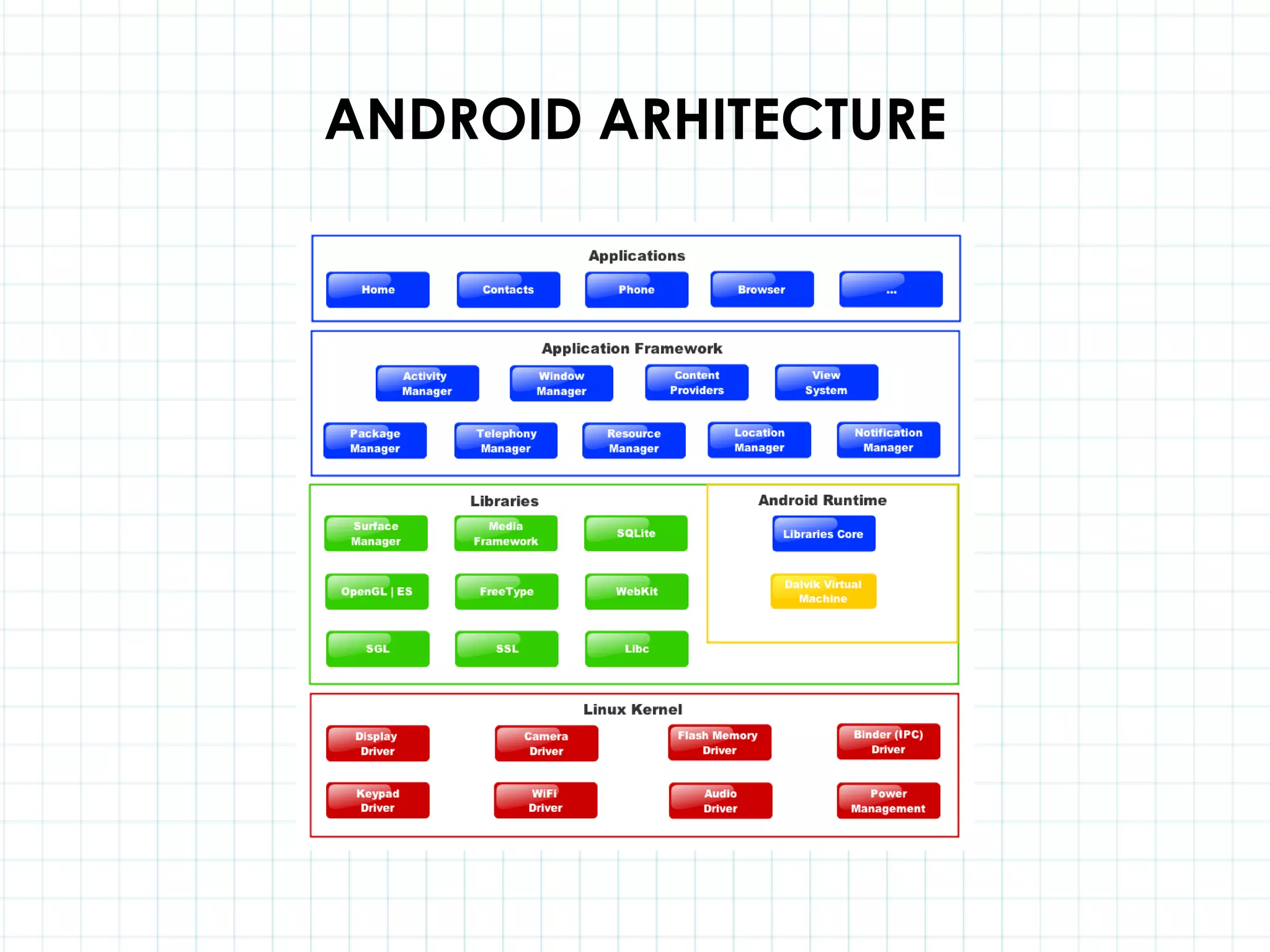
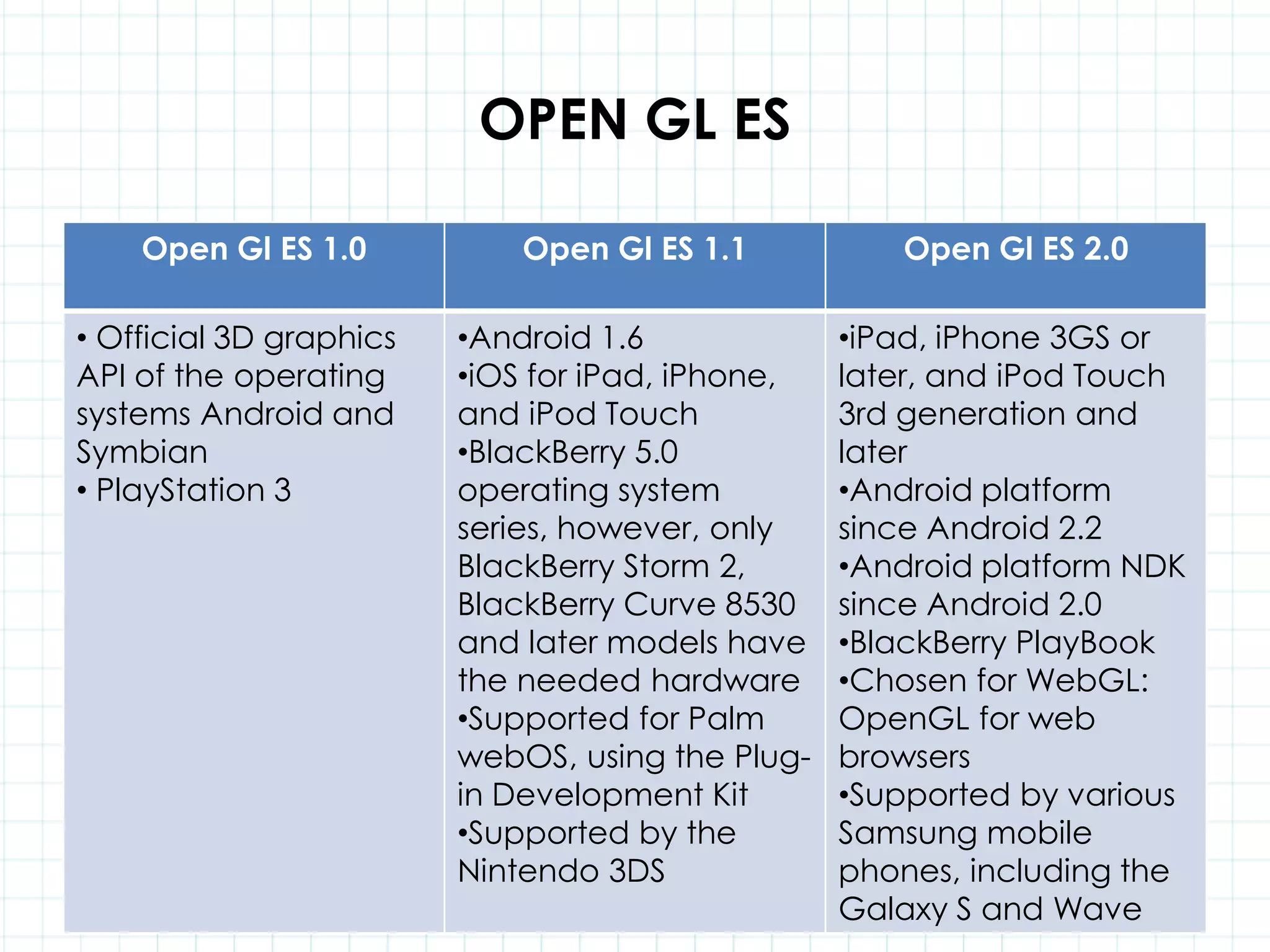
