Group B analyzed the role of social media in the Arab Spring uprisings that began in 2010 in Tunisia. They outlined how social media:
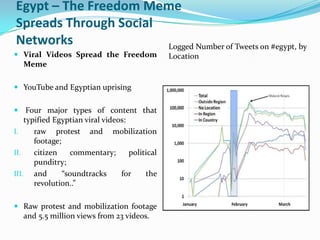
1) Put a human face on political oppression stories and inspired dissidents to organize protests through sharing on Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube.
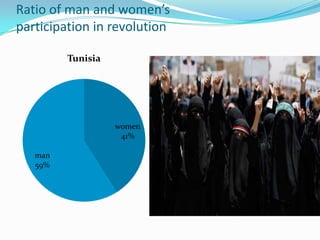
2) Played a central role in shaping political debates, with social media demographics showing high youth and women participation online.
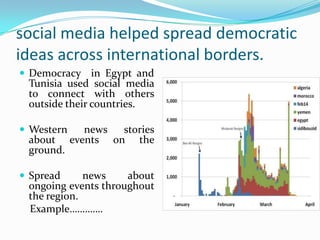
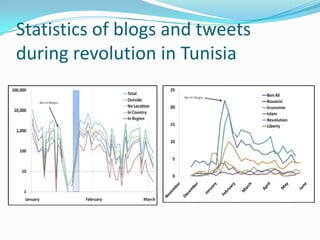
3) Helped spread democratic ideas and news of events across international borders, accelerating protests and putting pressure on governments.