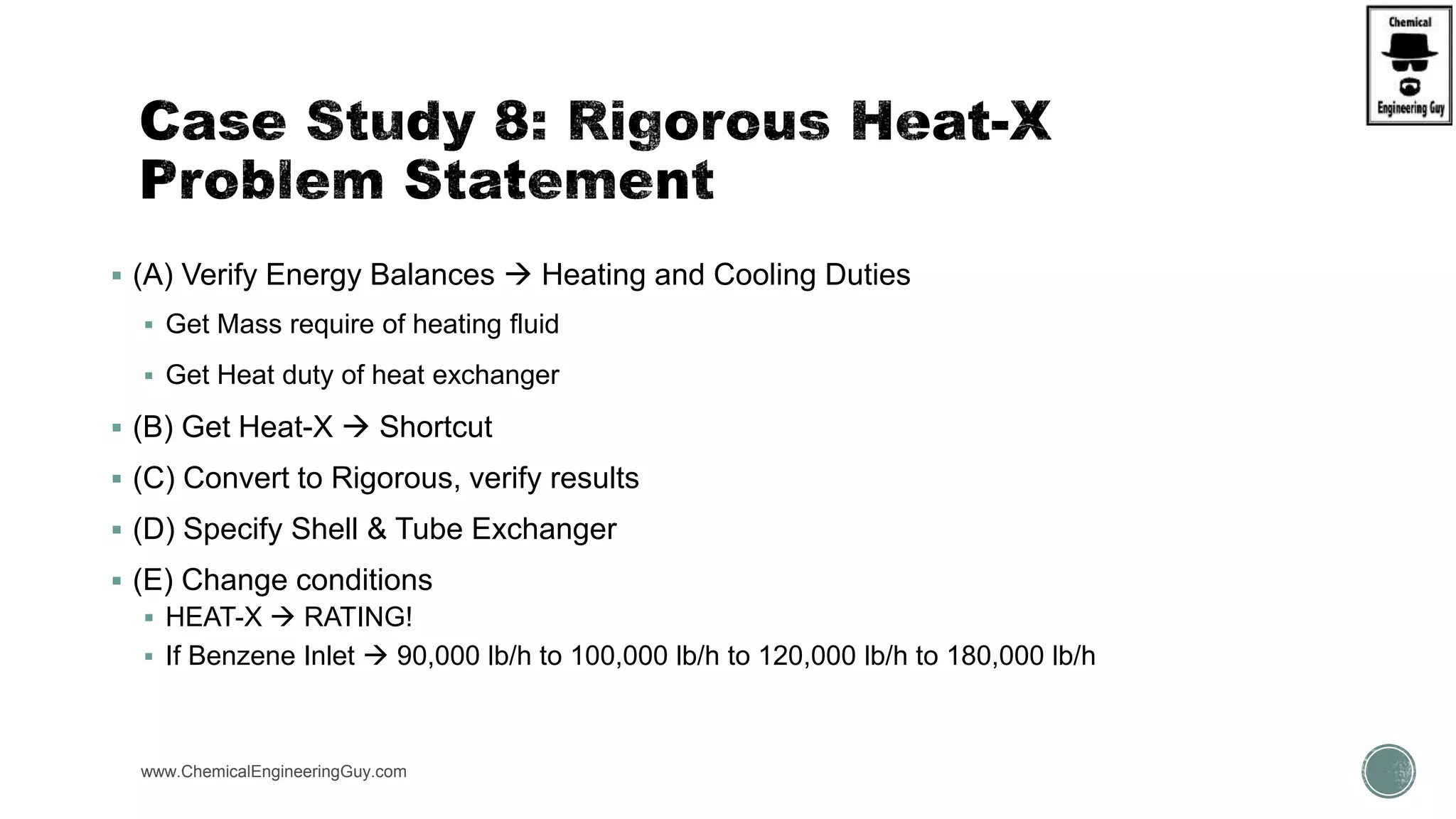
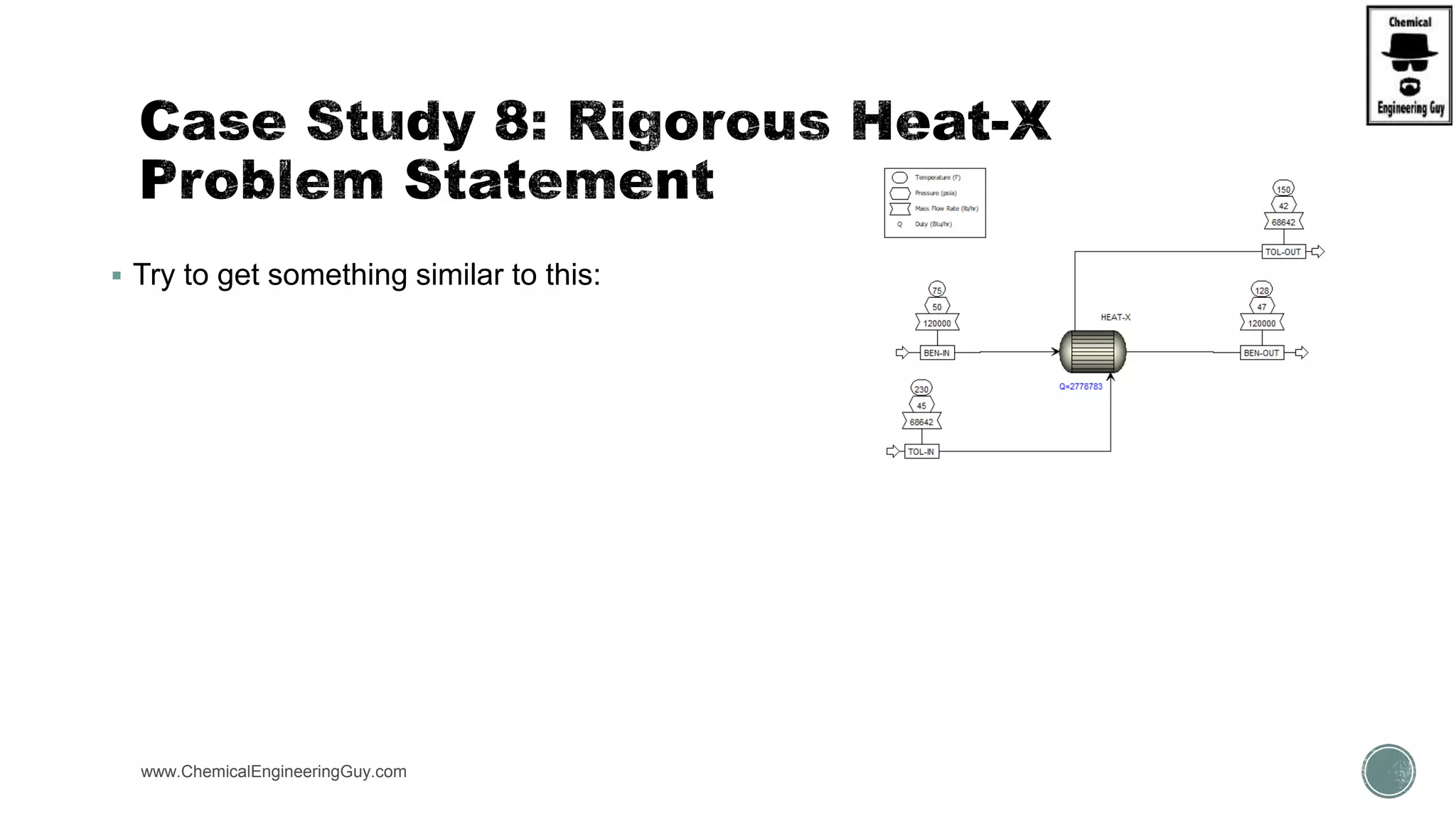
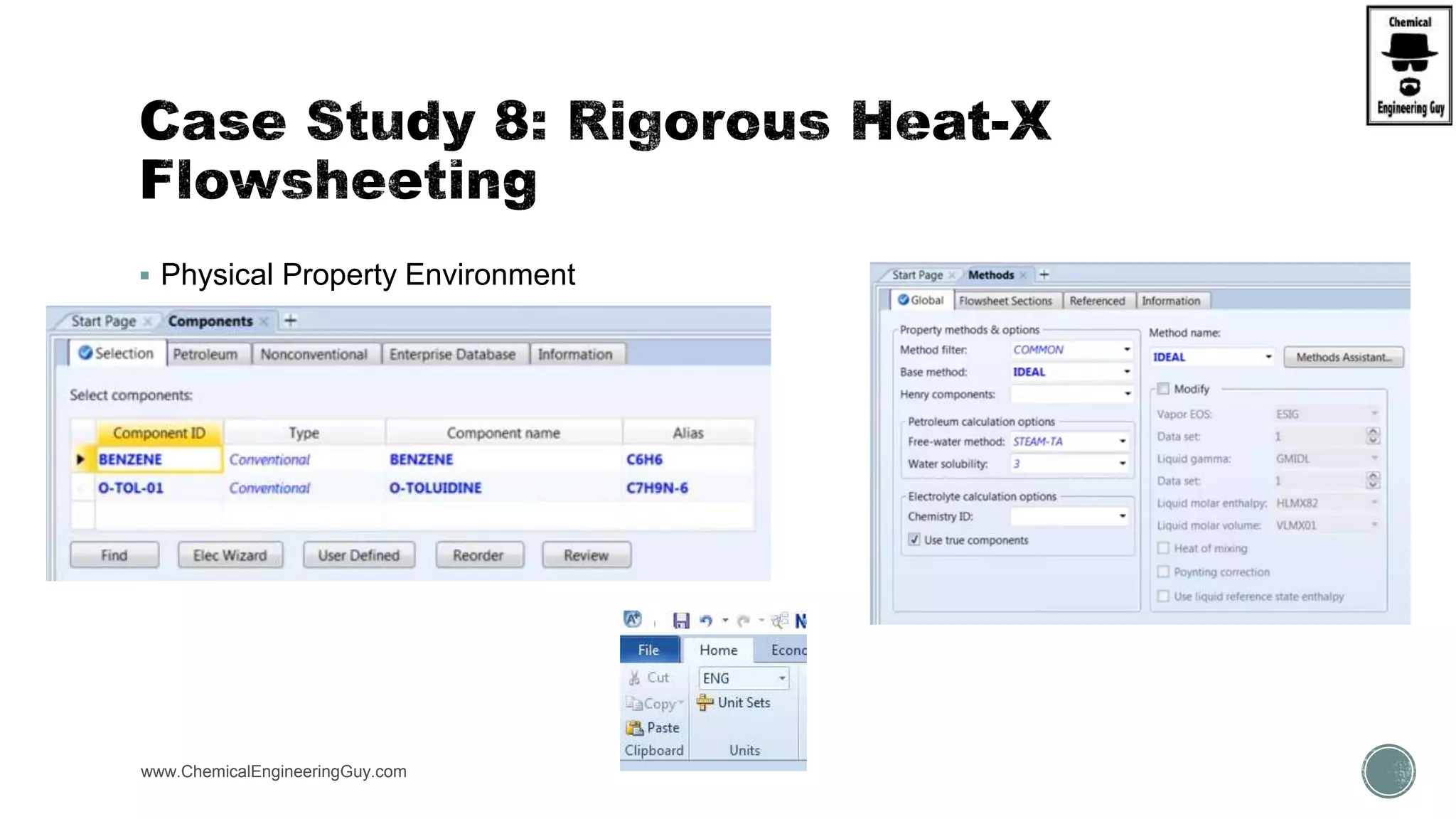
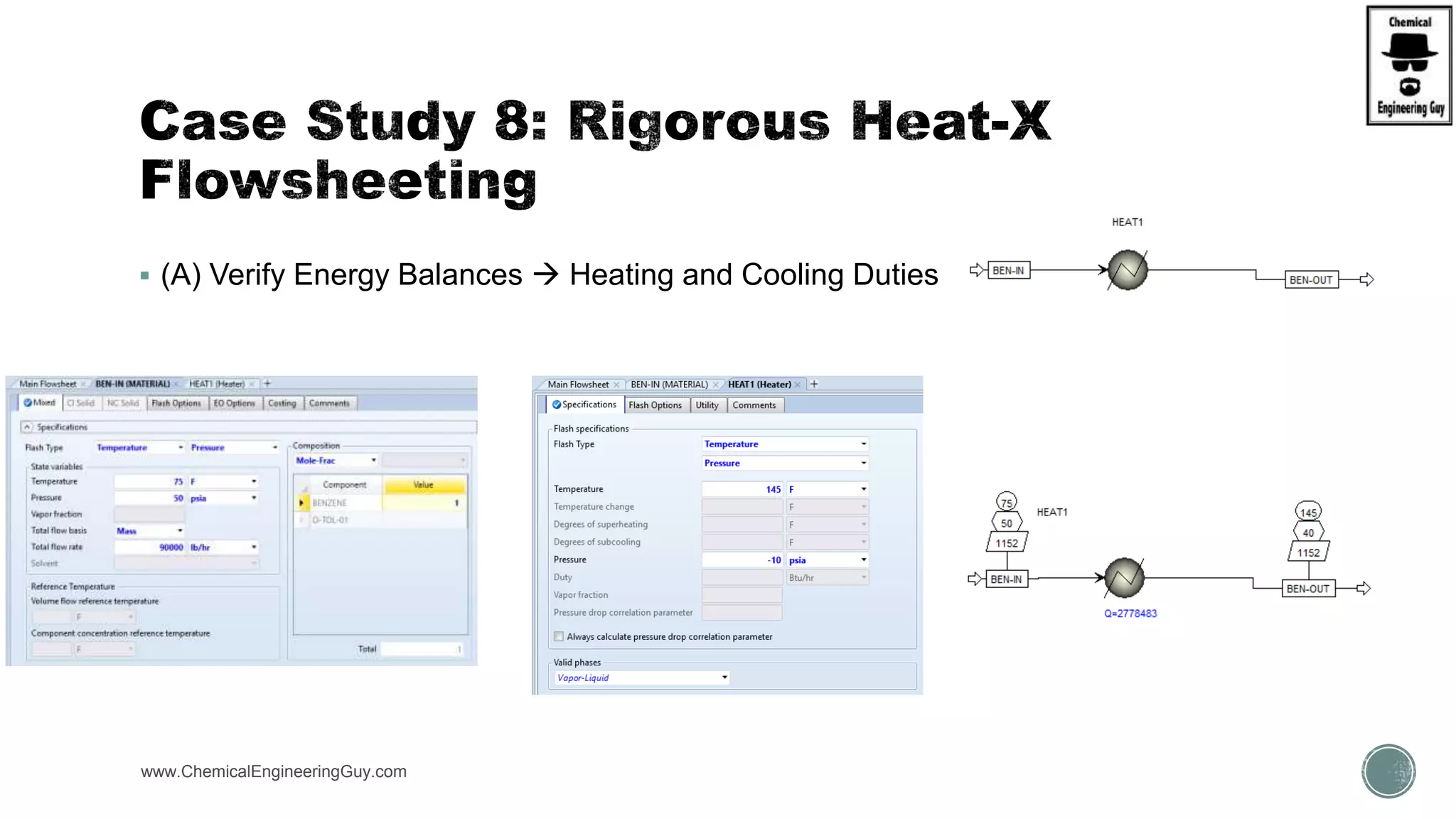
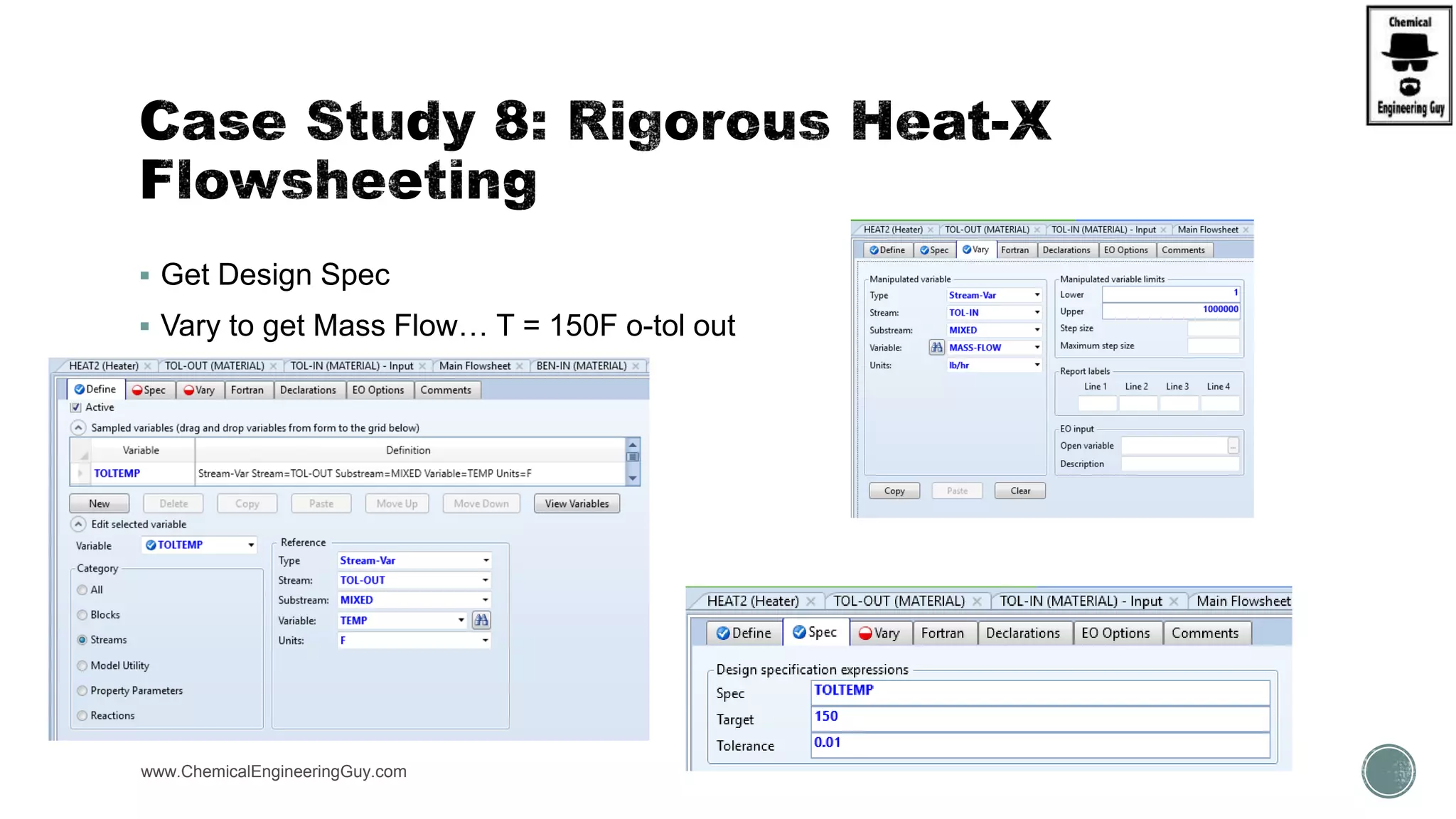
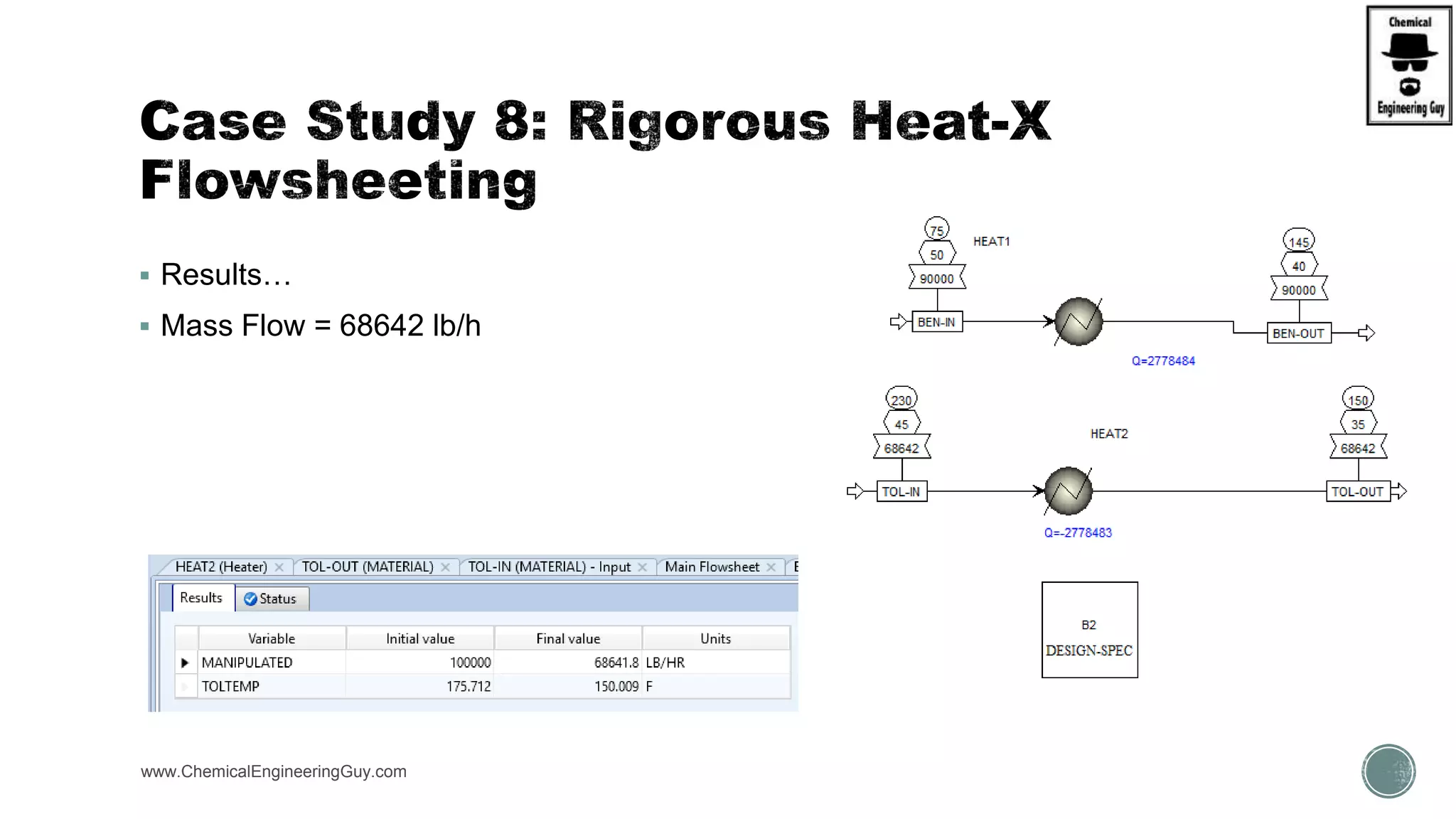
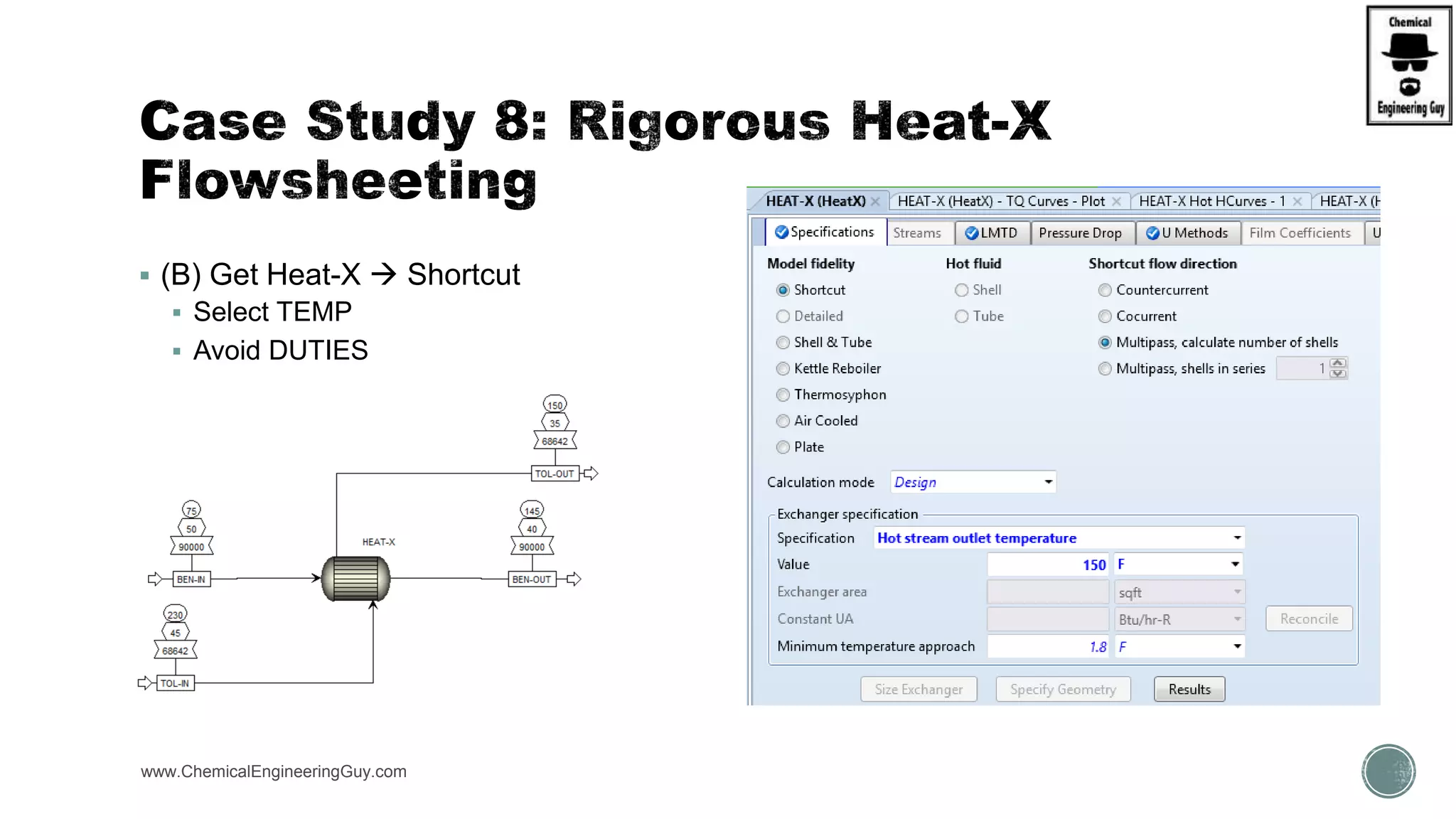
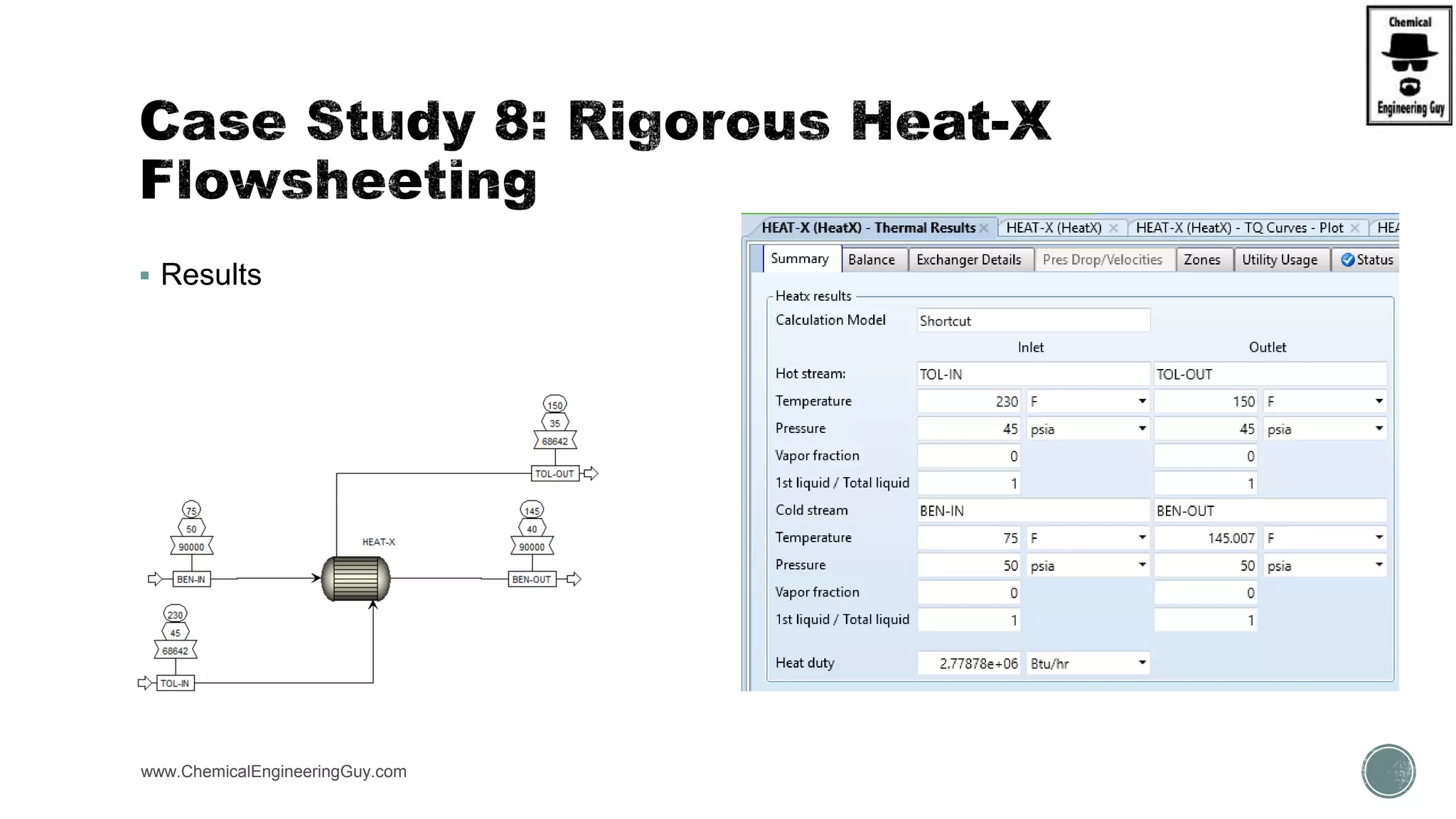
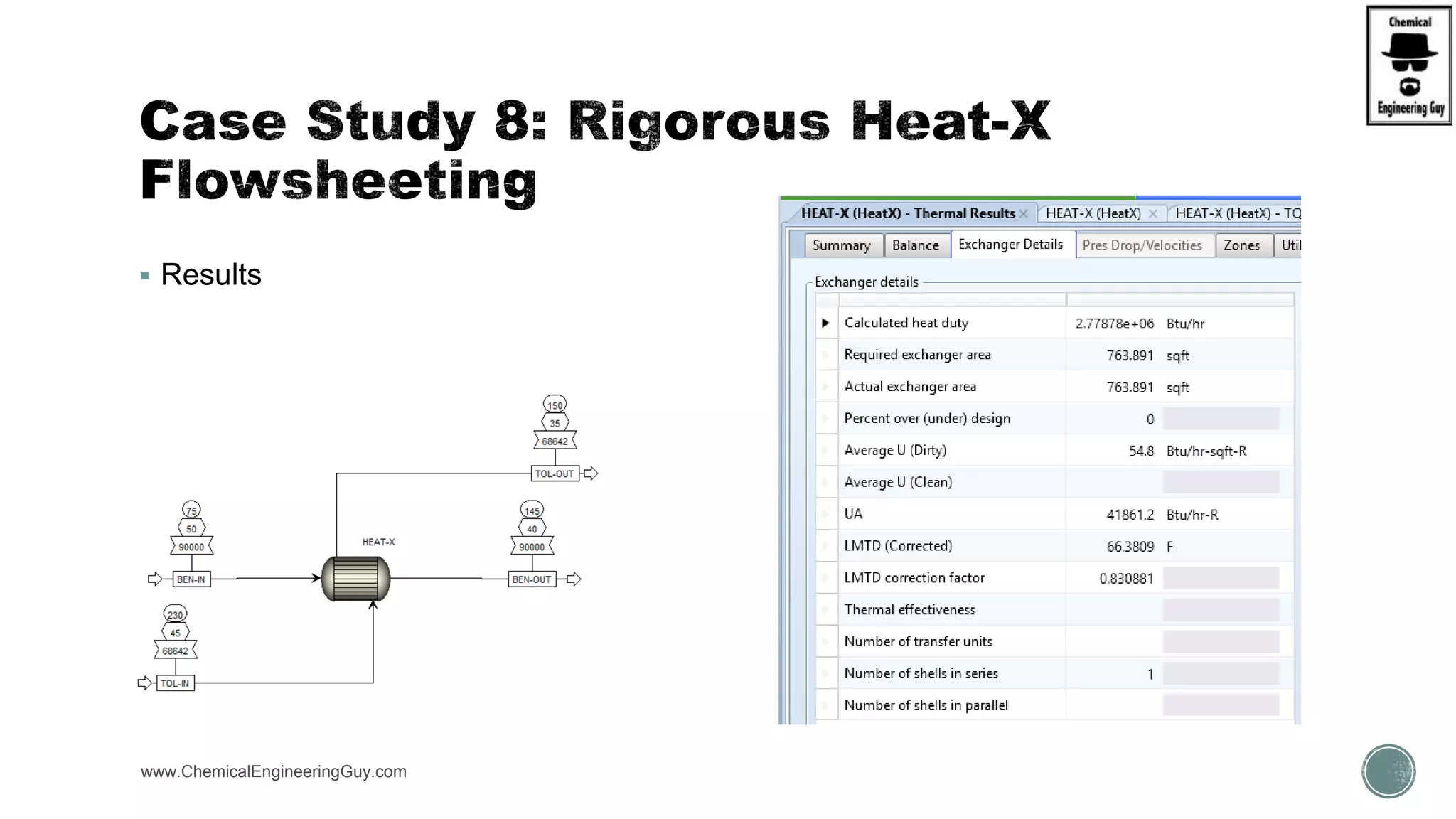
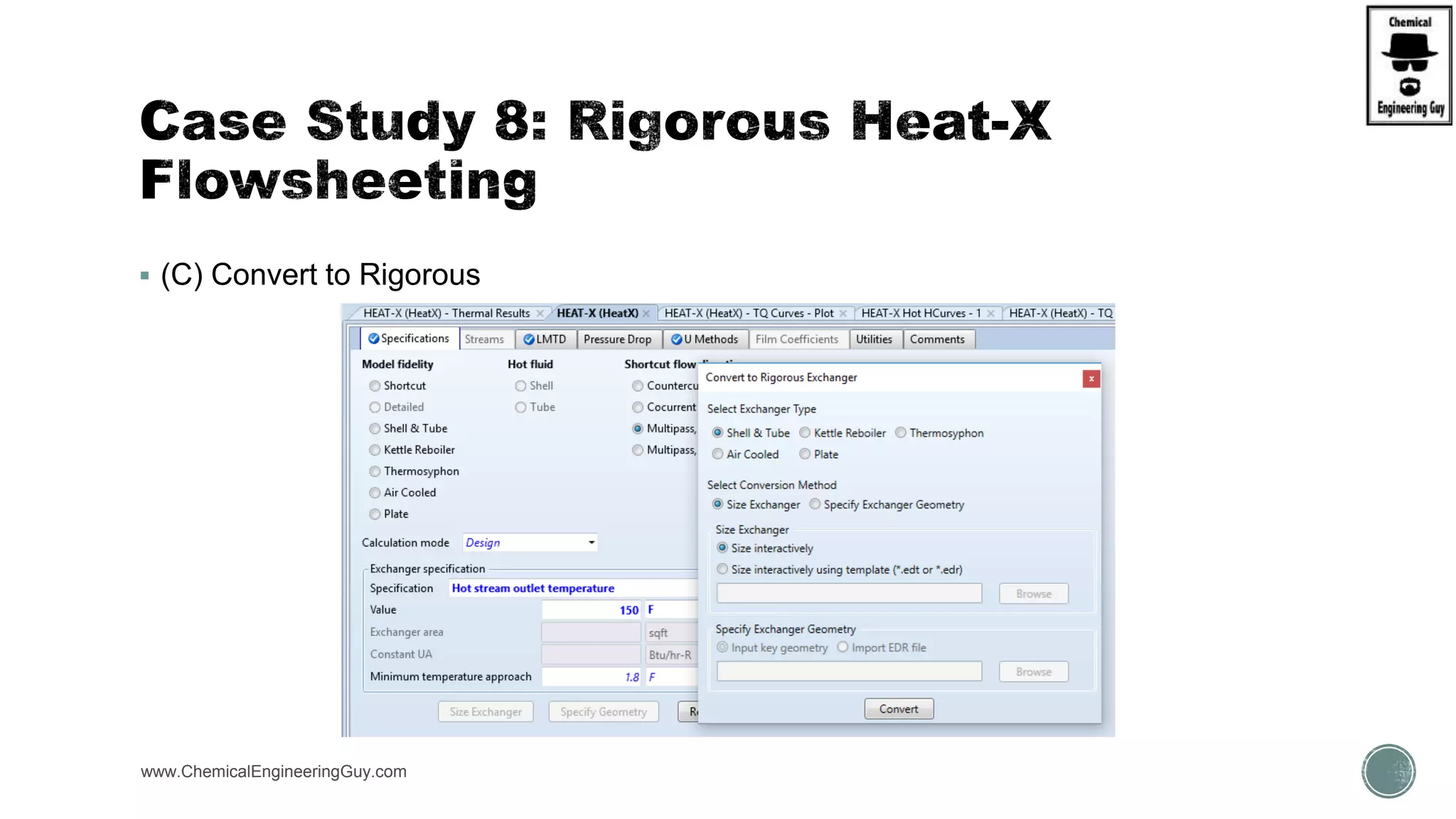