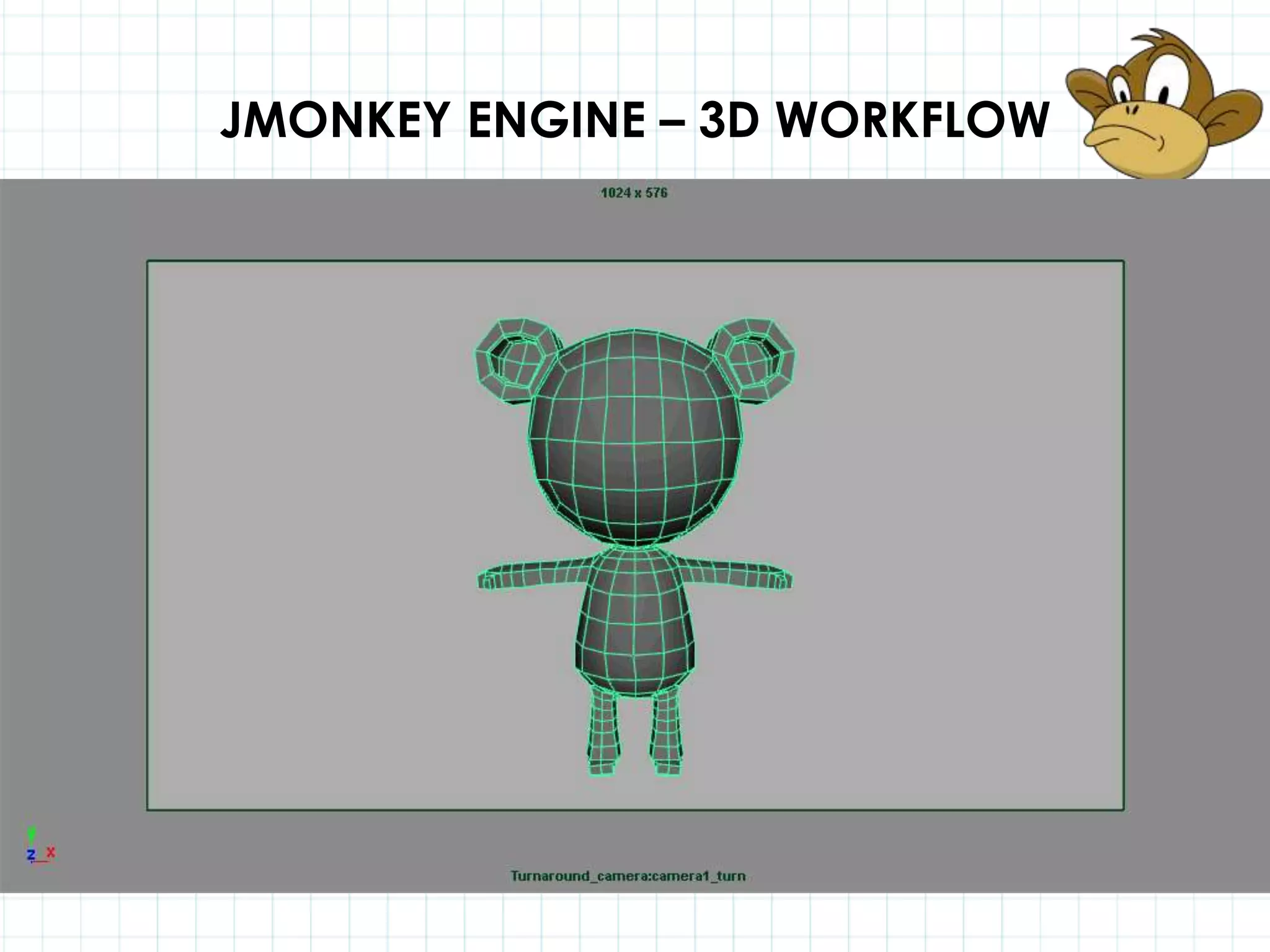
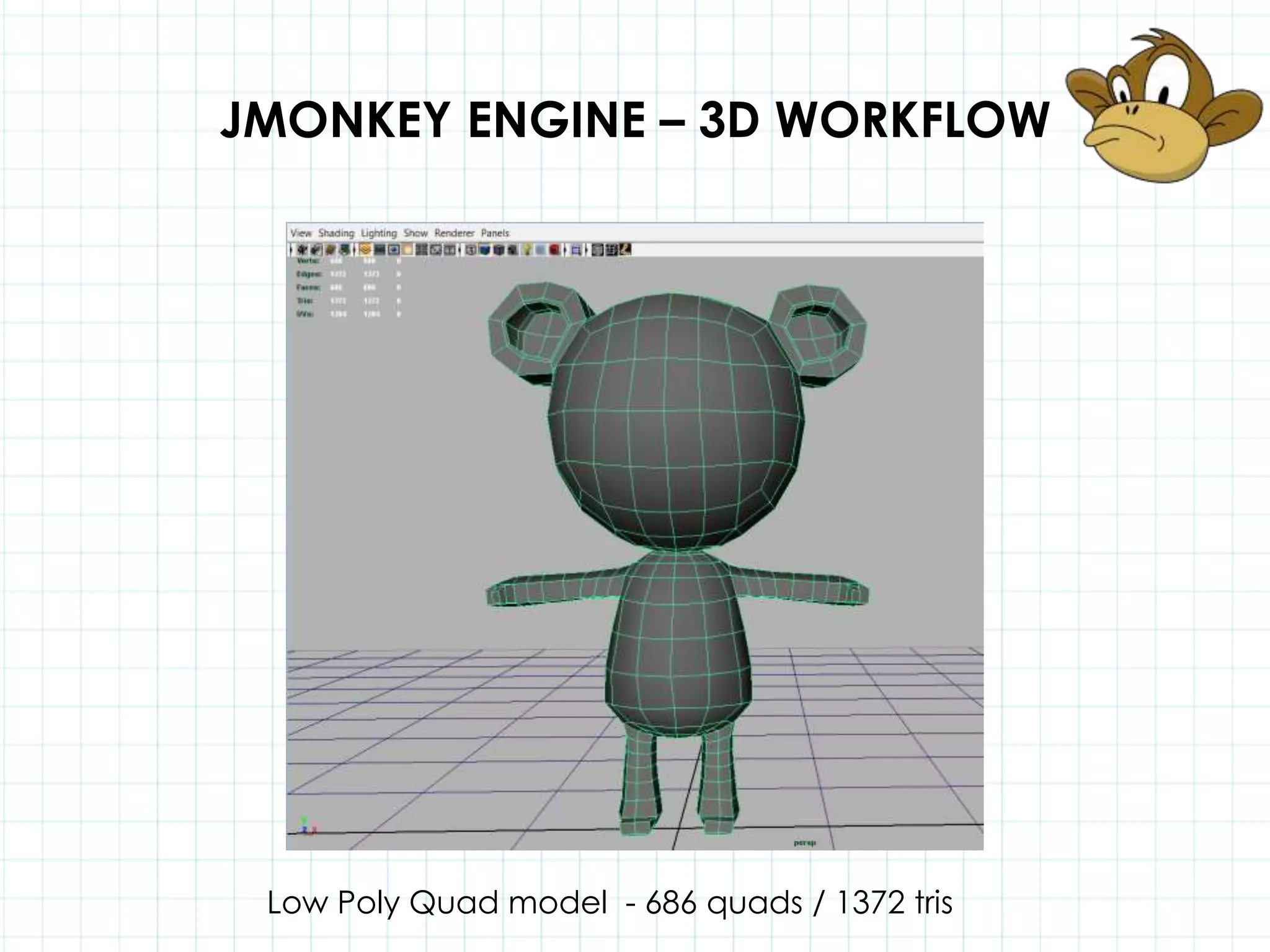
