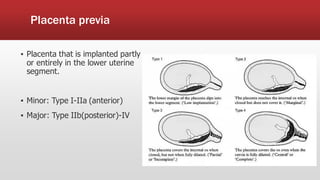
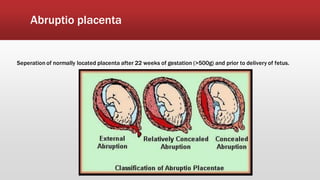
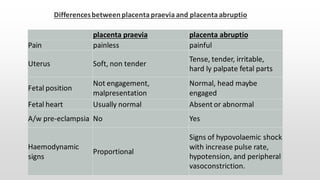
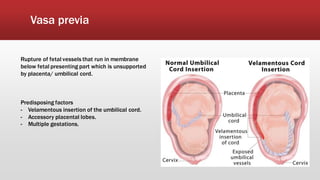
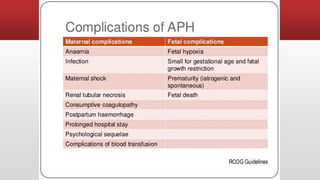
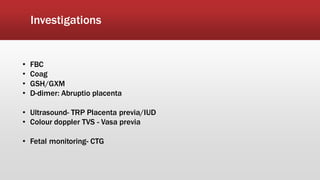
This document discusses antepartum hemorrhage (APH), or bleeding from the genital tract during pregnancy before labor begins. APH affects 3-3% of pregnancies and is more common in multiparous women. It is considered an obstetric emergency and can threaten the lives of the mother and fetus if left untreated. Causes include placenta previa, placenta abruption, and vasa previa. Management involves monitoring the mother and fetus, appropriate testing, and often early delivery to reduce risks of complications.