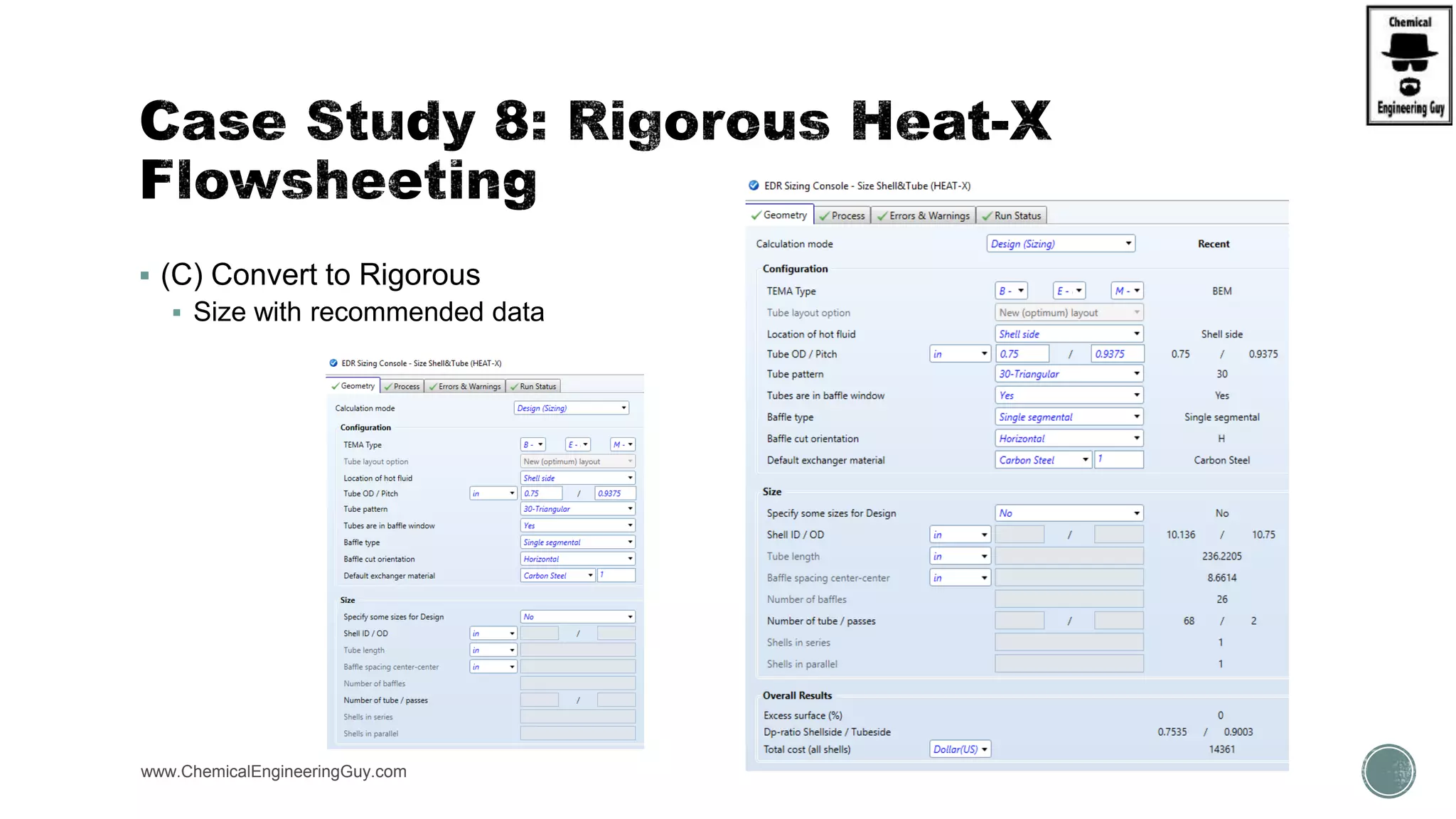
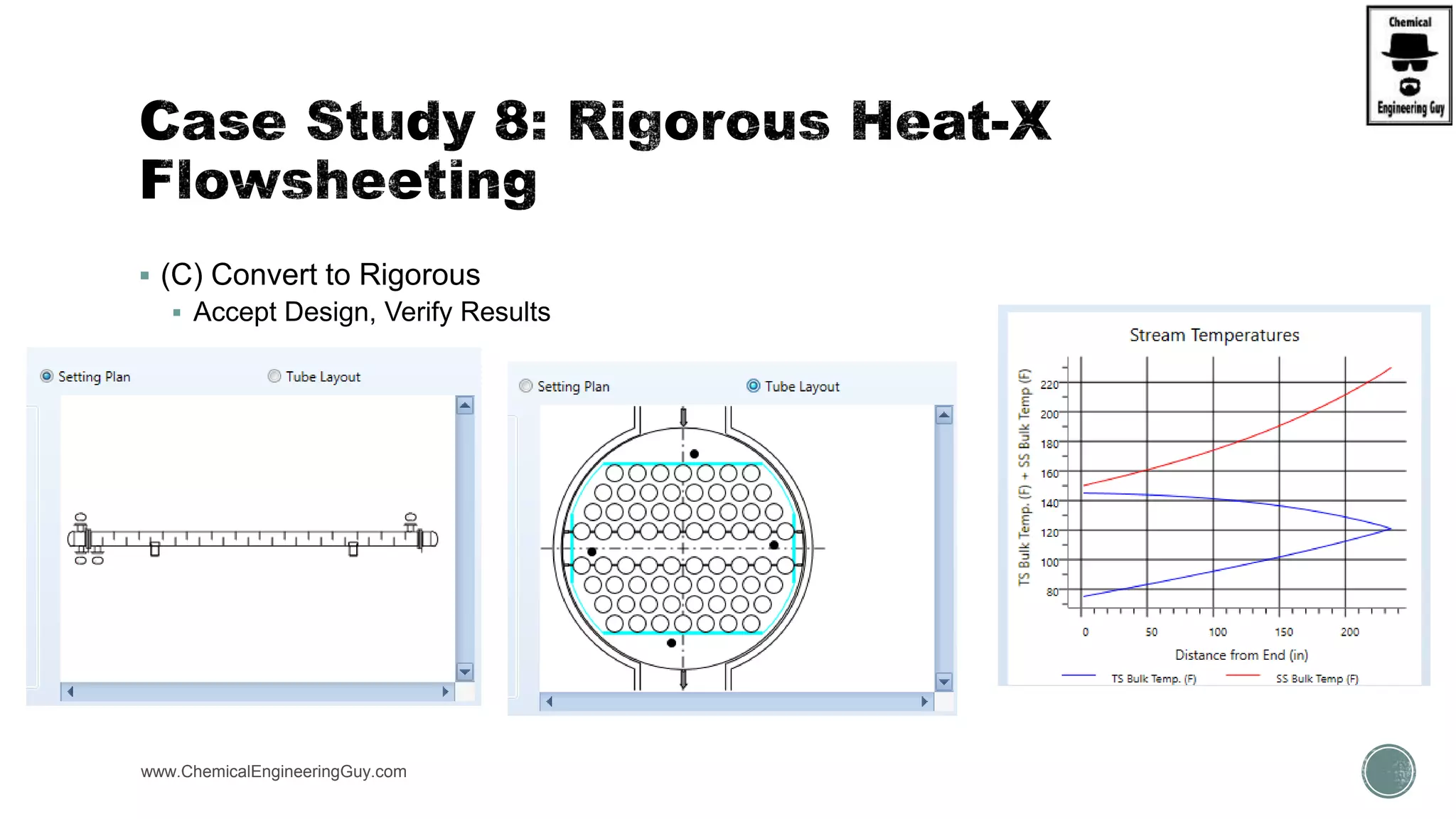
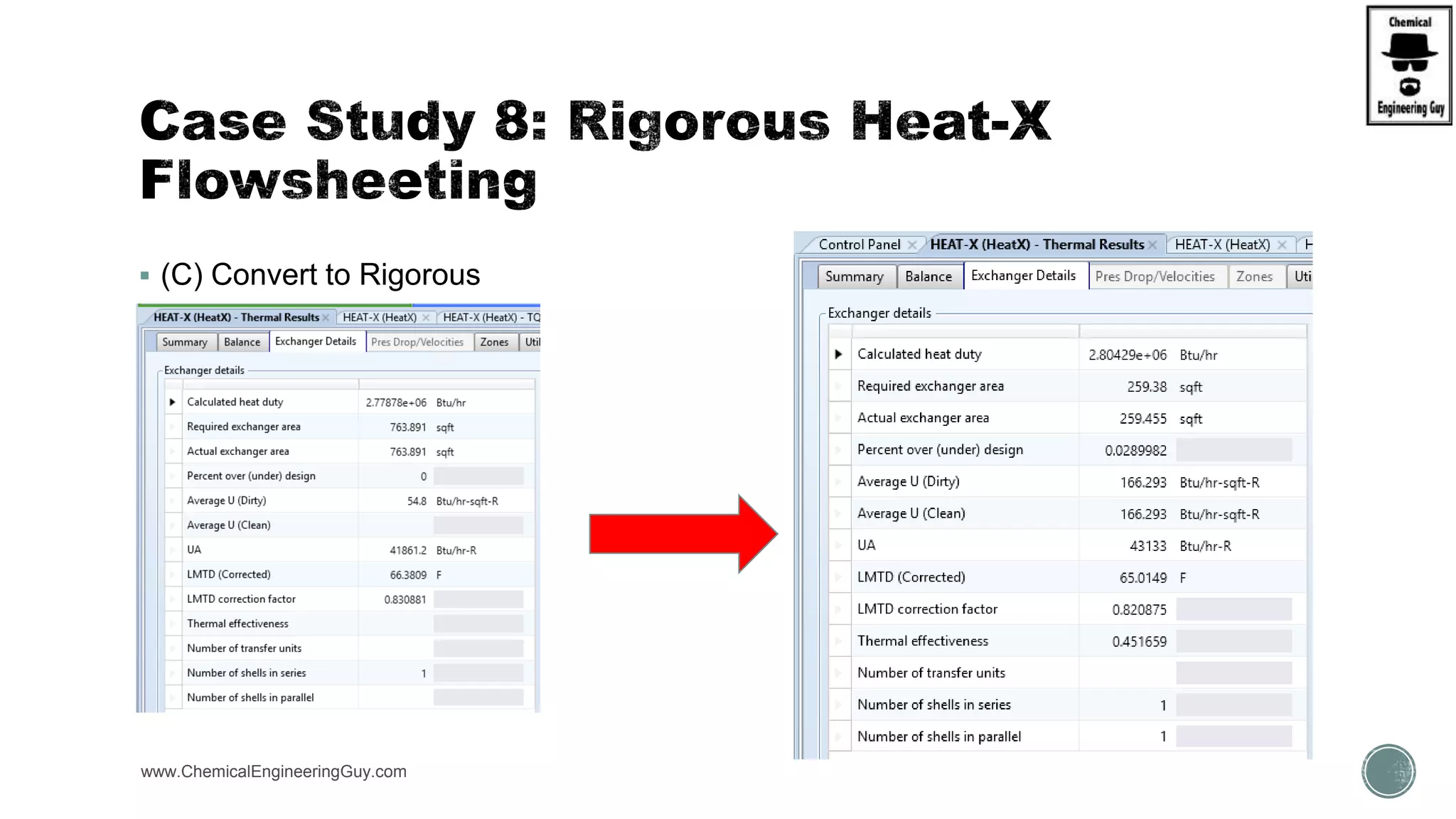
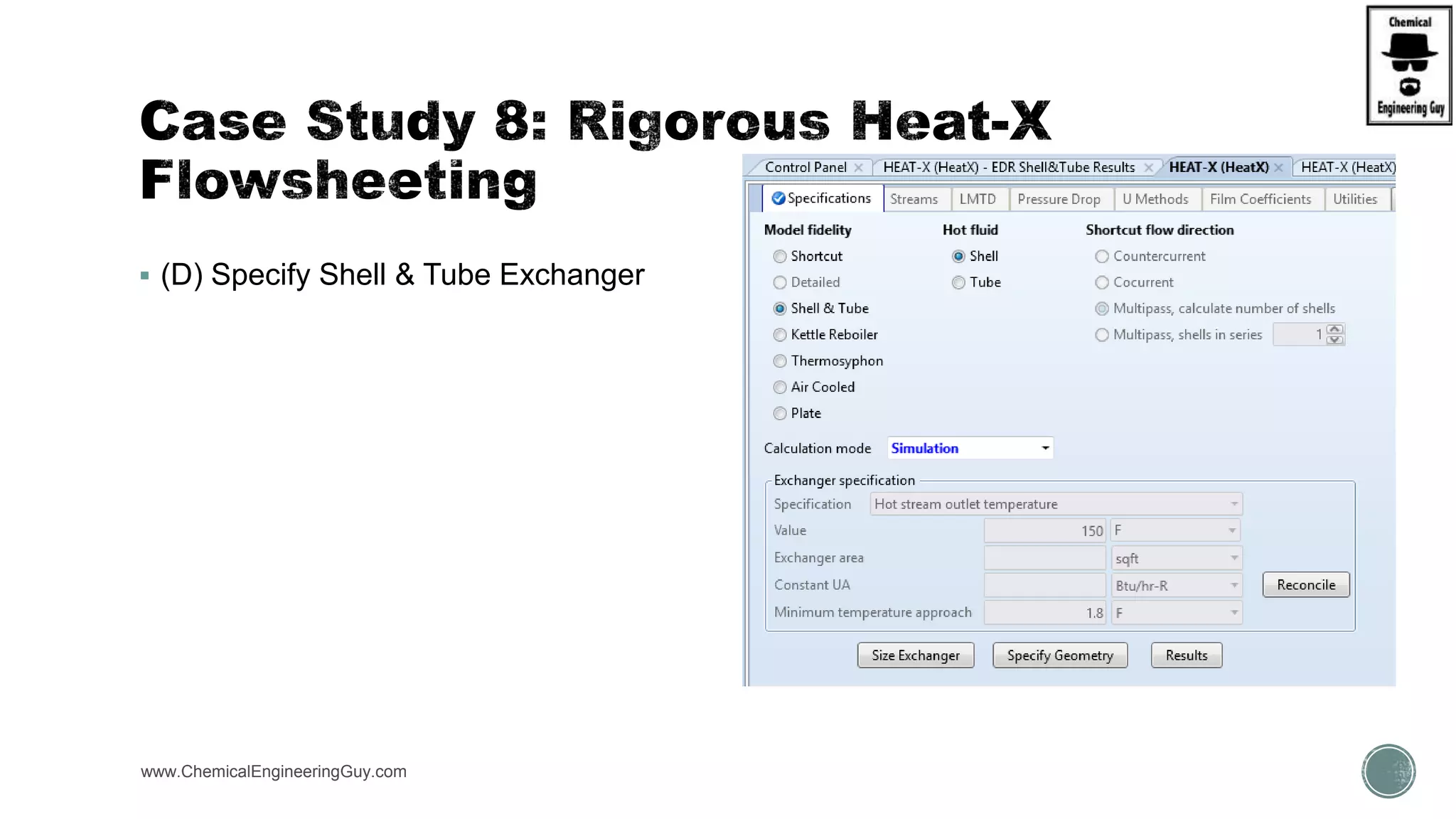
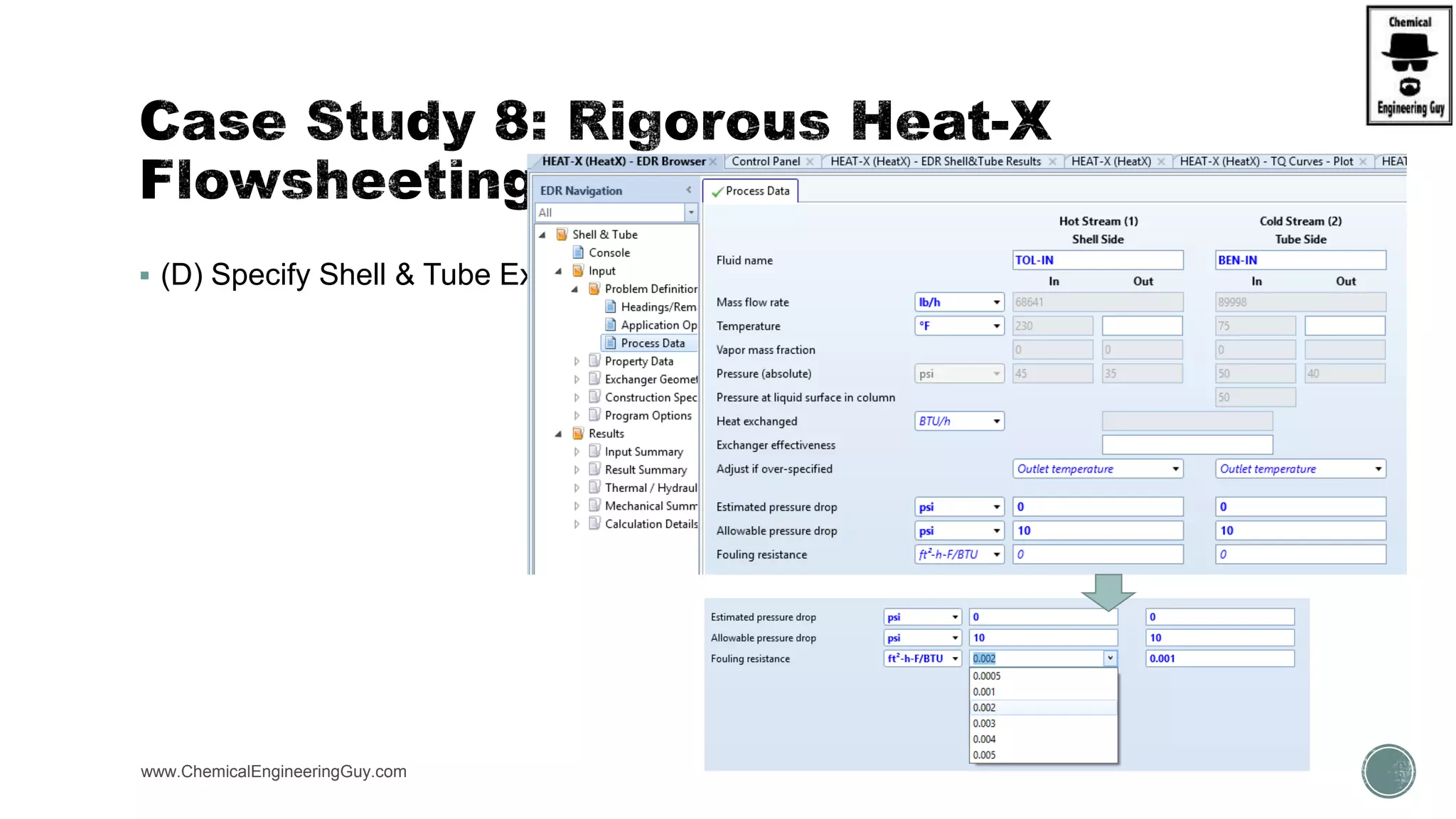
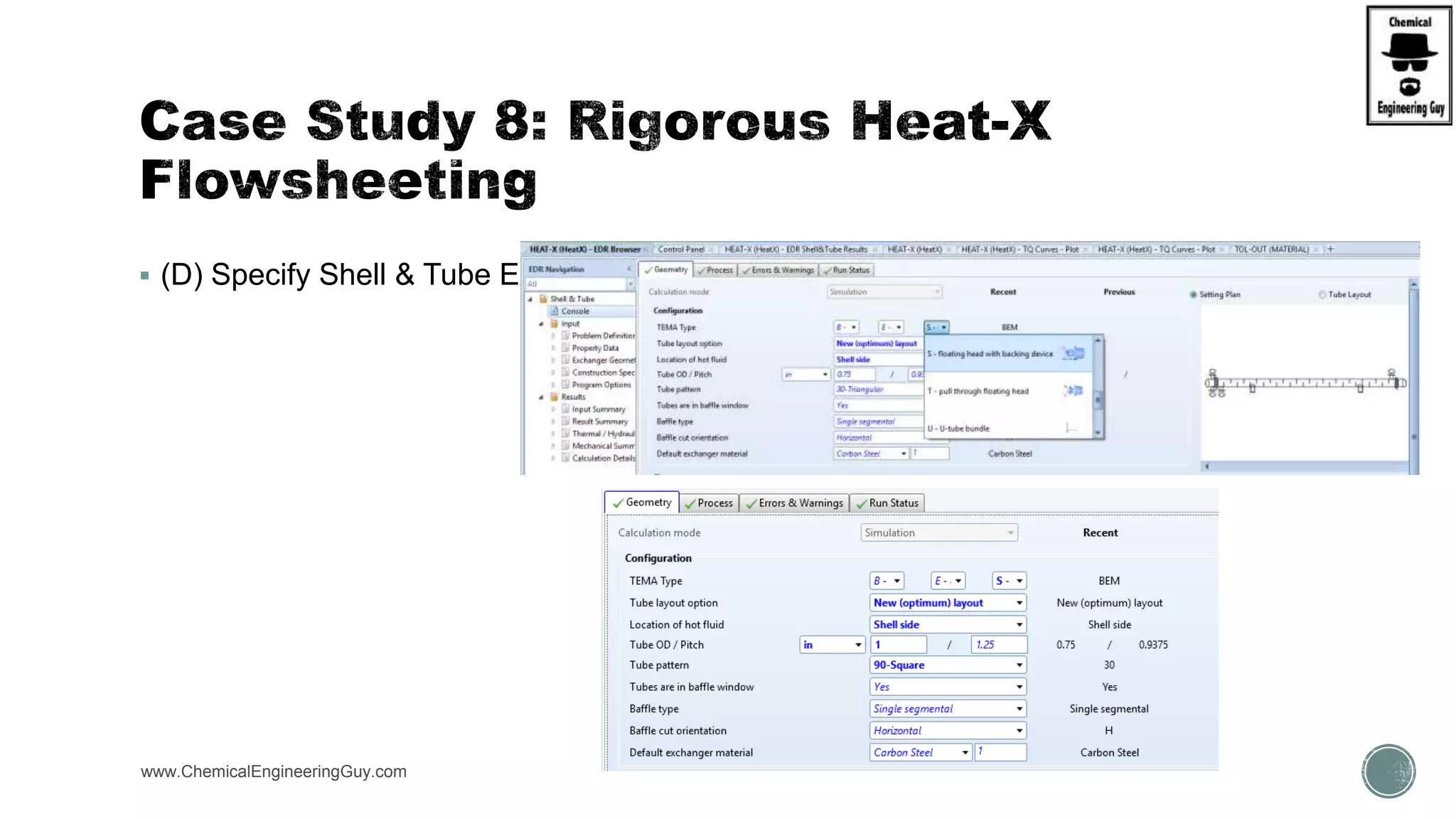
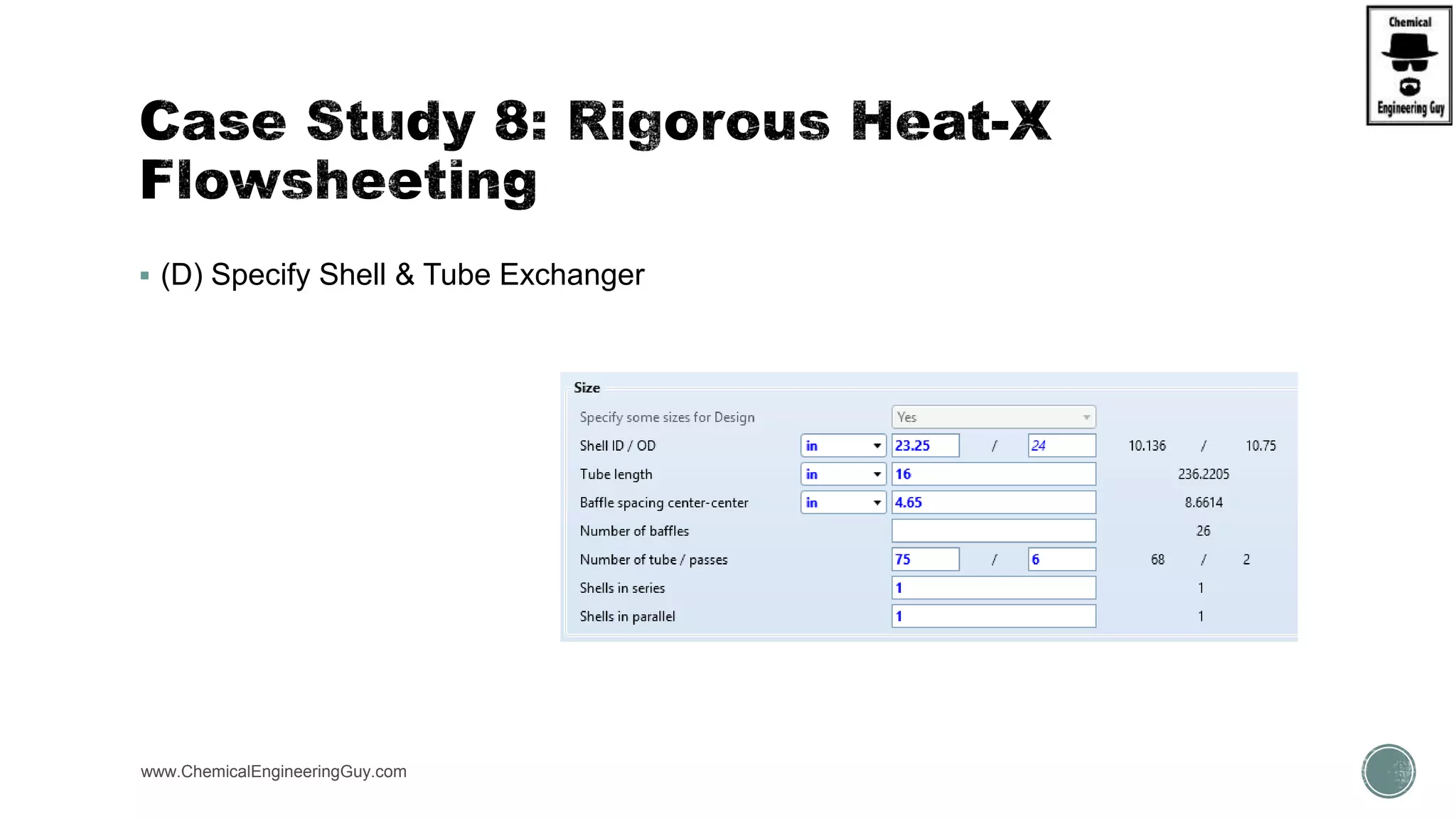
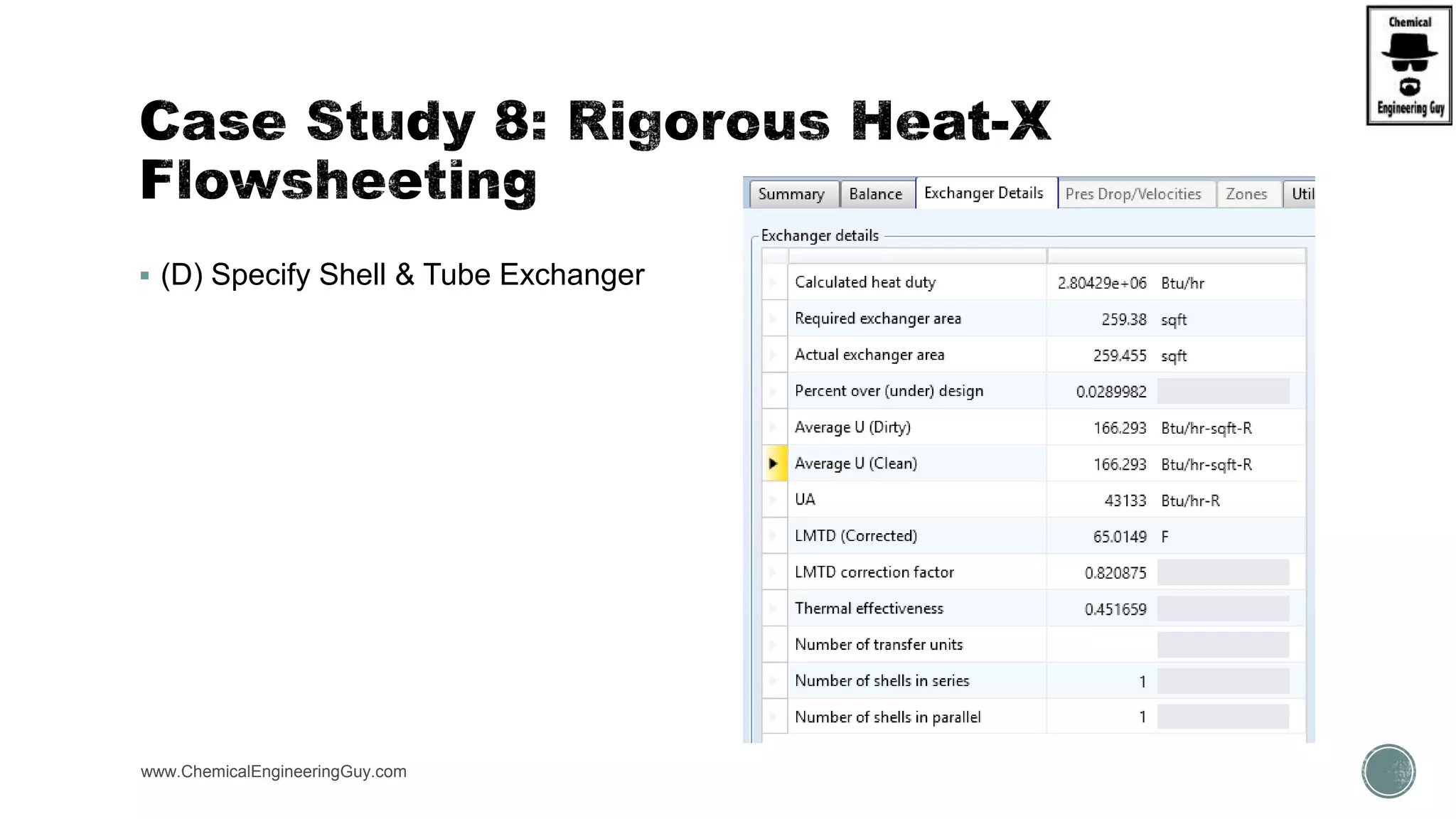
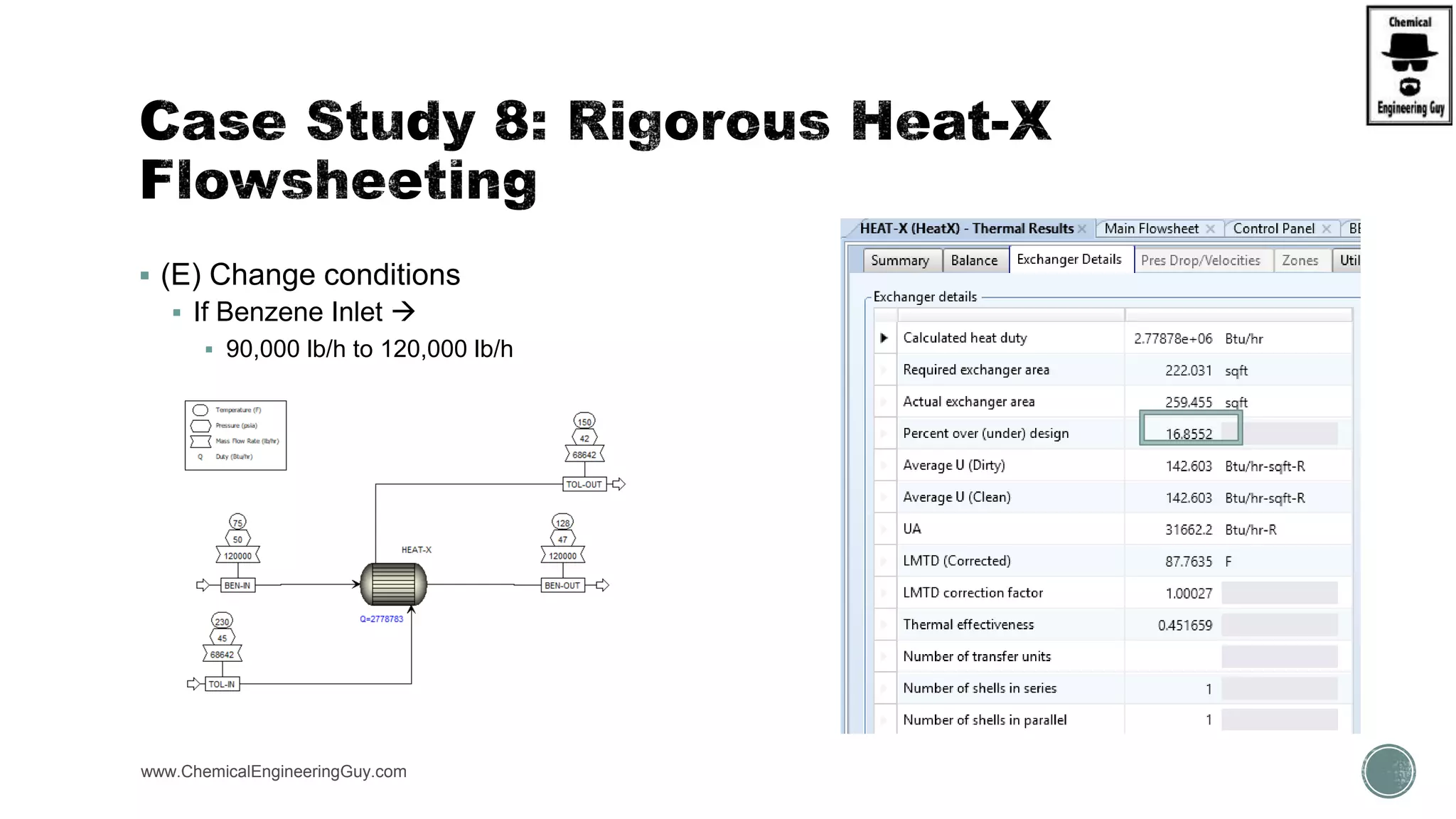
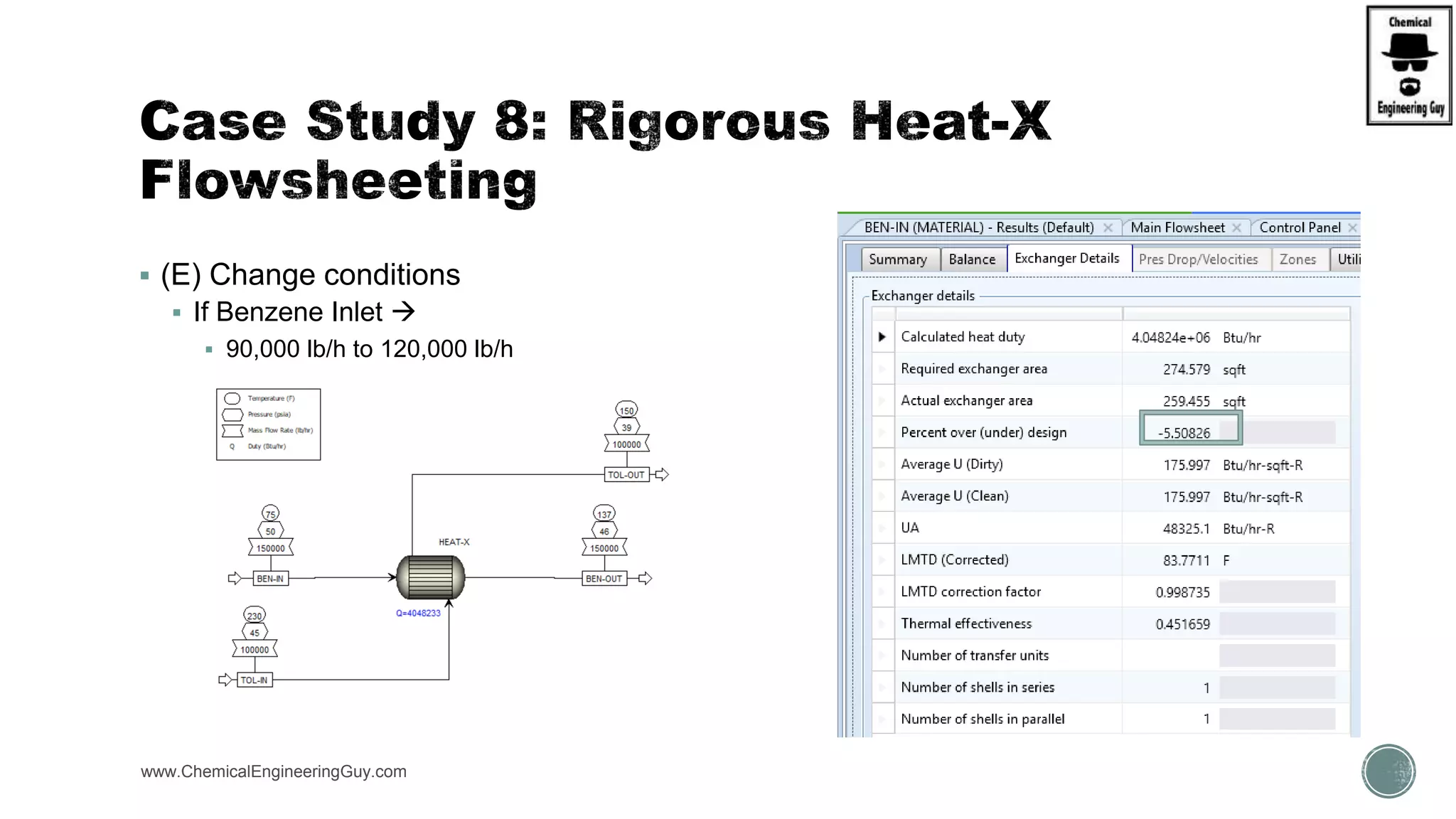