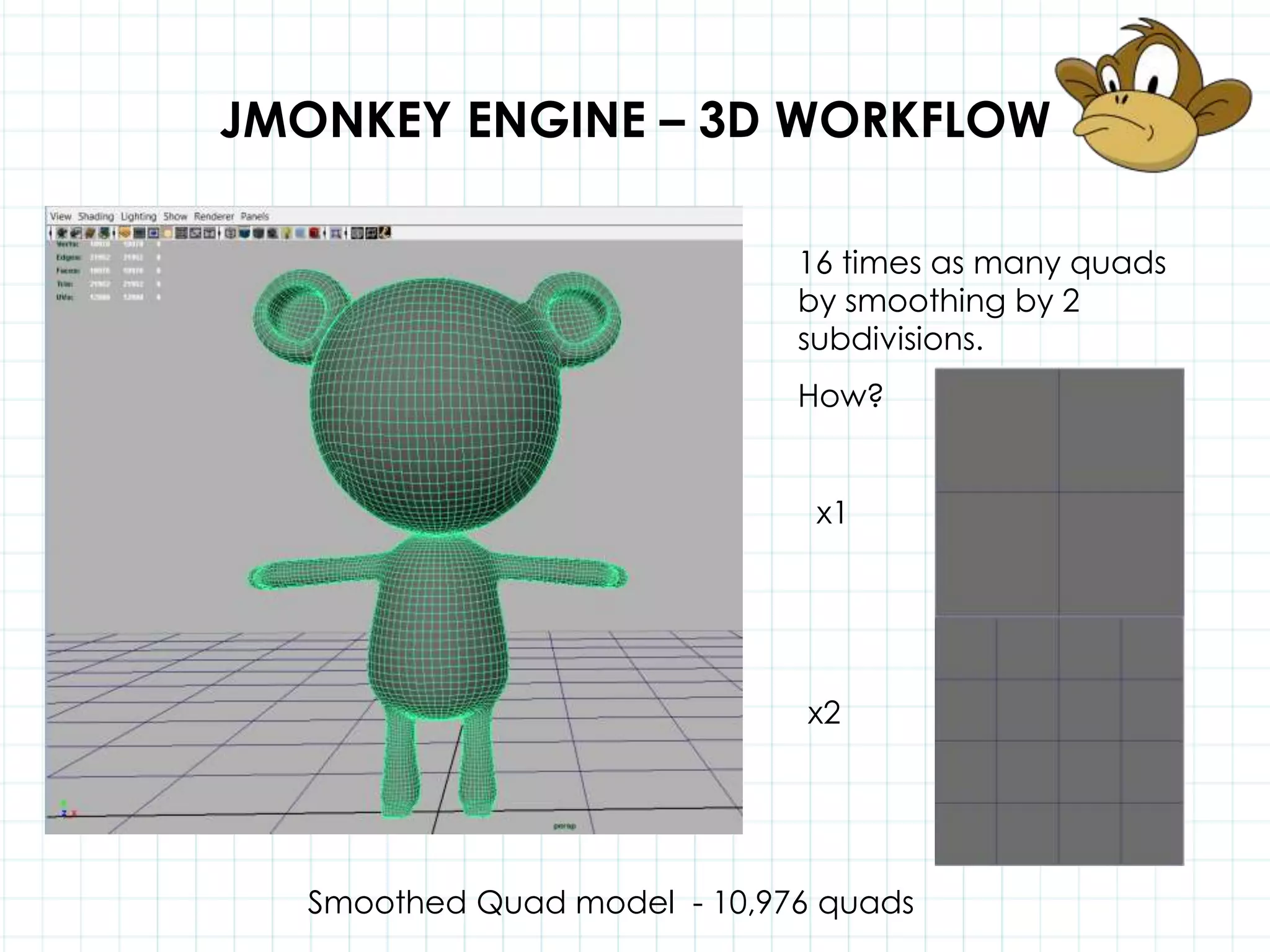
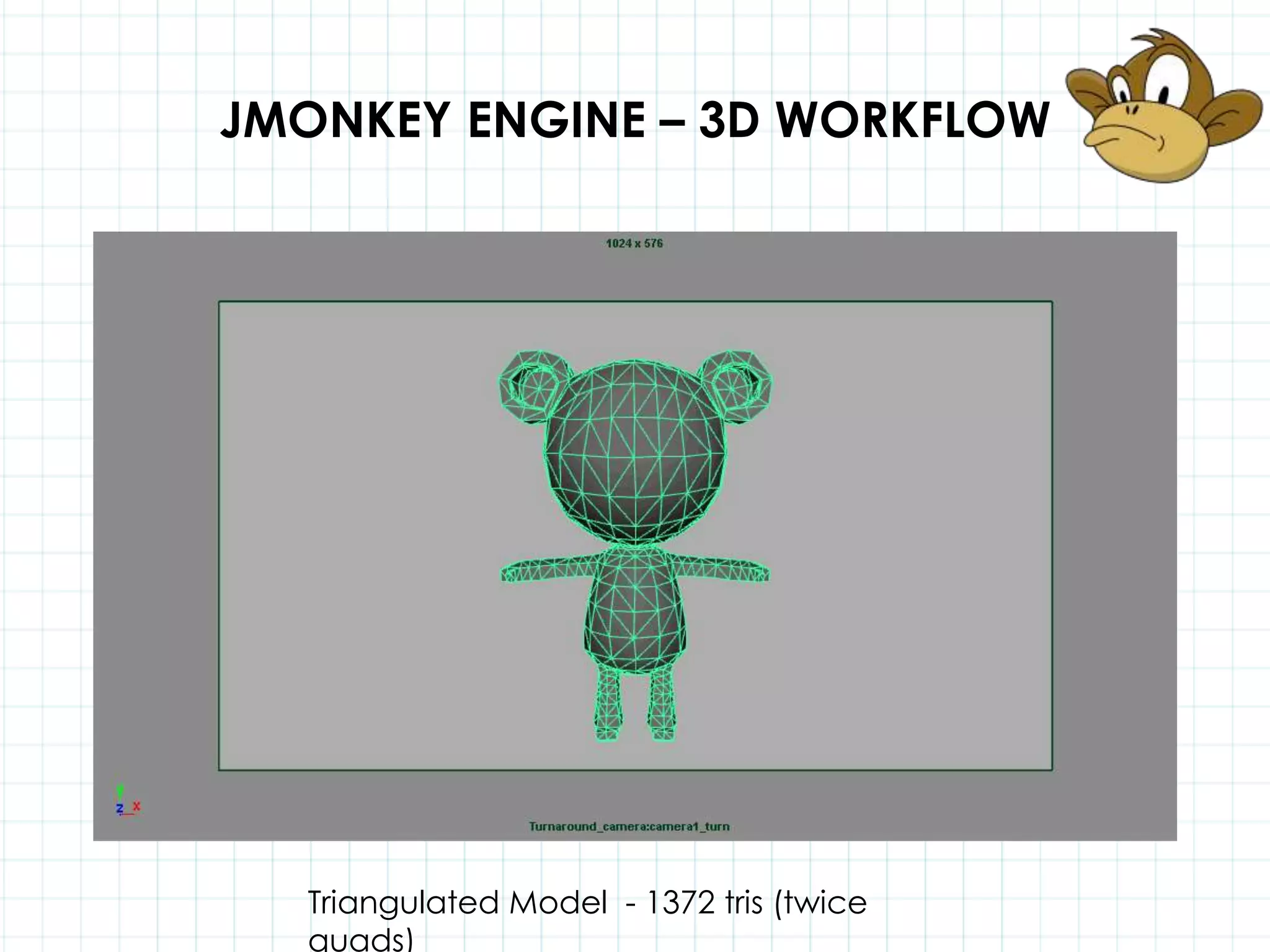
