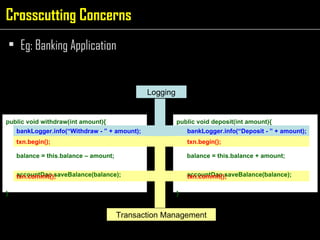
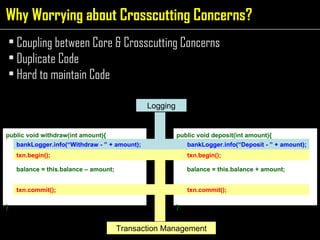
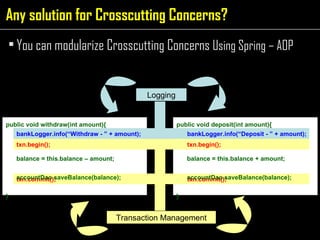
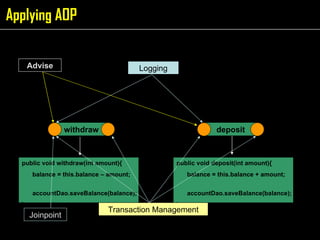
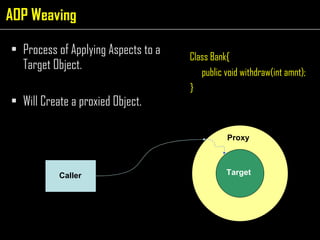
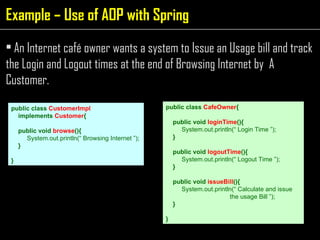
The document discusses aspect-oriented programming (AOP) using Spring to modularize cross-cutting concerns like transaction management and logging. It provides examples of how logging and transaction code is duplicated across methods in a banking application. It then introduces AOP concepts like joinpoints, pointcuts, advice, and aspects to extract cross-cutting behavior into separate modules. Finally, it demonstrates how Spring AOP can be used to add login/logout advice around a customer's browsing method to track internet cafe usage.