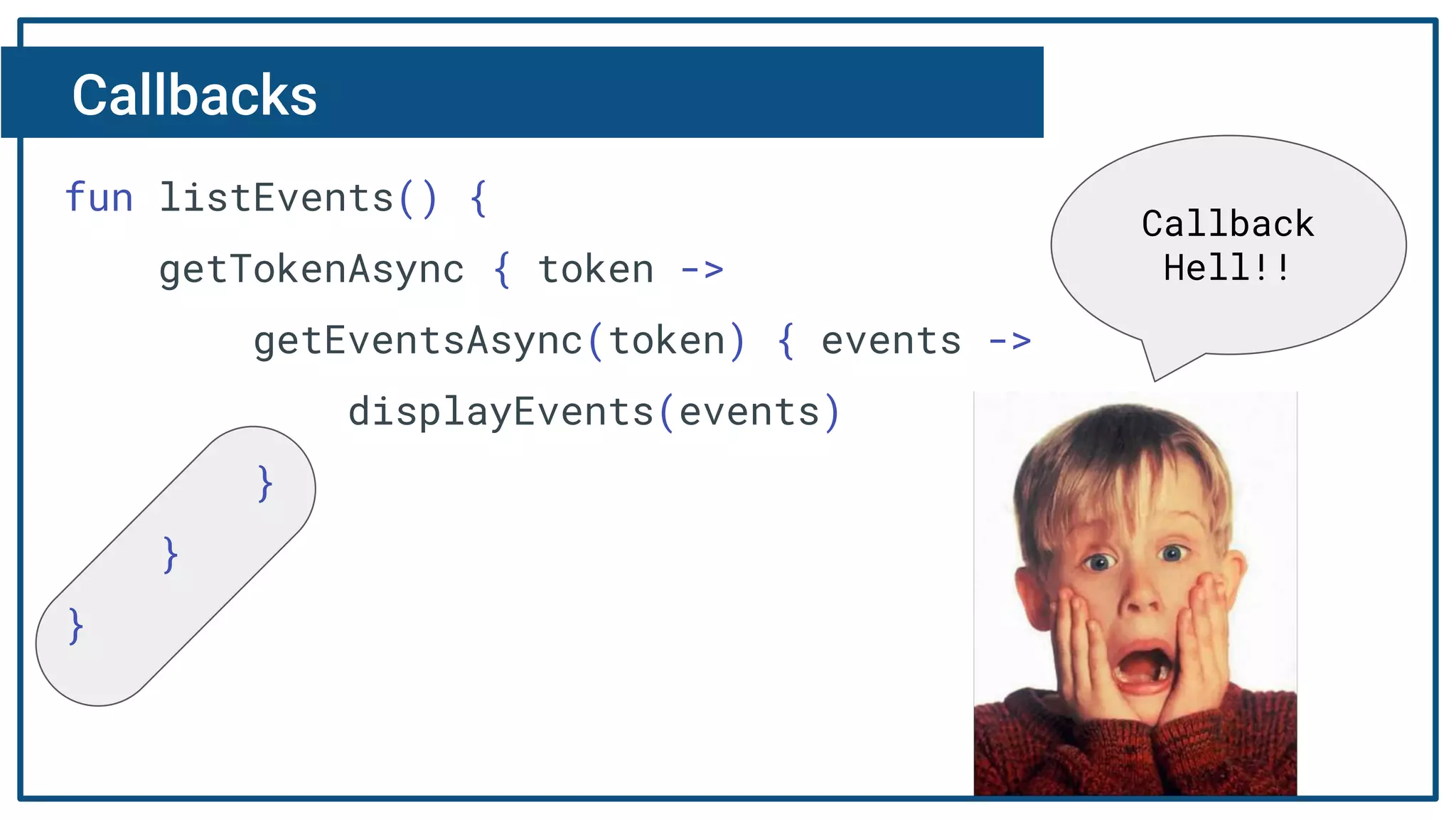
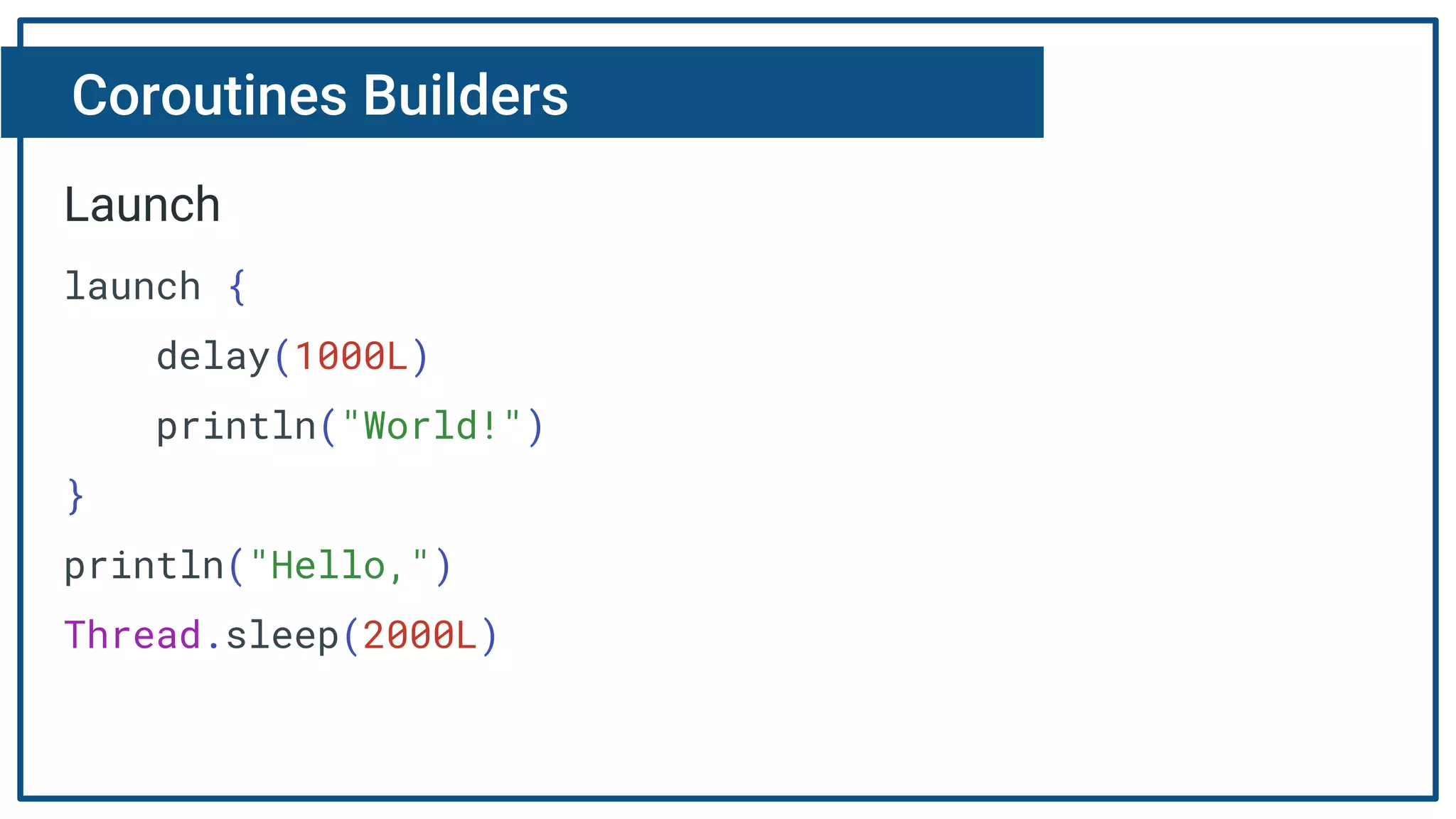
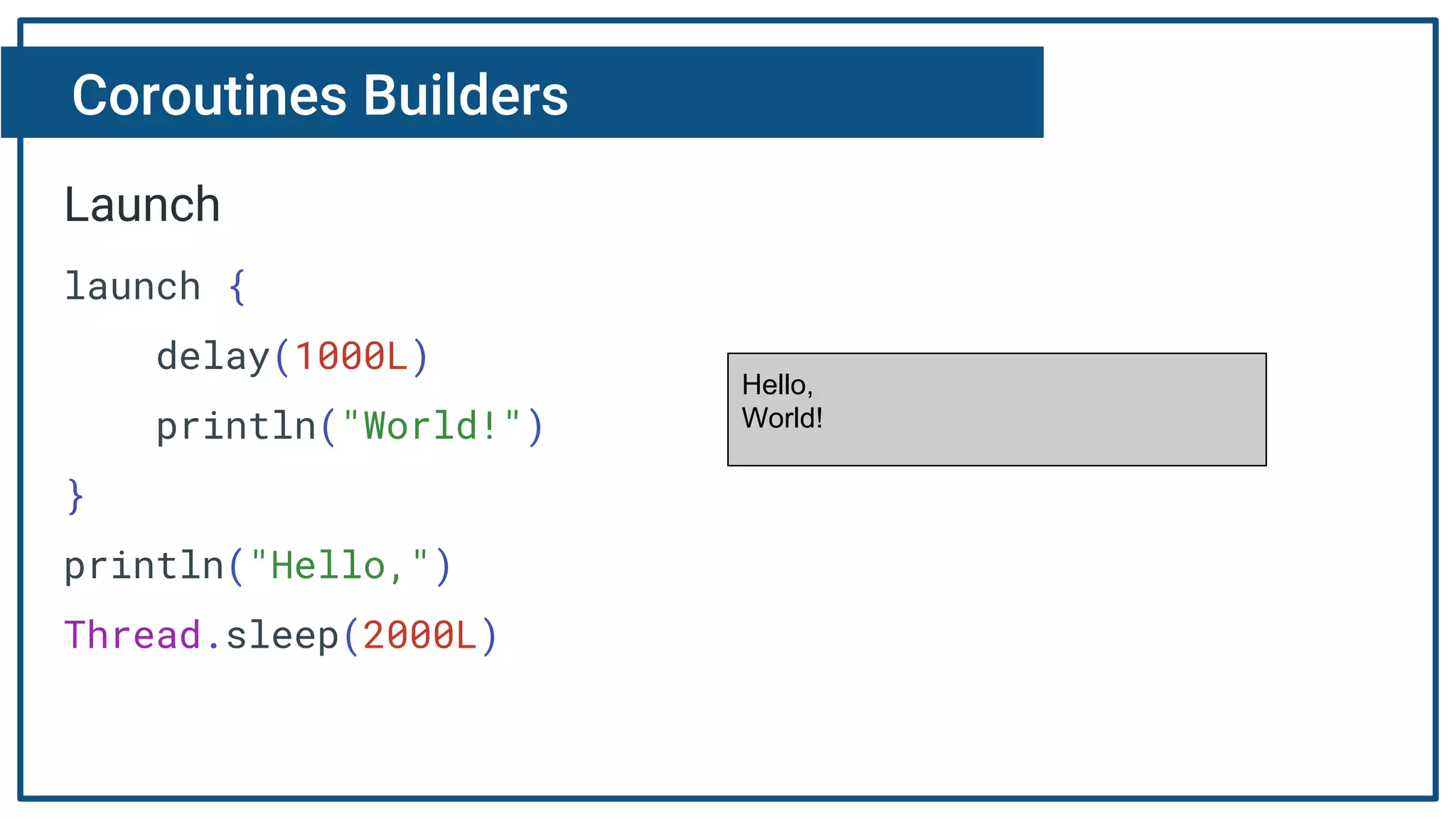
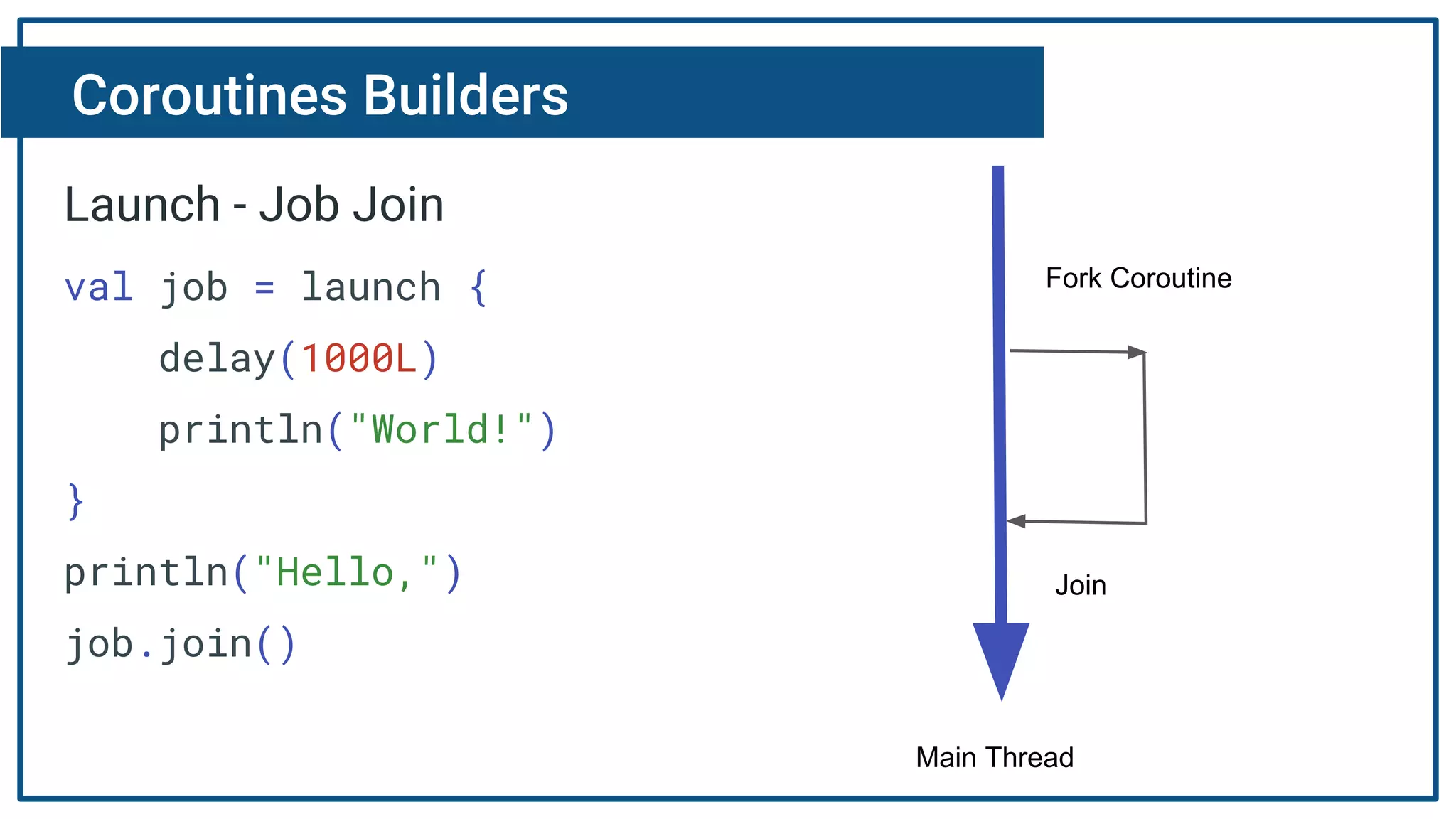