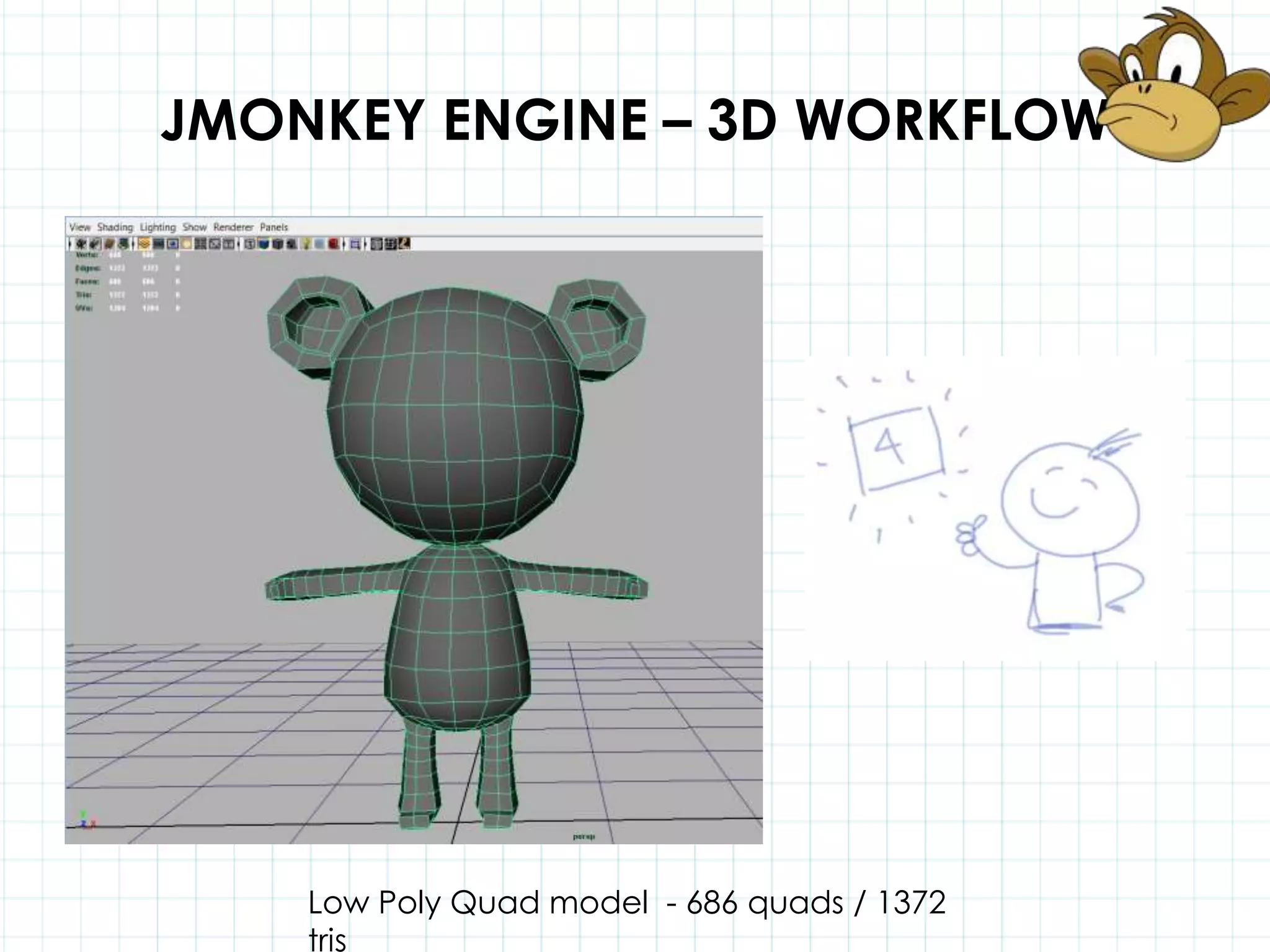
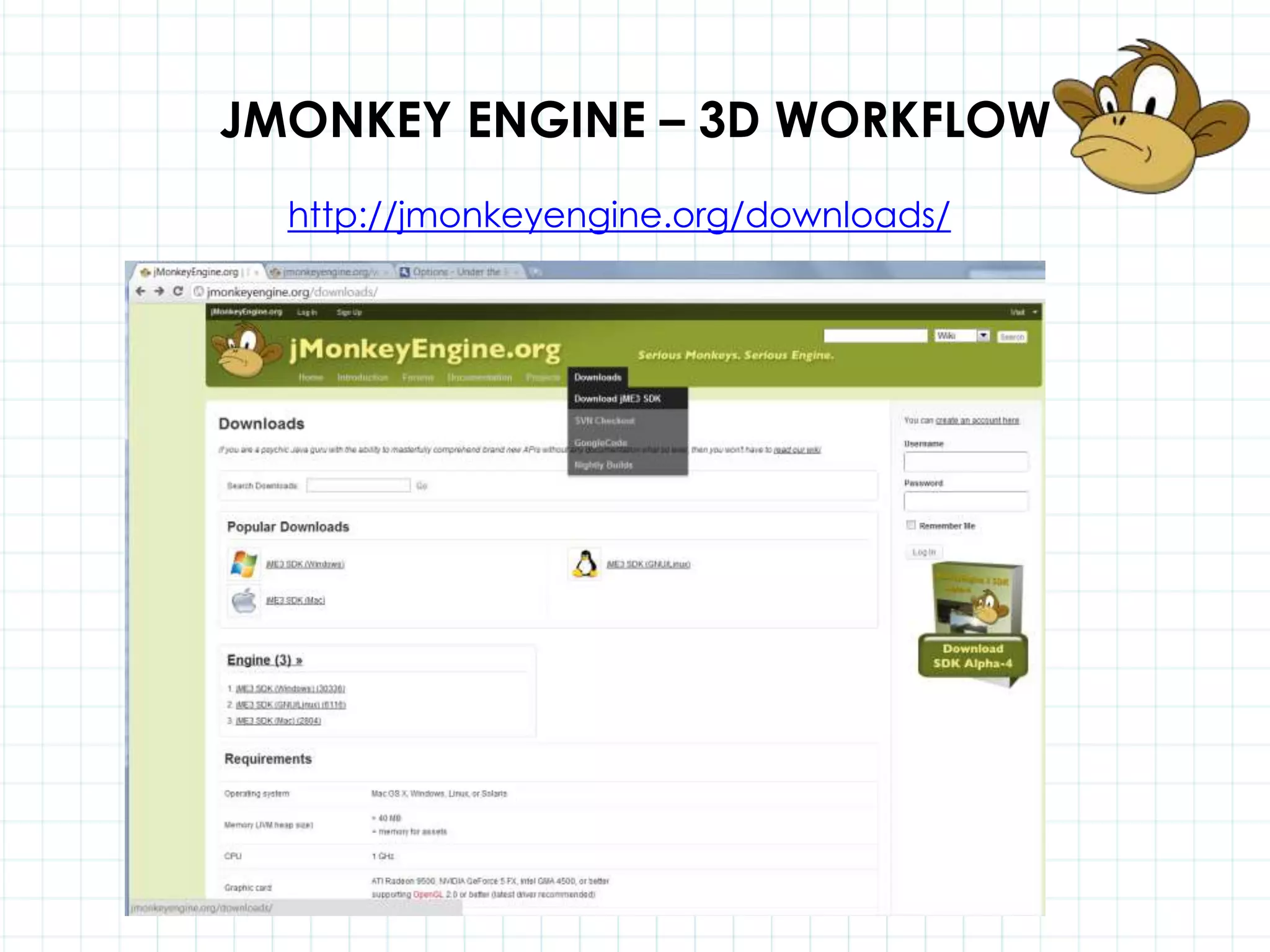
