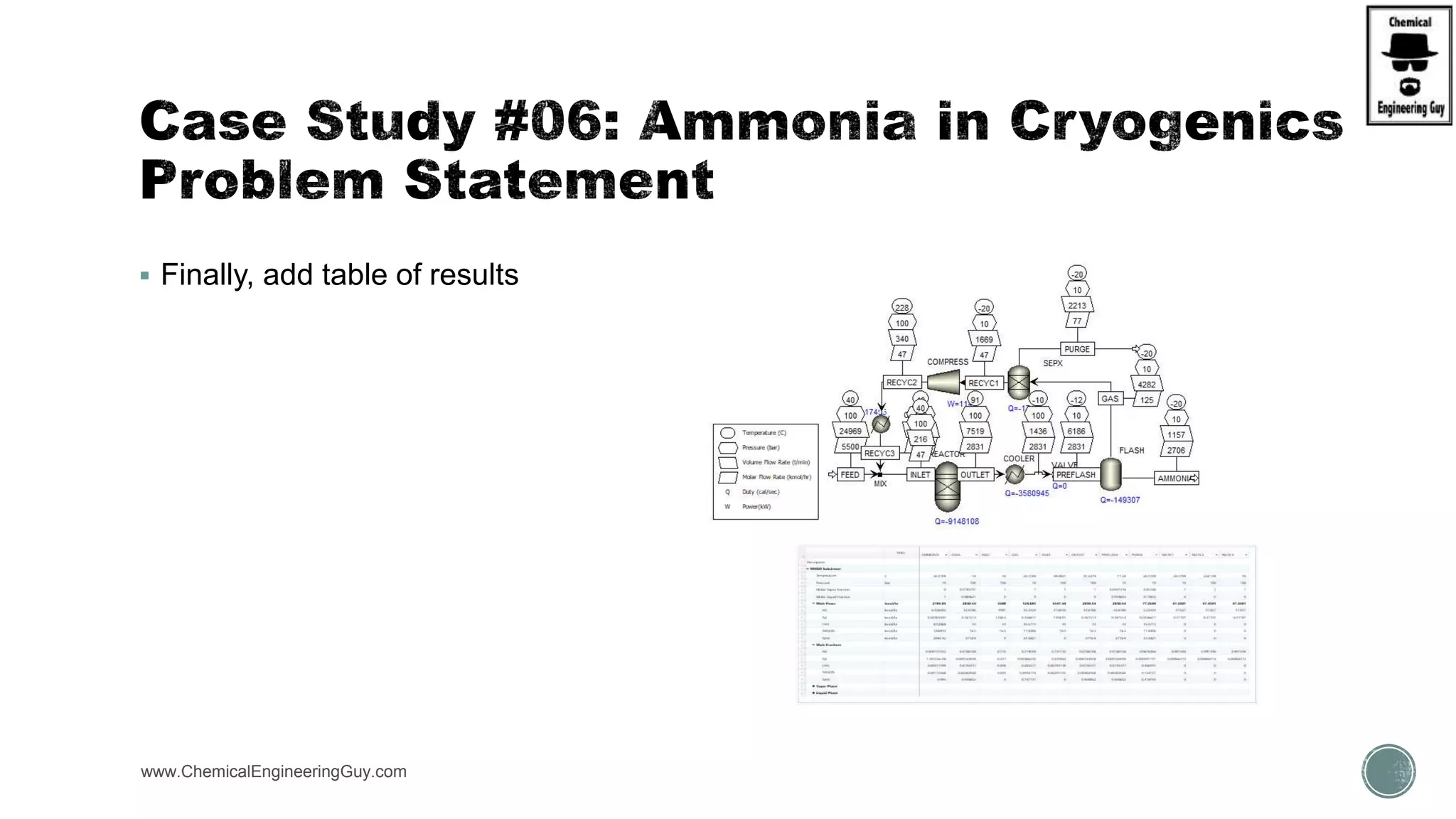
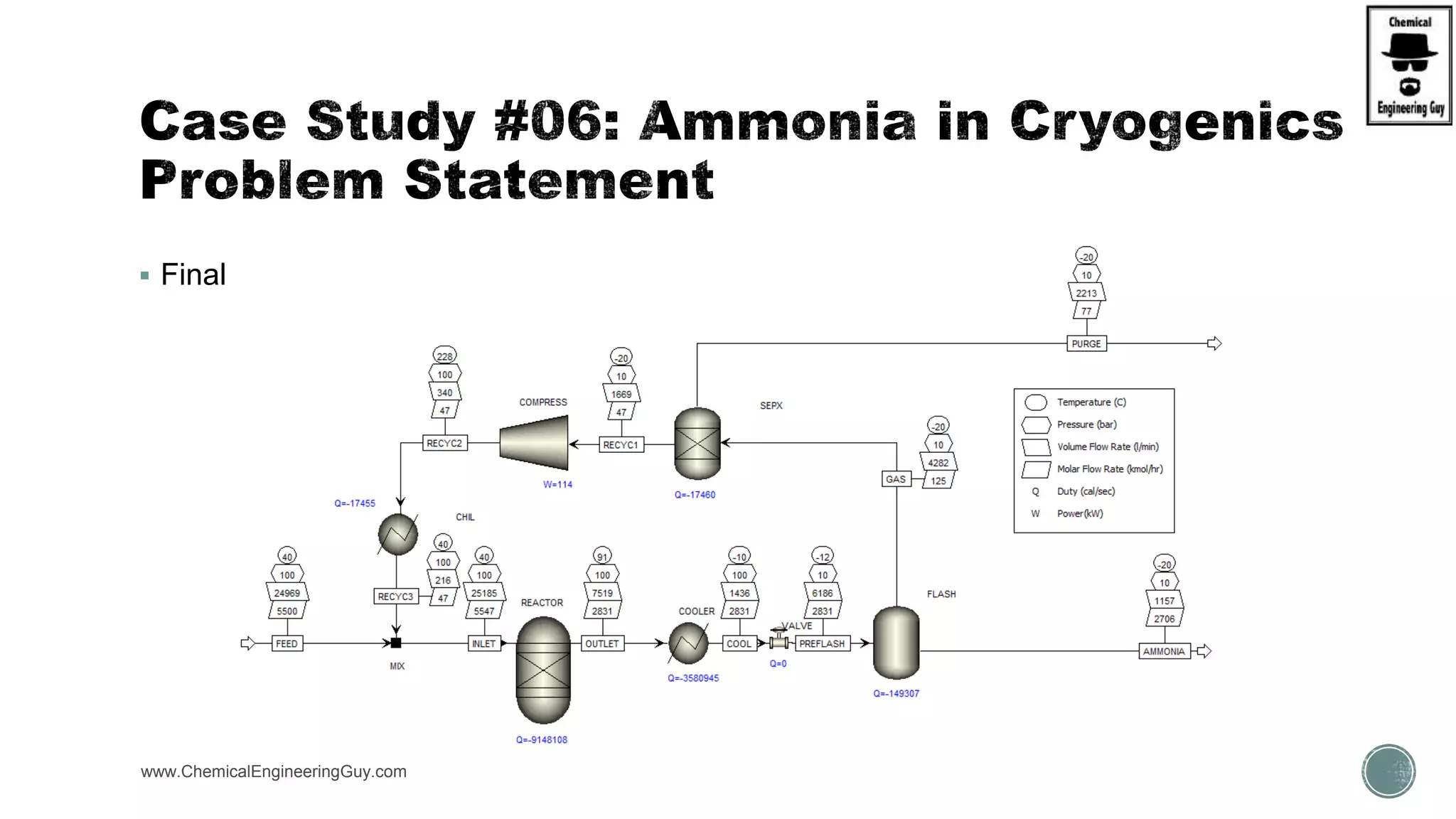
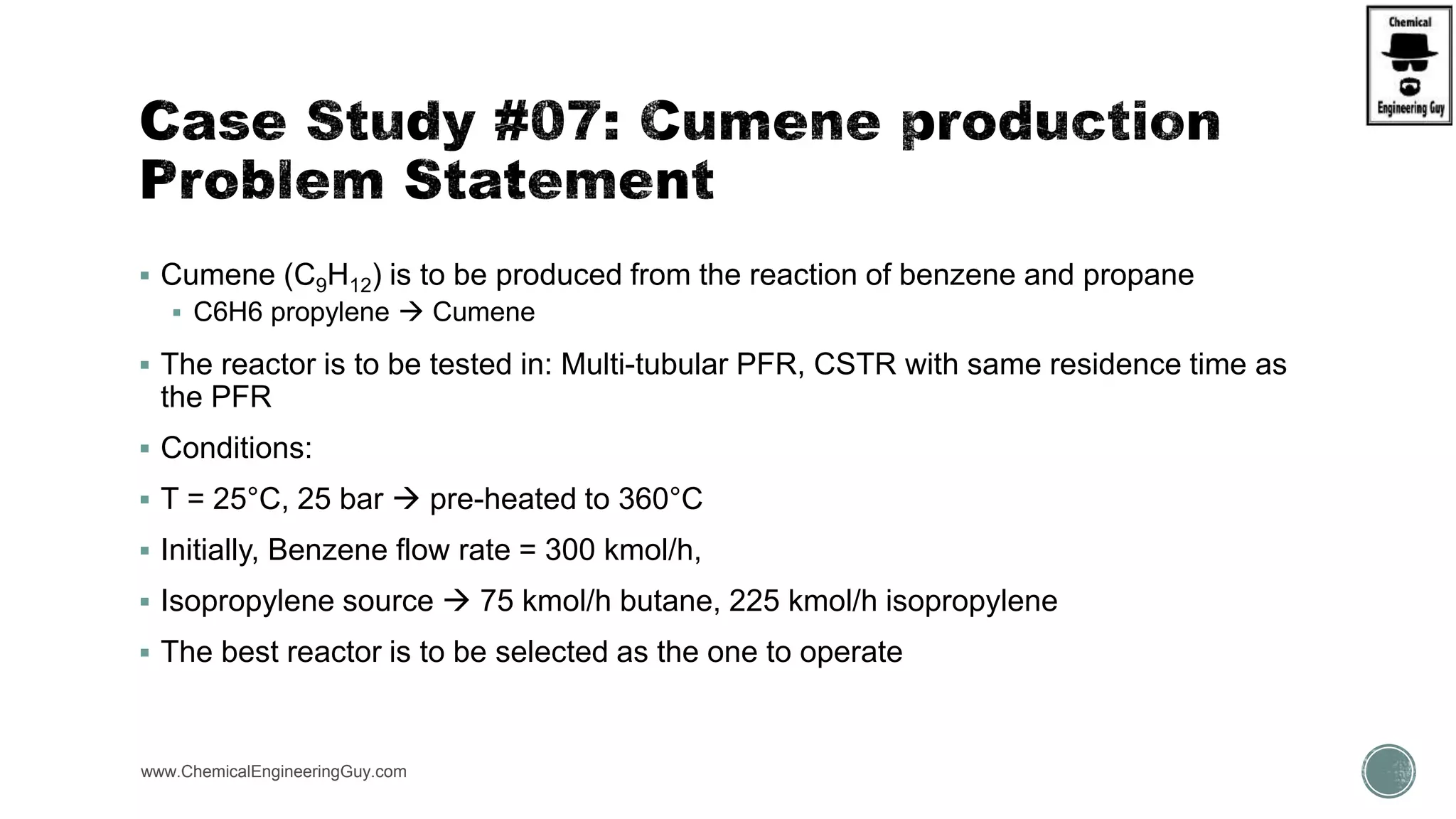