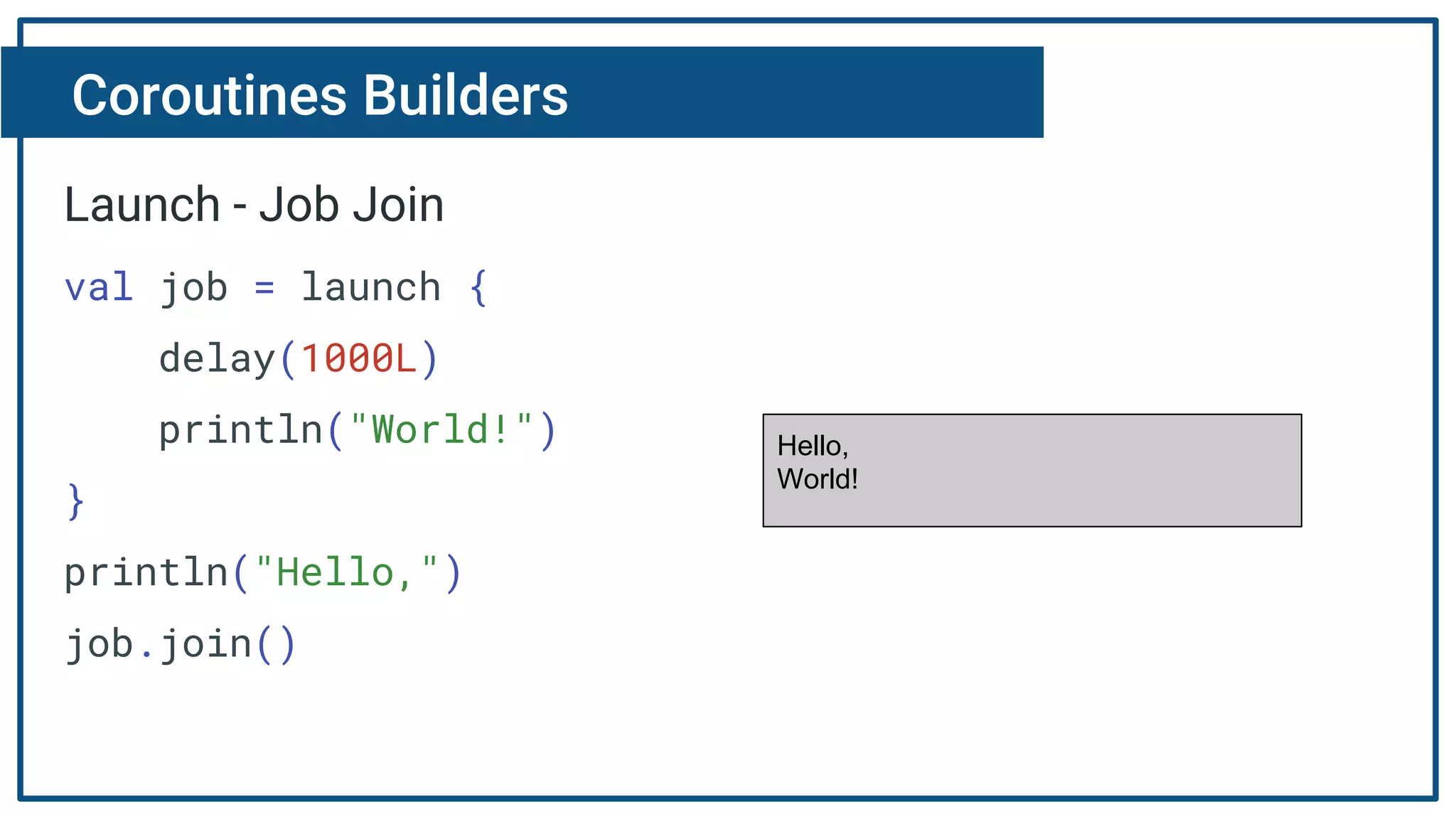
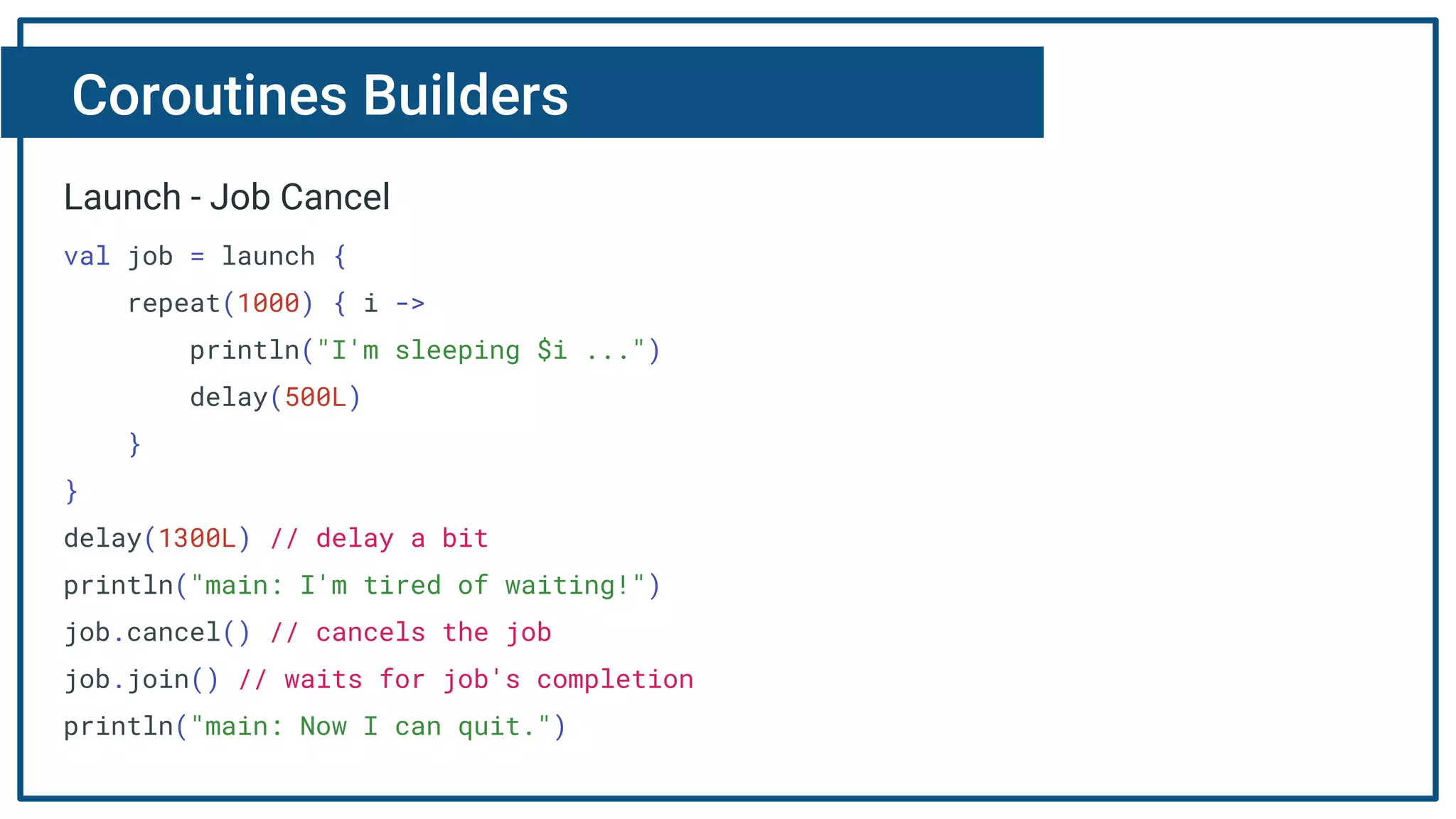
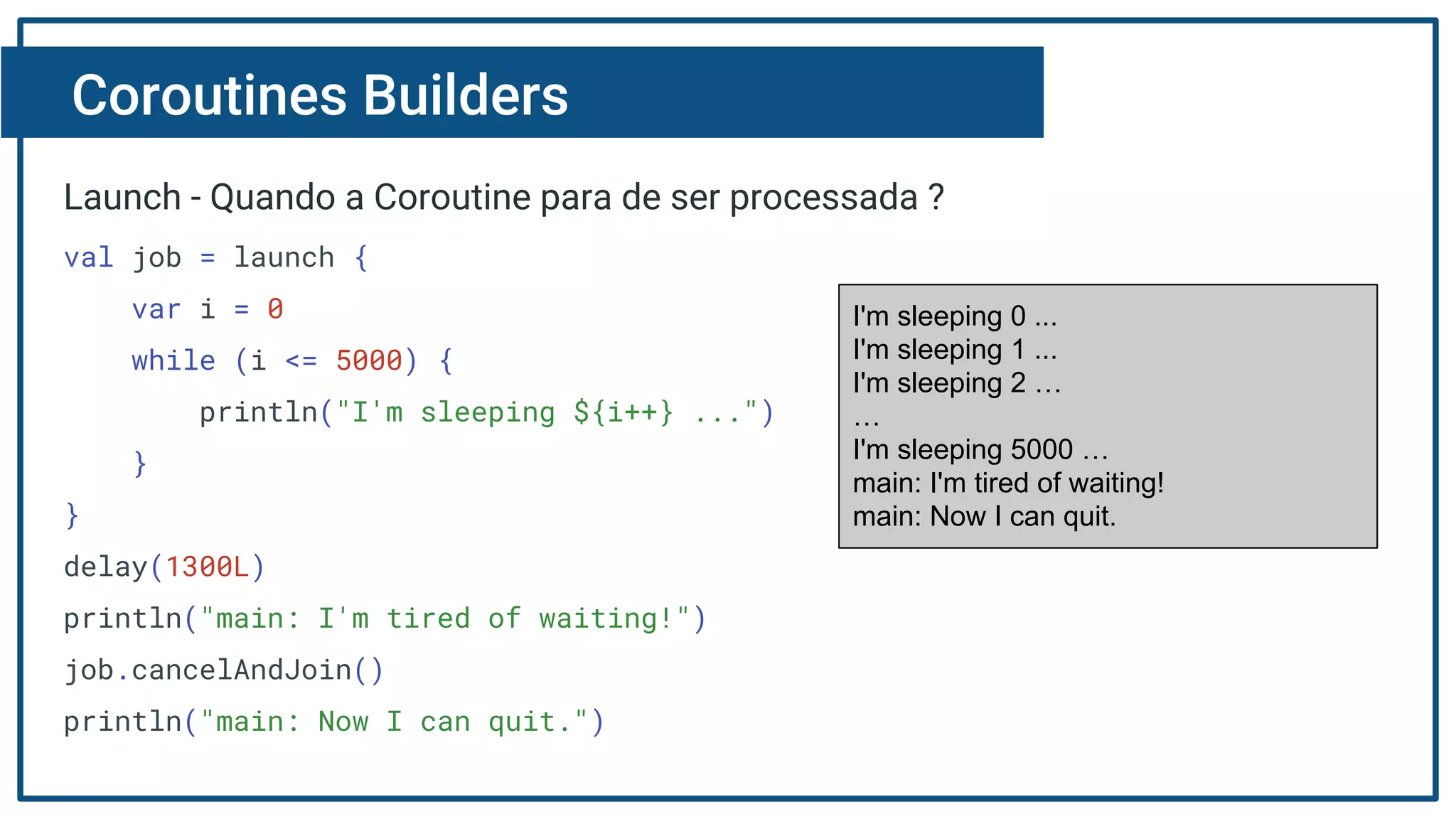
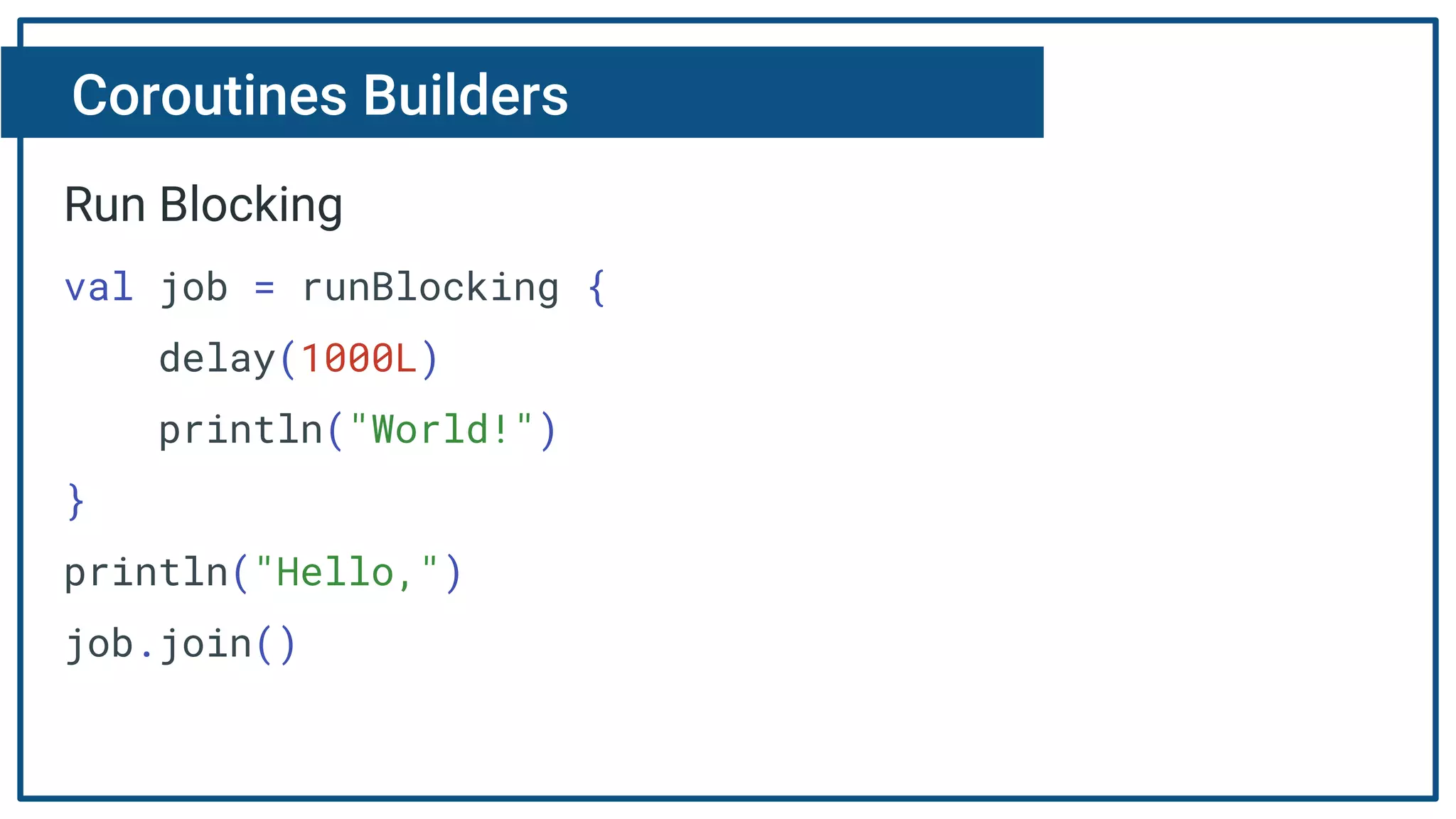
