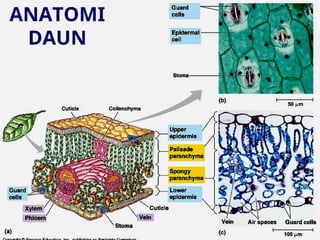
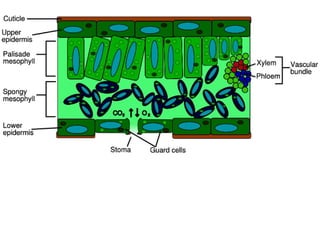
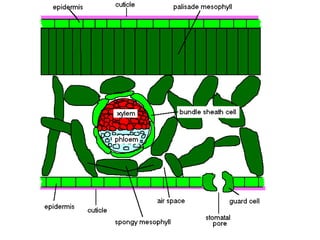
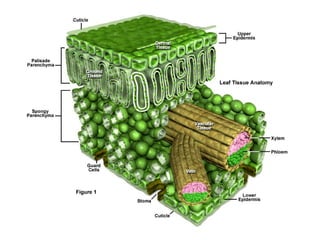
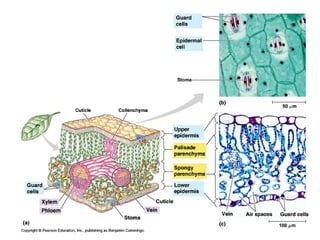
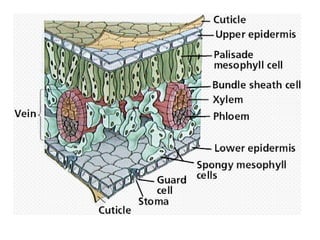
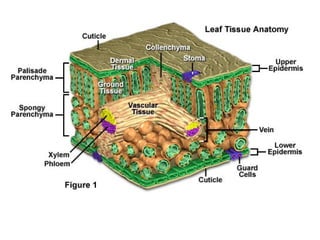
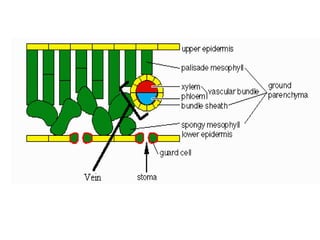
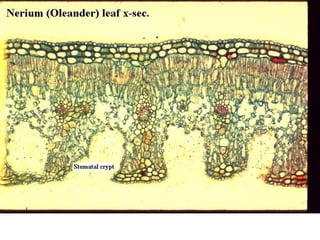
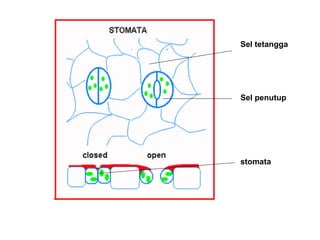
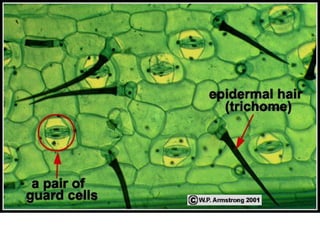
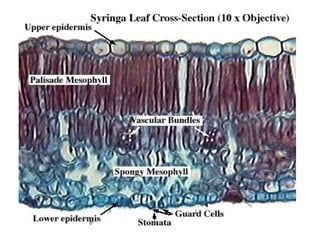
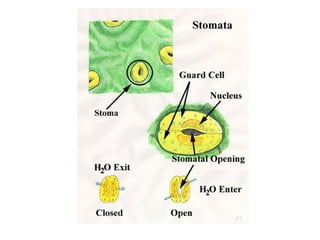
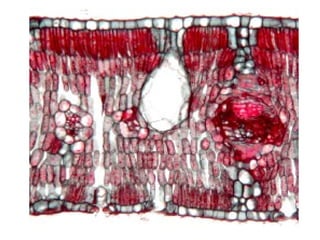
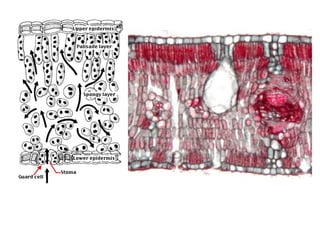
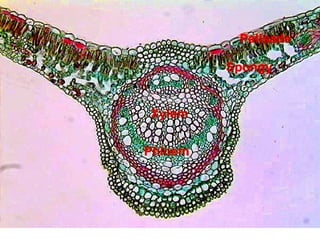
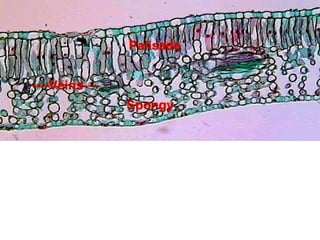