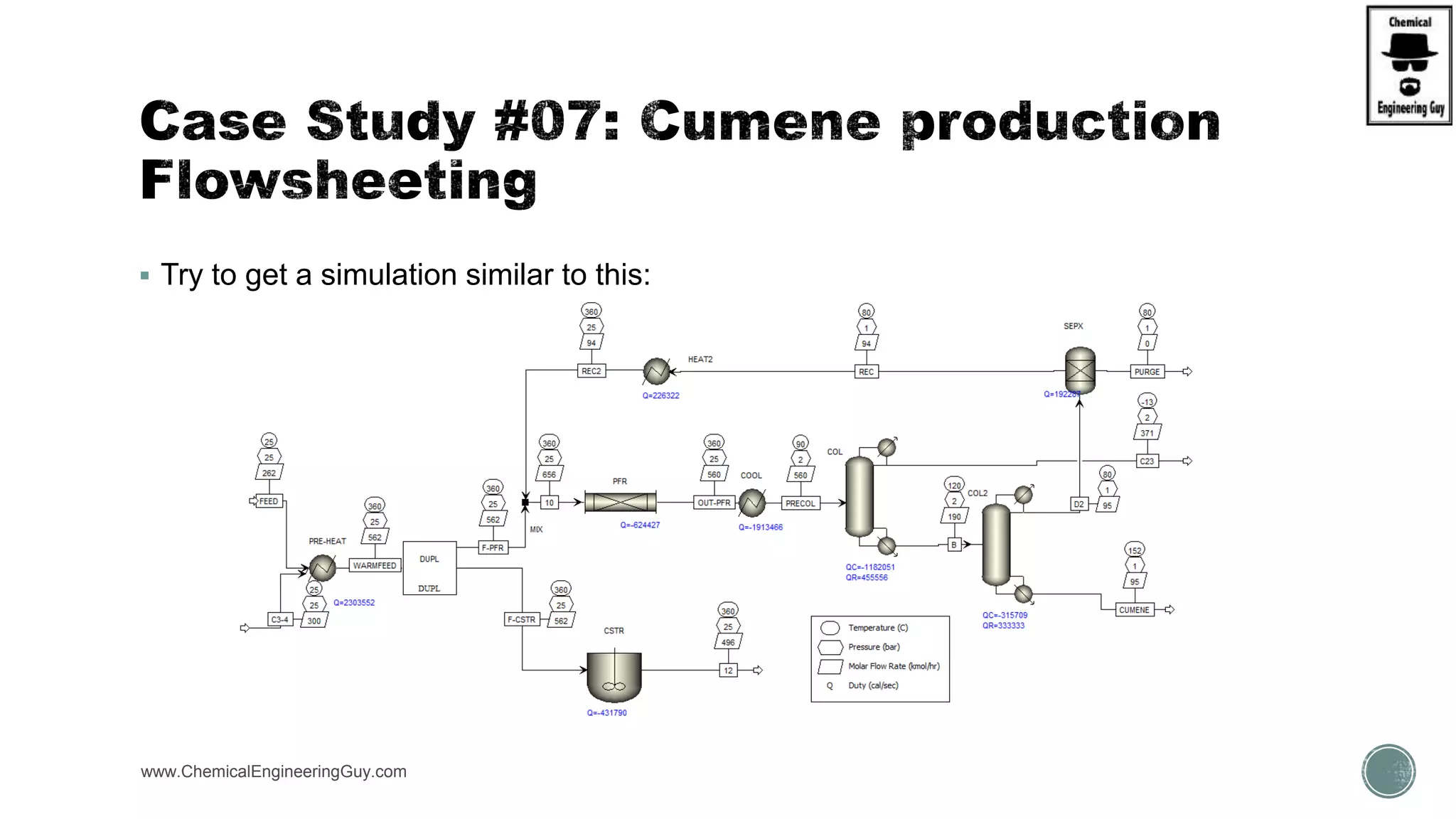
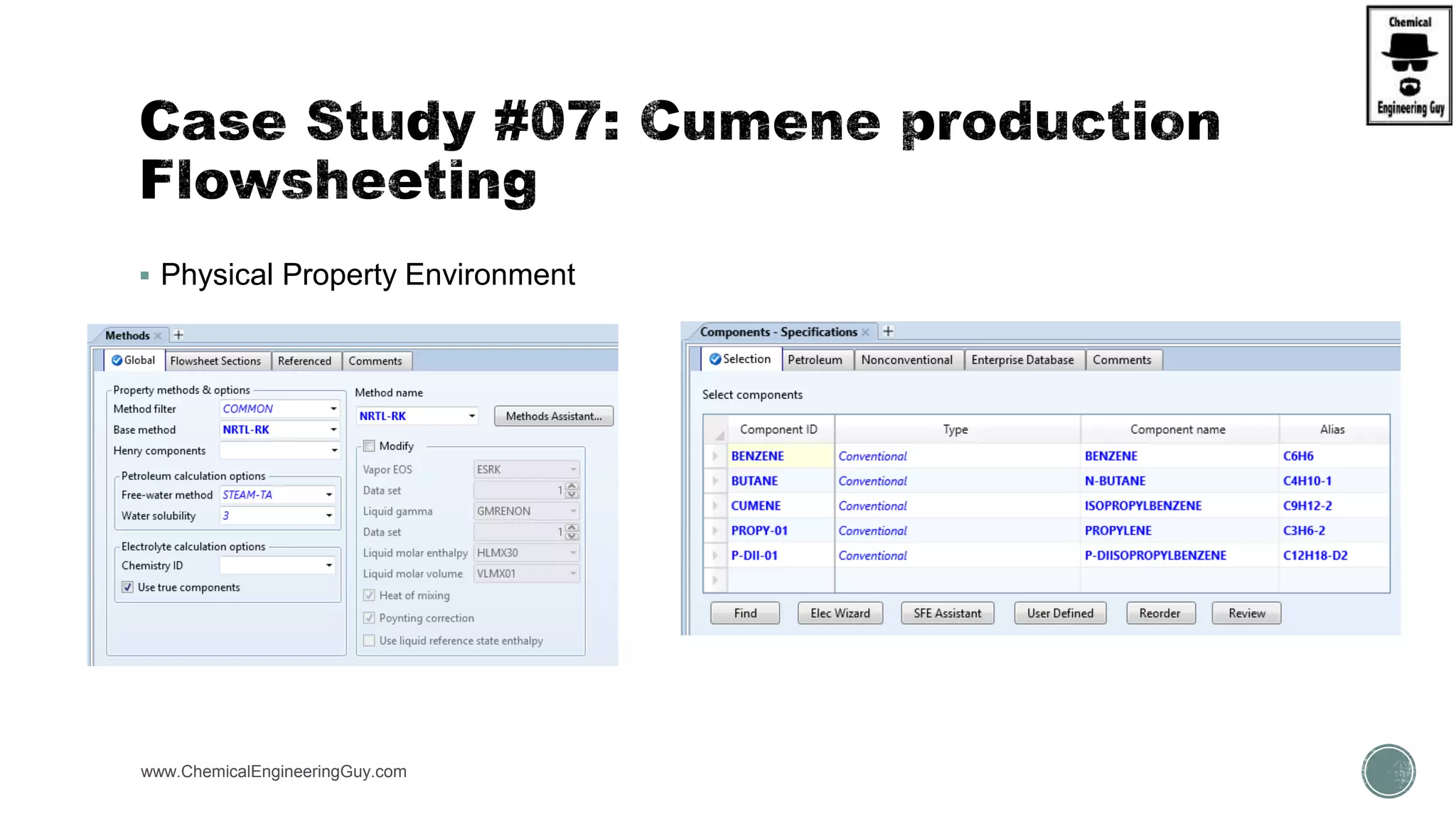
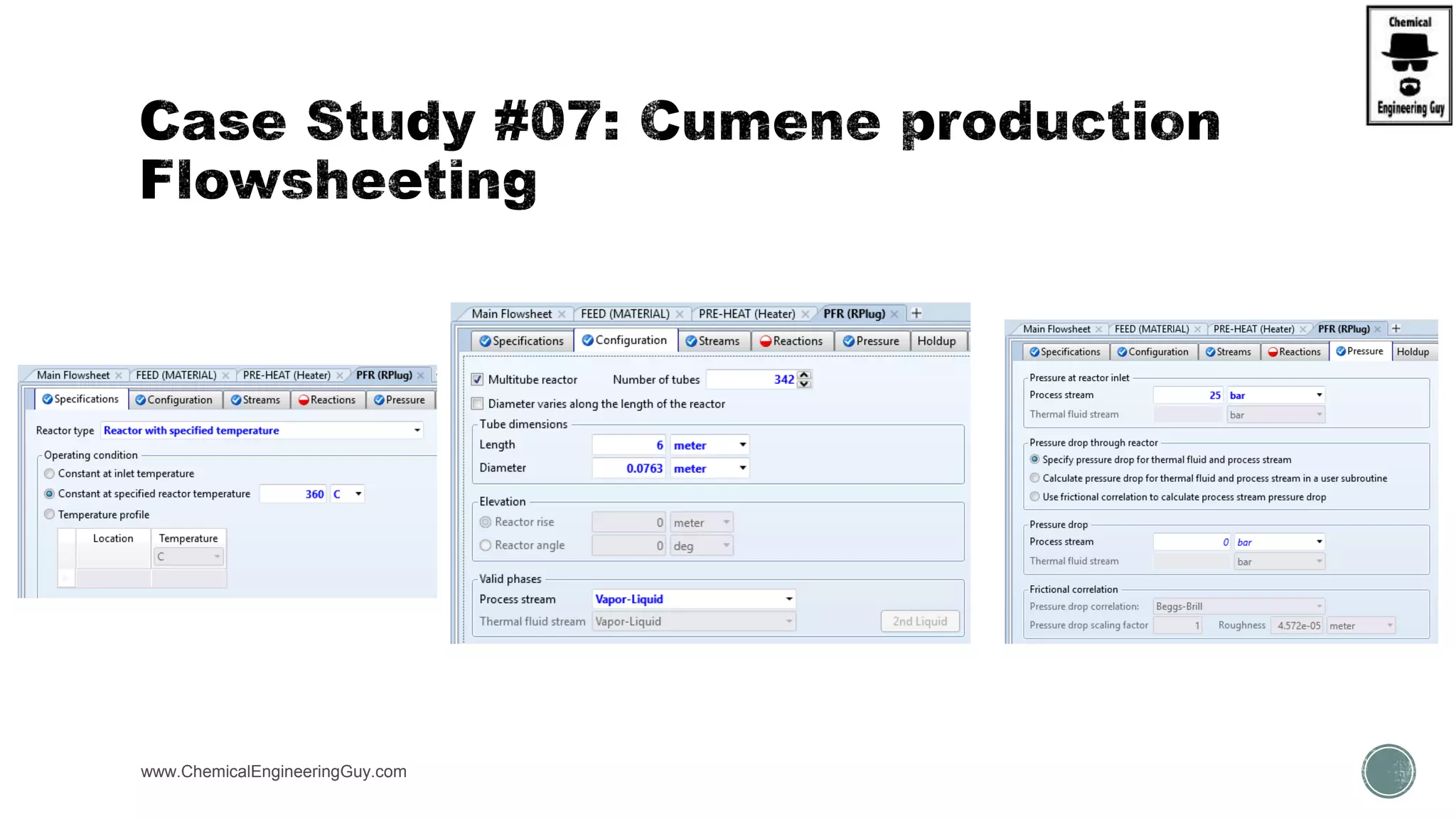