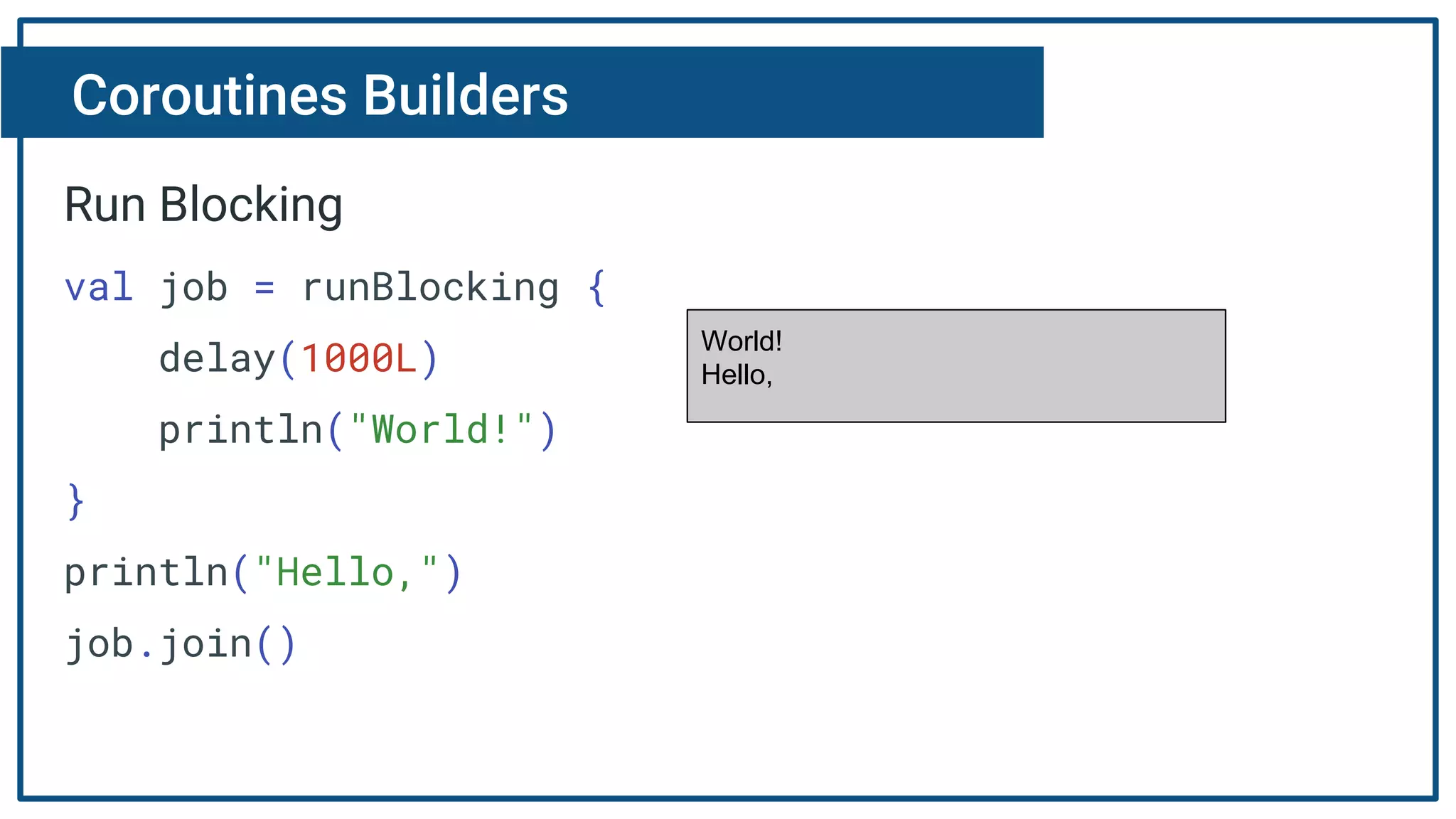
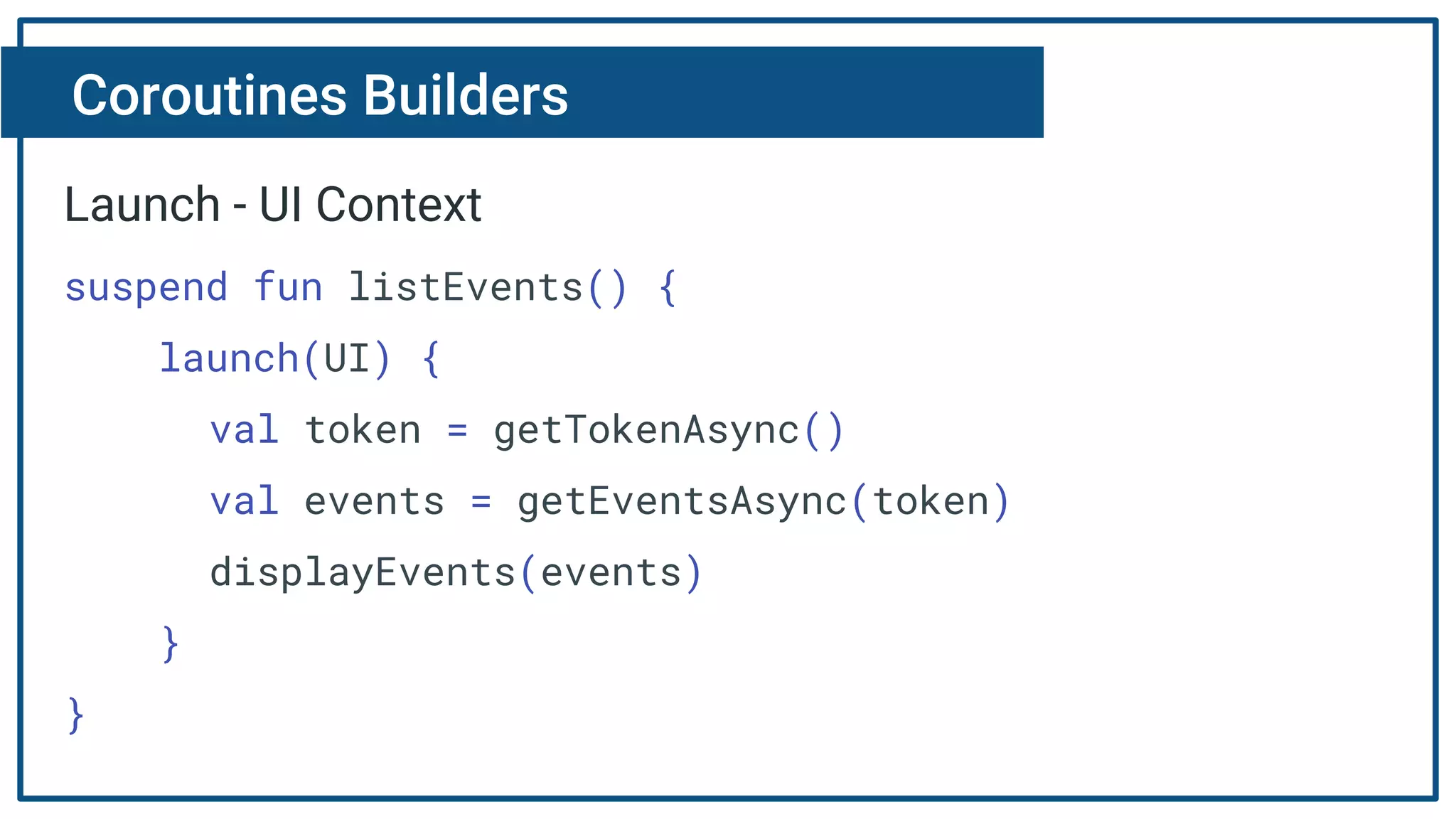
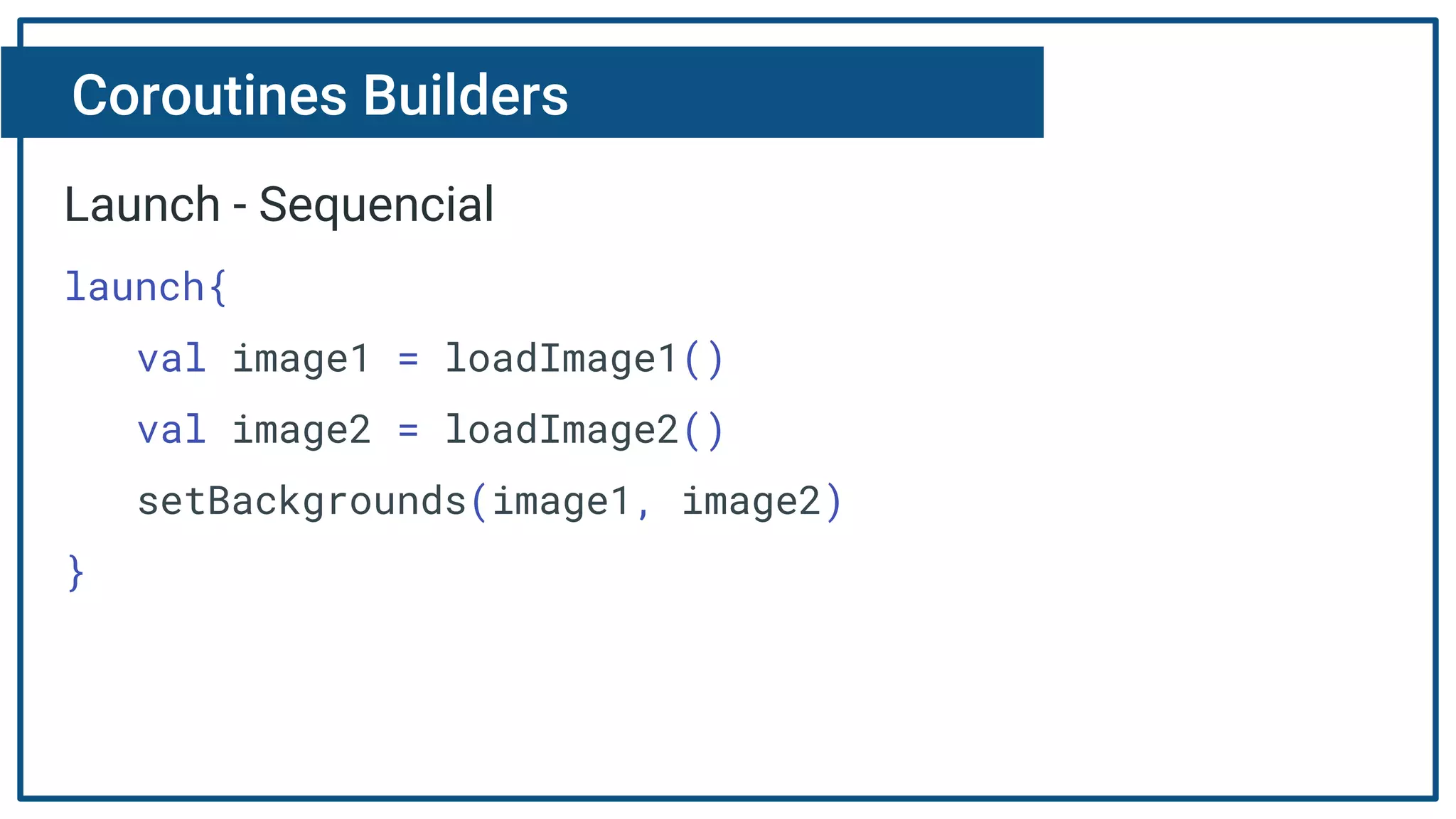
