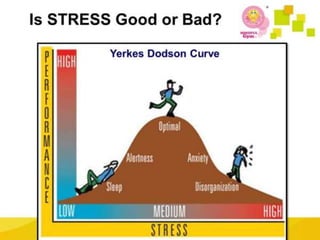
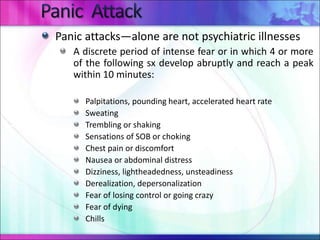
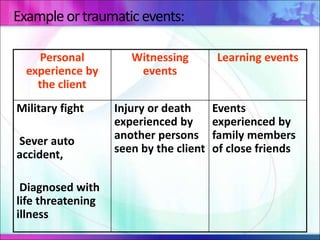
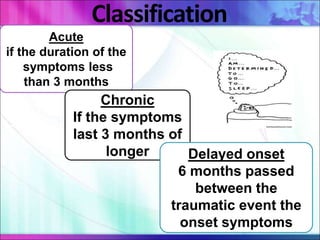
This document defines anxiety and anxiety disorders, listing their etiological factors and types. It discusses levels of anxiety from mild to panic, as well as genetic, biochemical, psychoanalytical, sociocultural, cognitive, and learning theories of causation. The major anxiety disorders described are generalized anxiety disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, phobias including social phobia and specific phobia, and panic disorder. Nursing care plans aim to help patients cope with anxiety and insomnia and reduce distress through reassurance, relaxation techniques, and controlling environmental stimuli.