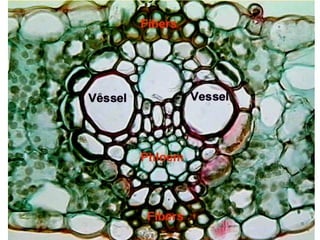
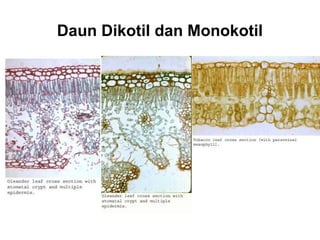
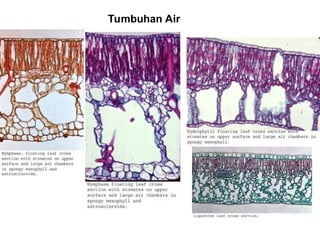
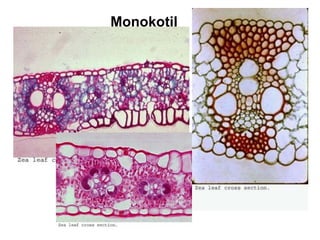
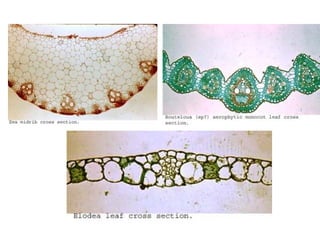
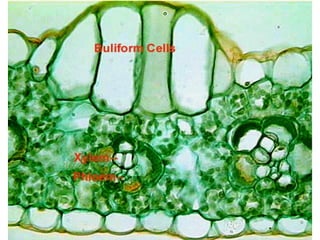
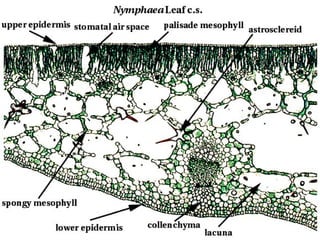
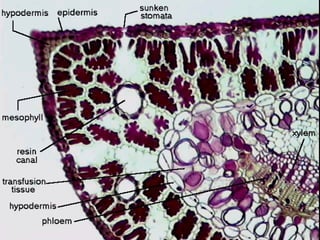
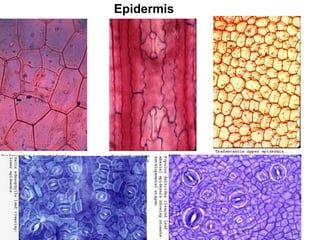
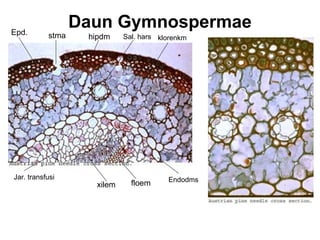
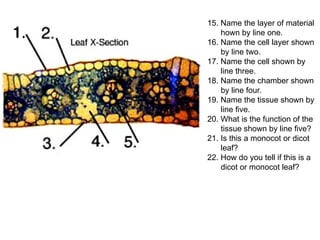
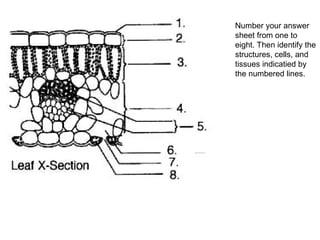
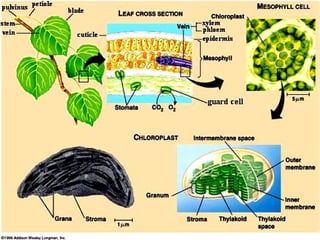
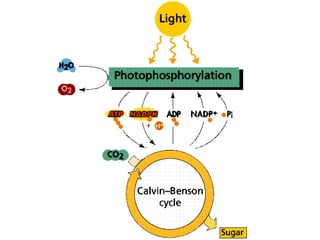
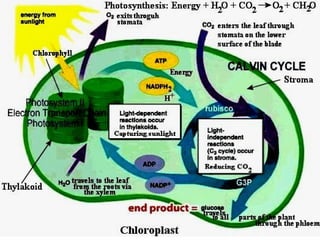
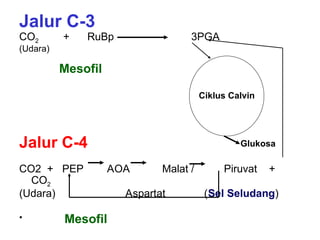