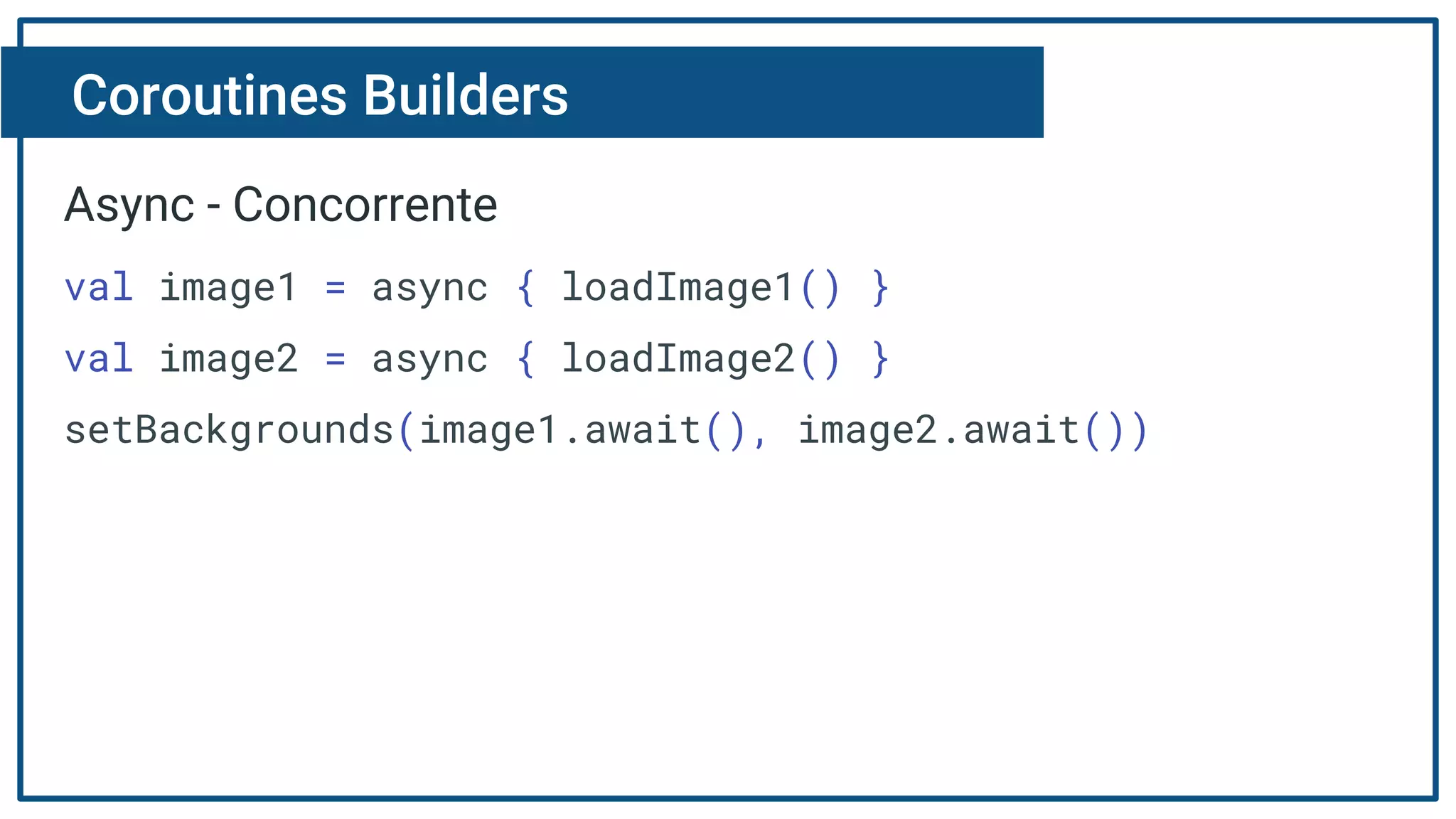
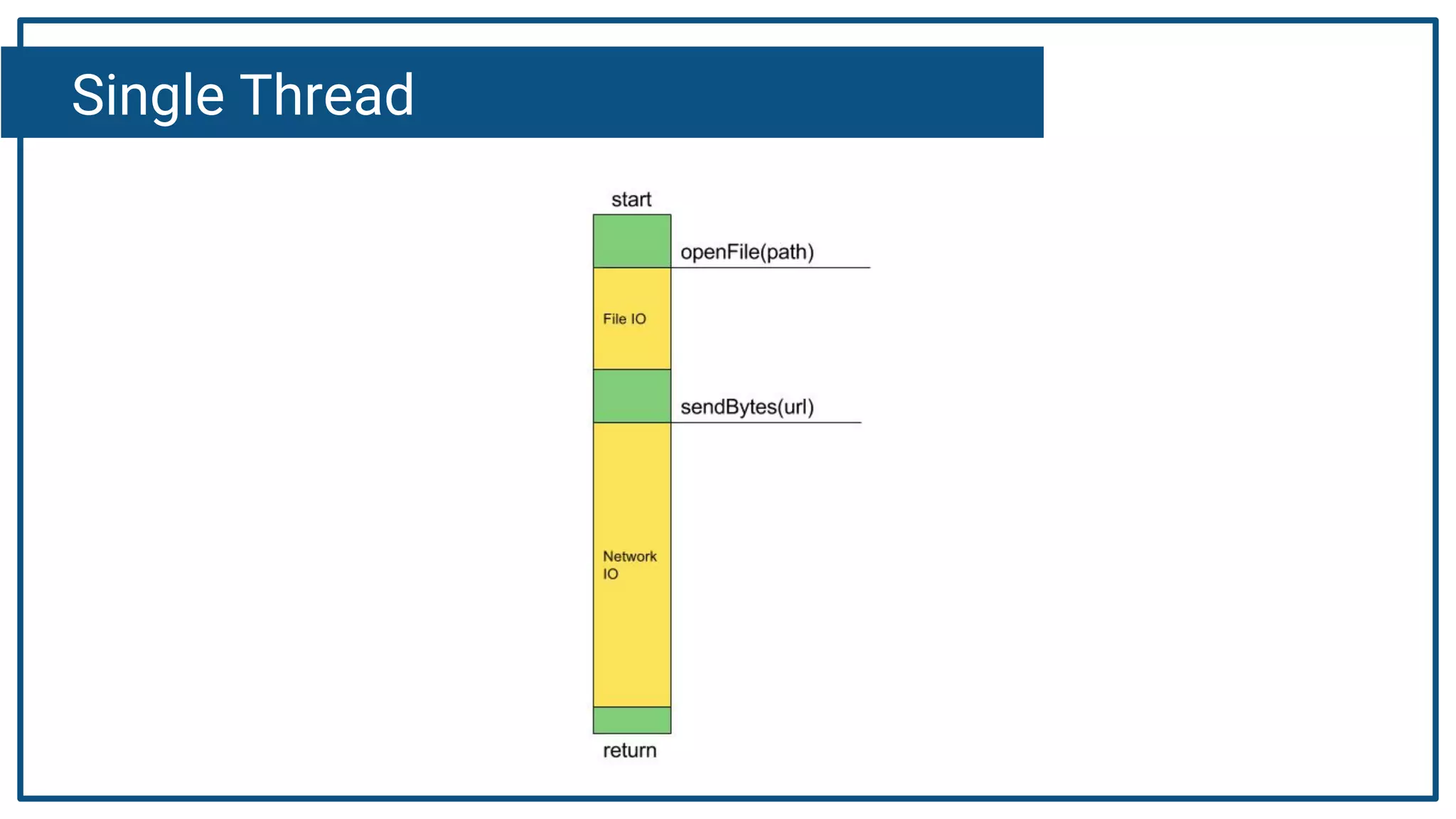
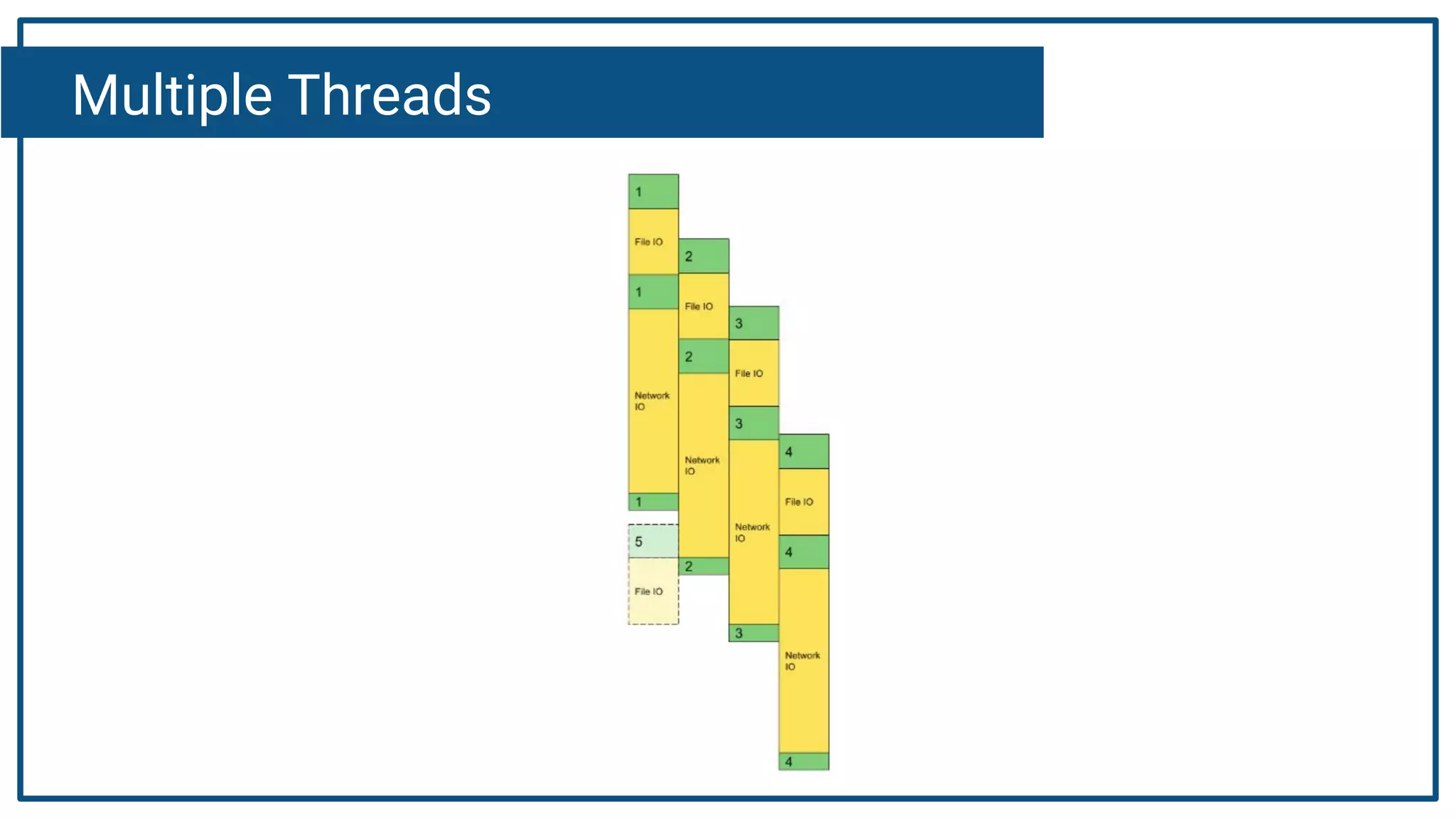
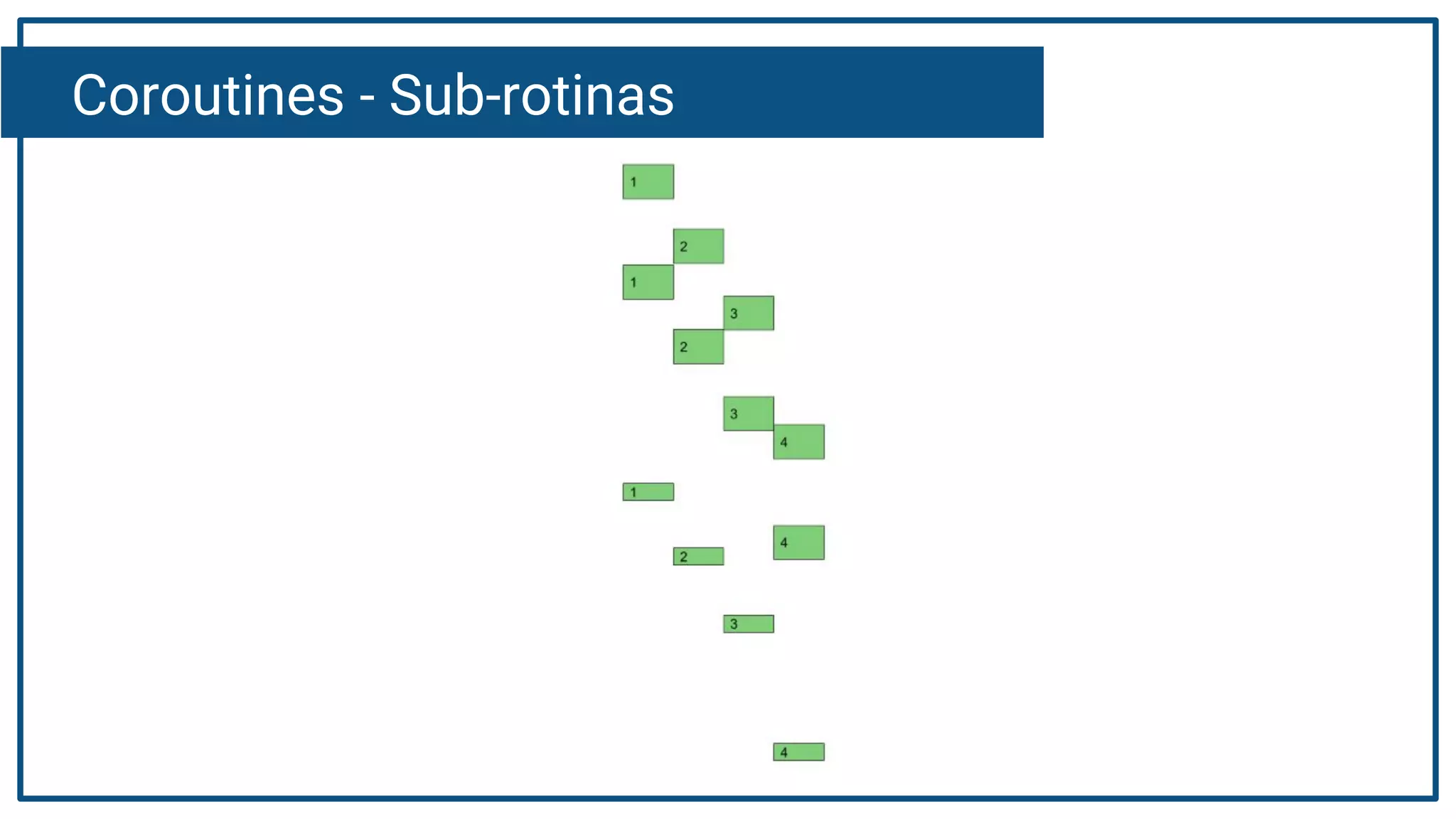