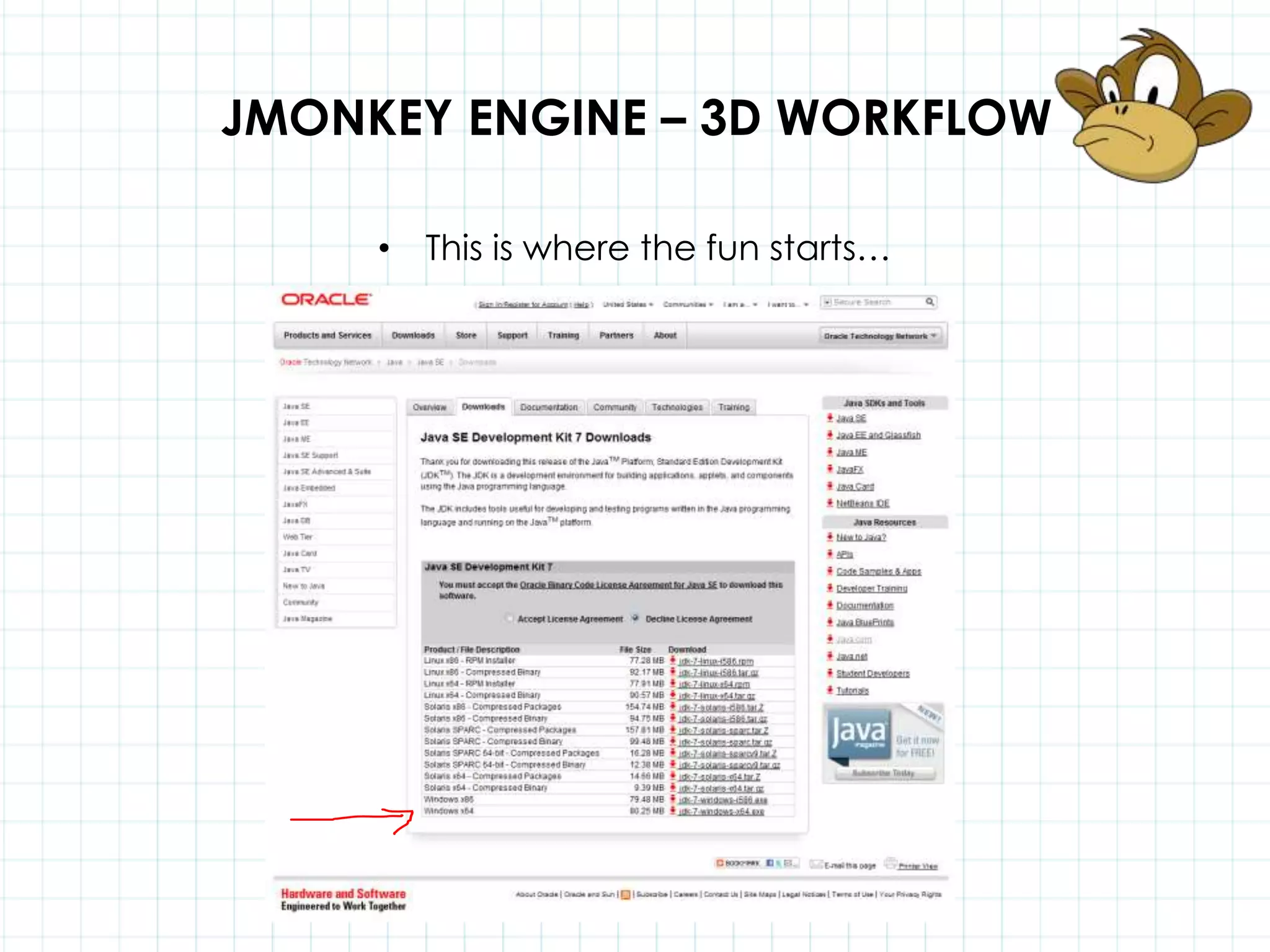
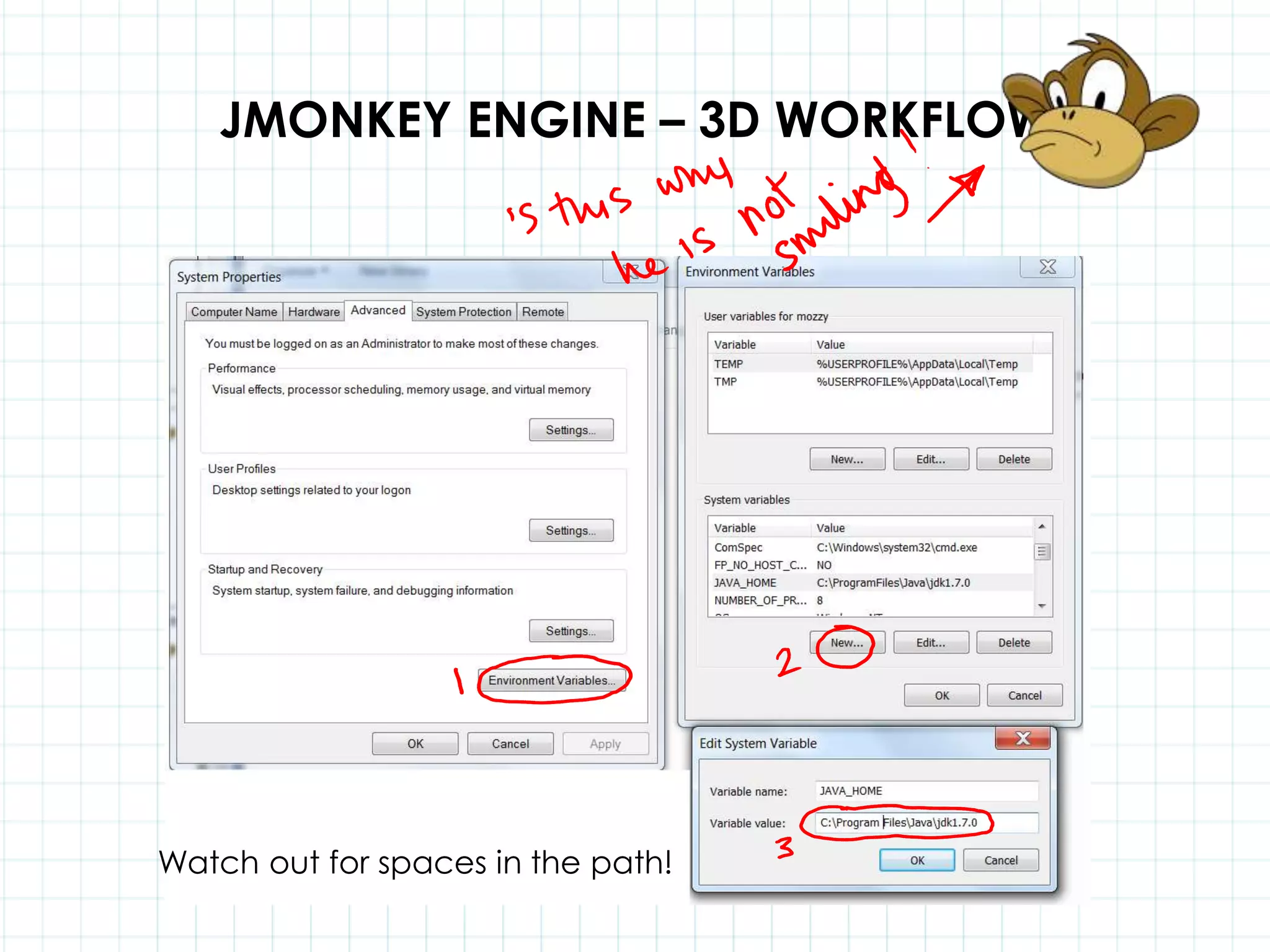
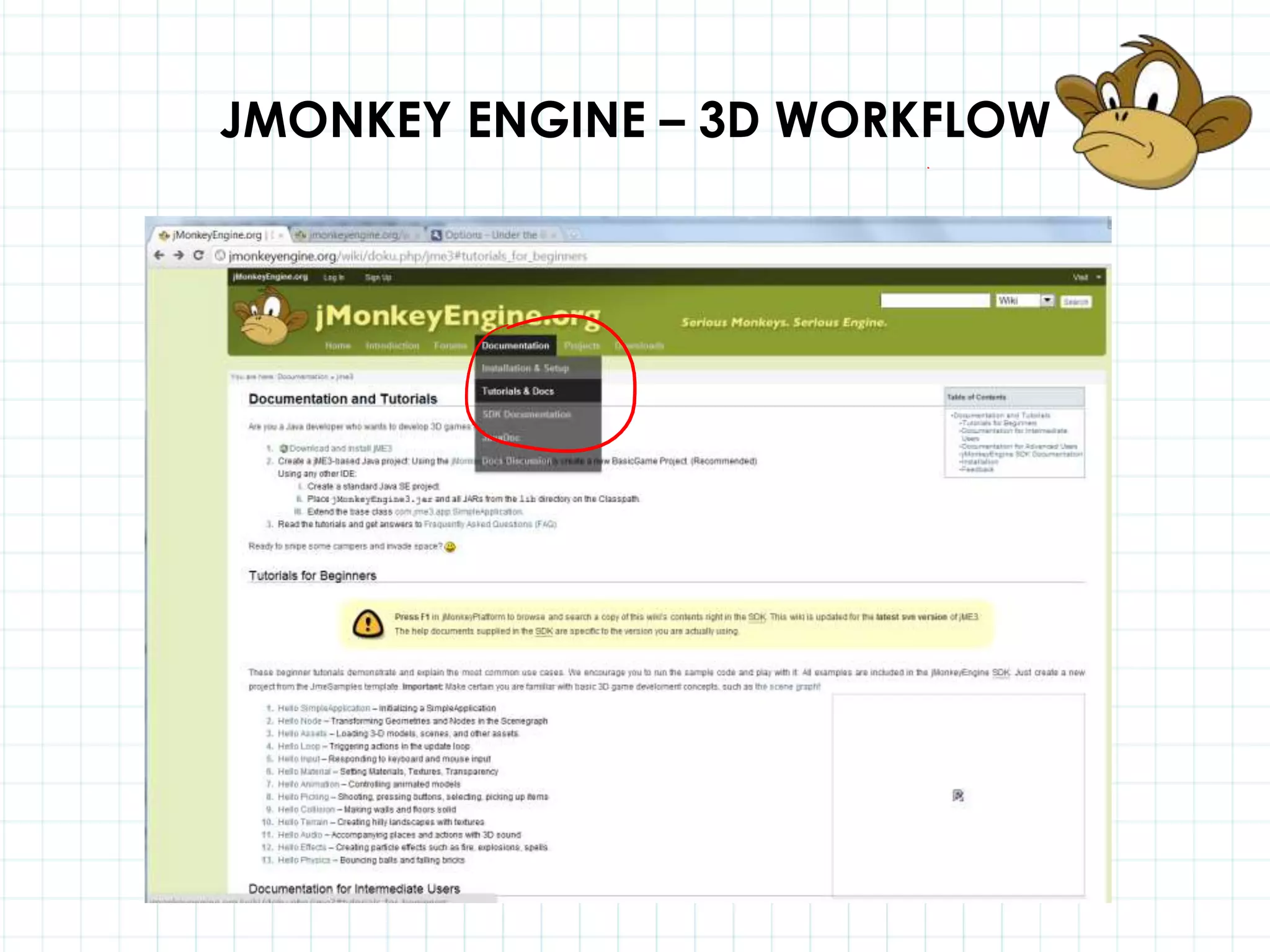
