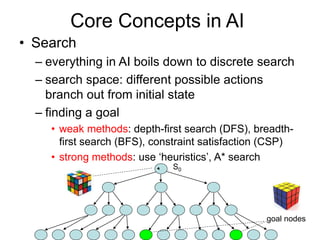
This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI) including definitions, applications, perspectives, and core concepts. It discusses what AI is, how it is used in practical applications like medical diagnosis and driverless cars, and the philosophical, psychological, and engineering perspectives. Some key concepts discussed include search, knowledge representation, expert systems, planning, and machine learning. The document also outlines several sub-areas within AI like natural language processing, computer vision, and robotics.