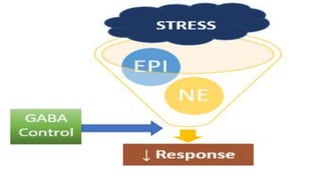
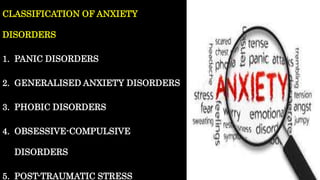
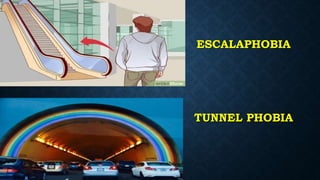
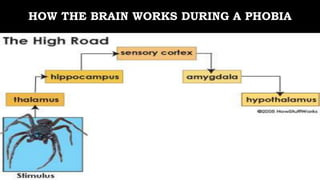
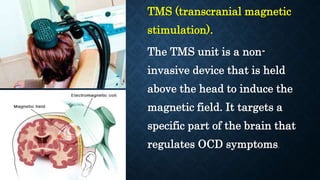
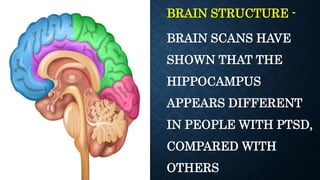
The document discusses various types of anxiety disorders including generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, phobias, obsessive compulsive disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder. It covers the defining features, potential causes and risk factors, symptoms, and common treatment approaches for each disorder which typically involve psychotherapy such as cognitive behavioral therapy and medication. Anxiety is described as a normal emotion but anxiety disorders involve excessive fear or worry that interferes with daily functioning.