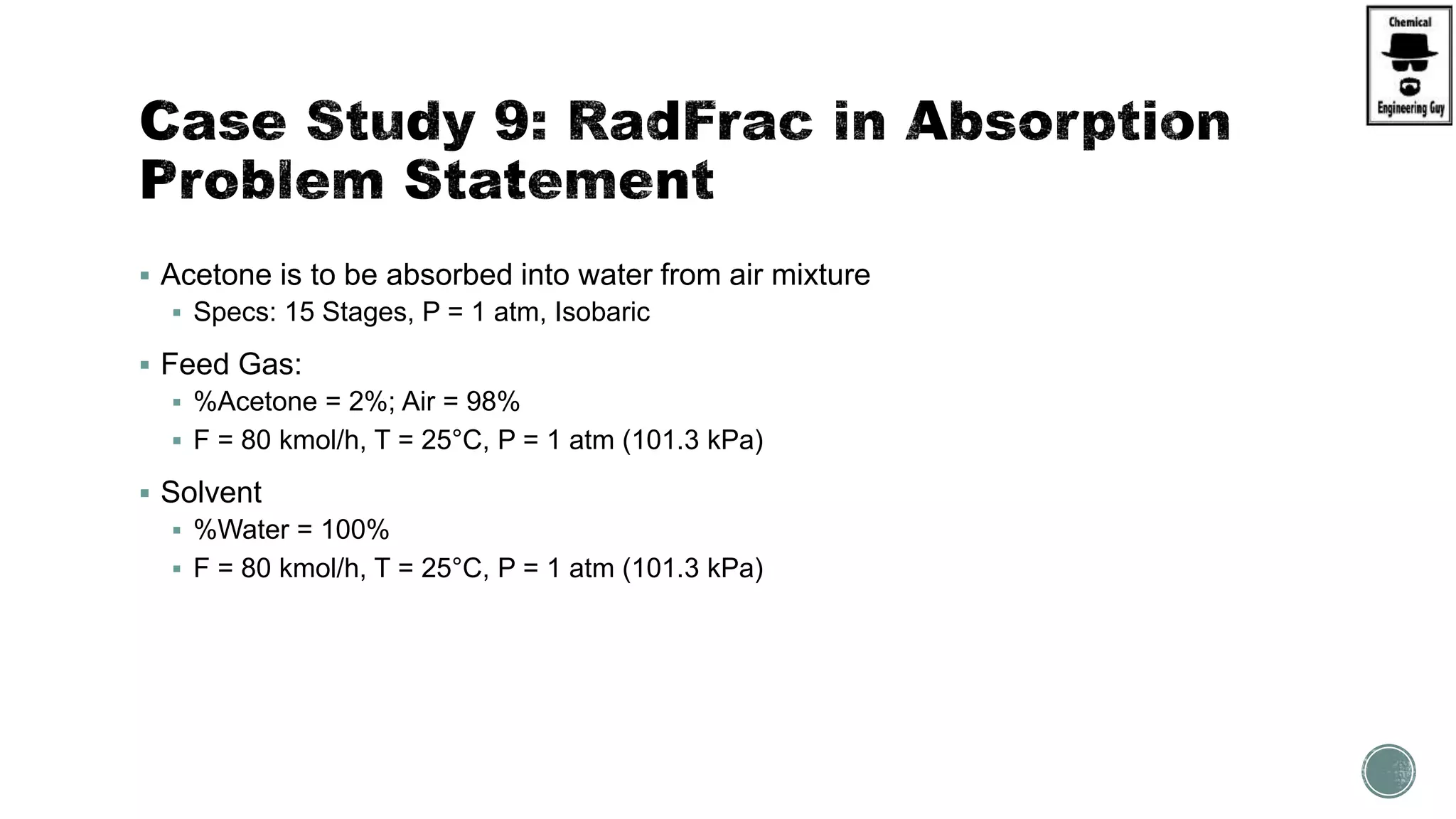
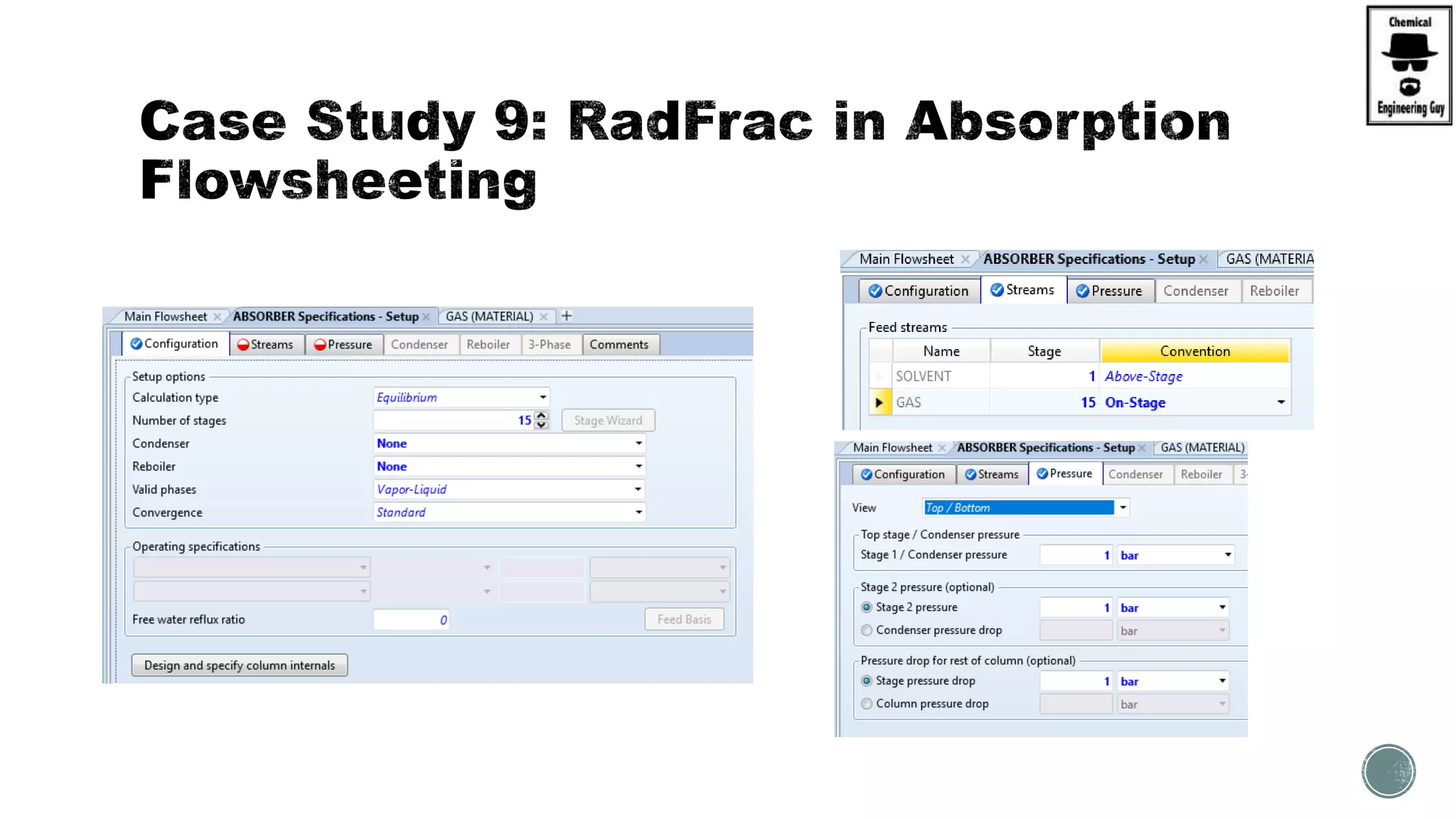
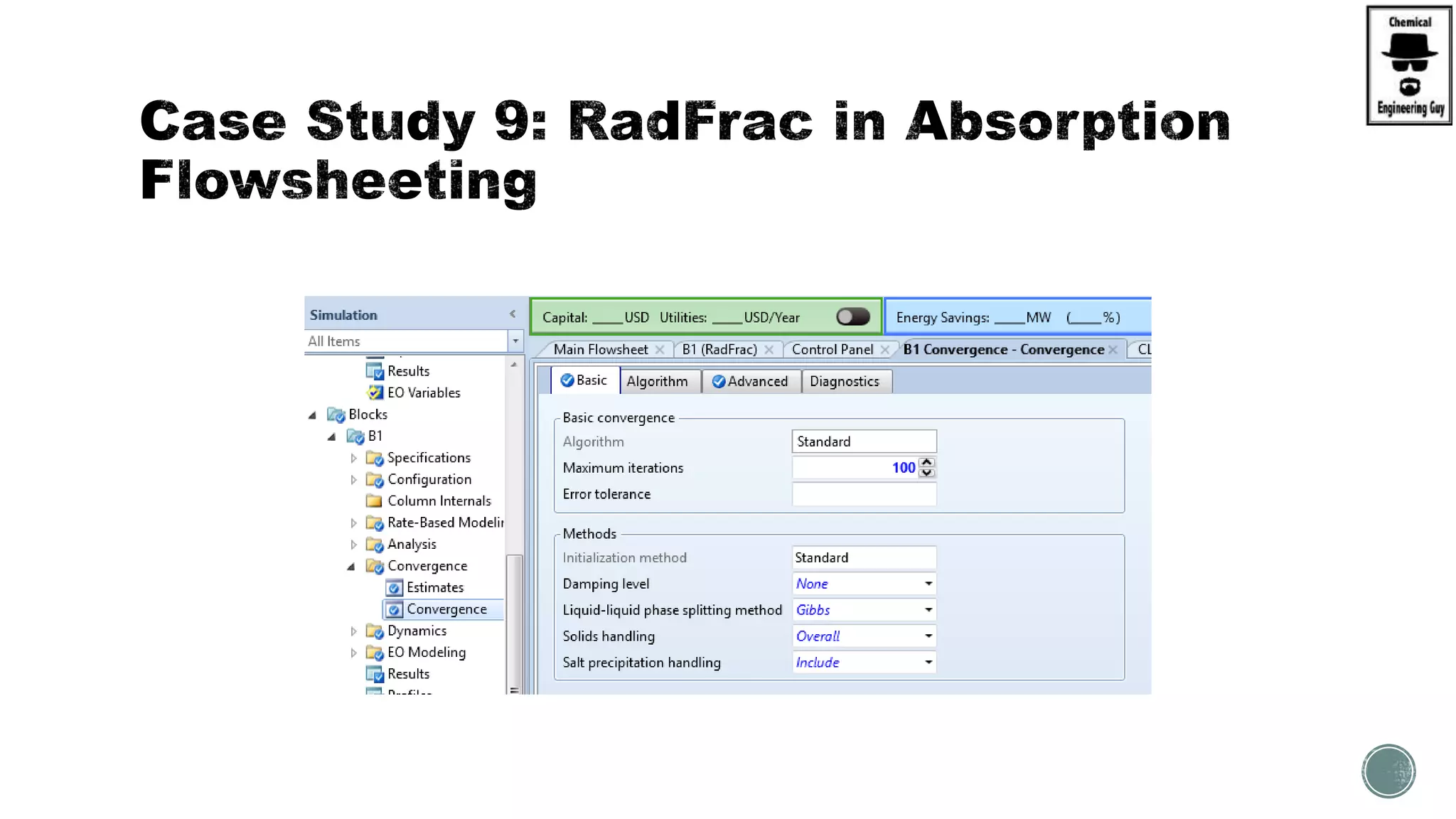
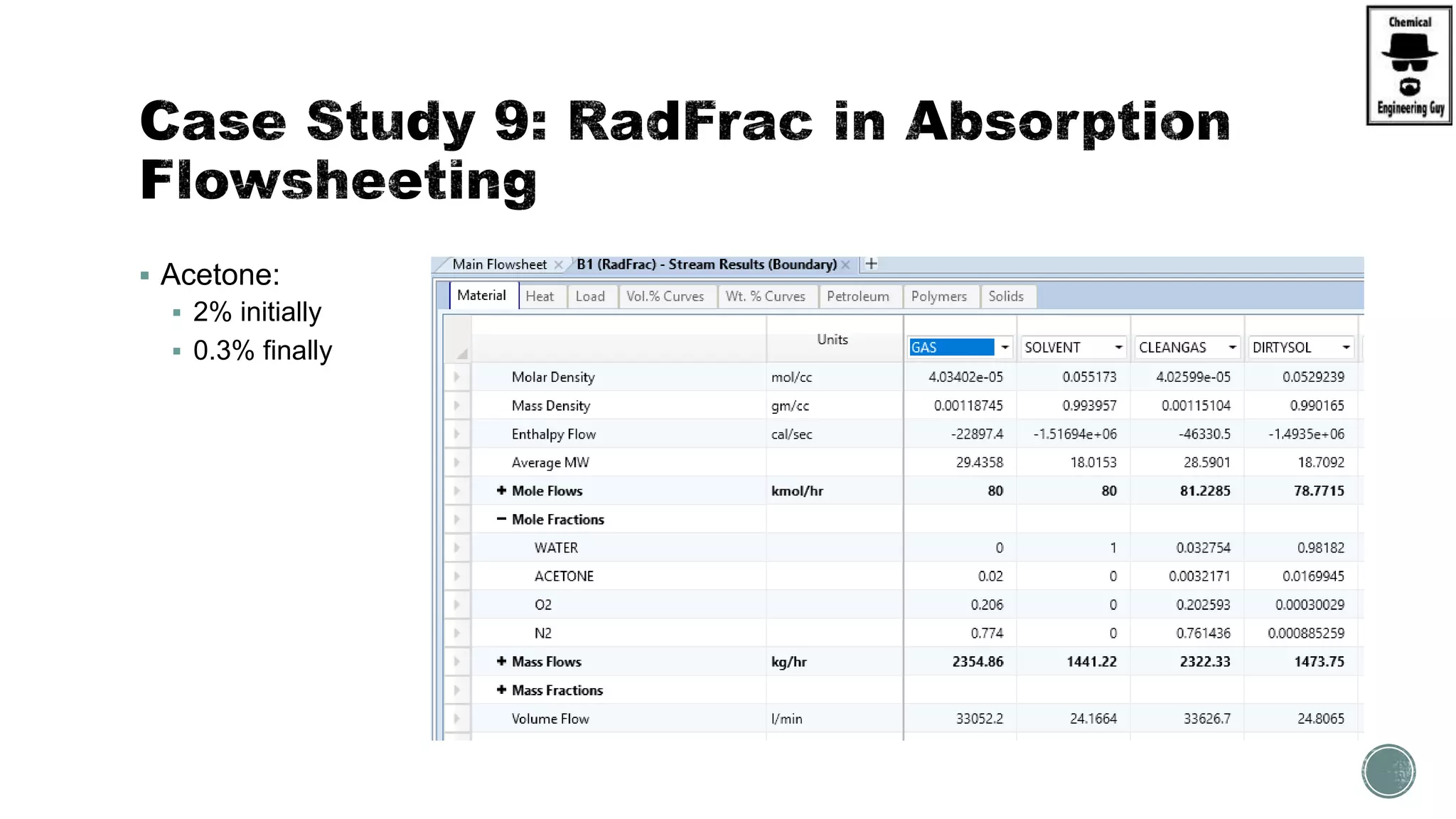
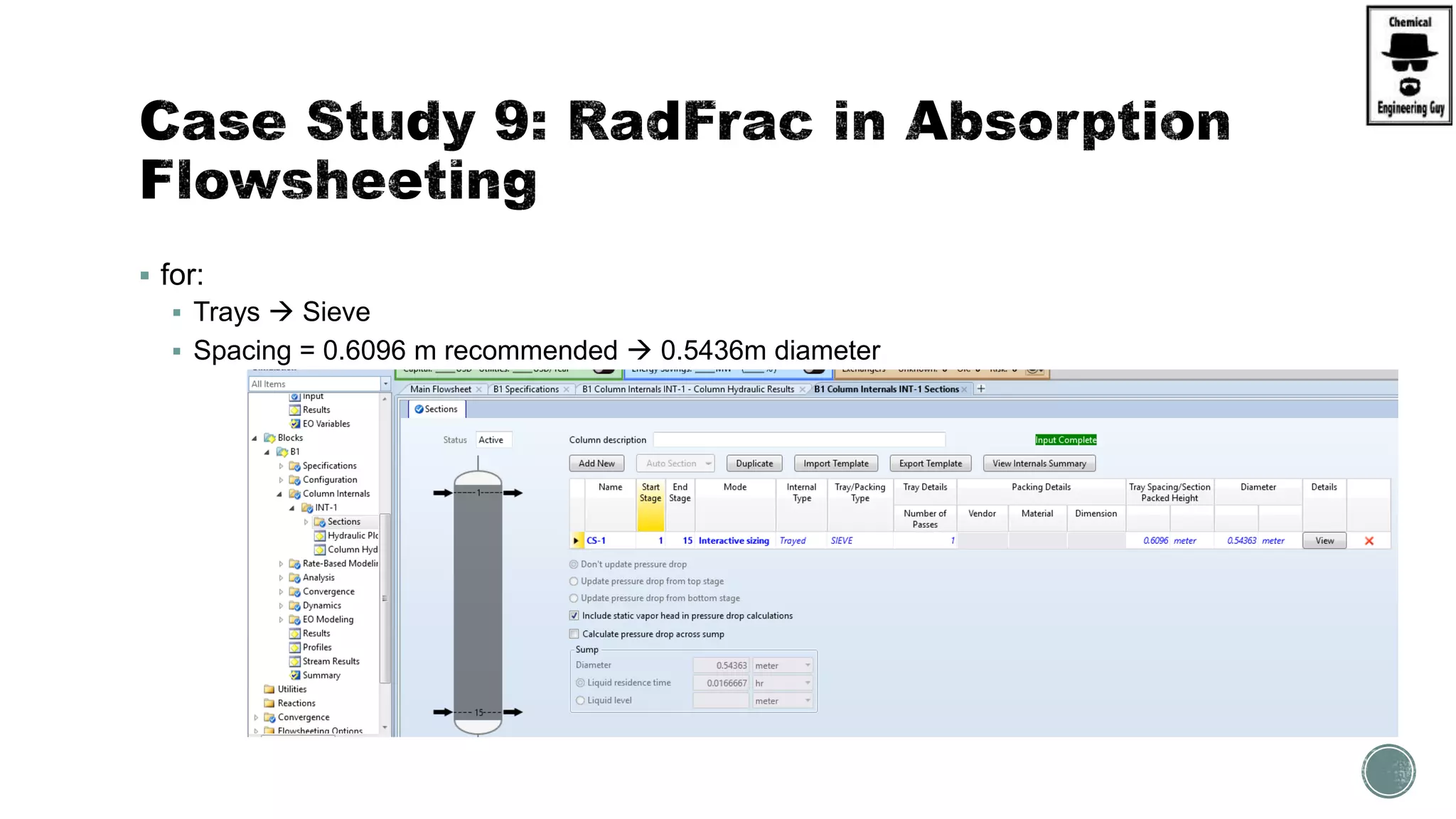
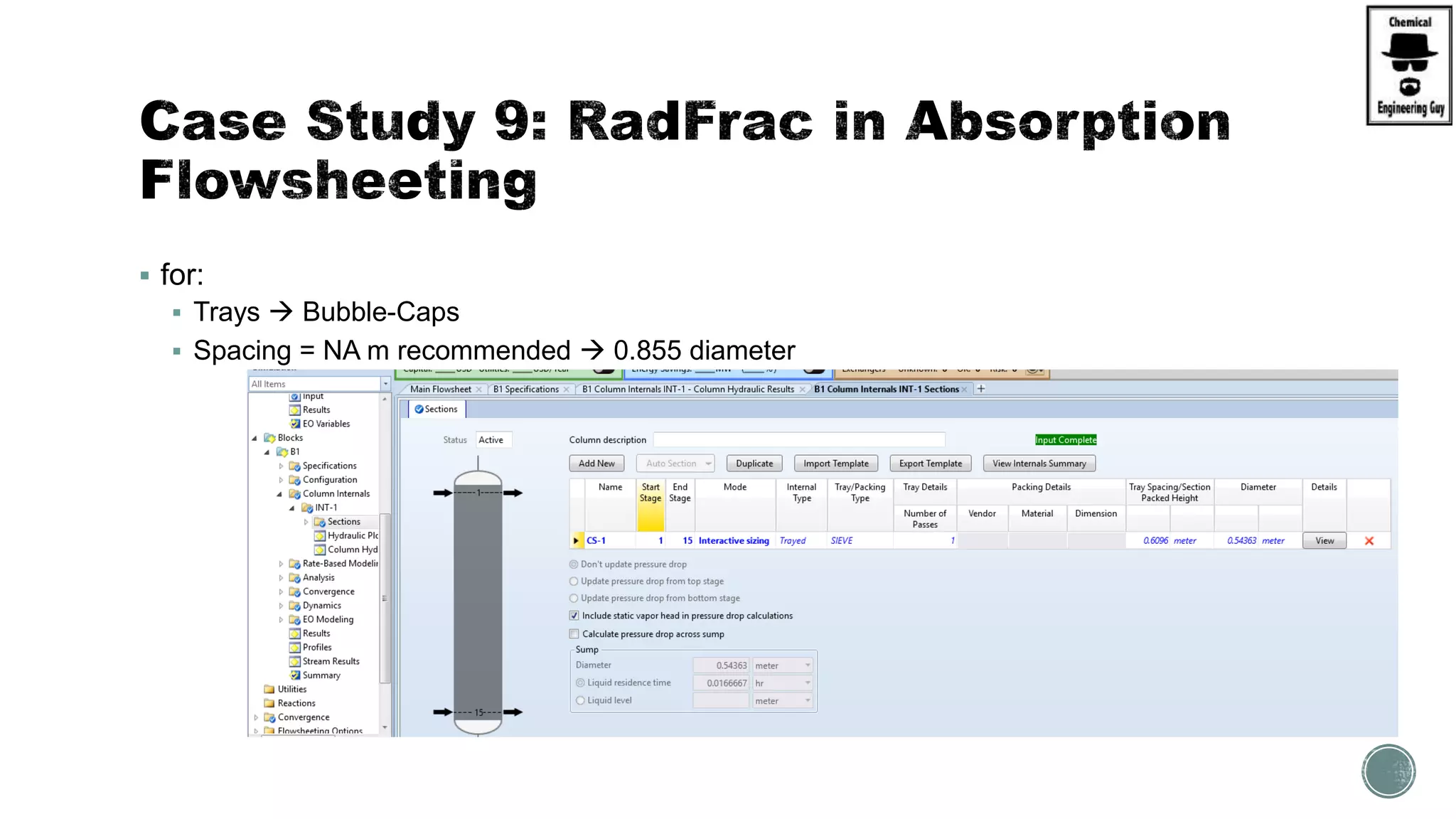
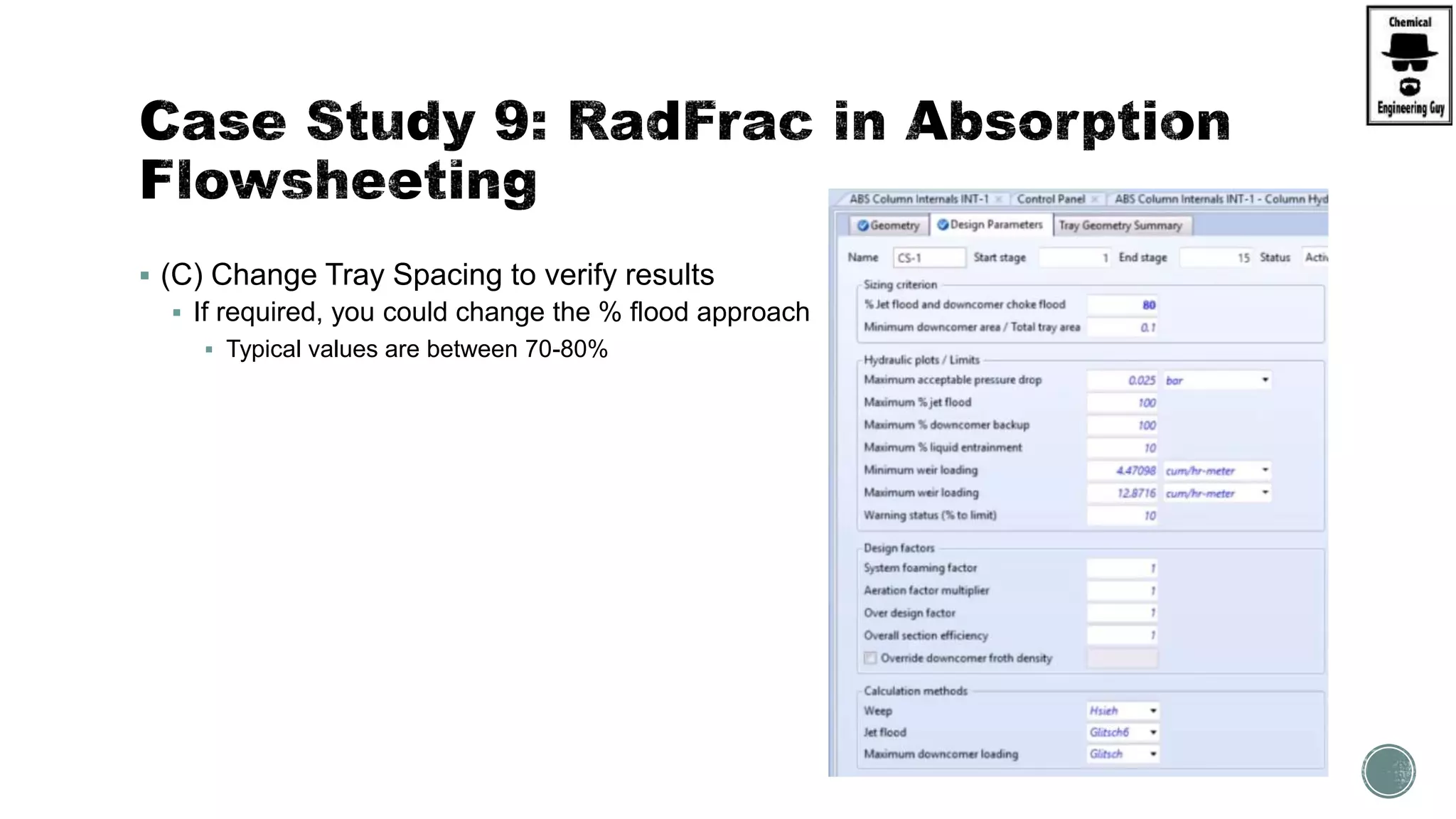
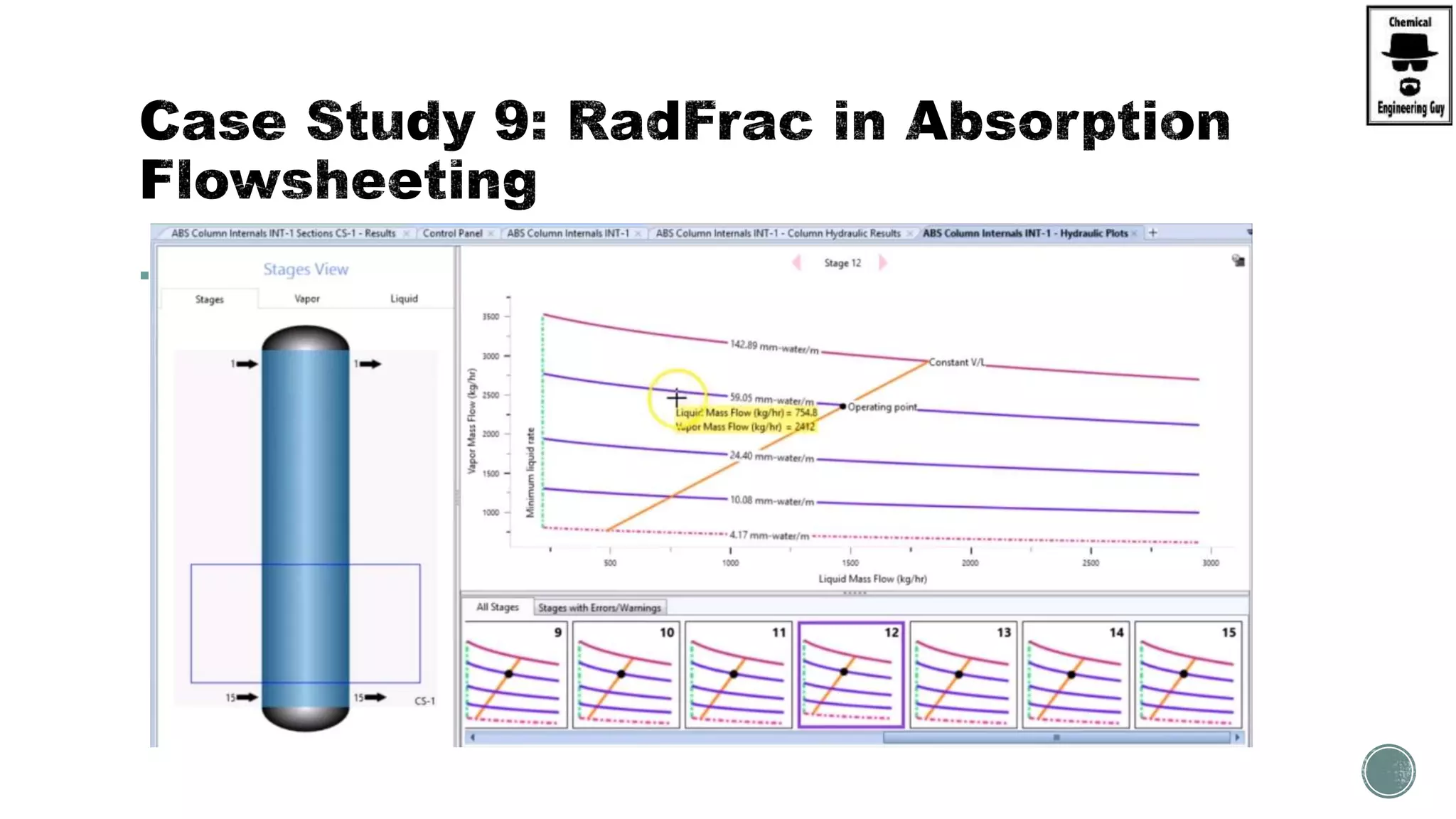
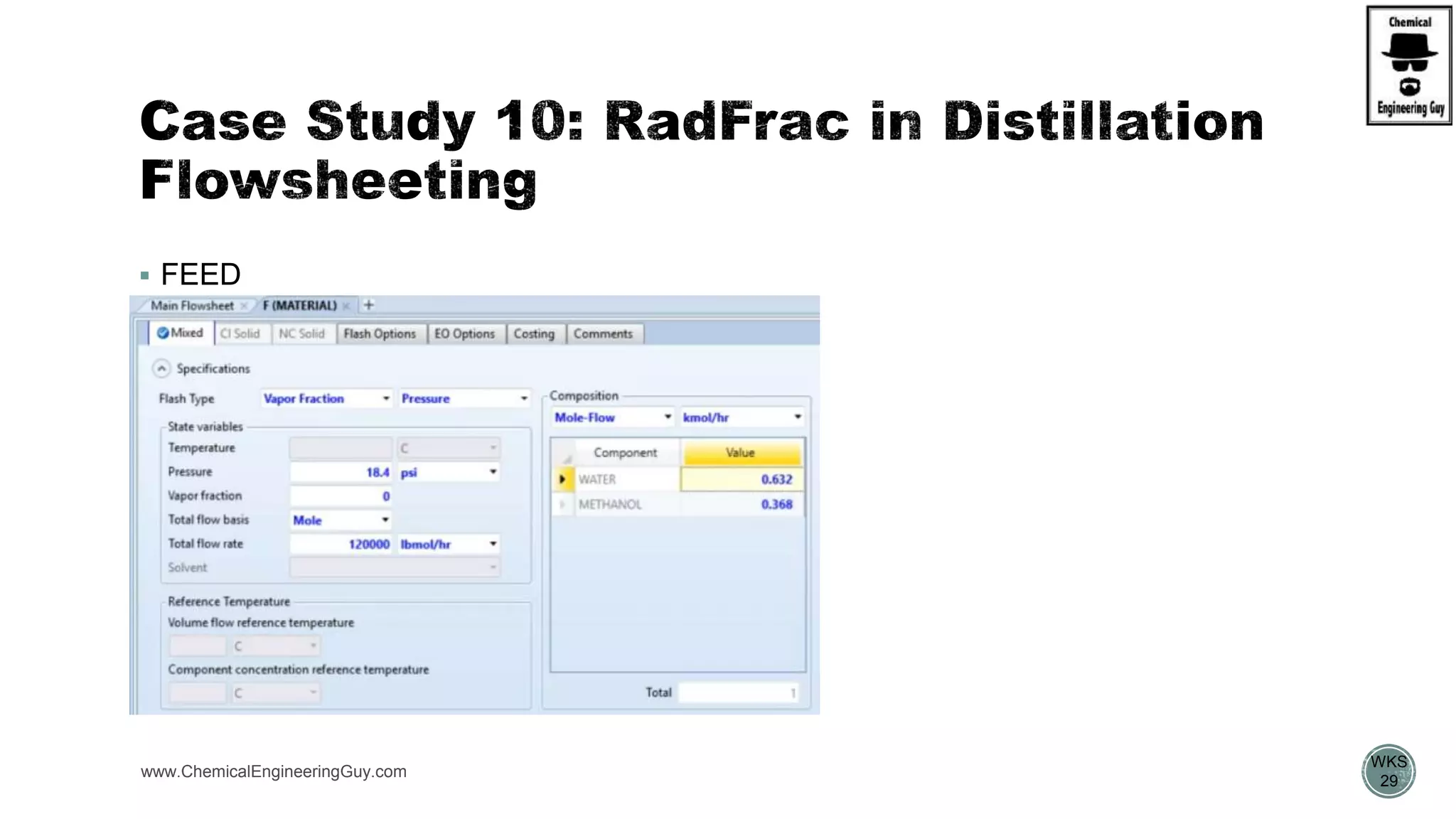
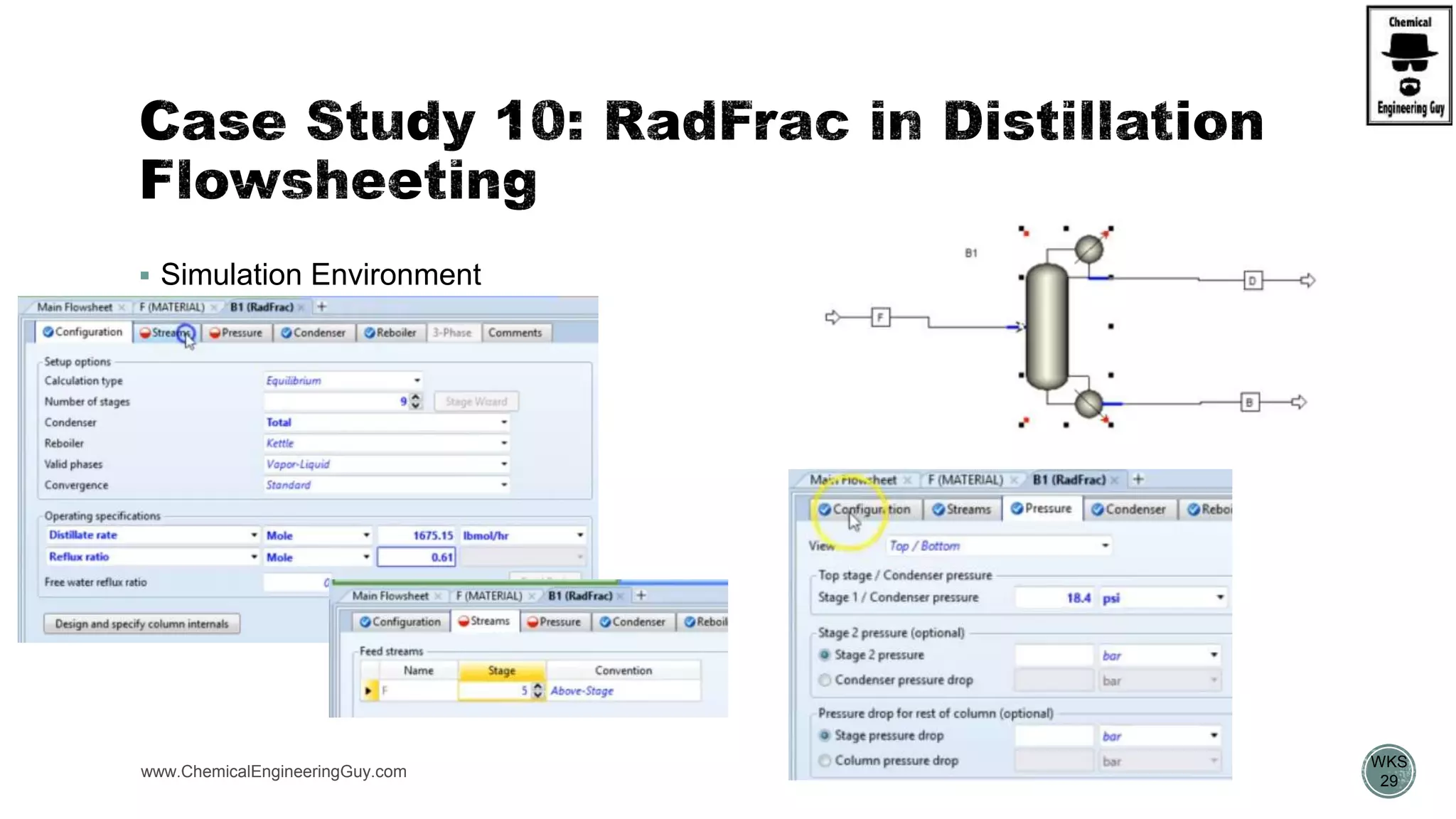
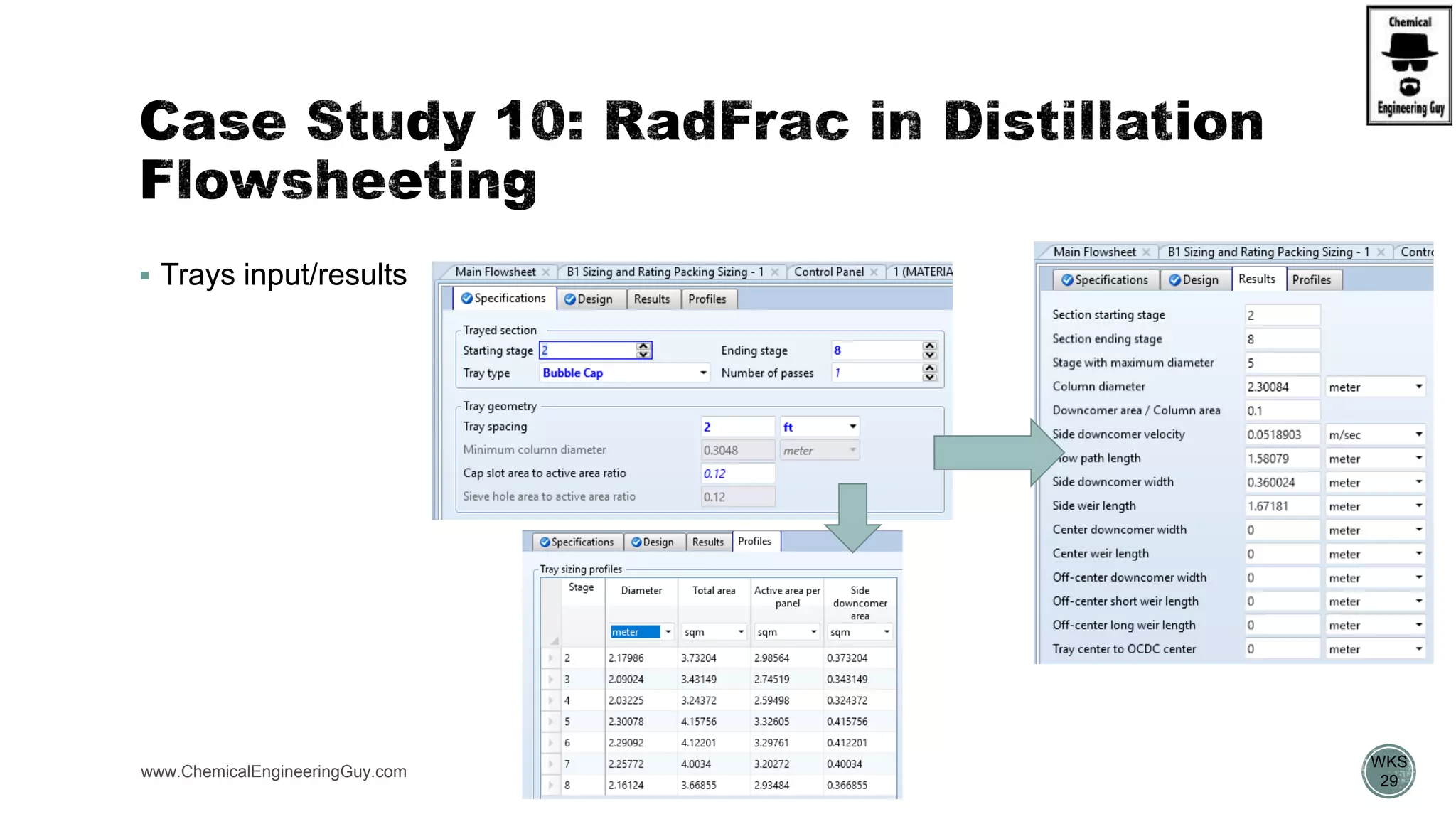
