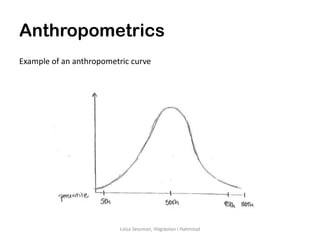
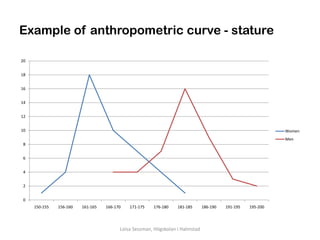
Anthropometrics is the measurement of human dimensions, proportions, postures, and ranges of motion. It is useful for designing workplaces, tools, furniture, and clothing. Anthropometric data describes human limitations and biomechanical issues. Most body dimensions follow a normal distribution across populations, with standard deviations around mean values. Anthropometric measurements need to be standardized, reliable, and valid. Data comes from sources like Pheasant & Haslegrave (2005) and self-collected data. Anthropometry is applied by designing for average individuals, the largest/smallest percentiles, or the entire population including those with disabilities.