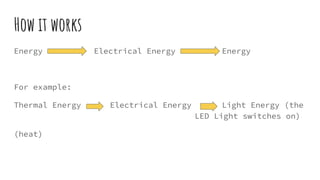
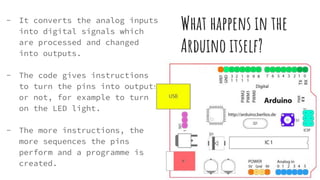
Arduino microcontrollers take in inputs from sensors measuring various types of energy like heat, light, movement etc. and output responses through devices like LED lights or motors. Sensors convert properties like temperature, sound or distance into analog electrical signals that the Arduino reads and uses code to process into digital outputs. This allows Arduinos to be used in examples like automatically turning a heater on/off based on temperature readings, watering a plant based on soil moisture levels, or setting off an alarm if a motion sensor detects movement.