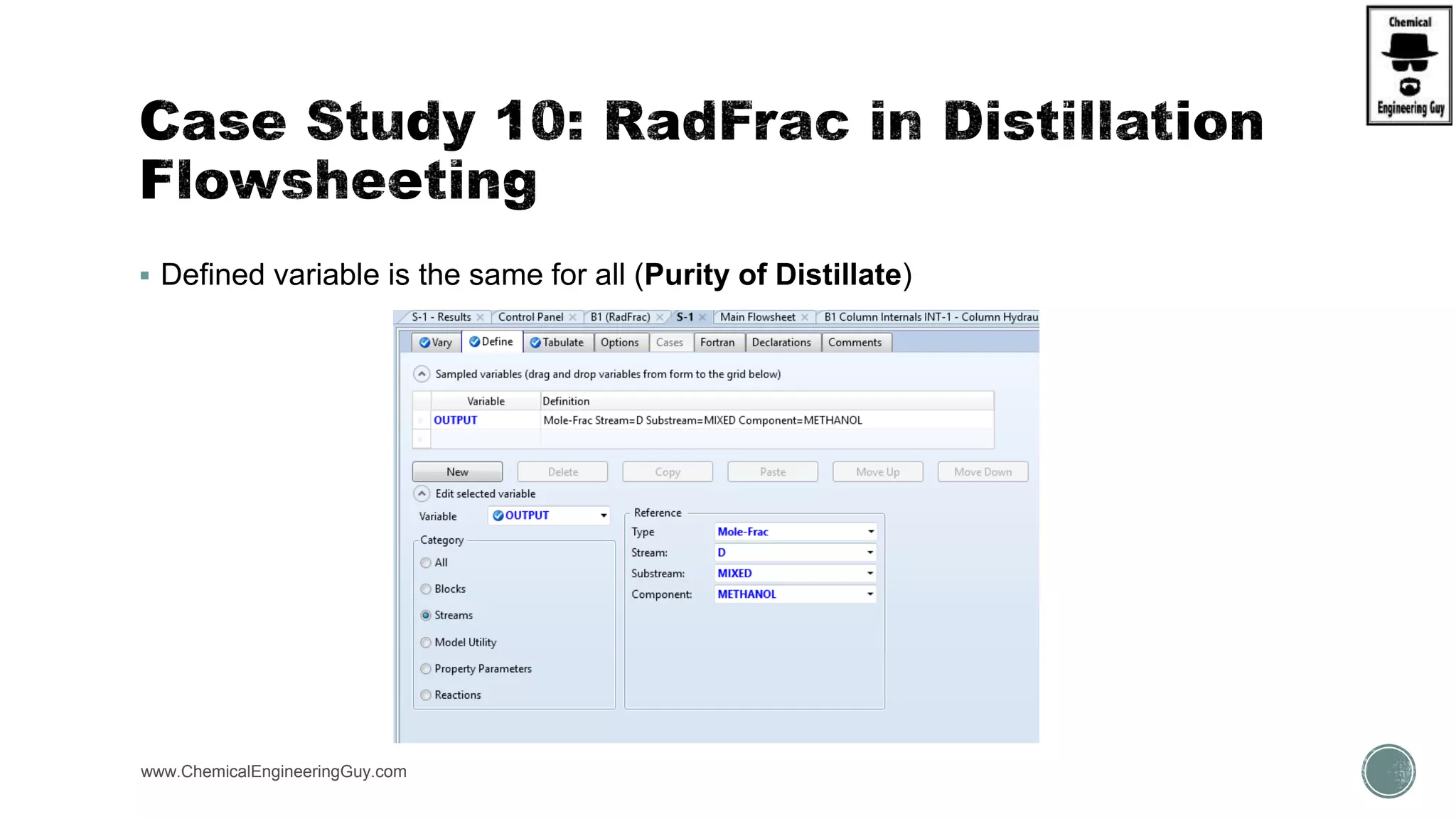
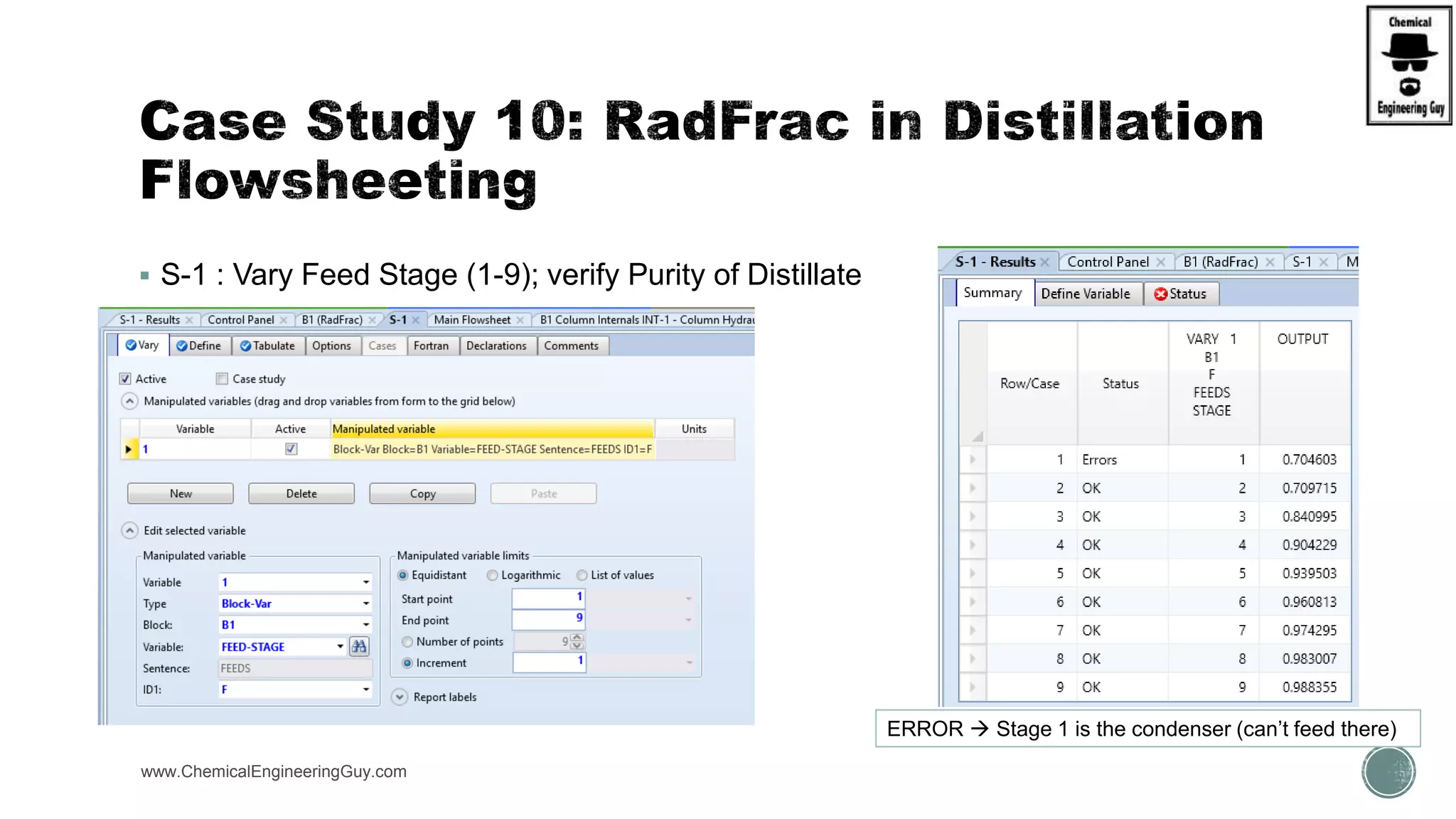
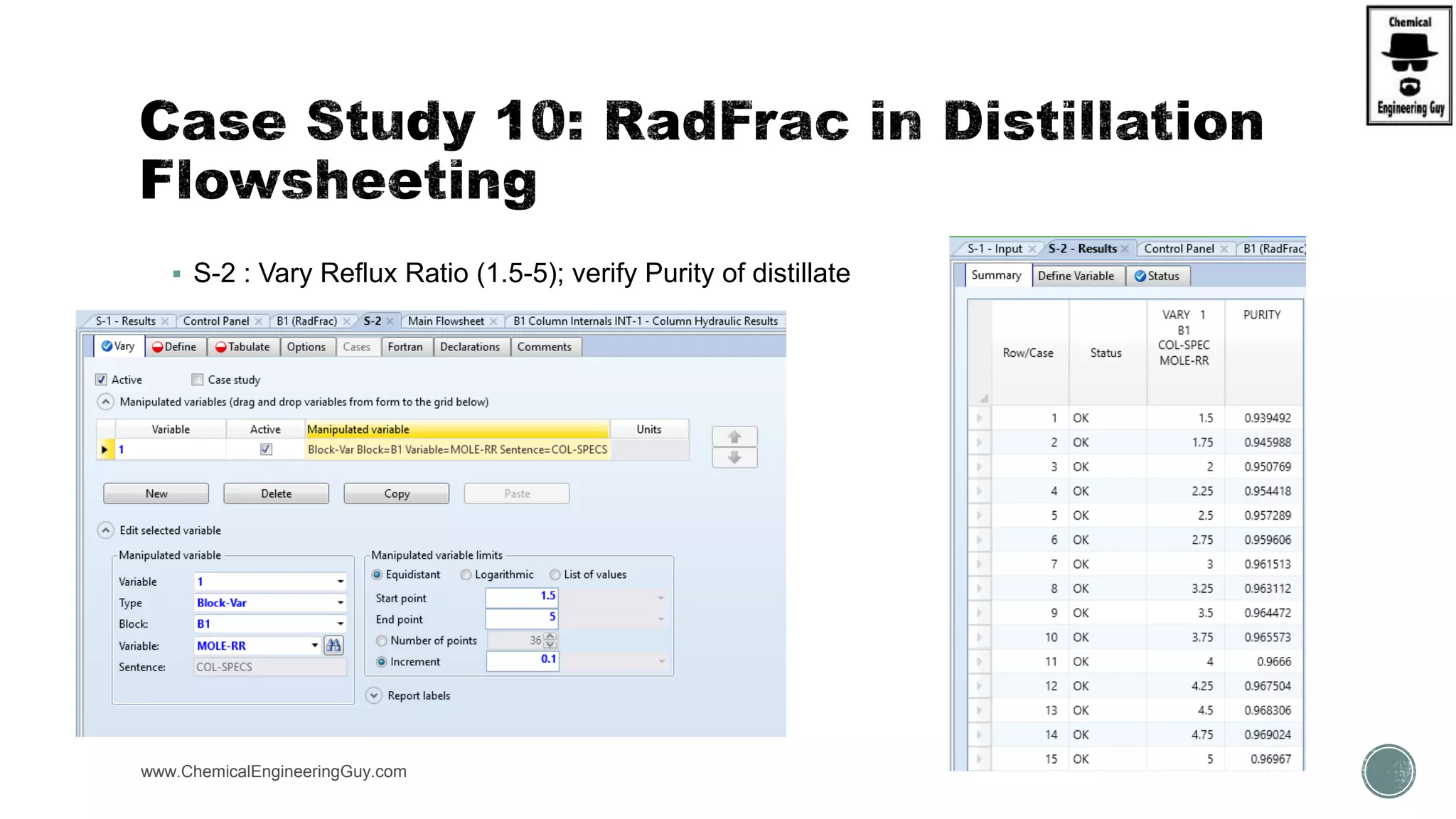
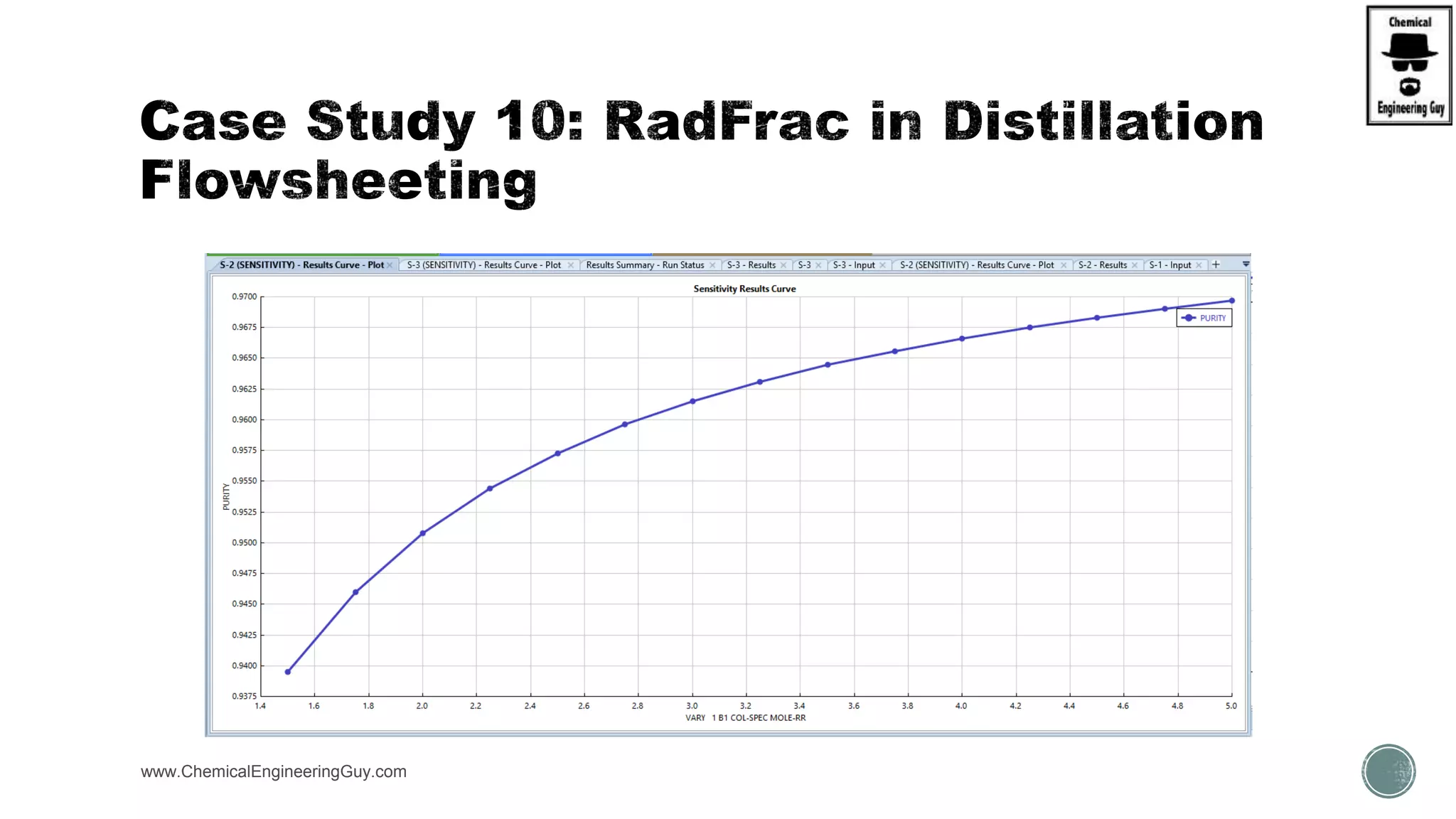
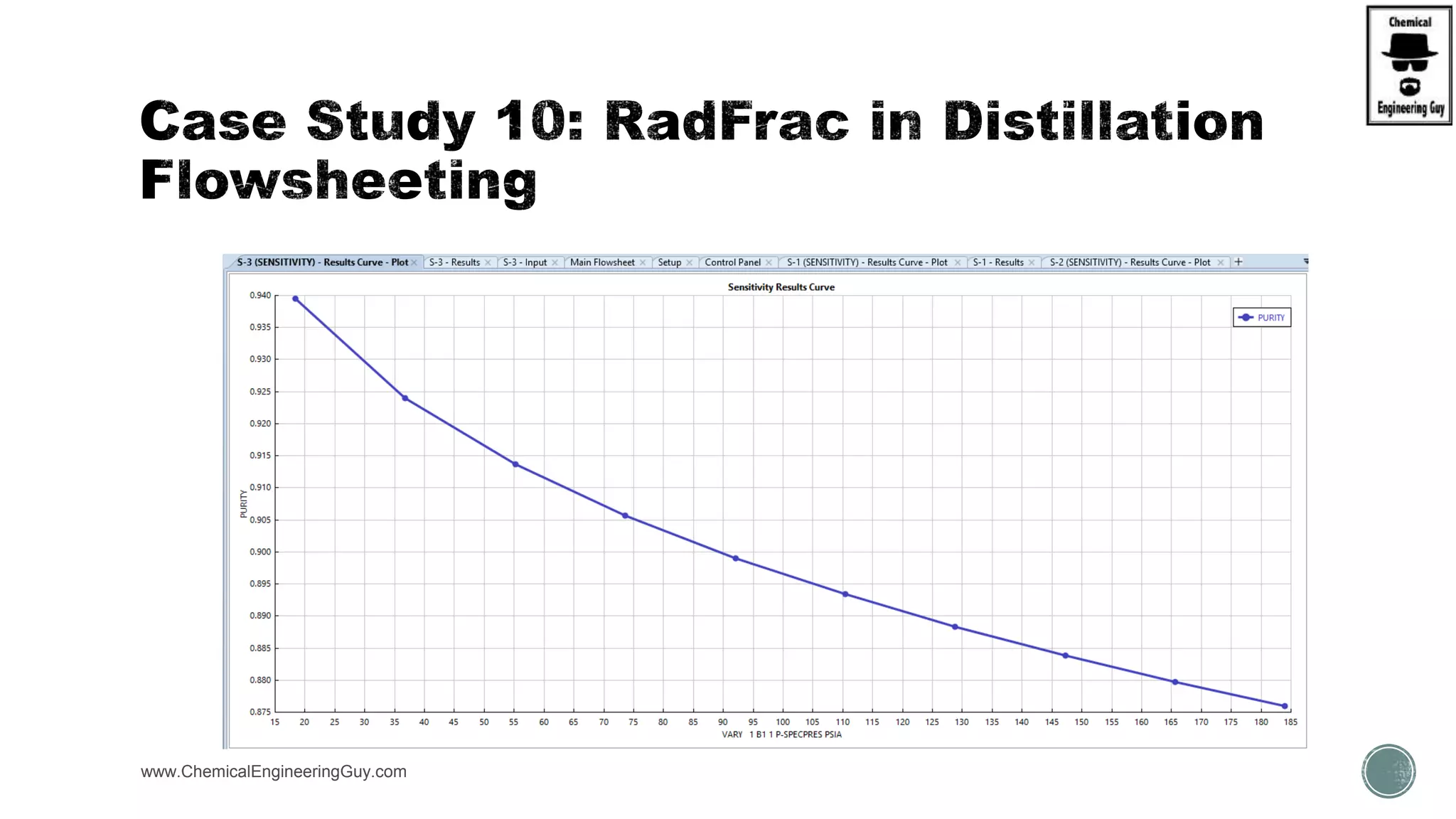
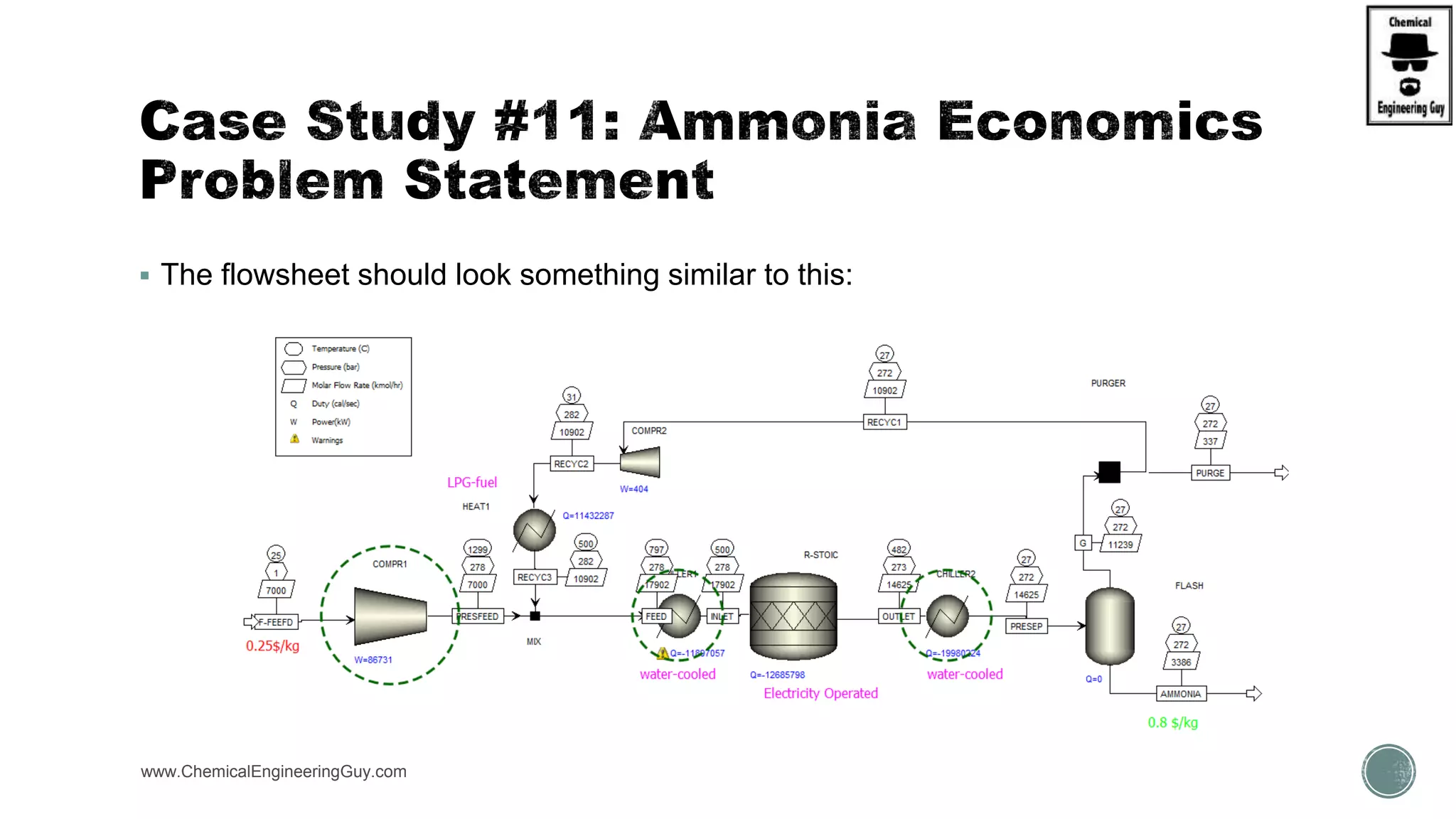
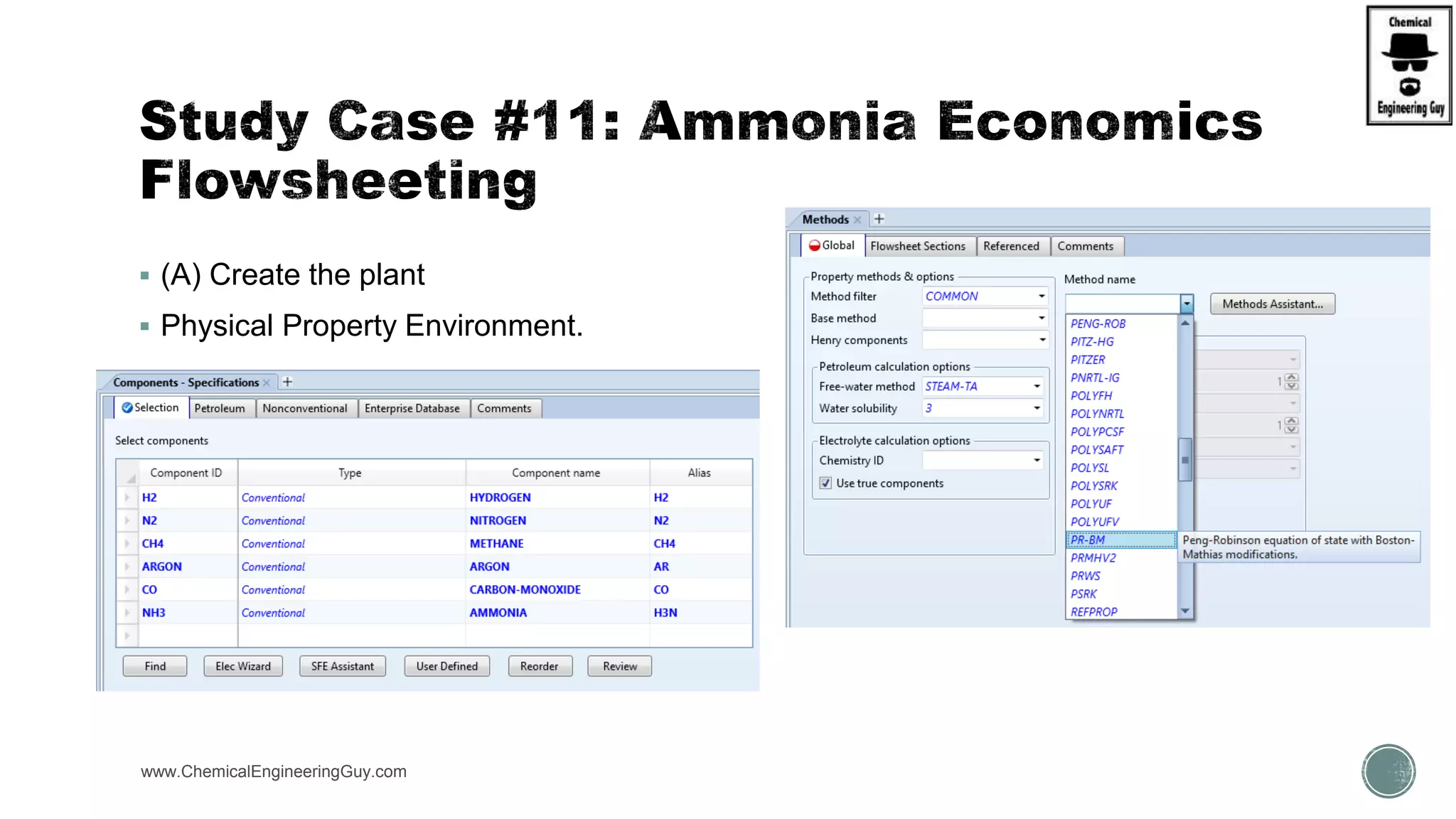
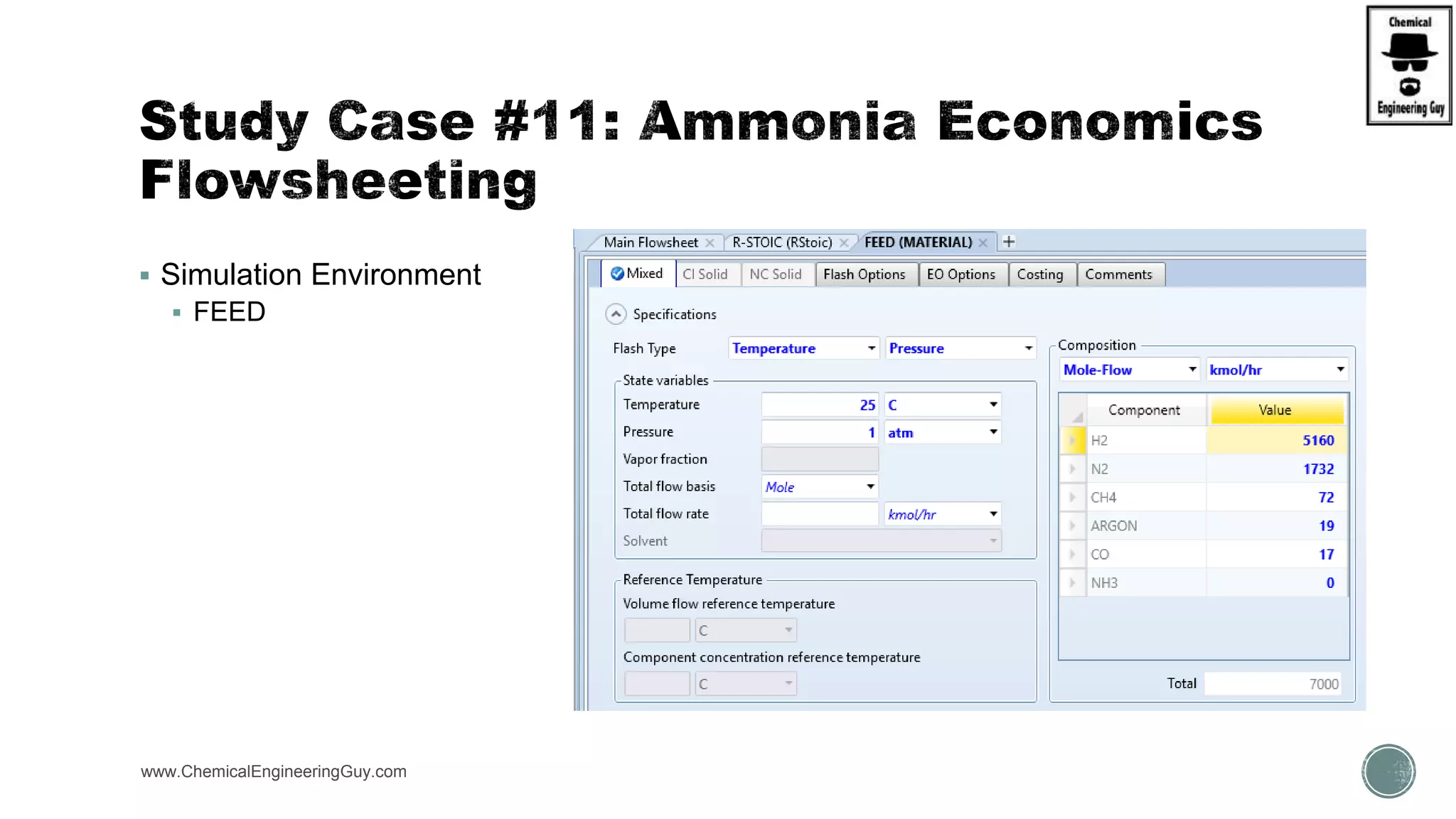
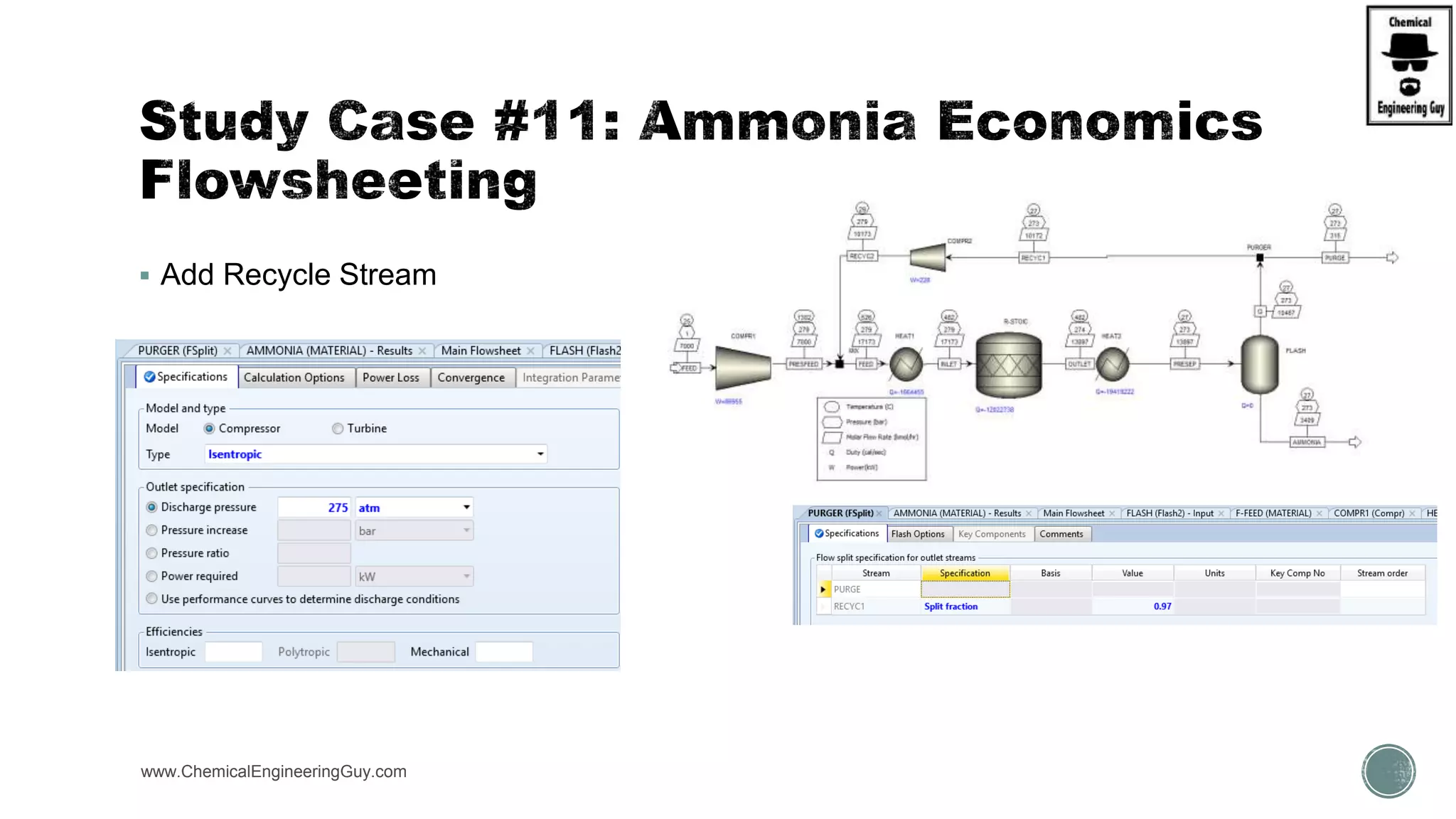
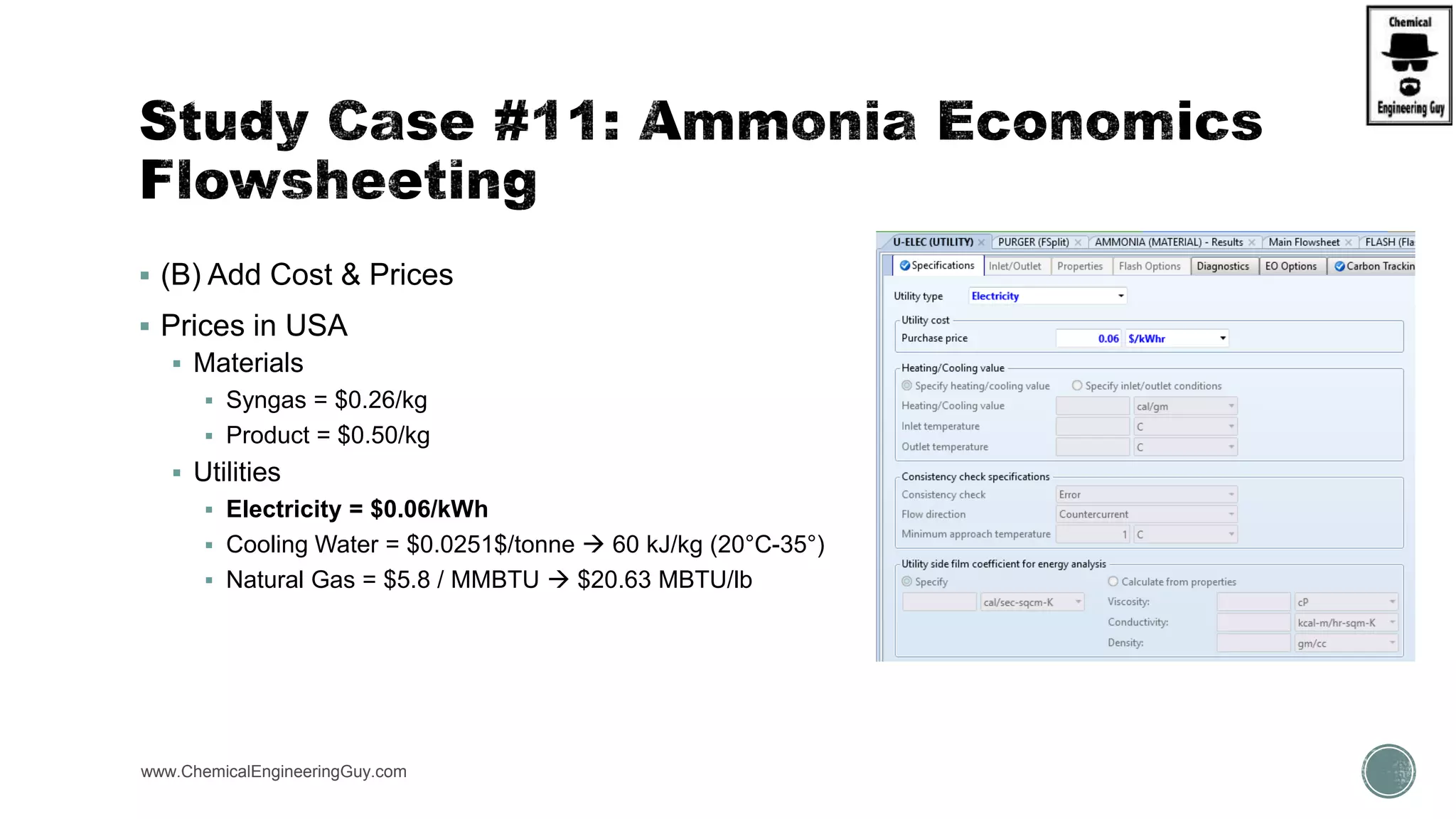