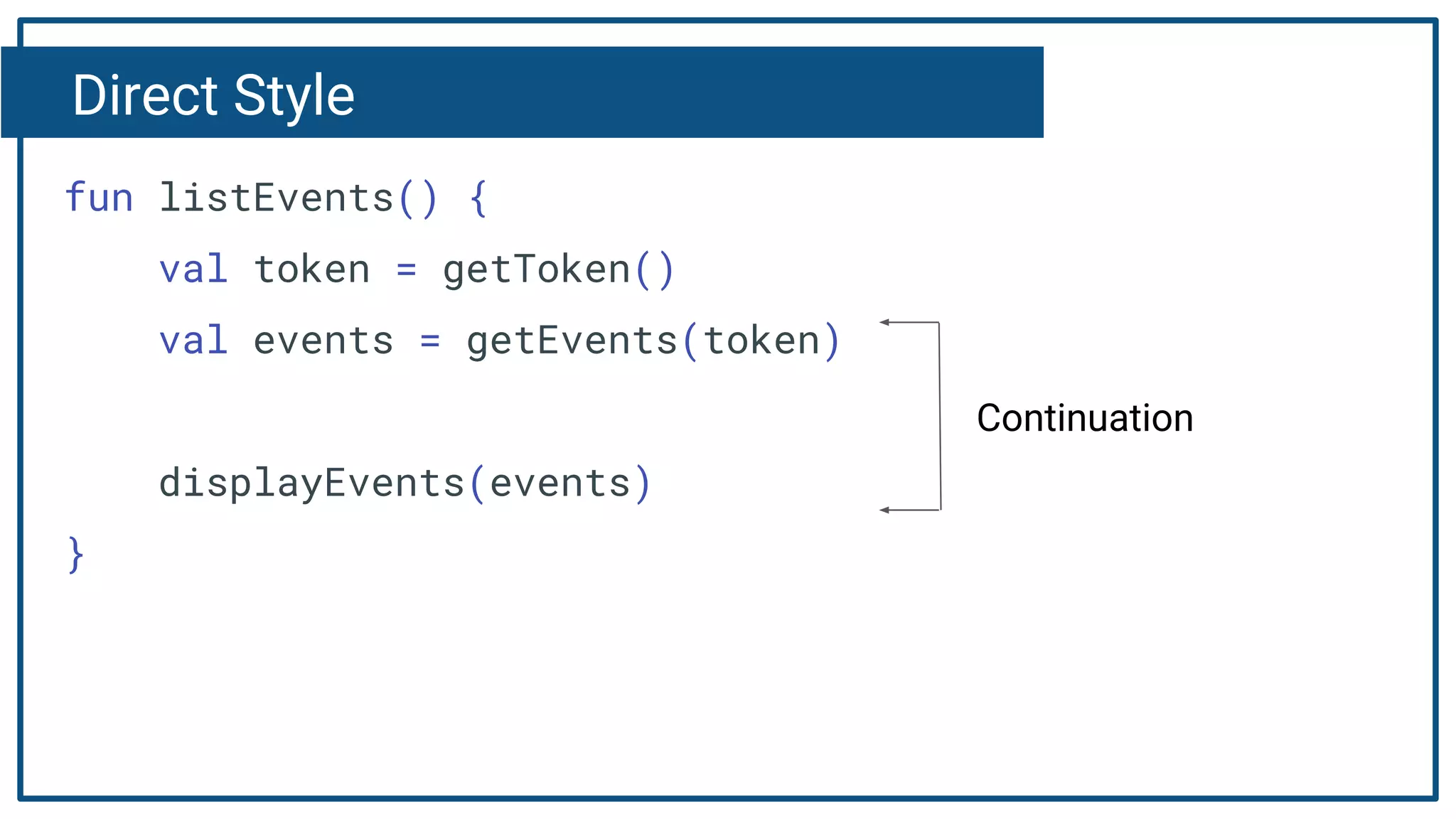
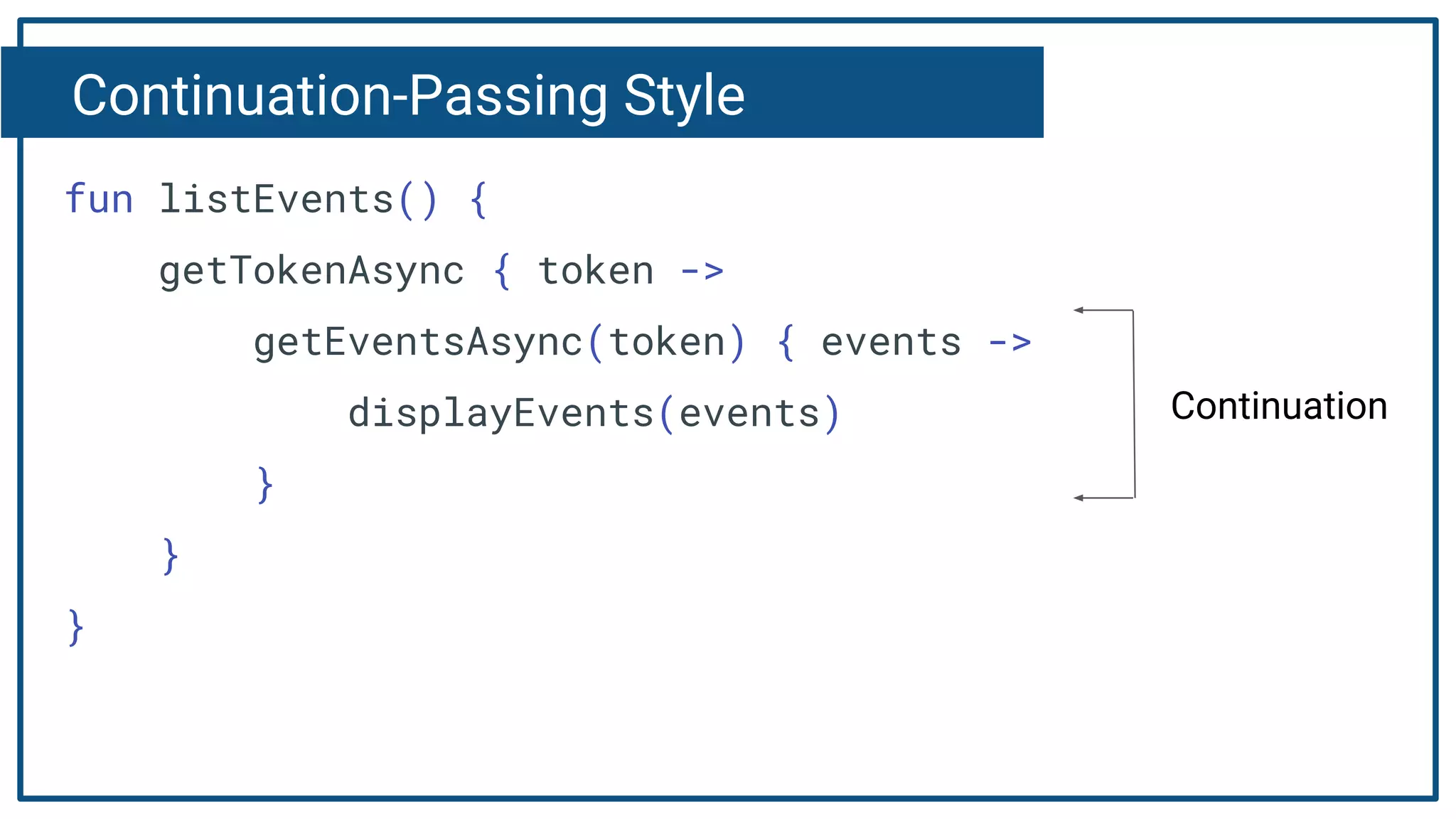
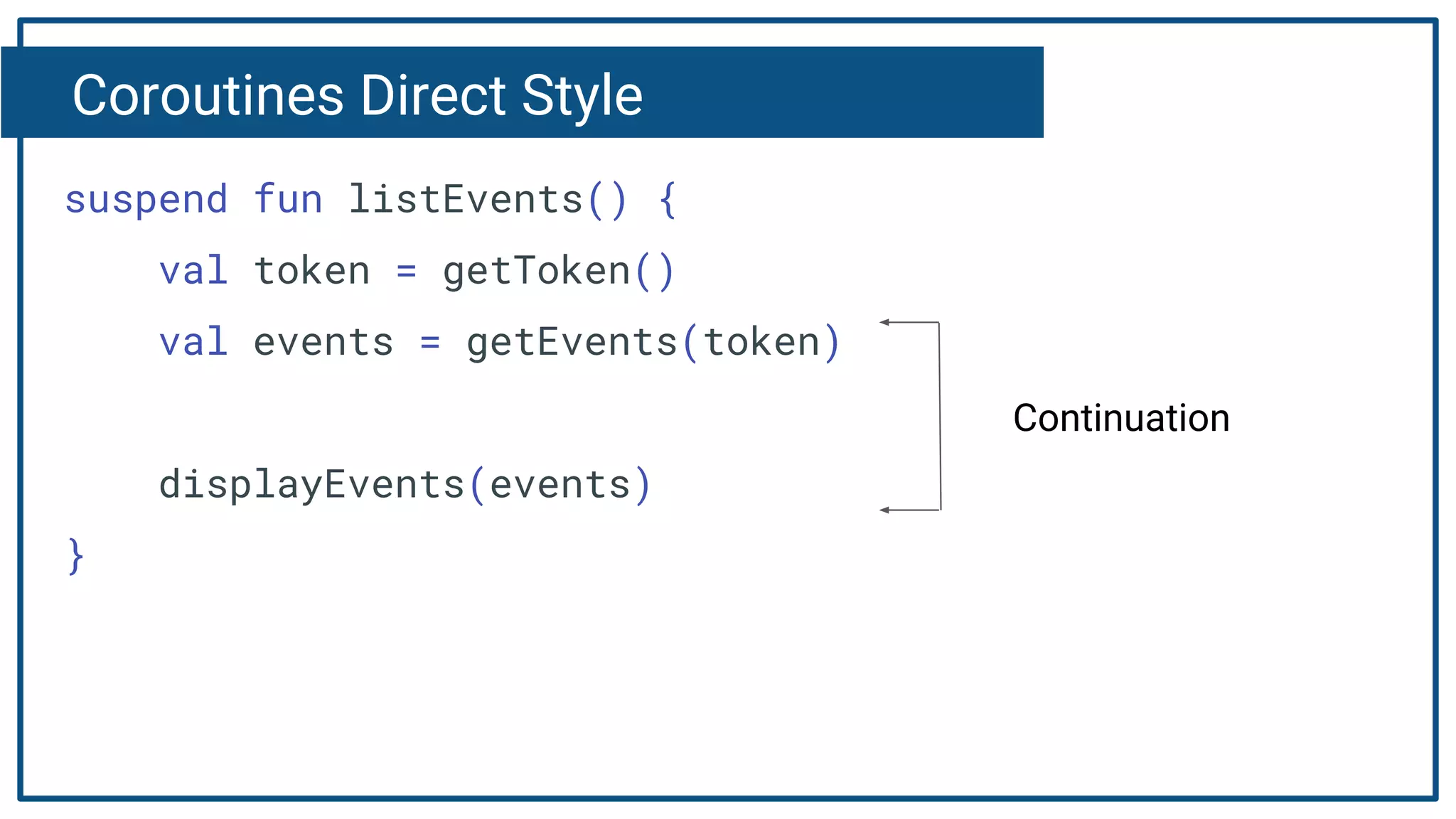
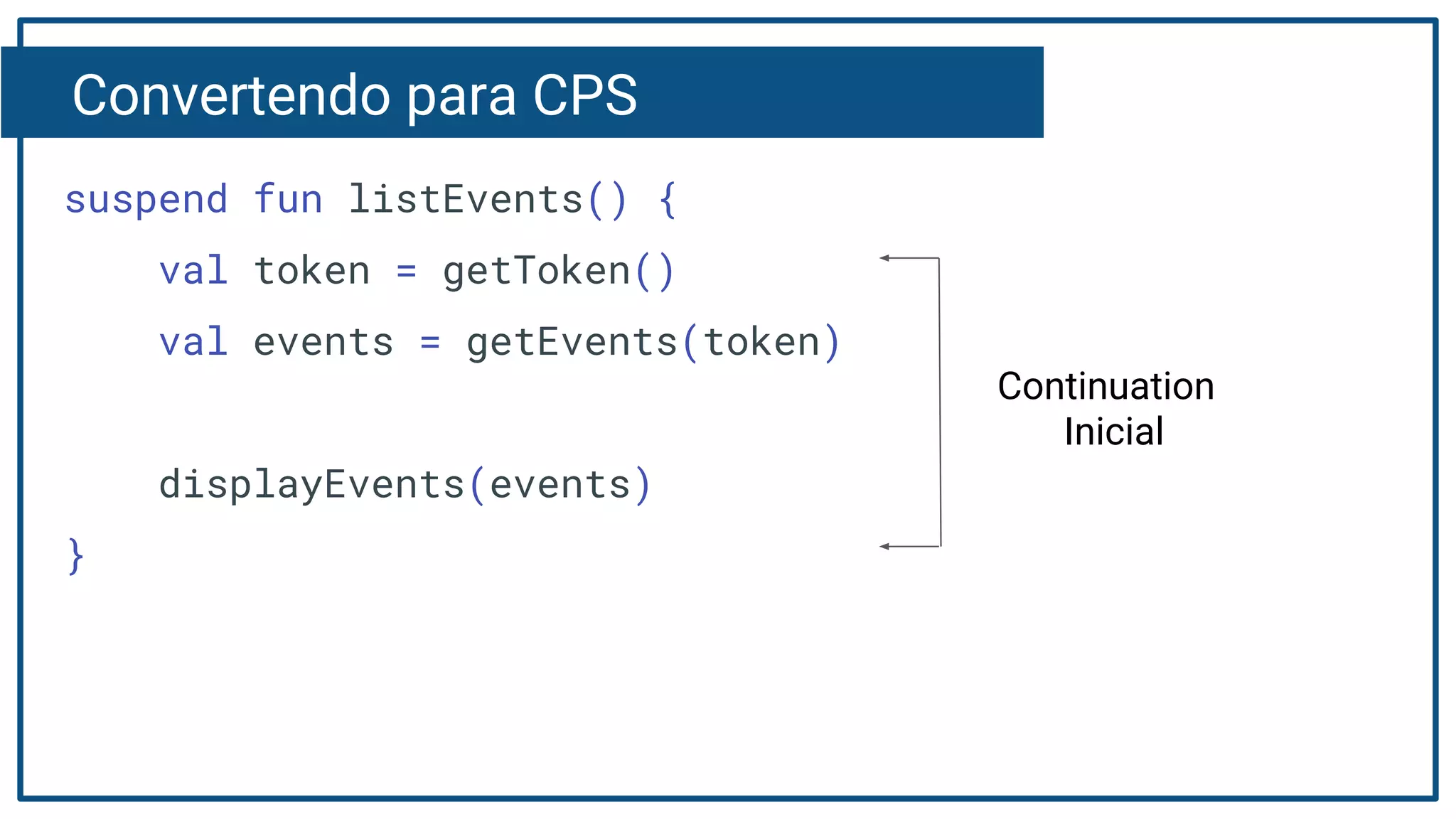