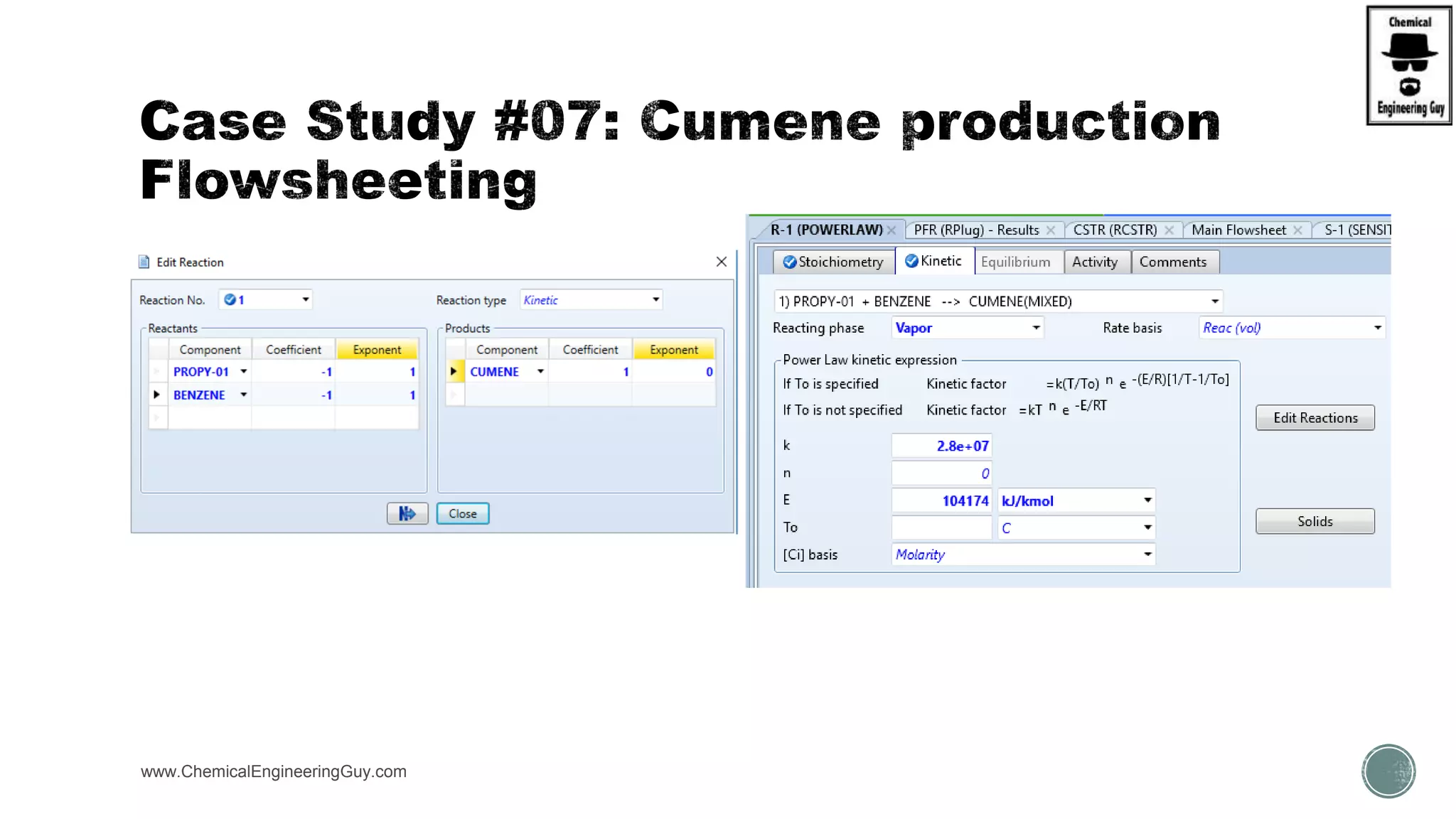
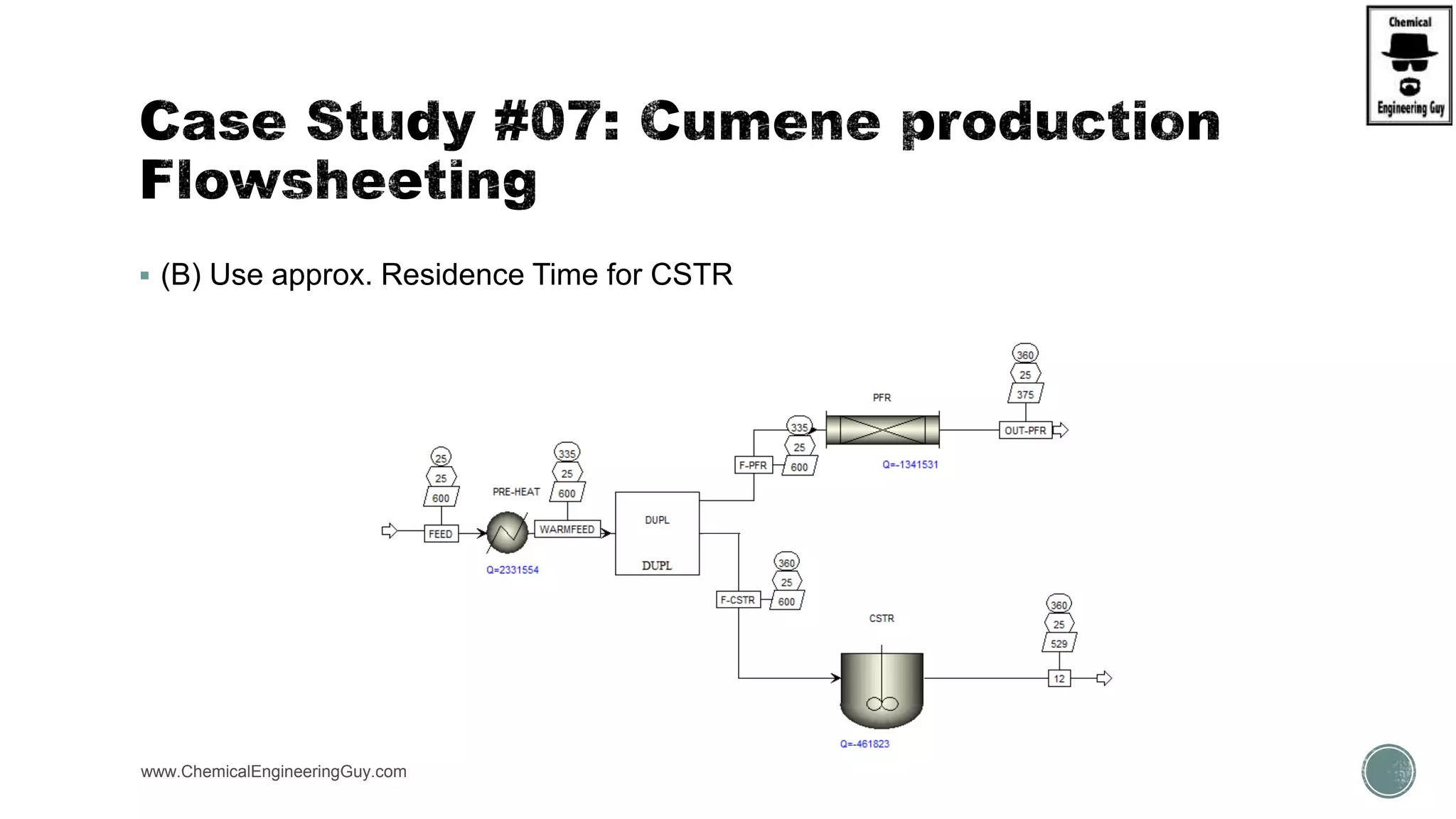
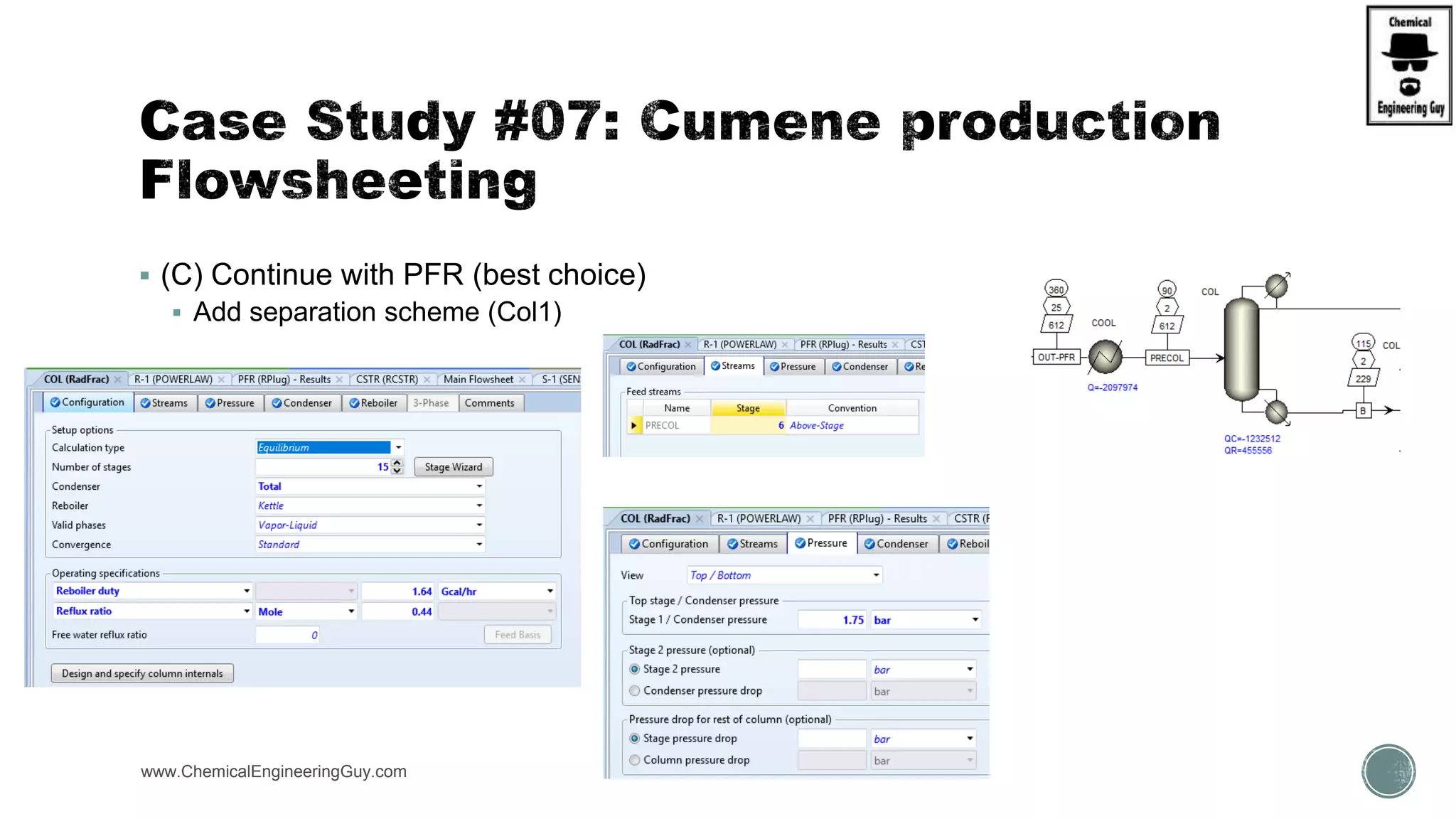