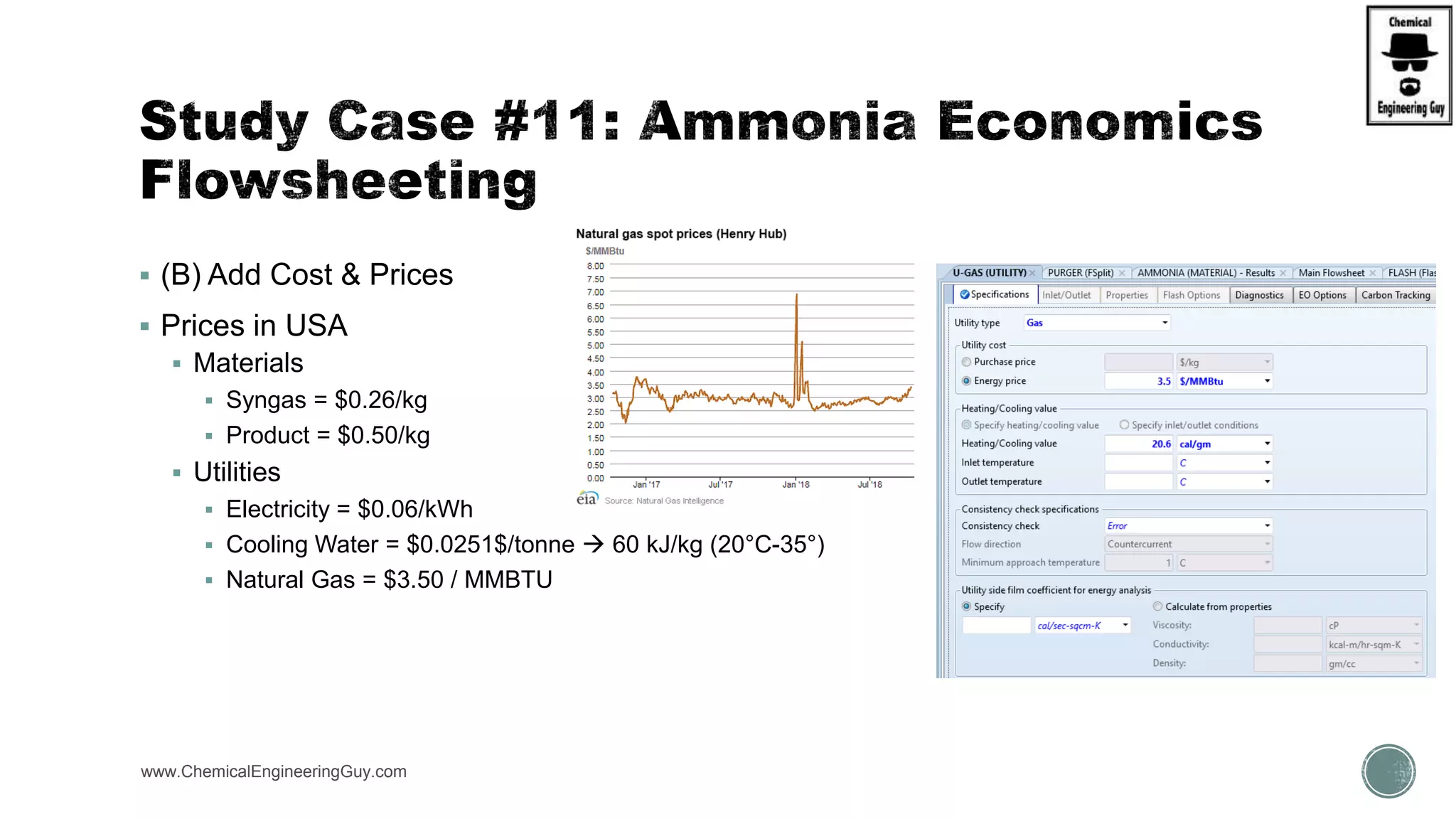
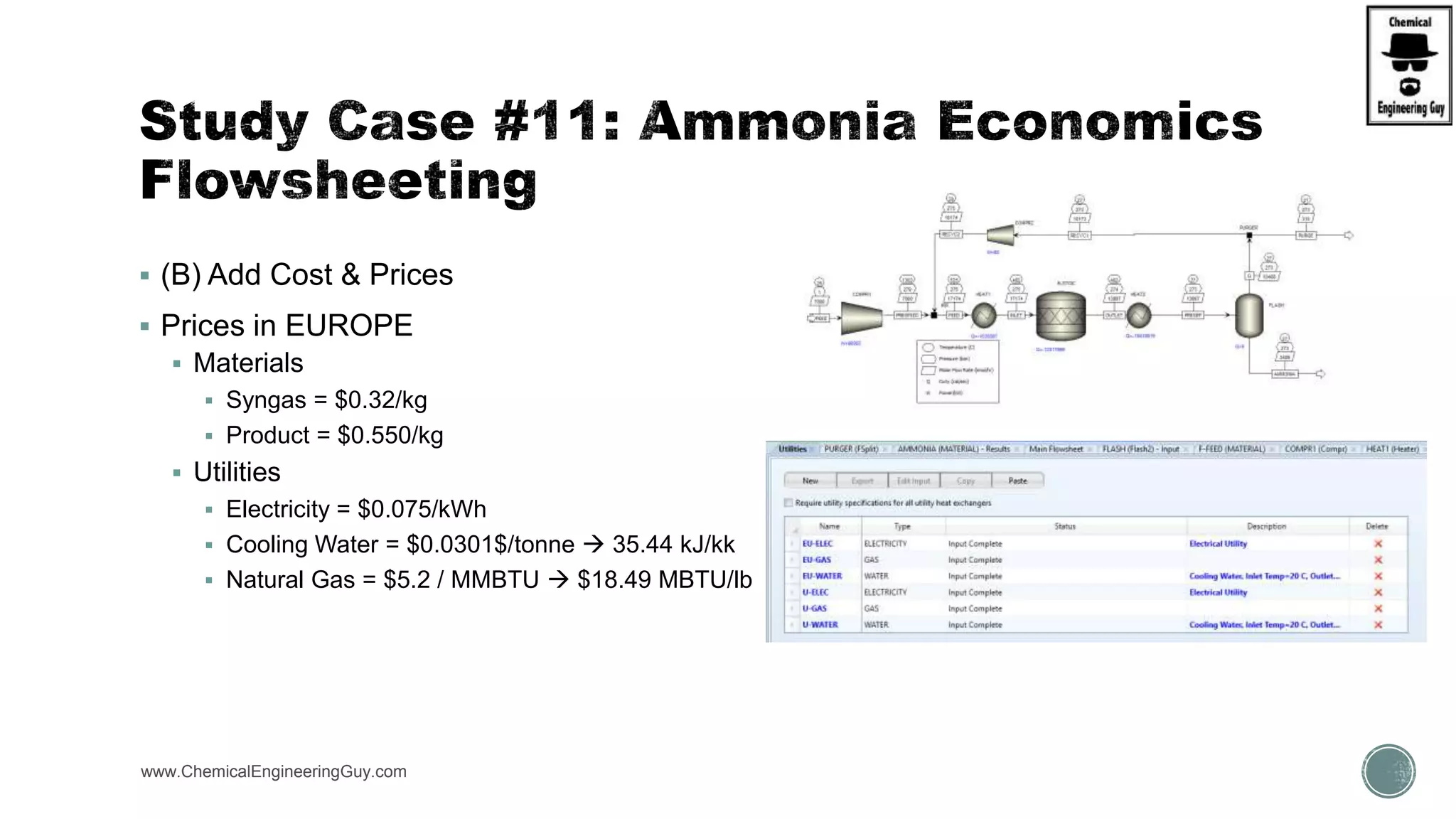
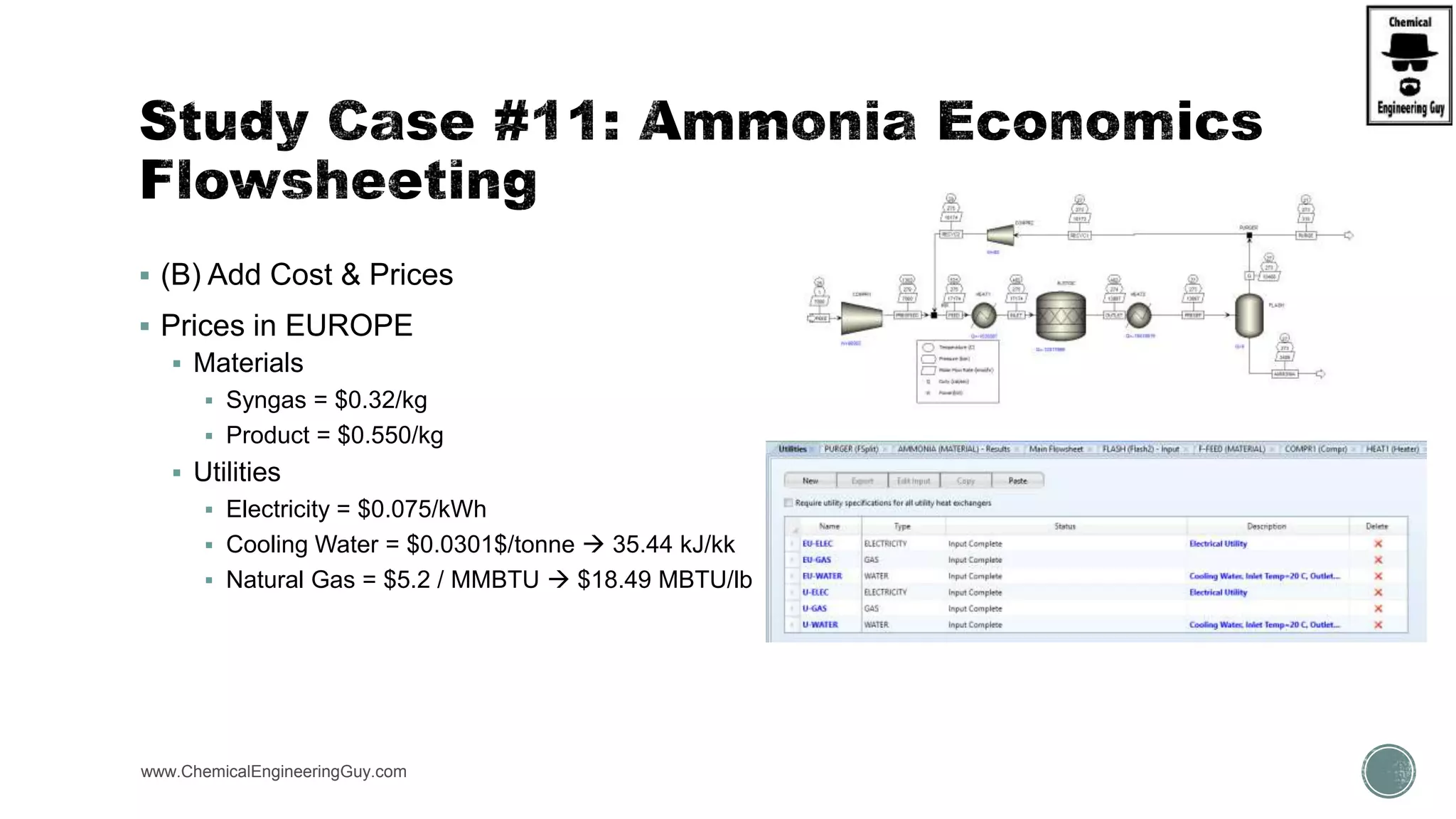
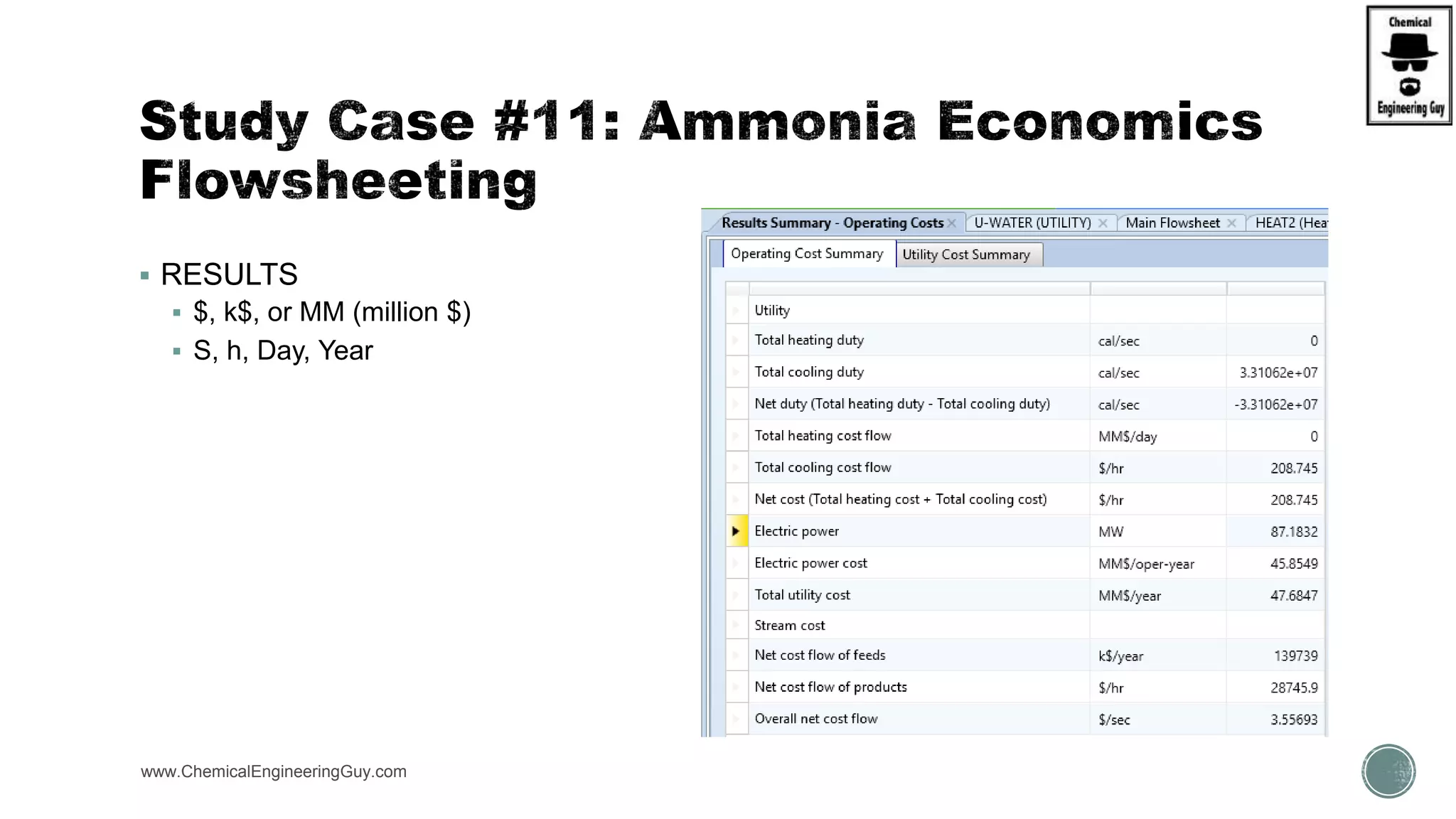
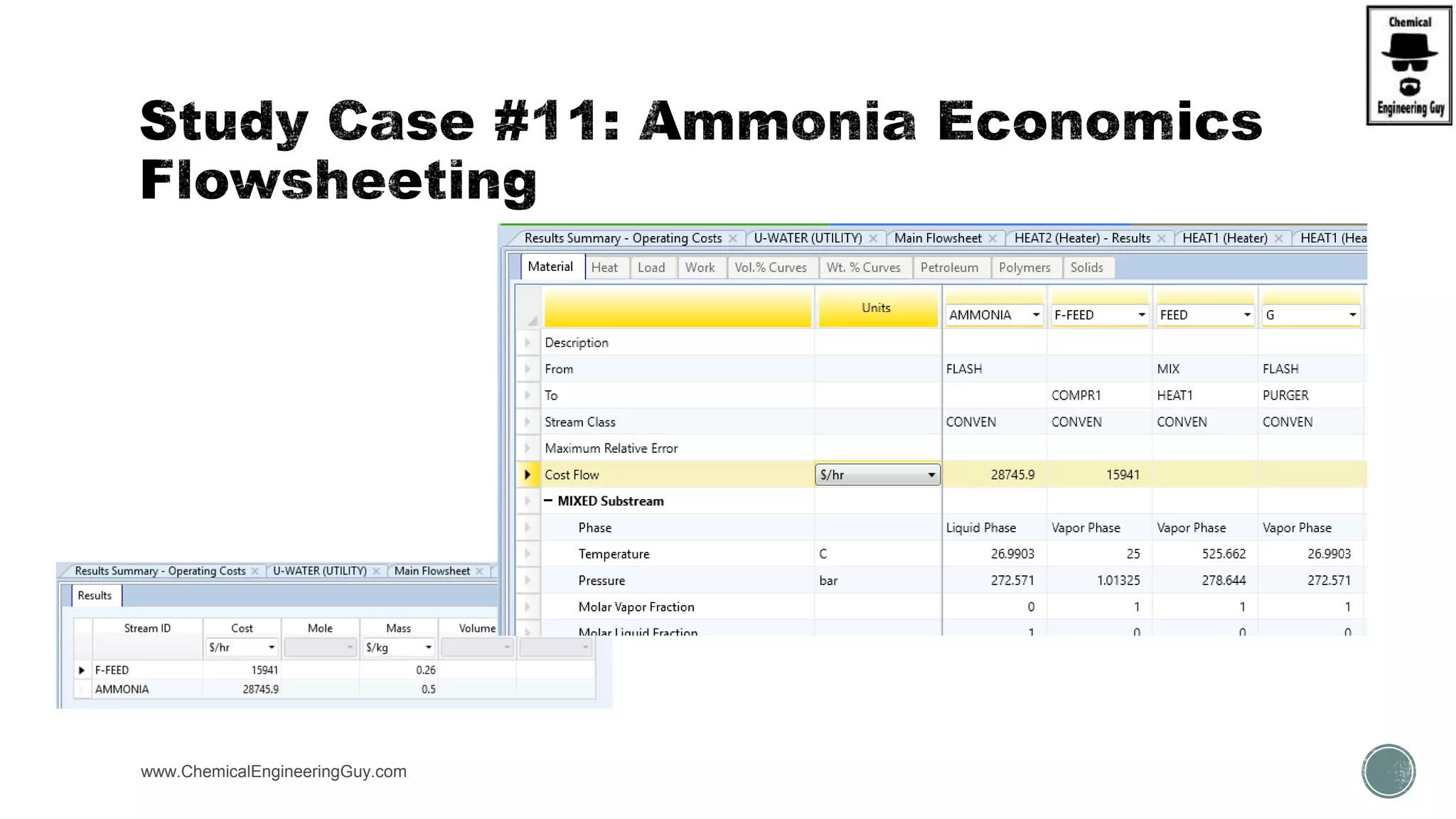
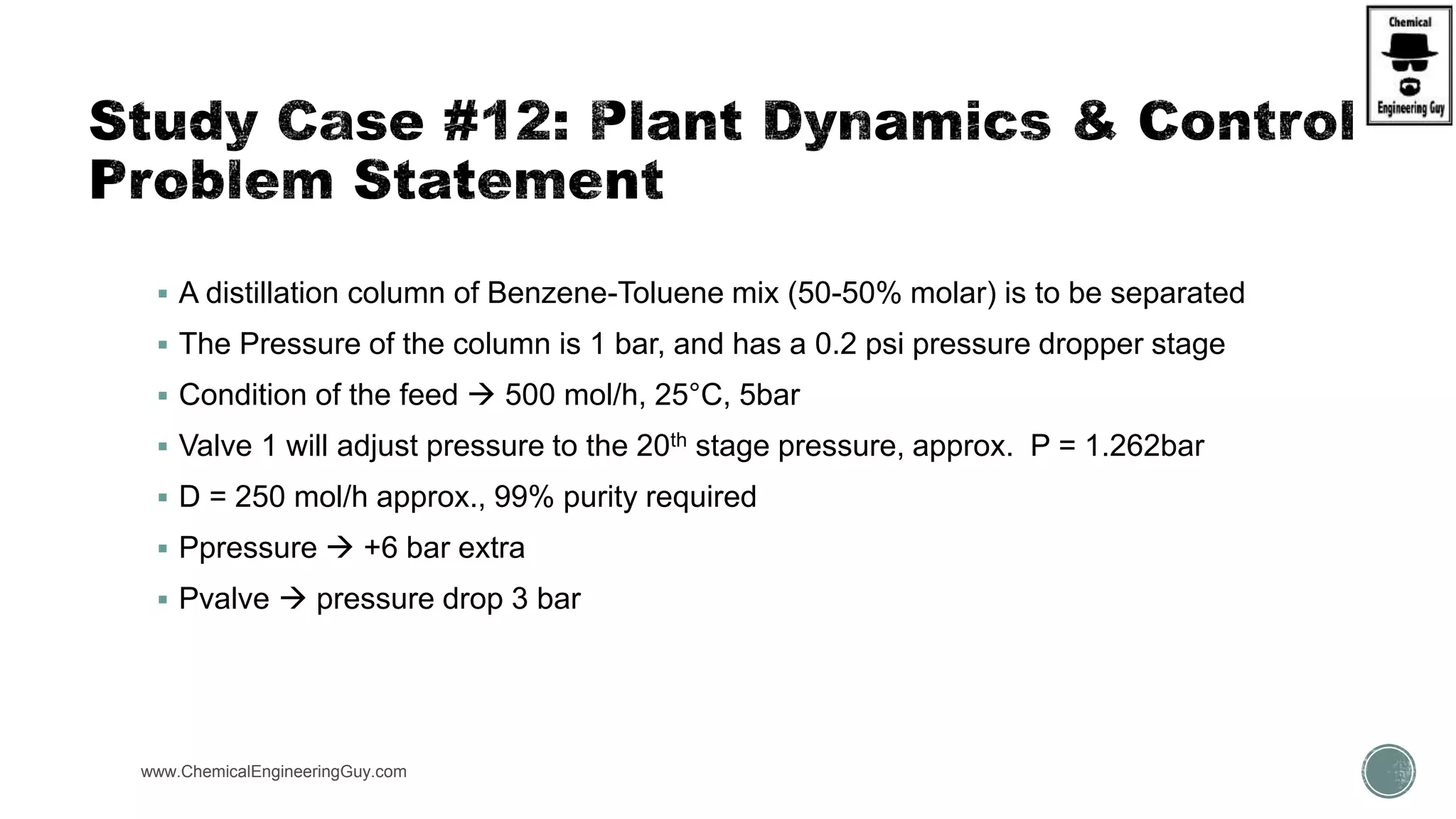
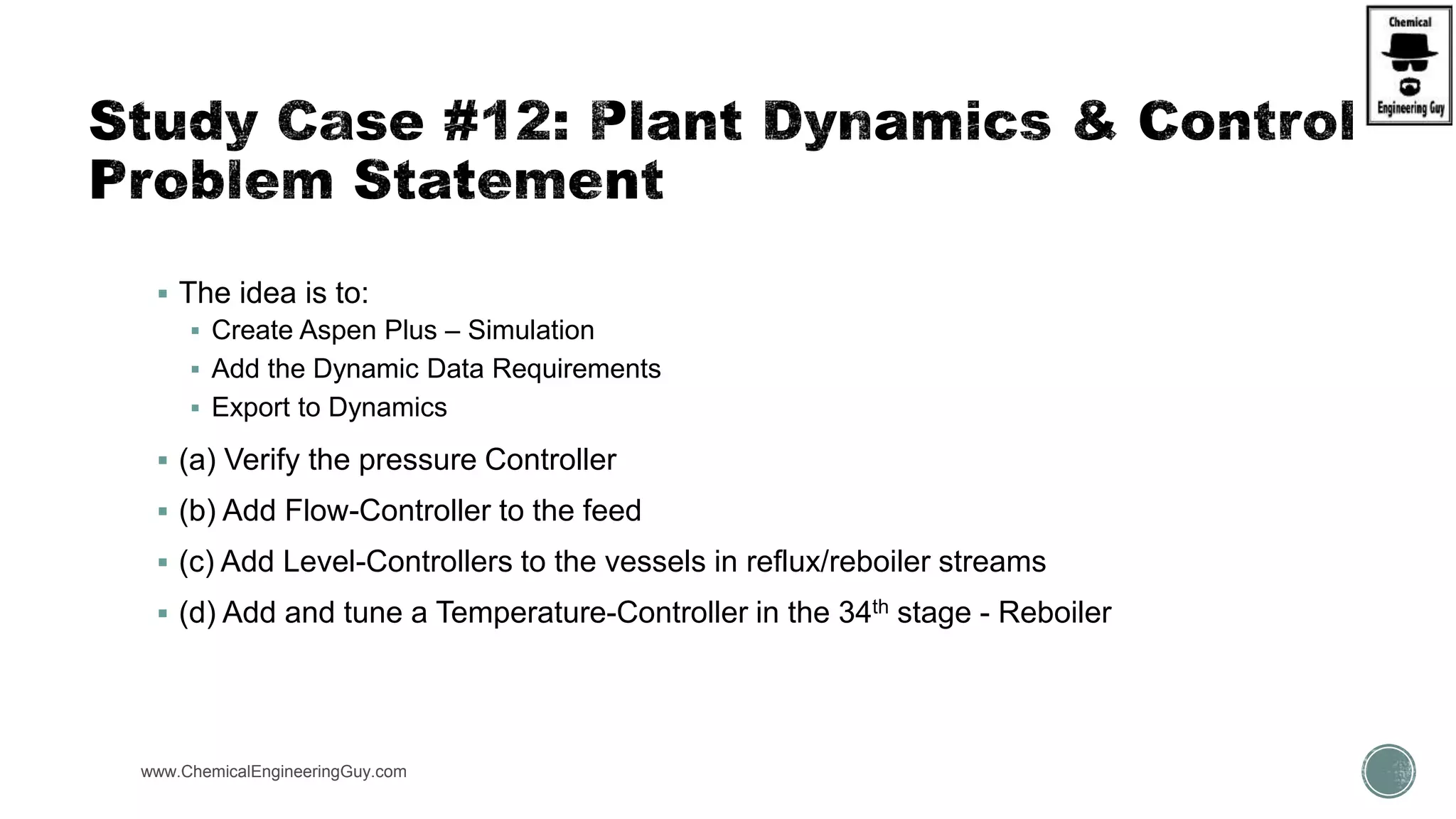
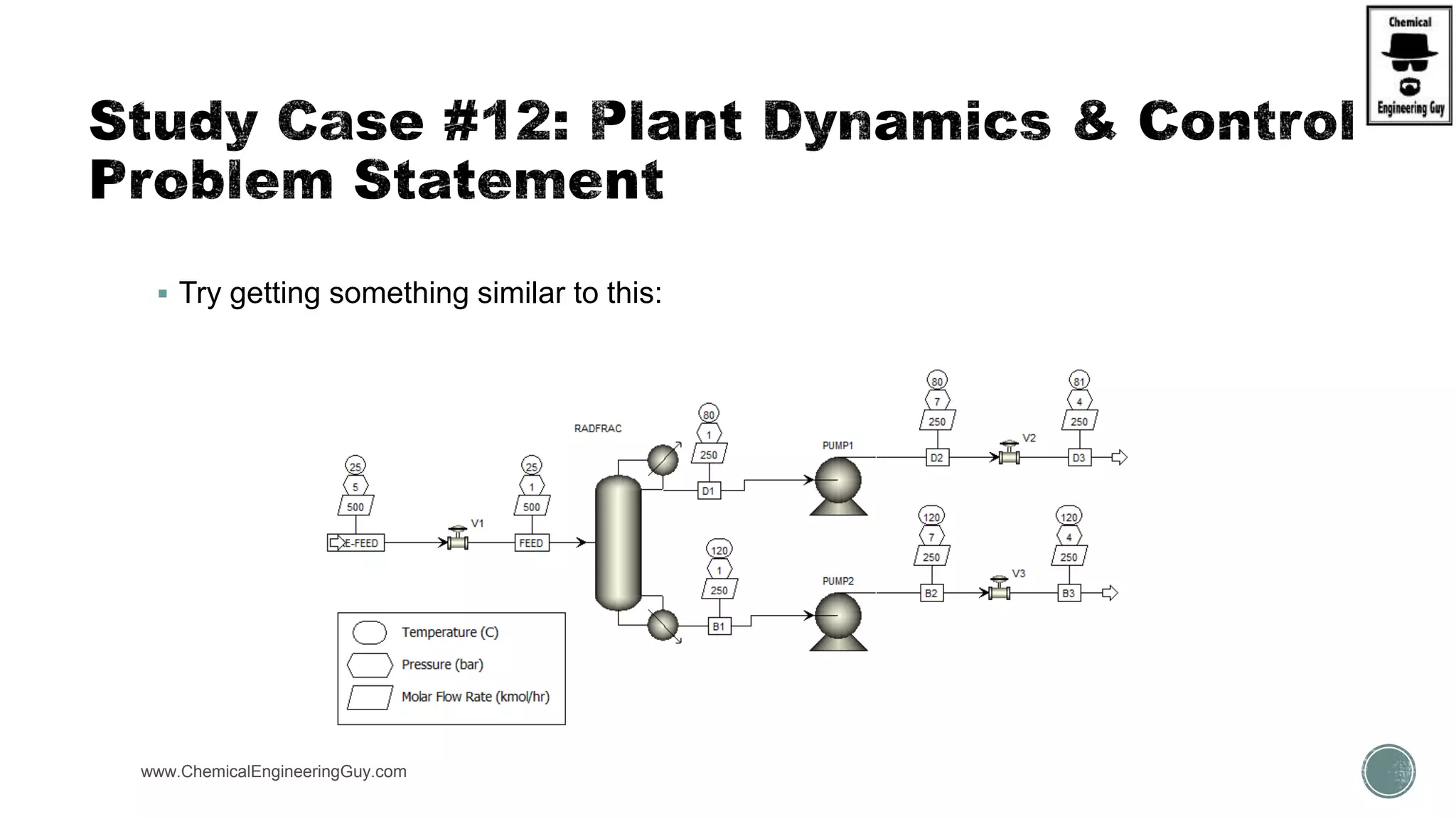
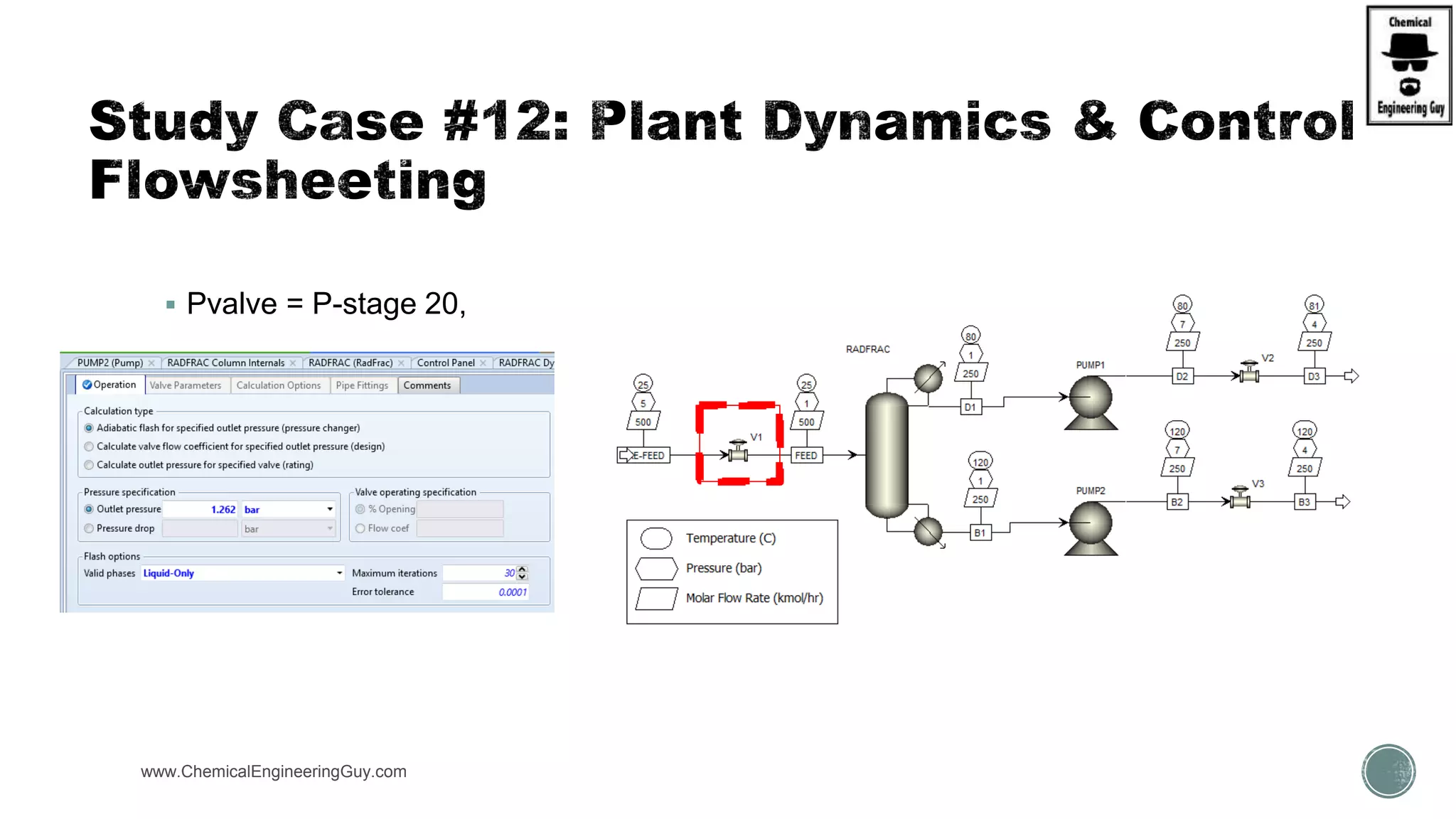
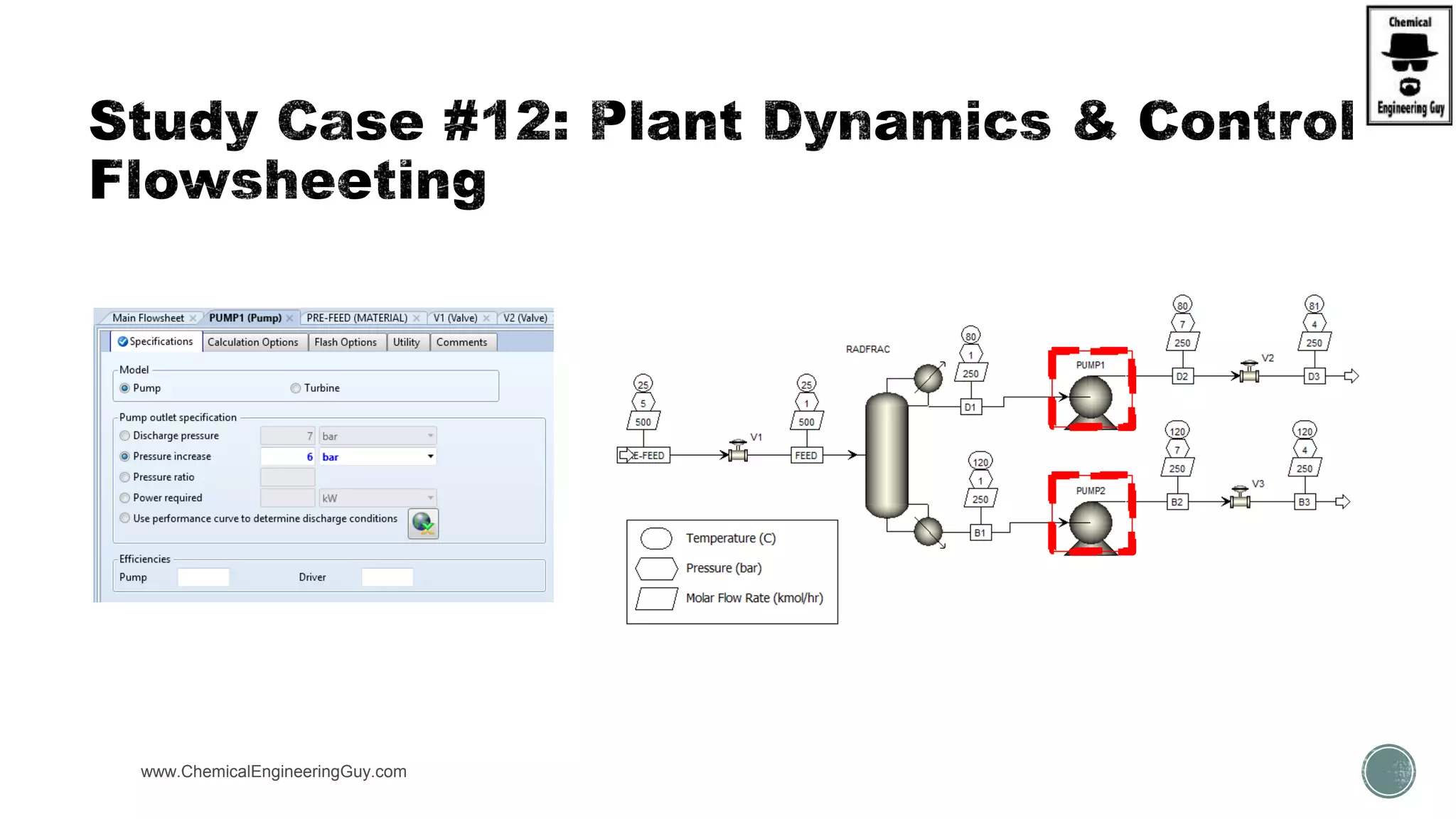