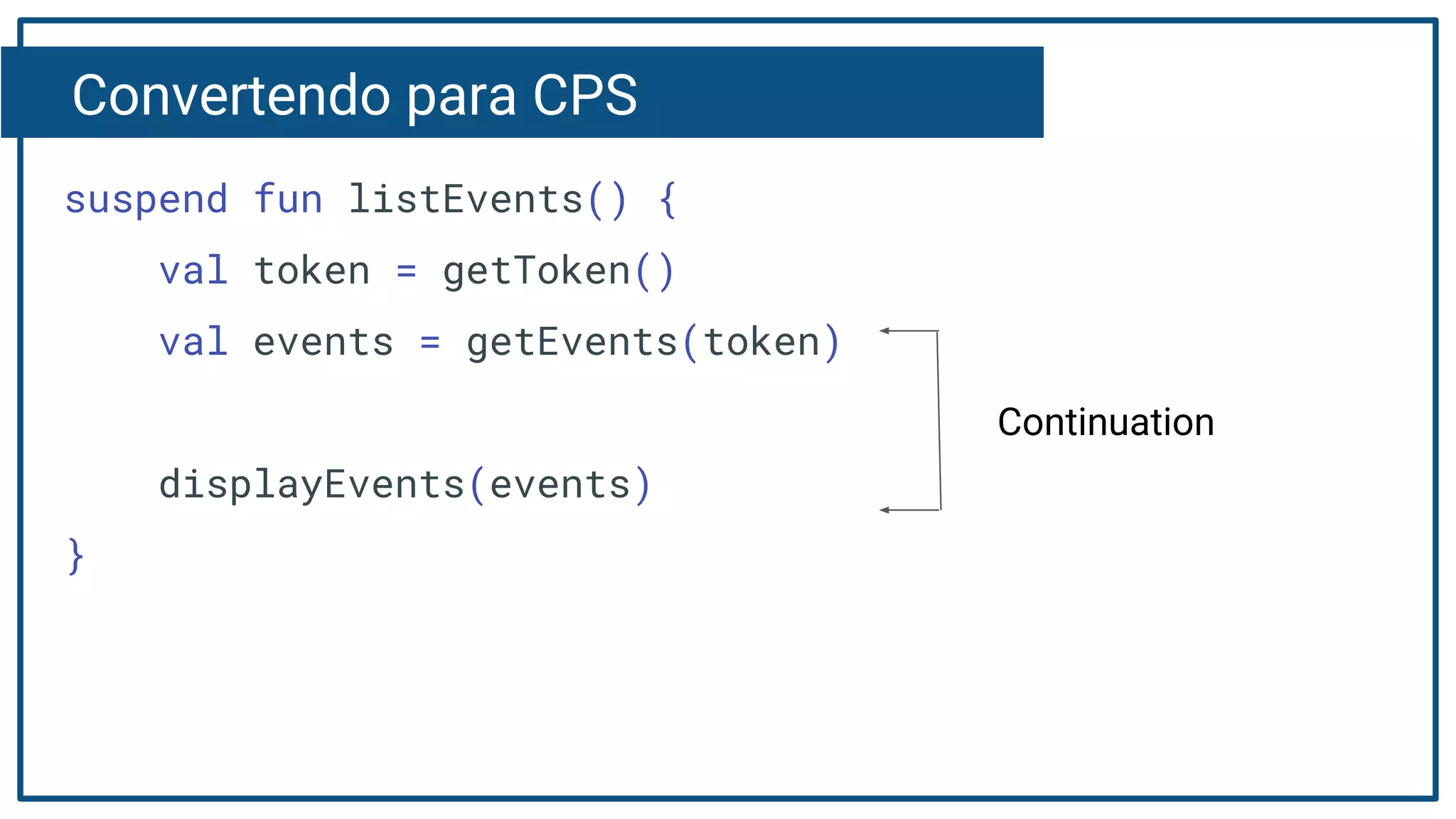
The document discusses Kotlin coroutines and how they allow writing asynchronous code in a sequential way. Coroutines create lightweight threads to handle asynchronous code, allowing developers to write code sequentially without callbacks. This is done by converting coroutine code internally to continuation-passing style. Libraries can also be adapted to work with coroutines by converting callback-based APIs to return suspensions.