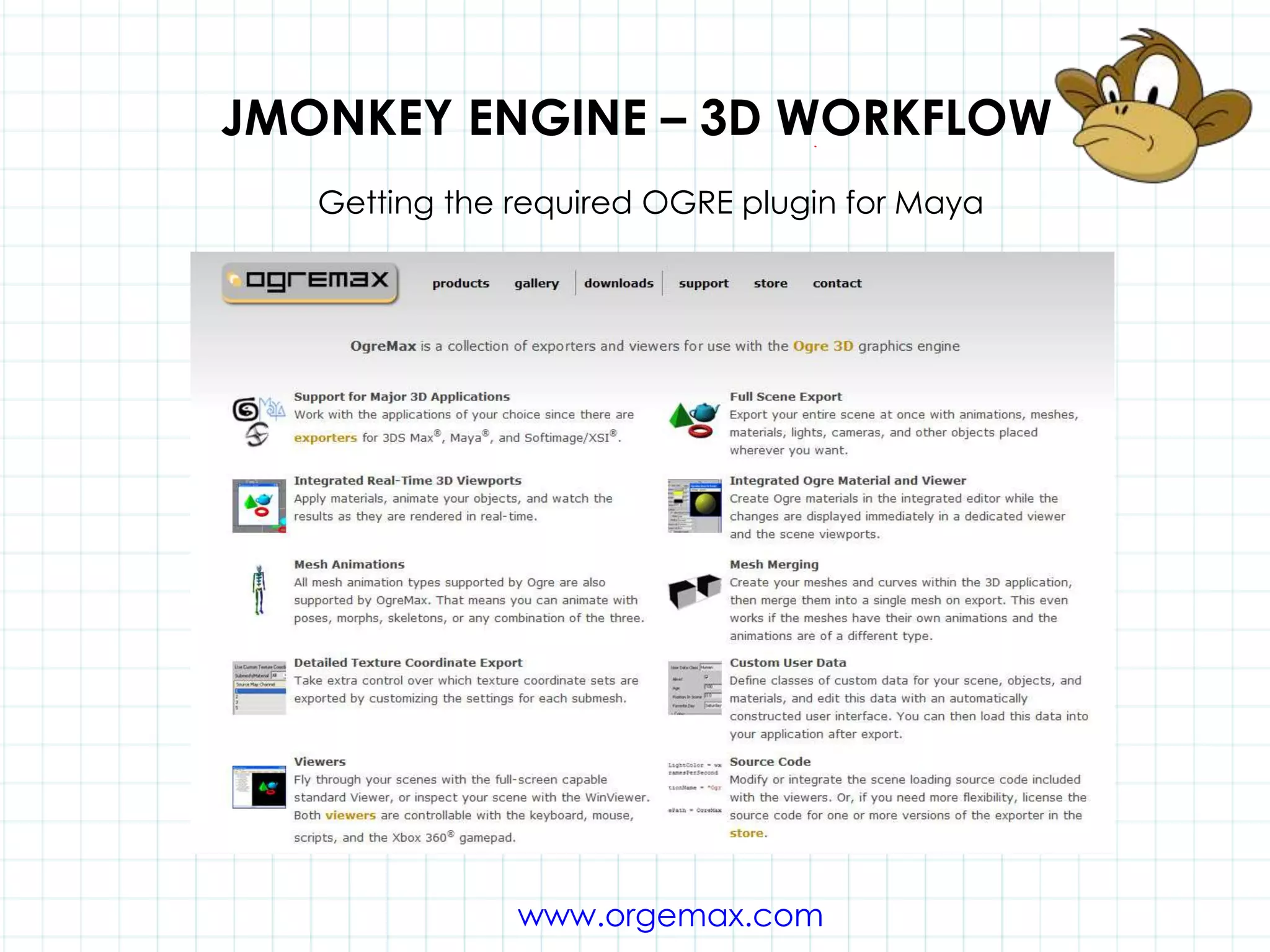
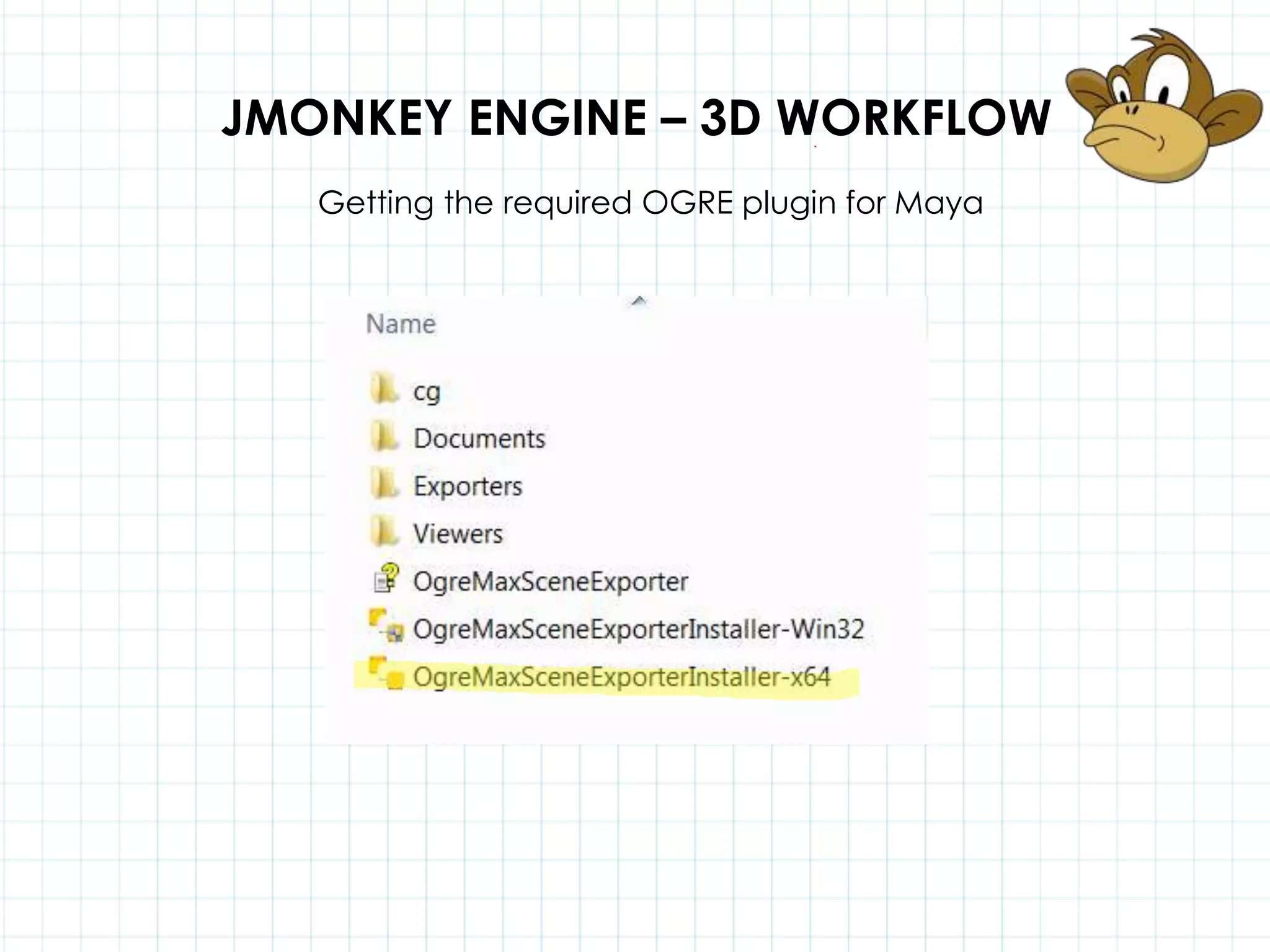