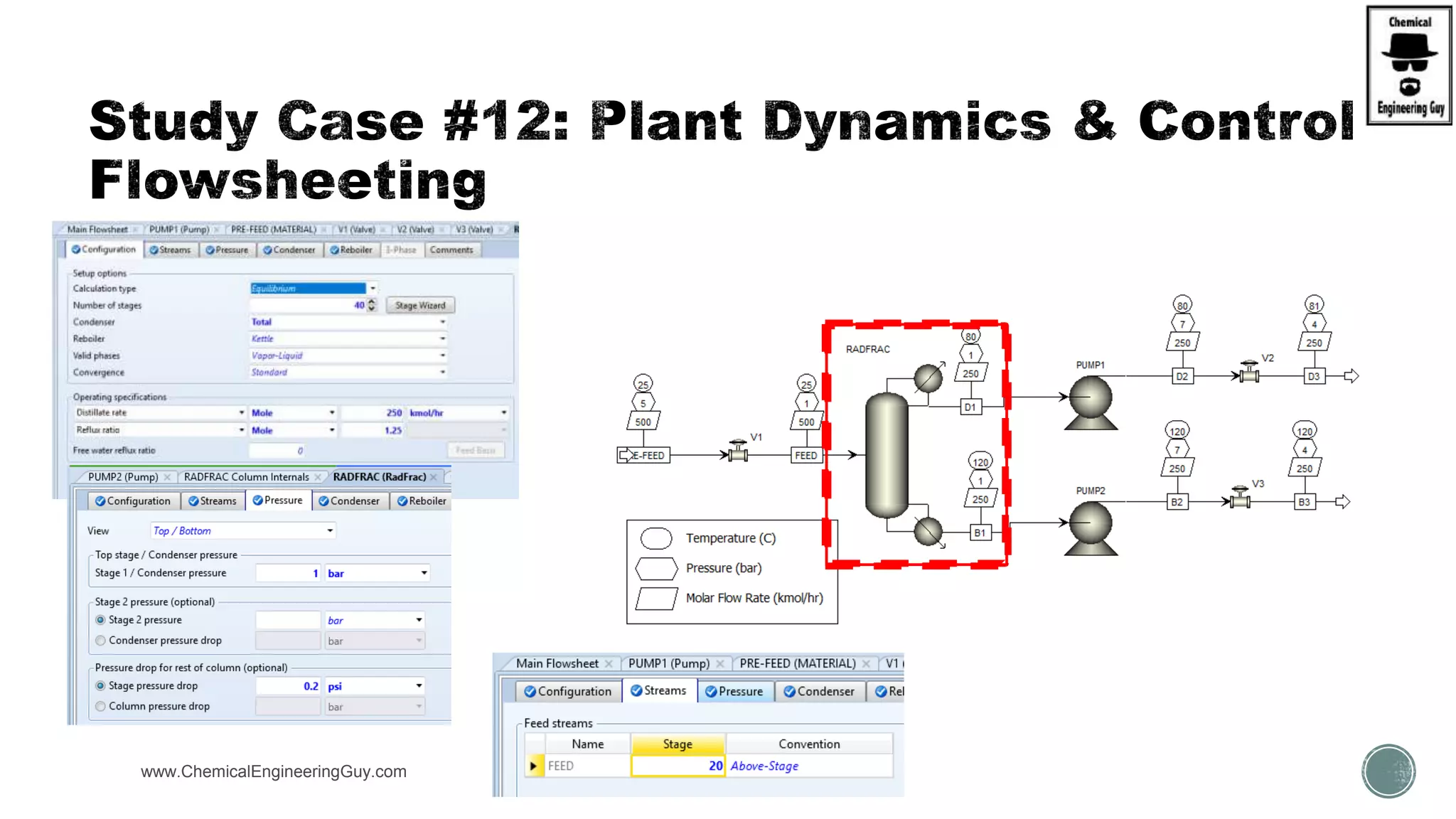
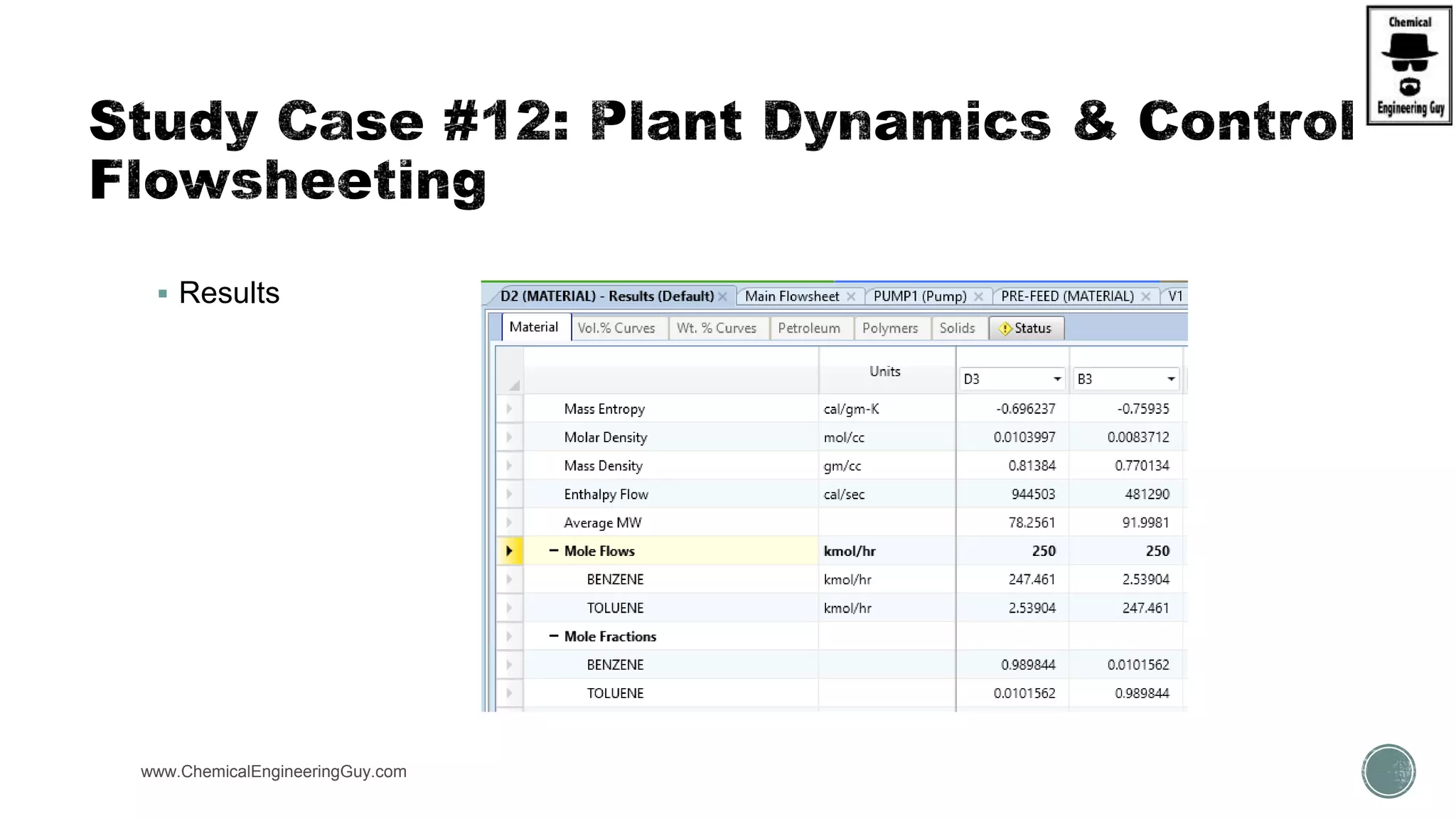
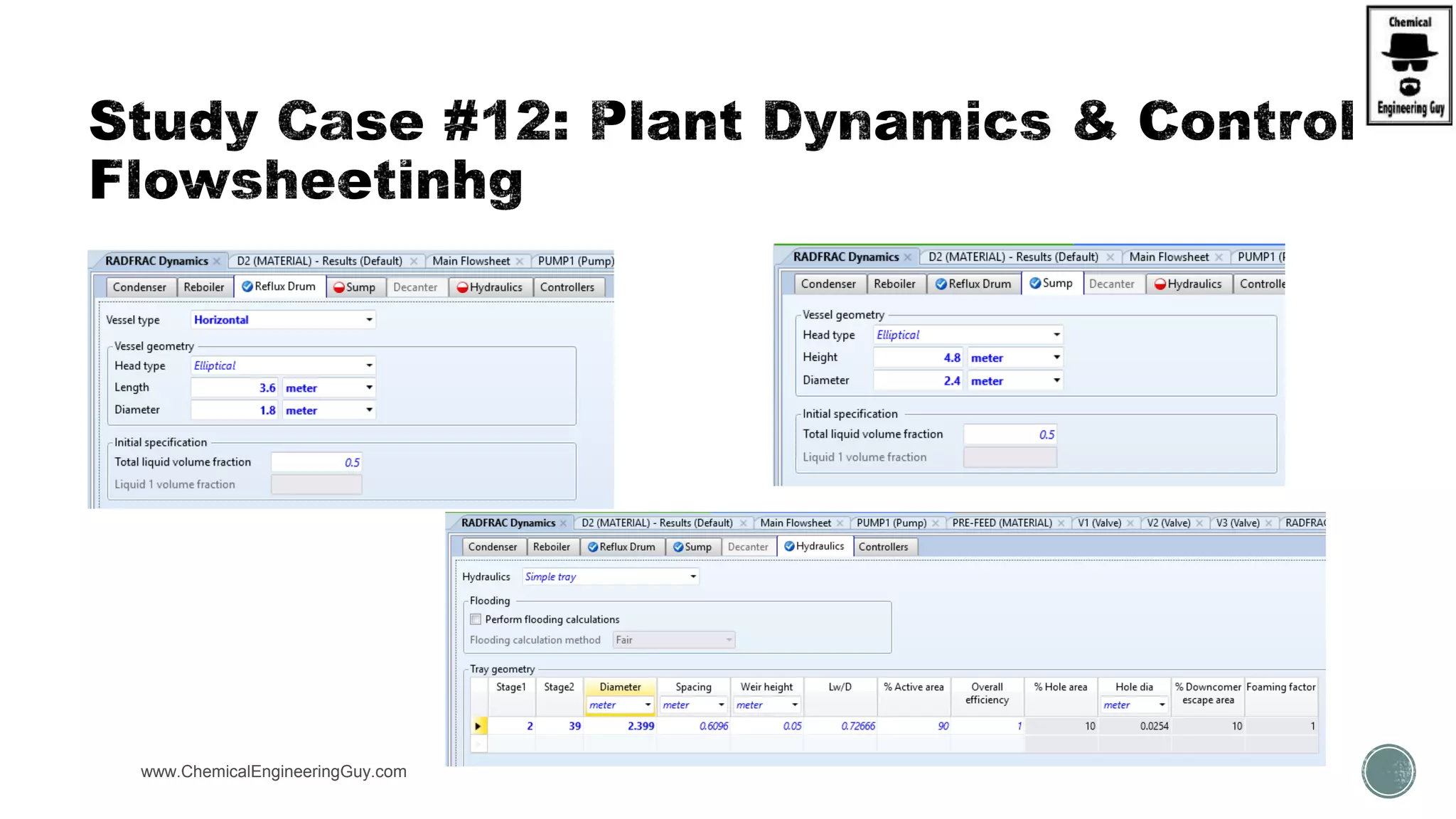
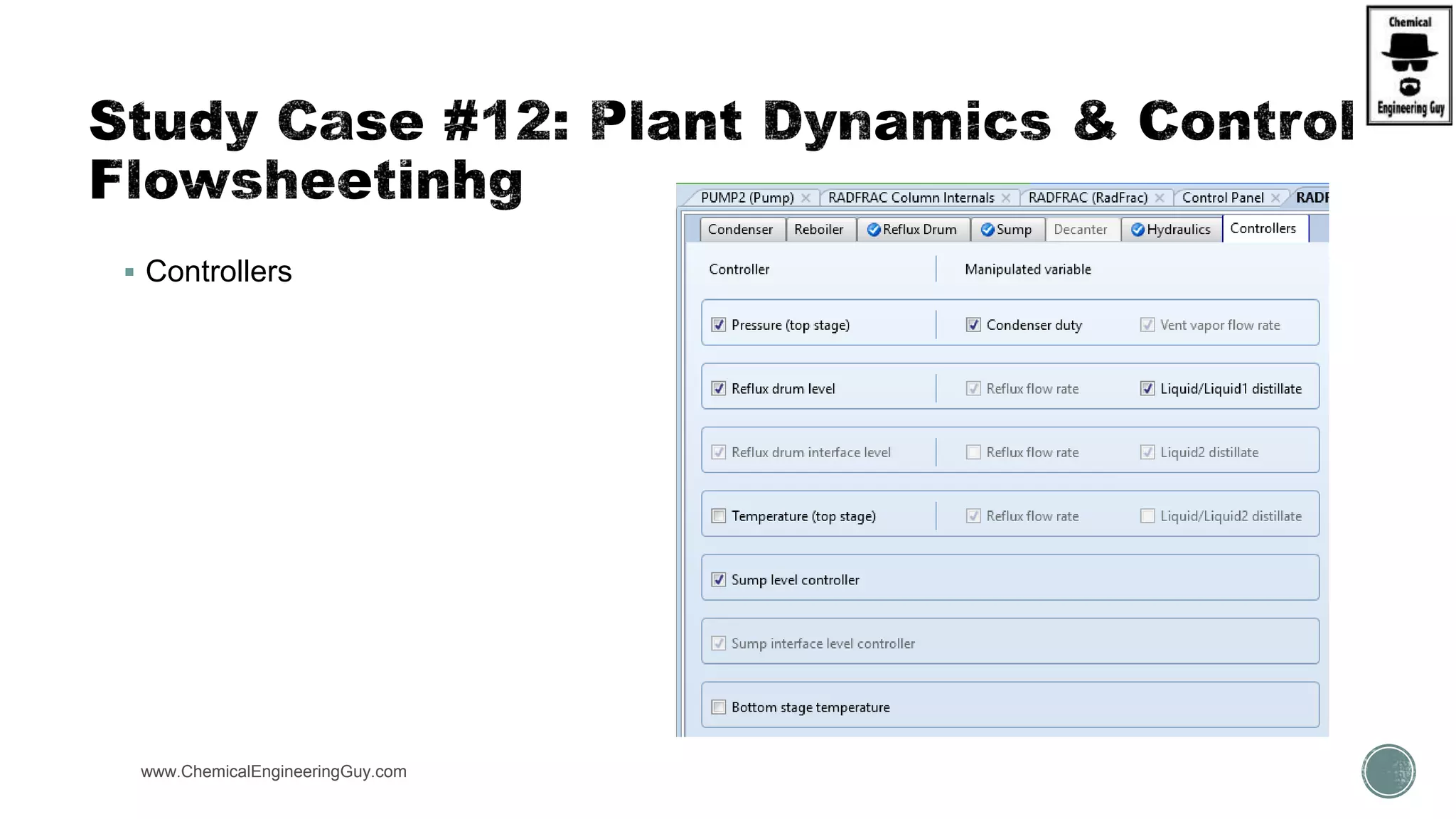
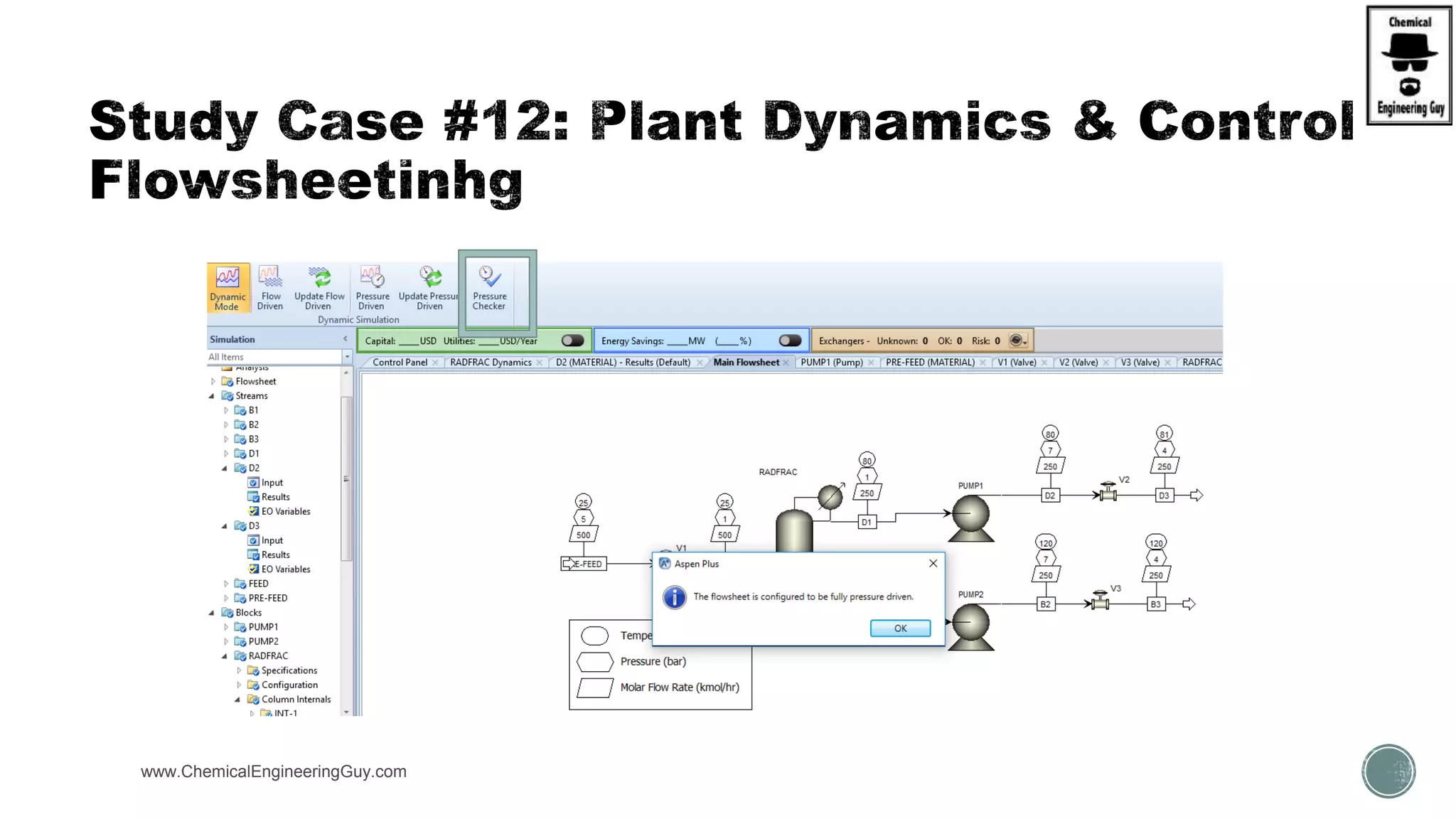
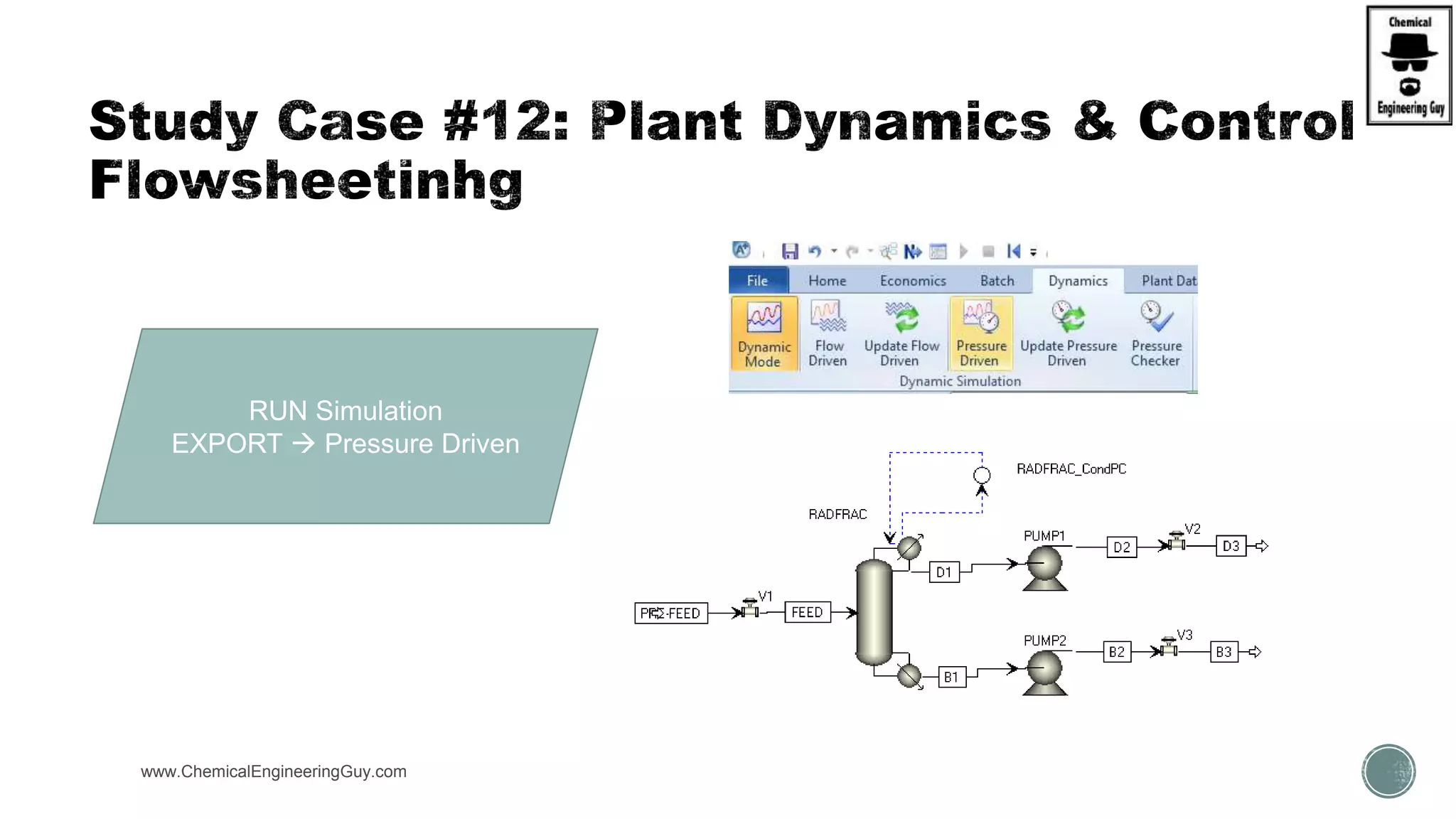
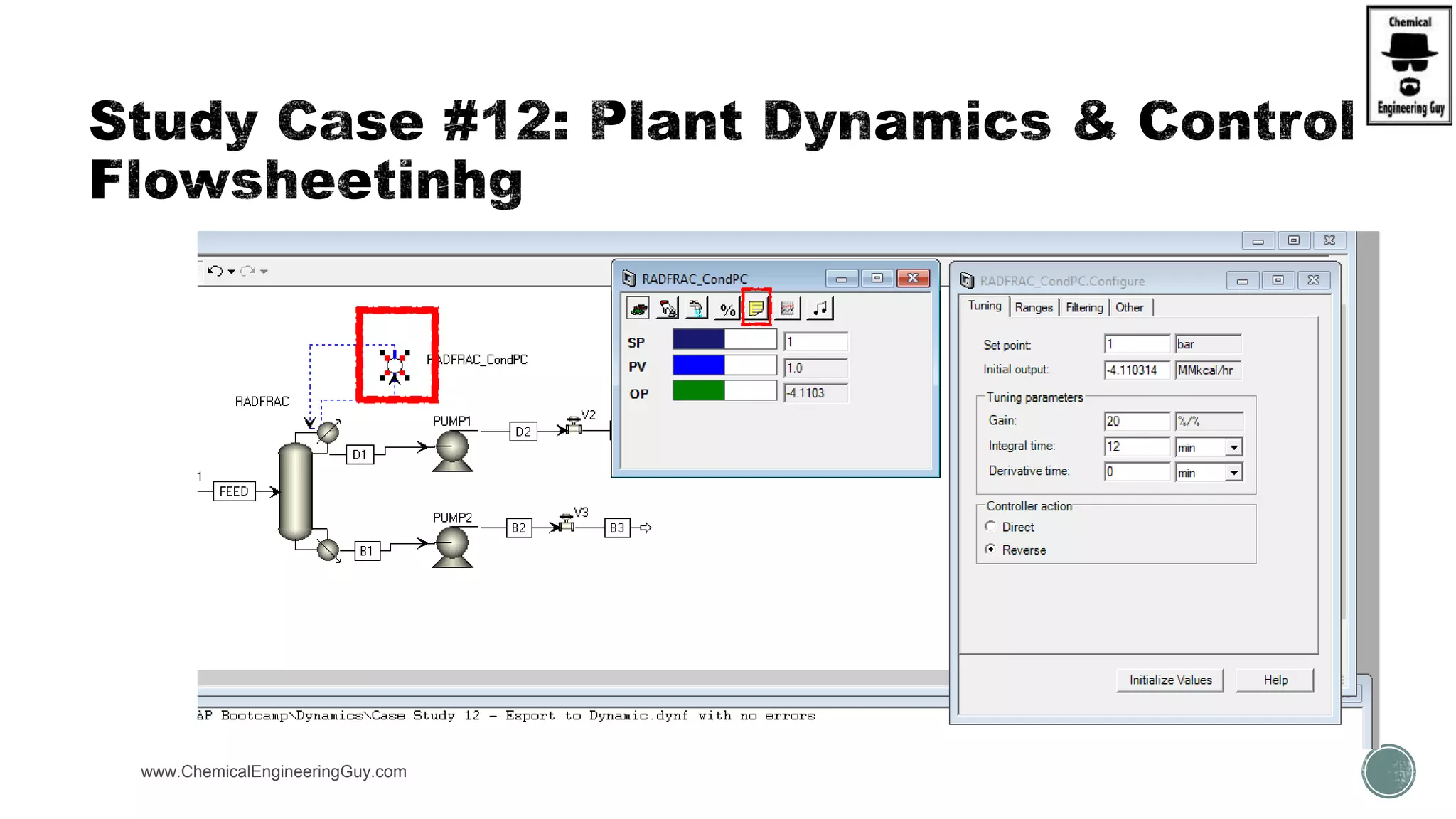
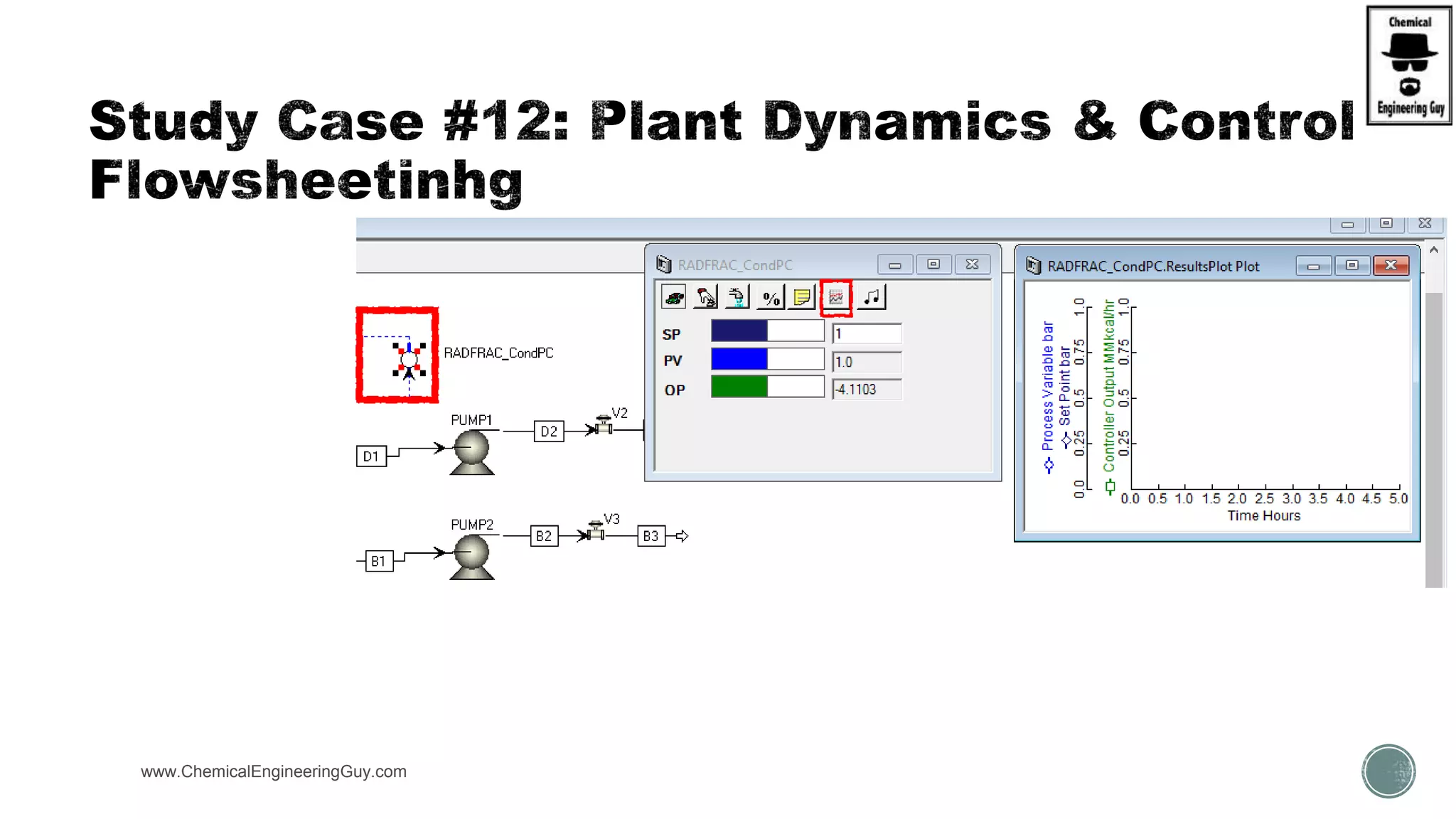
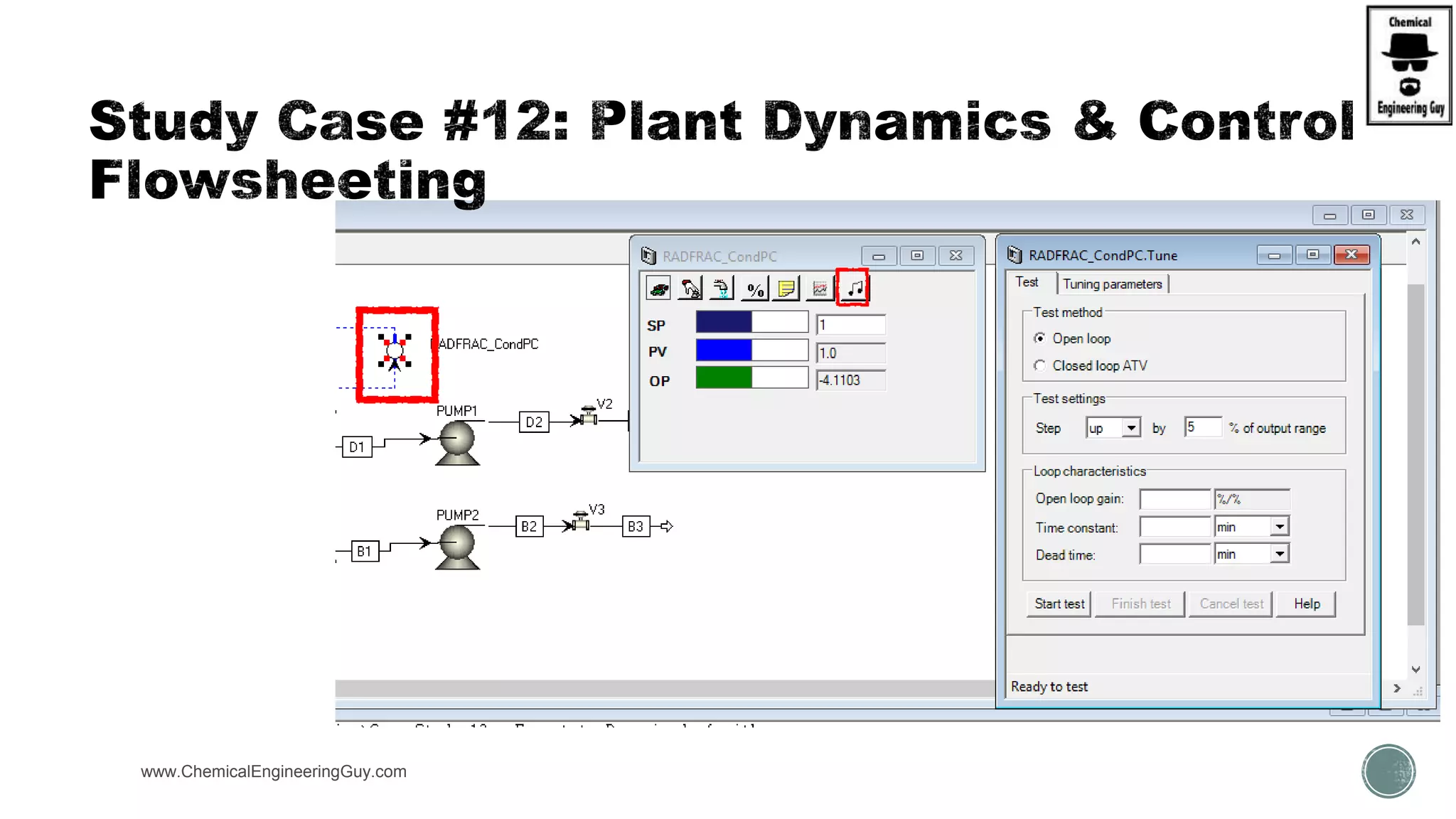
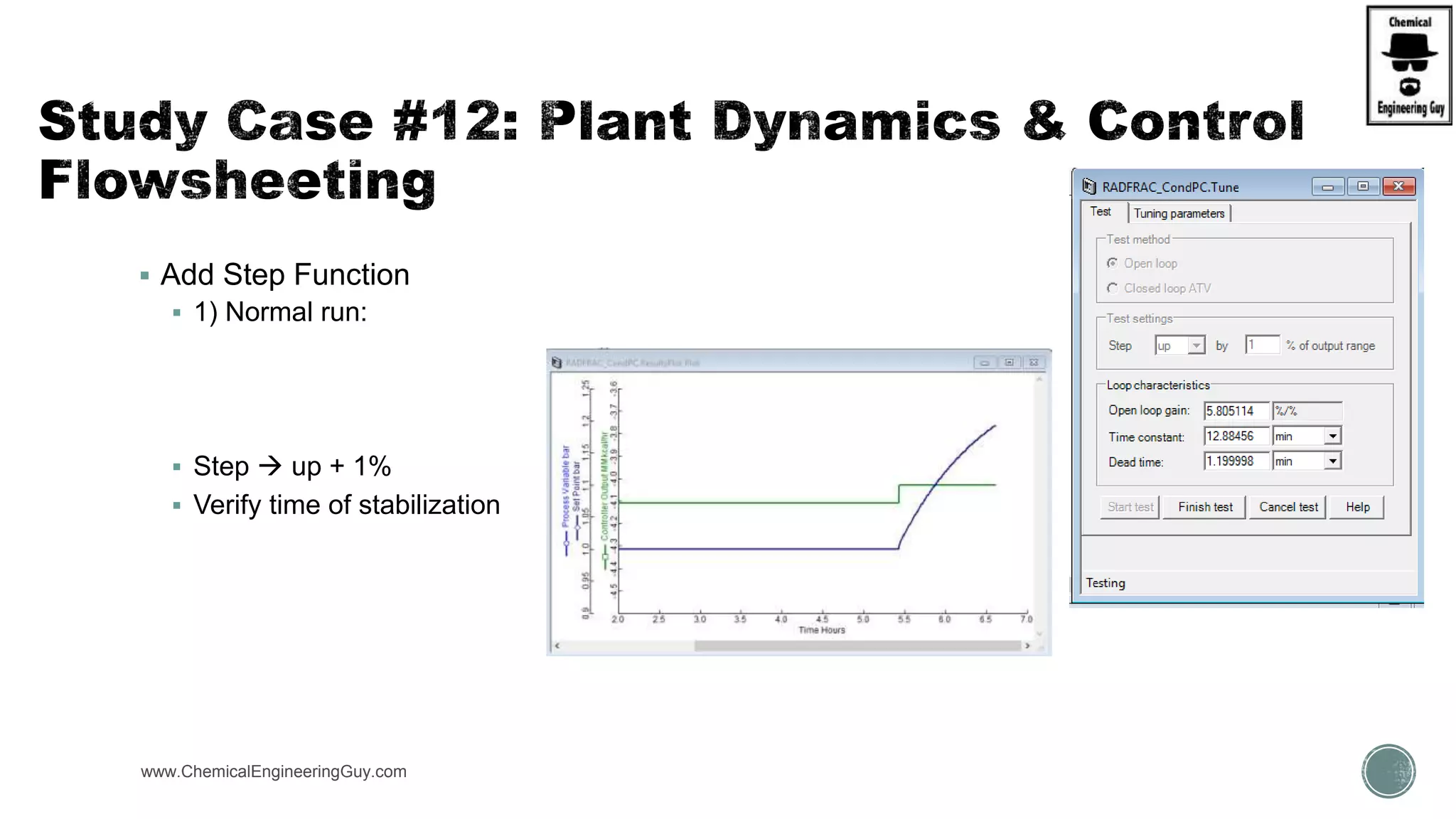