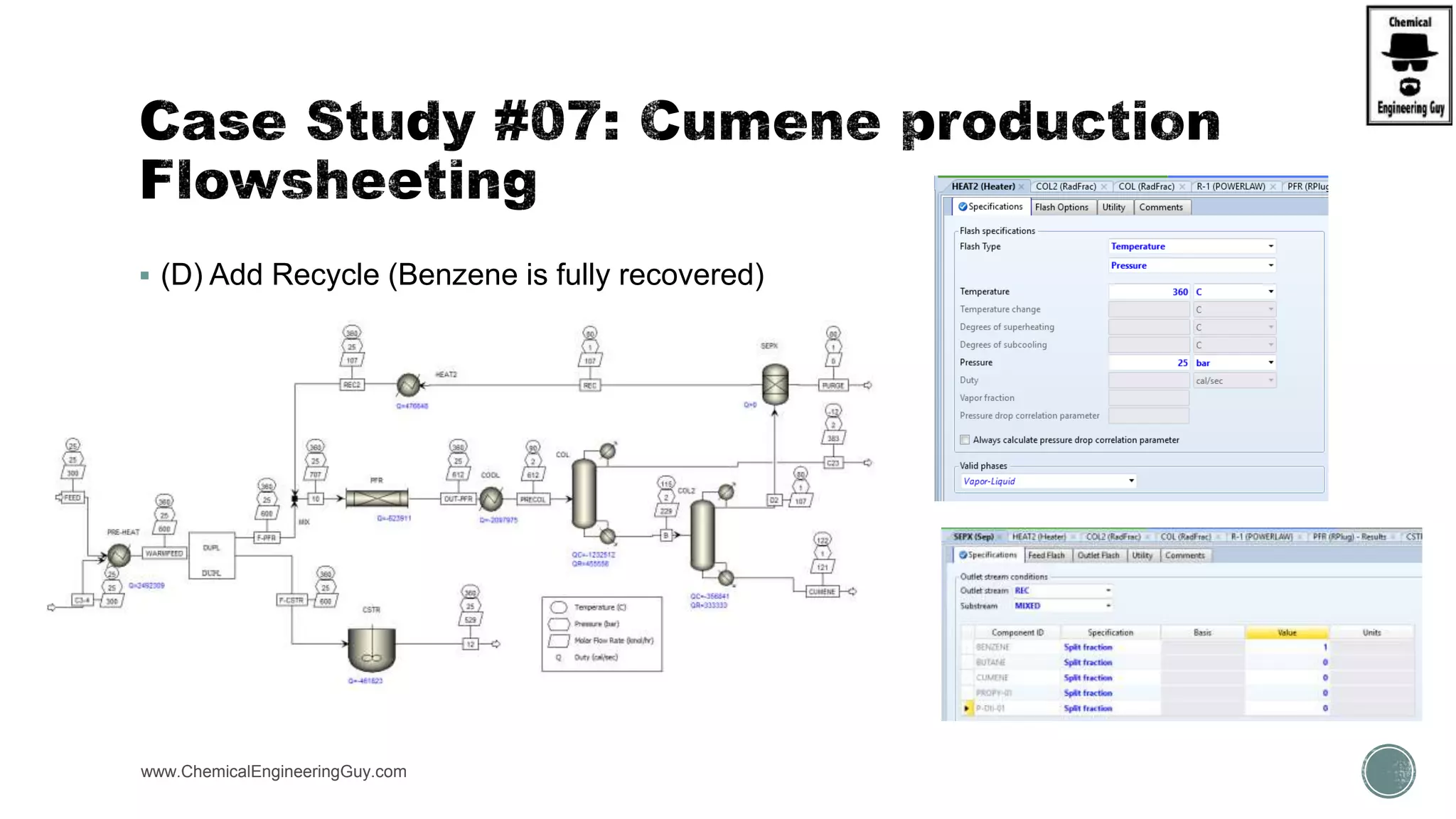
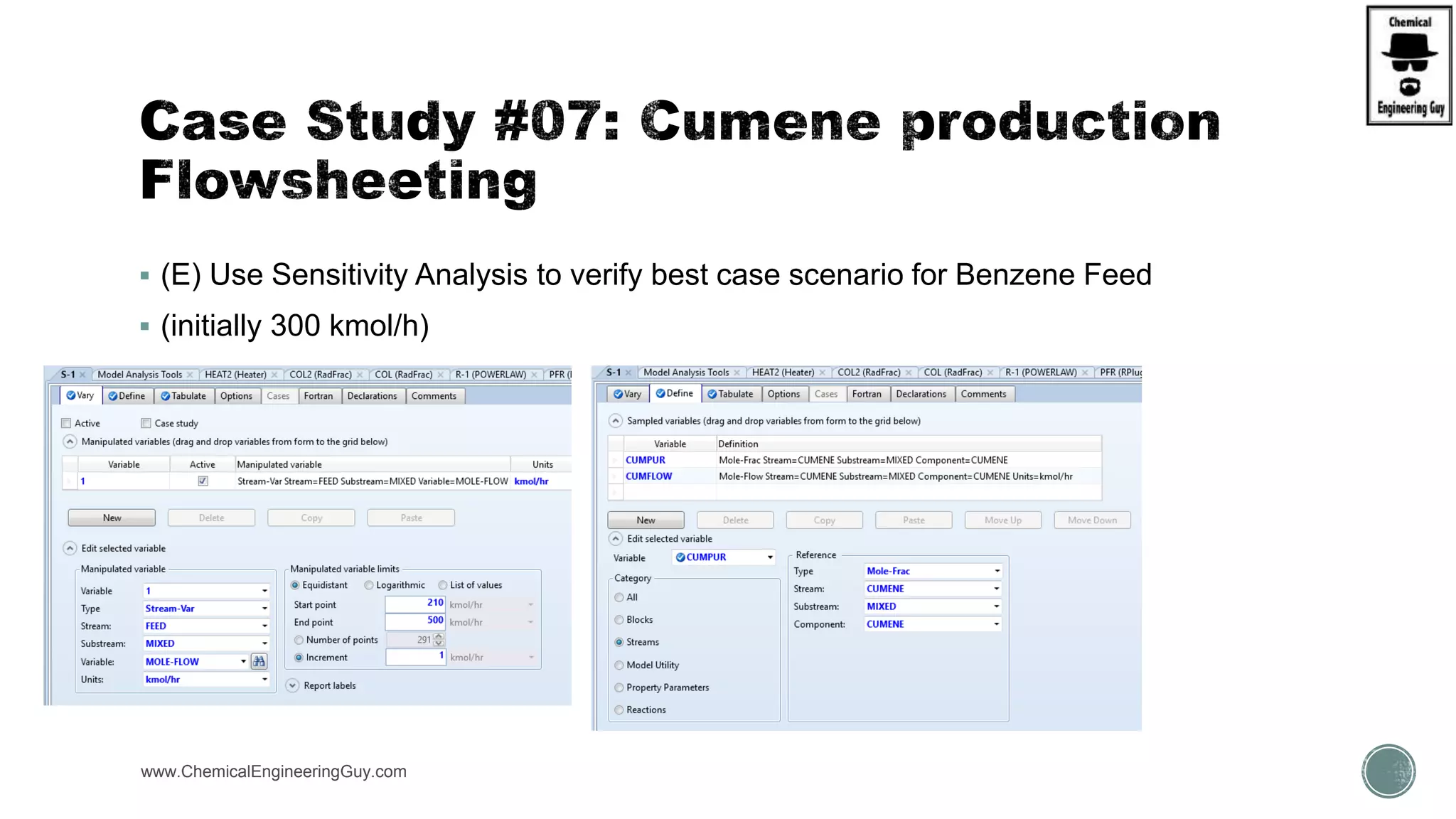
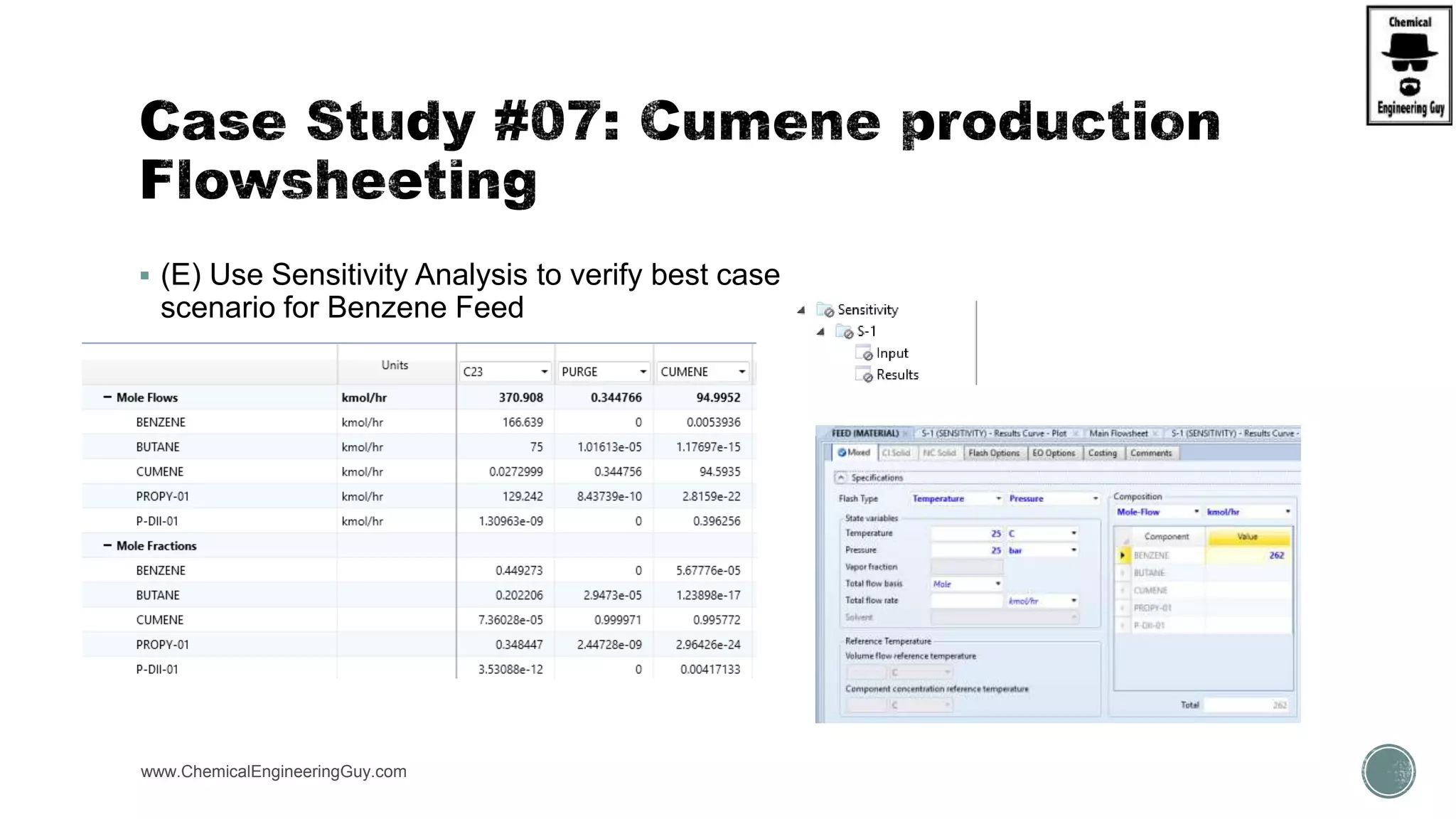
The document presents an overview of a chemical engineering bootcamp focused on the Aspen Plus software, including various study cases in chemical processes, process analysis, and rigorous unit operations. It targets engineers, students, and educators to enhance their skills in process simulation and optimize production-ready applications. The course is practical, intensive, and is designed to provide hands-on experience through case studies and simulations.