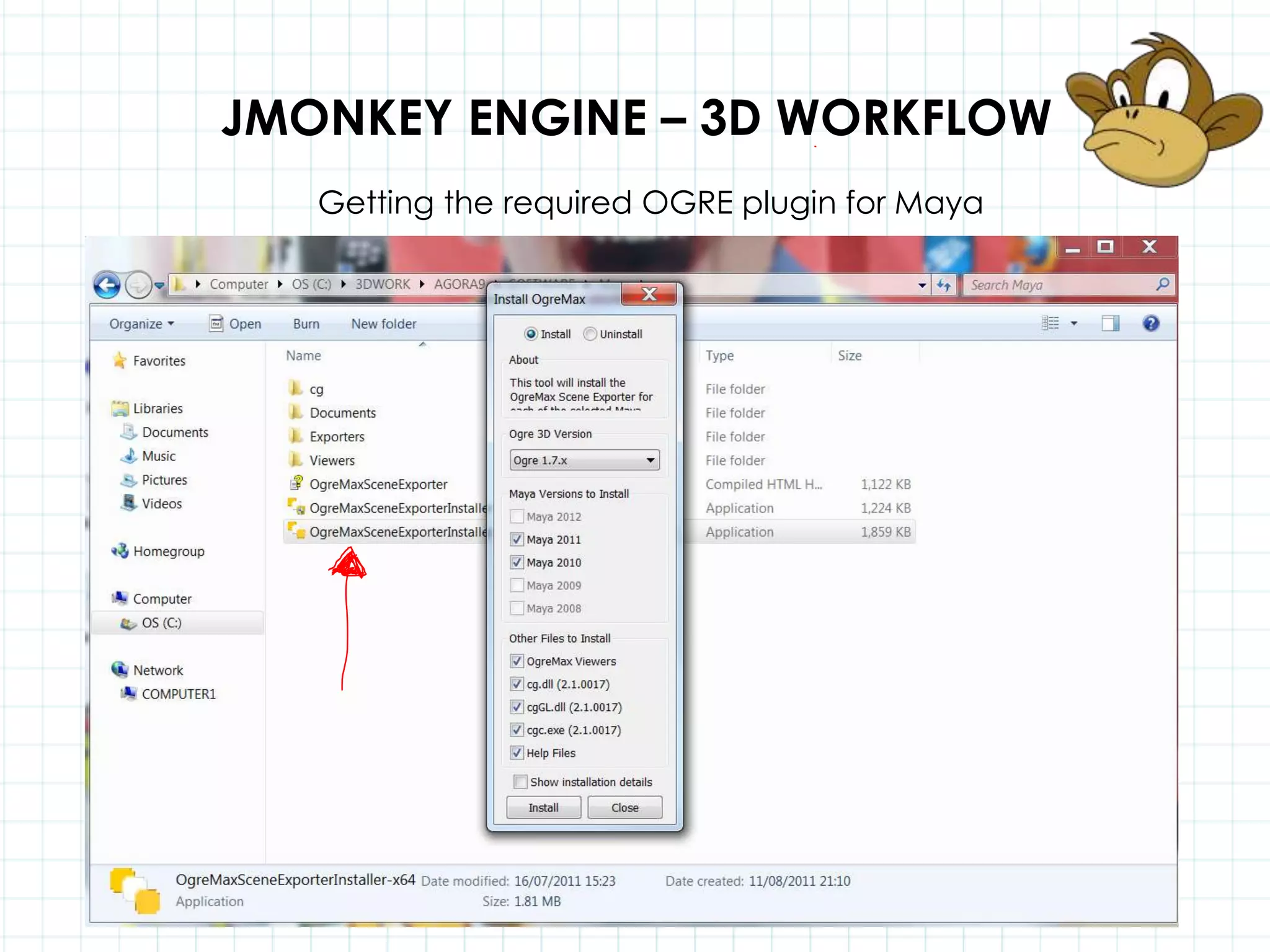
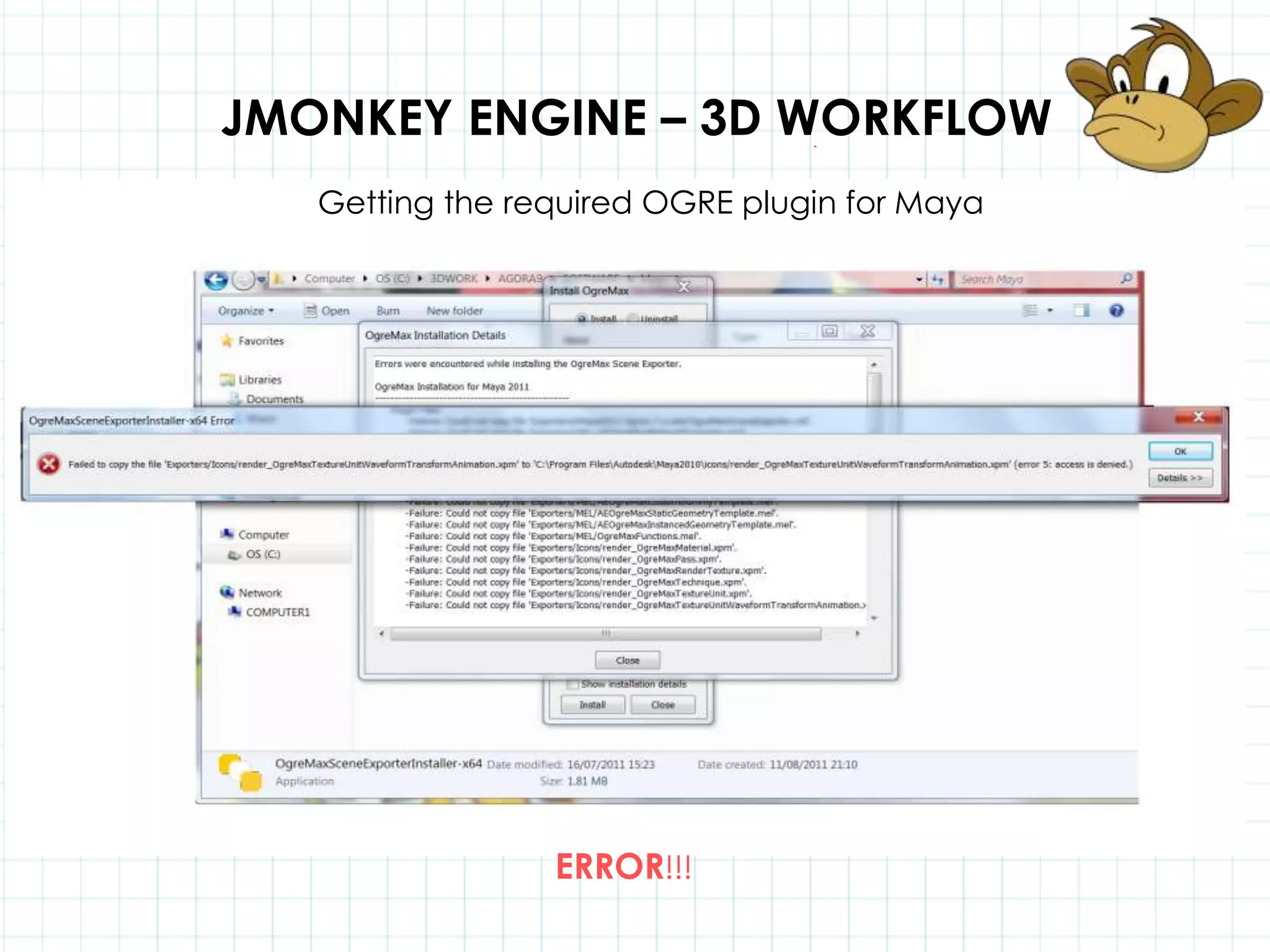
