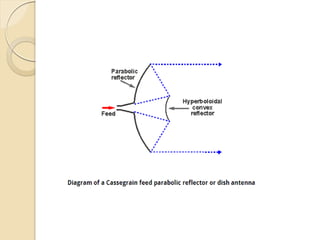
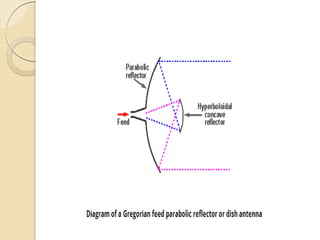
The document discusses the importance of feed systems for parabolic reflector antennas, emphasizing that the design of the feed element significantly affects overall performance. It outlines various types of feed systems, including focal, cassegrain, gregorian, and offset systems, each suited for different applications. Additionally, it describes how radiating elements illuminate the reflector and the challenges associated with achieving optimal performance at different frequencies.