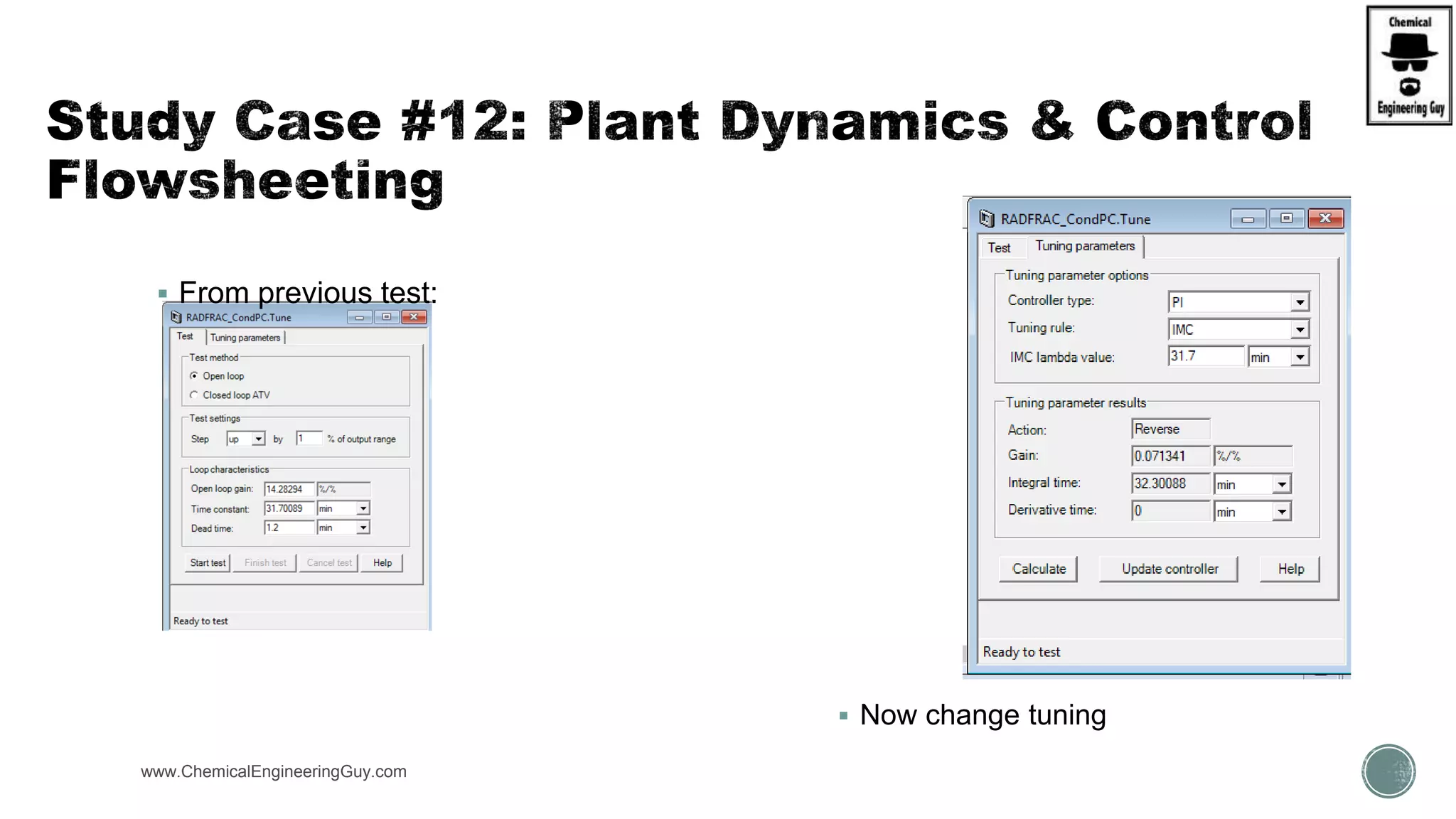
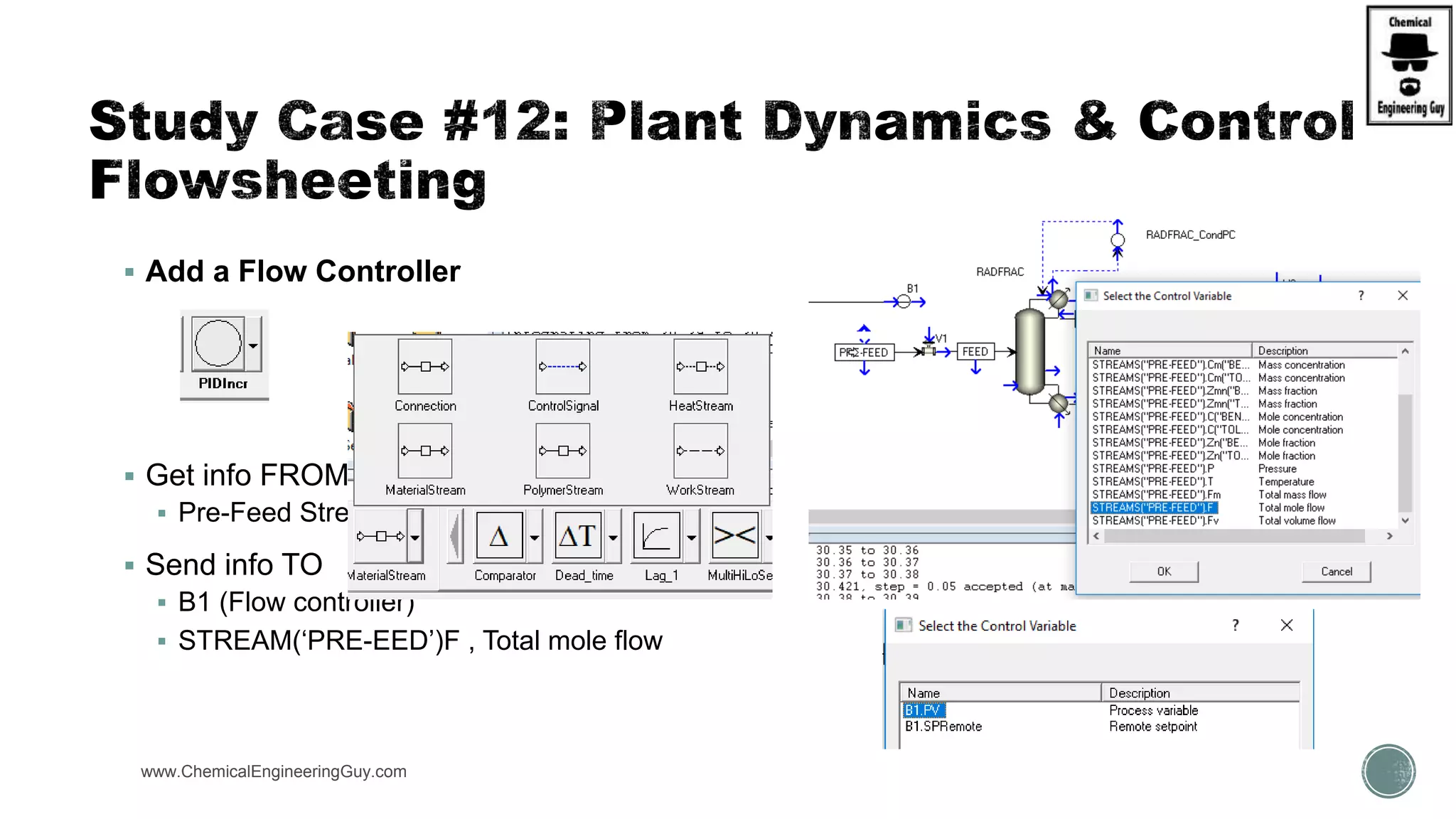
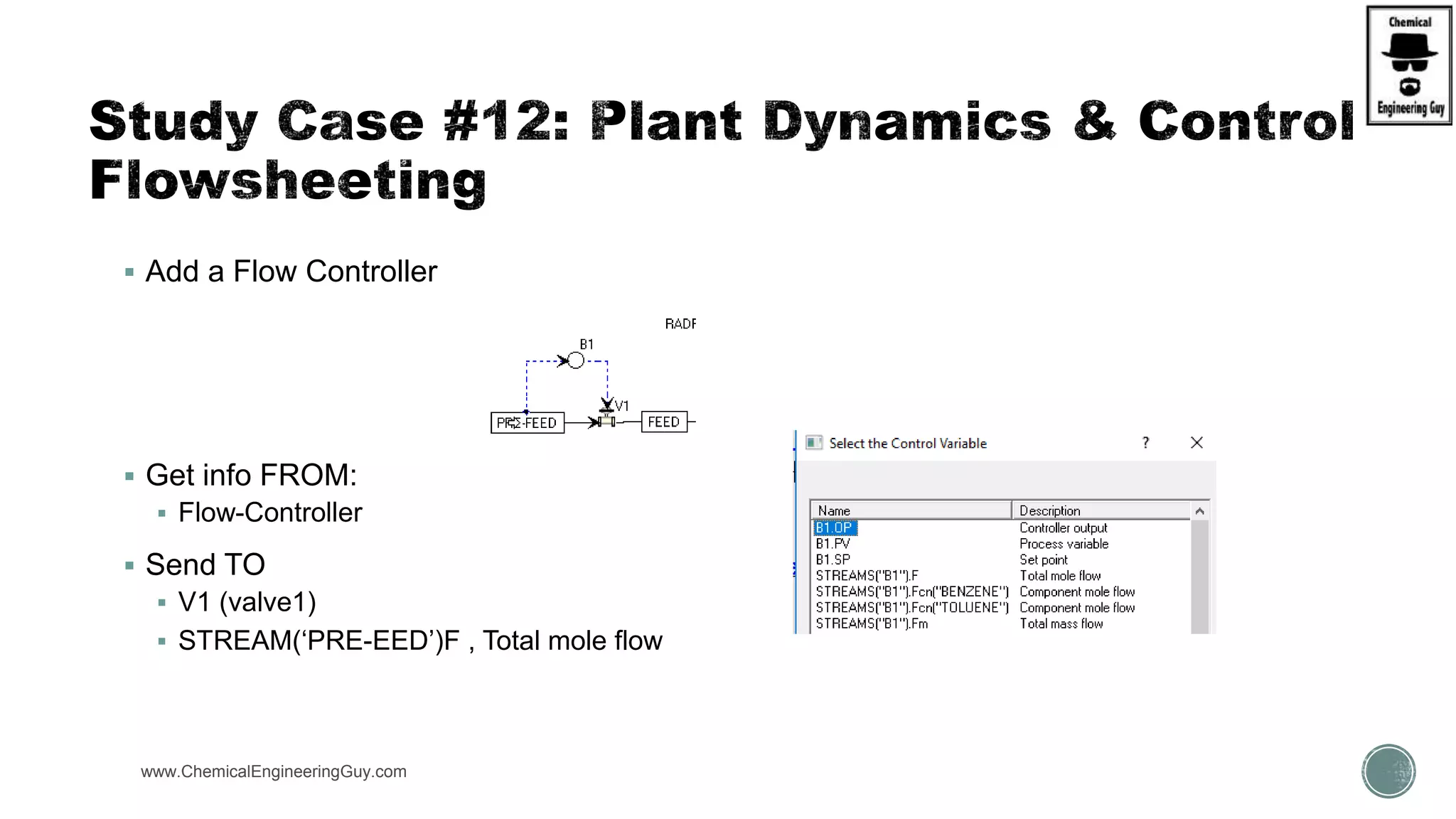
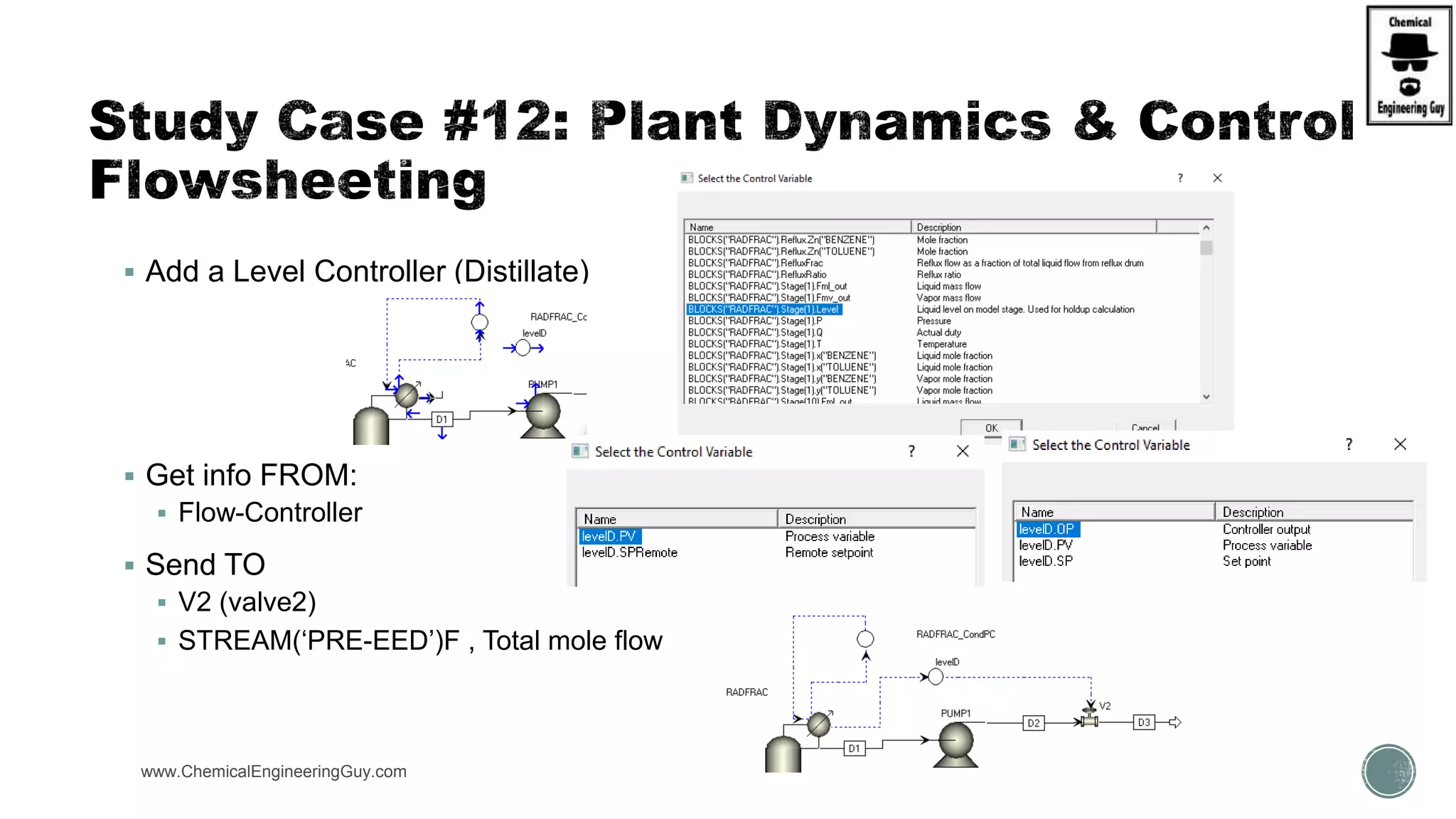
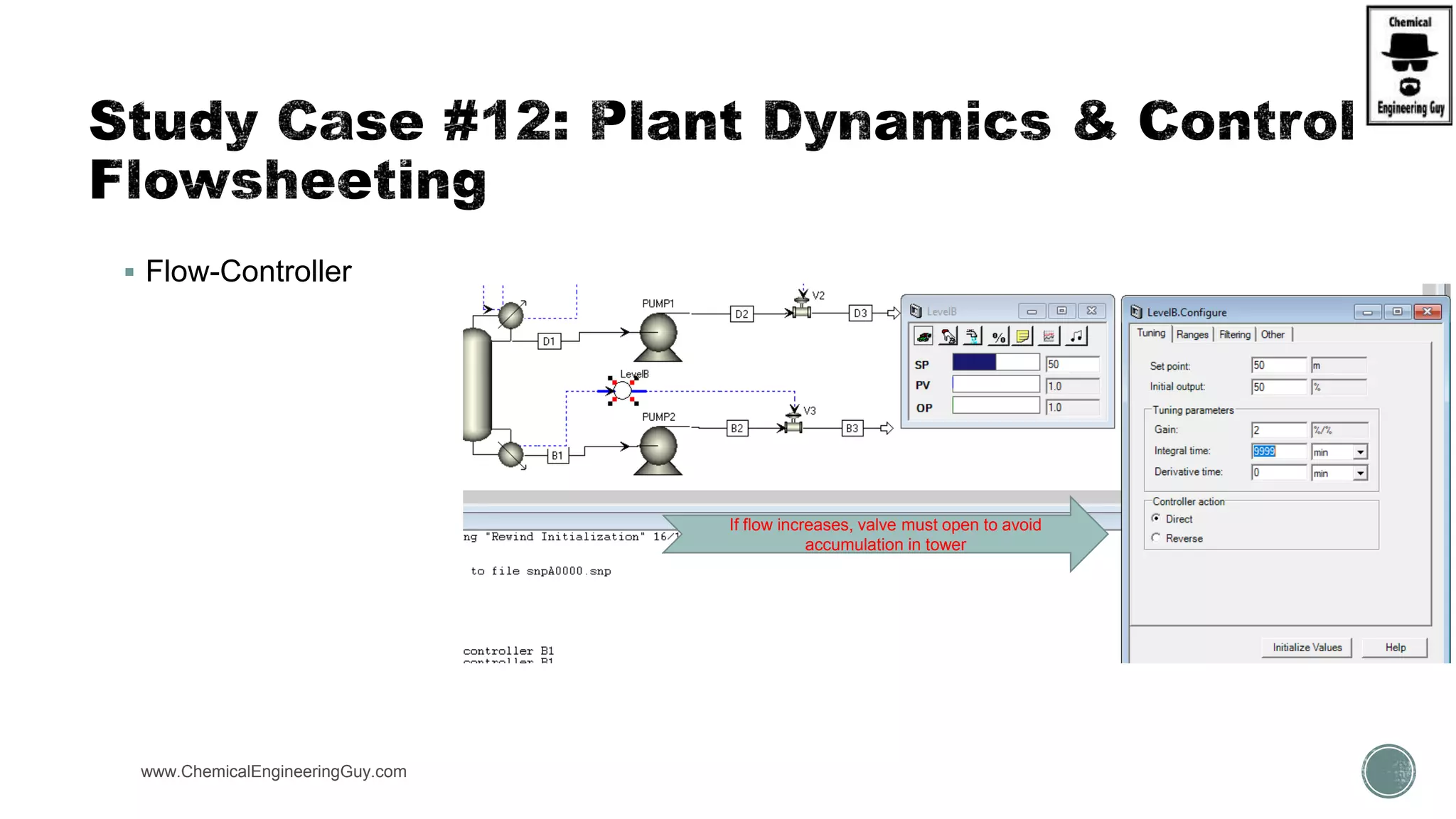
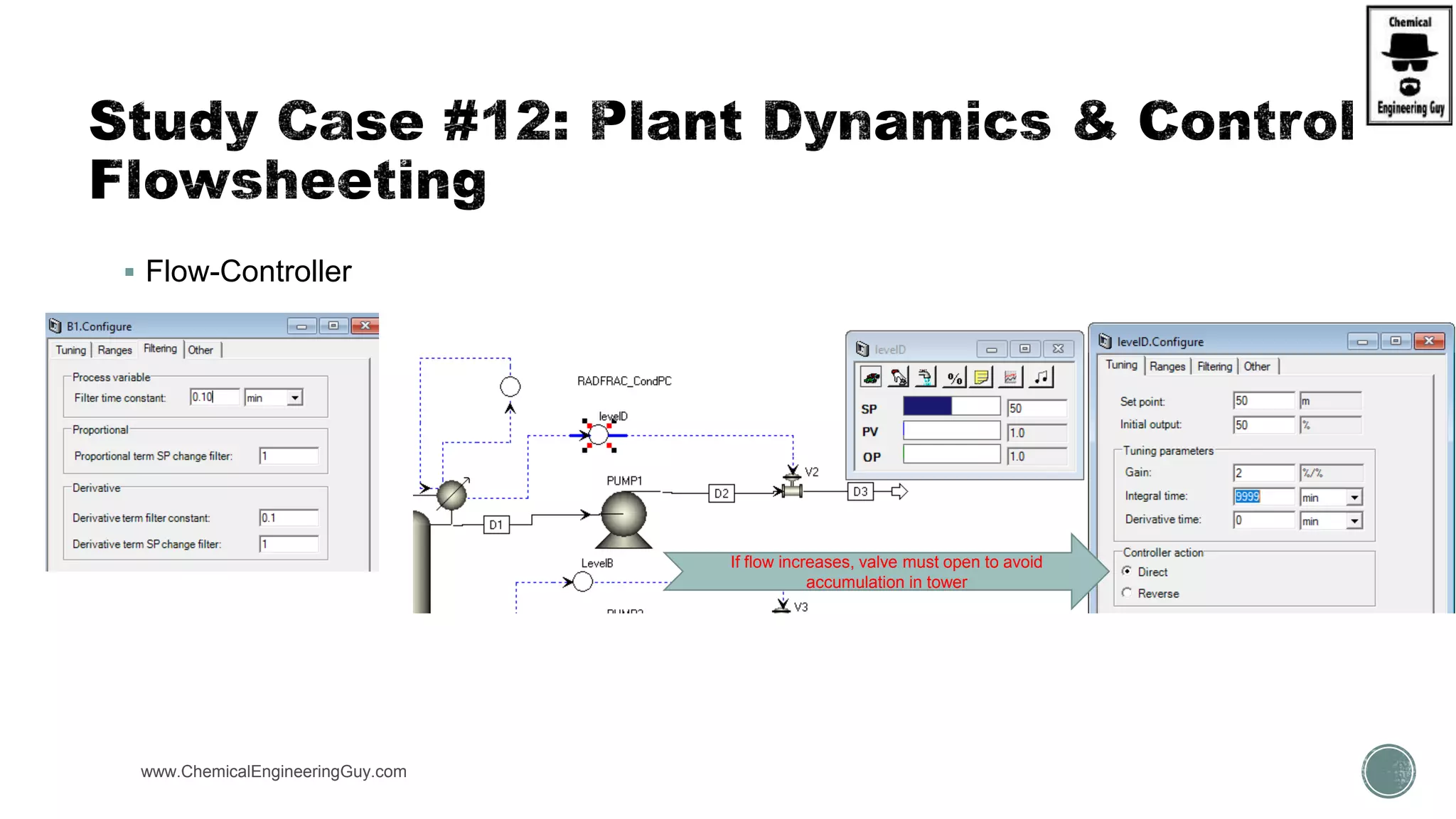
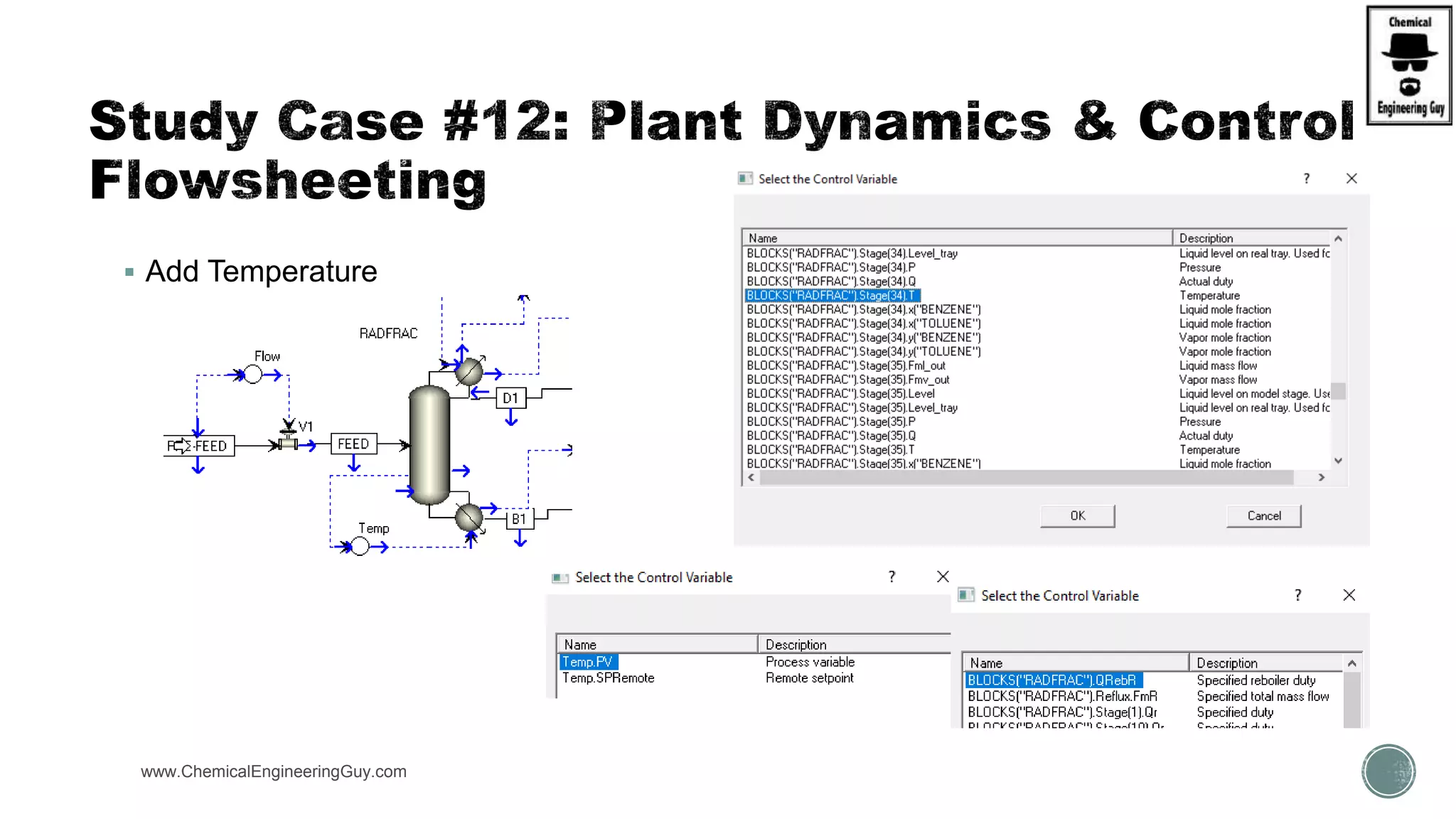
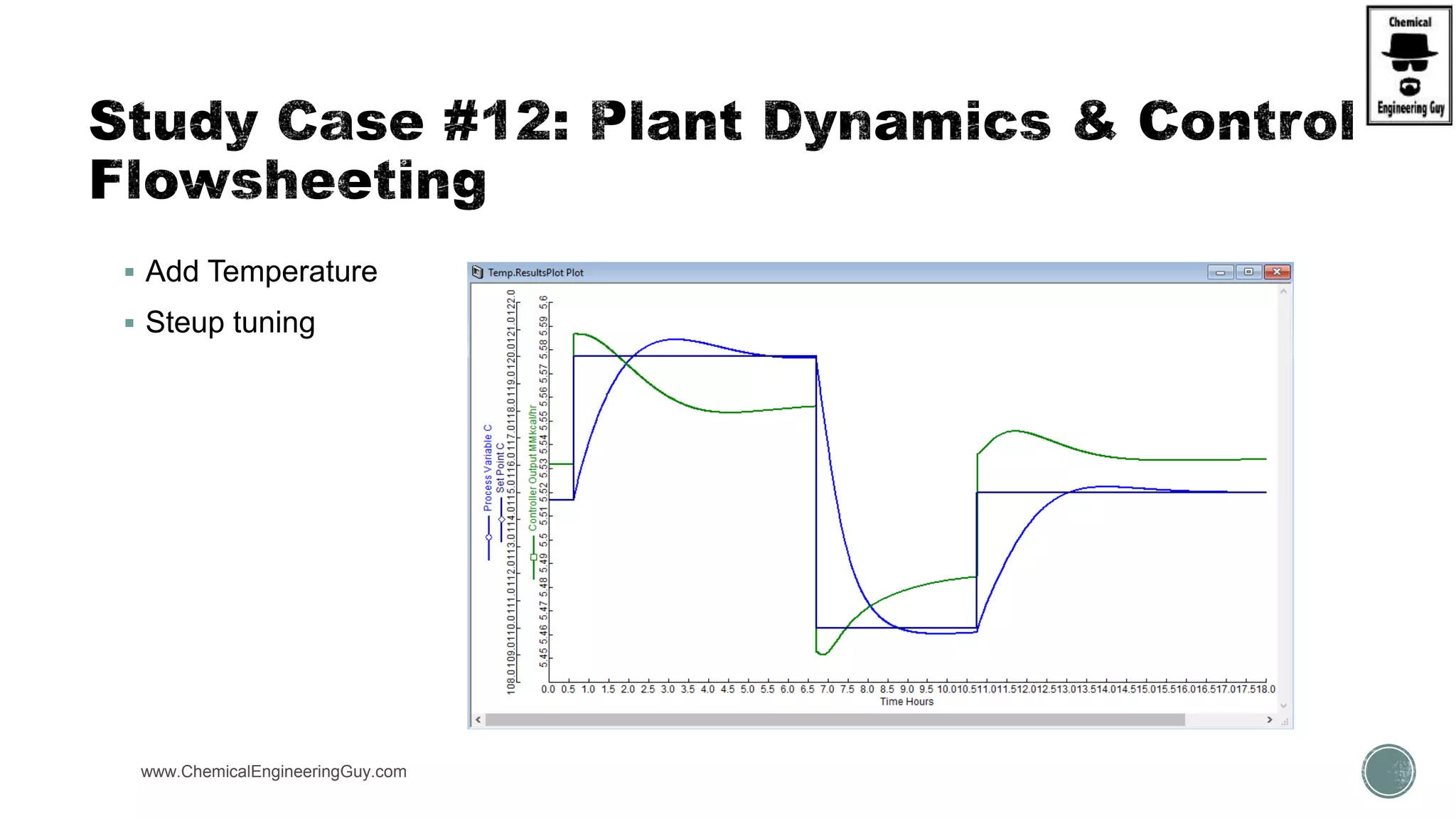
The document provides a preview of an Aspen Plus bootcamp focused on chemical engineering applications, including unit operations, heat exchangers, and absorption simulations. It outlines specific case studies involving energy balances, simulations for heating and cooling duties, and various distillation operations while addressing economic analyses for ammonia production. Additionally, it includes links to relevant videos and emphasizes the importance of comparing different column internals and conducting sensitivity analyses.