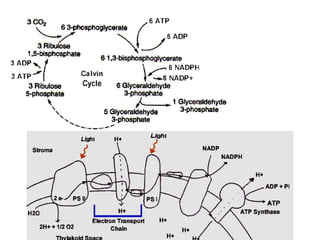
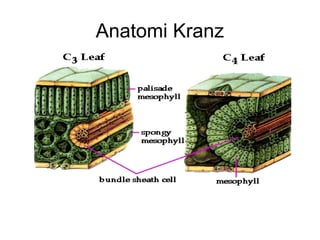
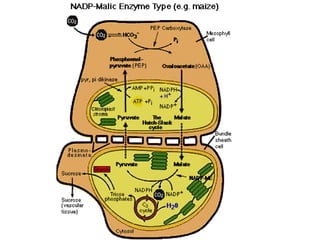
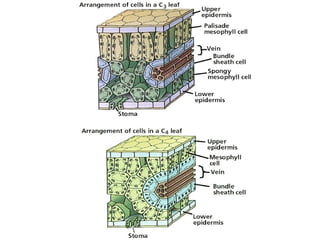
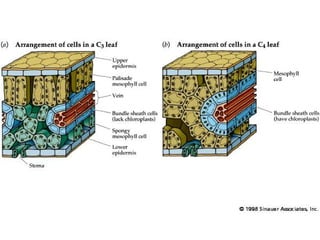
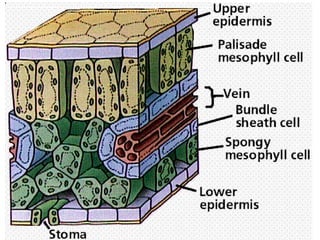
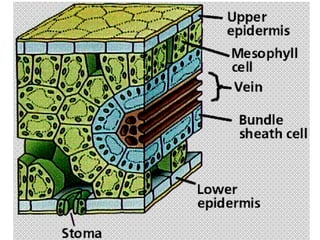
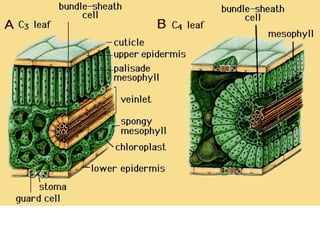
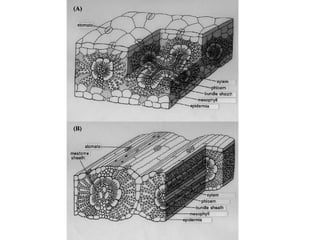
Dokumen ini menjelaskan anatomi daun dan fungsinya, termasuk bagian-bagian seperti epidermis, mesofil, dan berkas pengangkut. Fungsi utama daun terkait dengan fotosintesis, respirasi, dan transpirasi. Selain itu, ada juga penjelasan tentang adaptasi fisiologis seperti anatomi Kranz untuk efektivitas dalam jalur fotosintesis C-4.