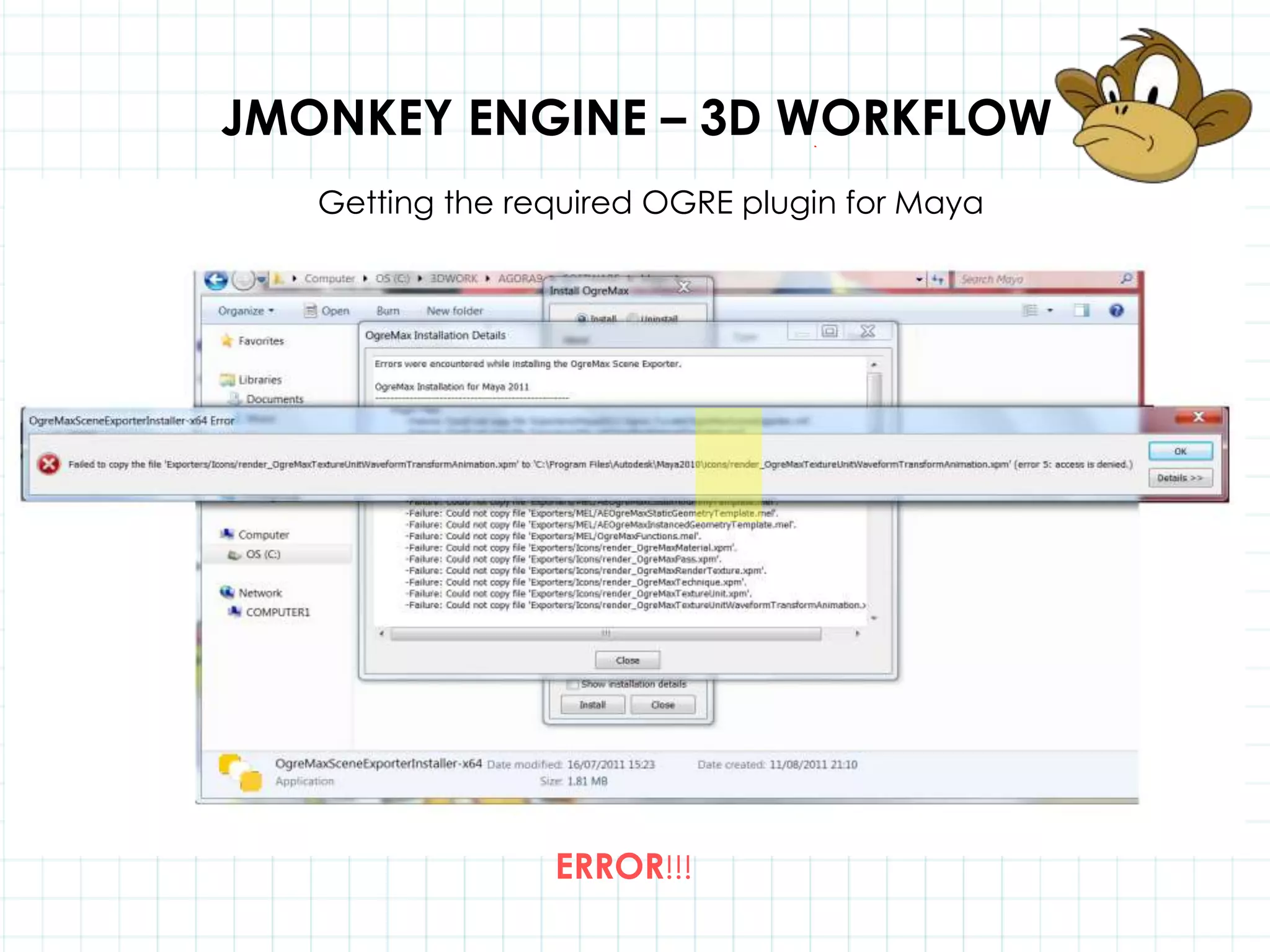
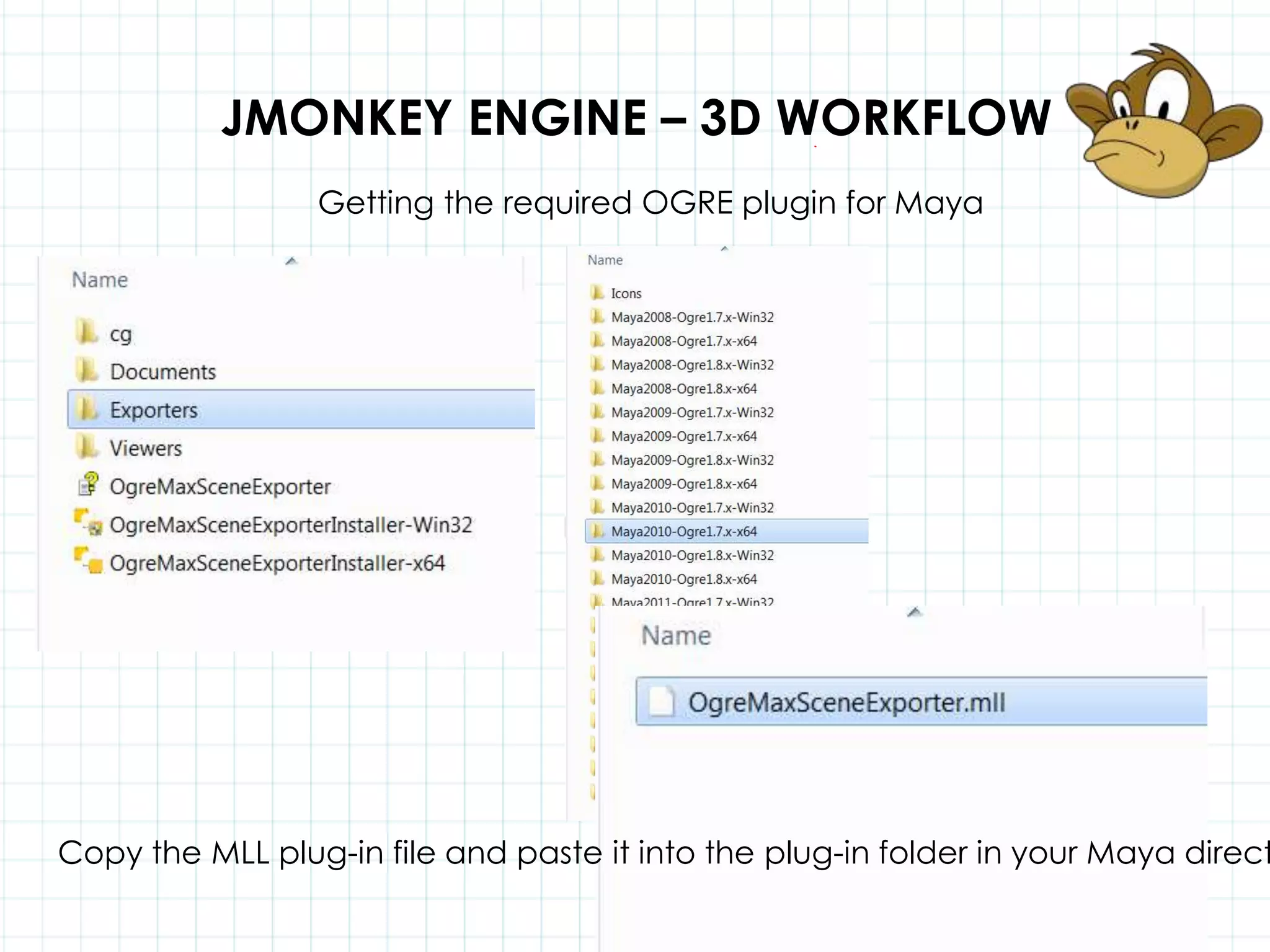
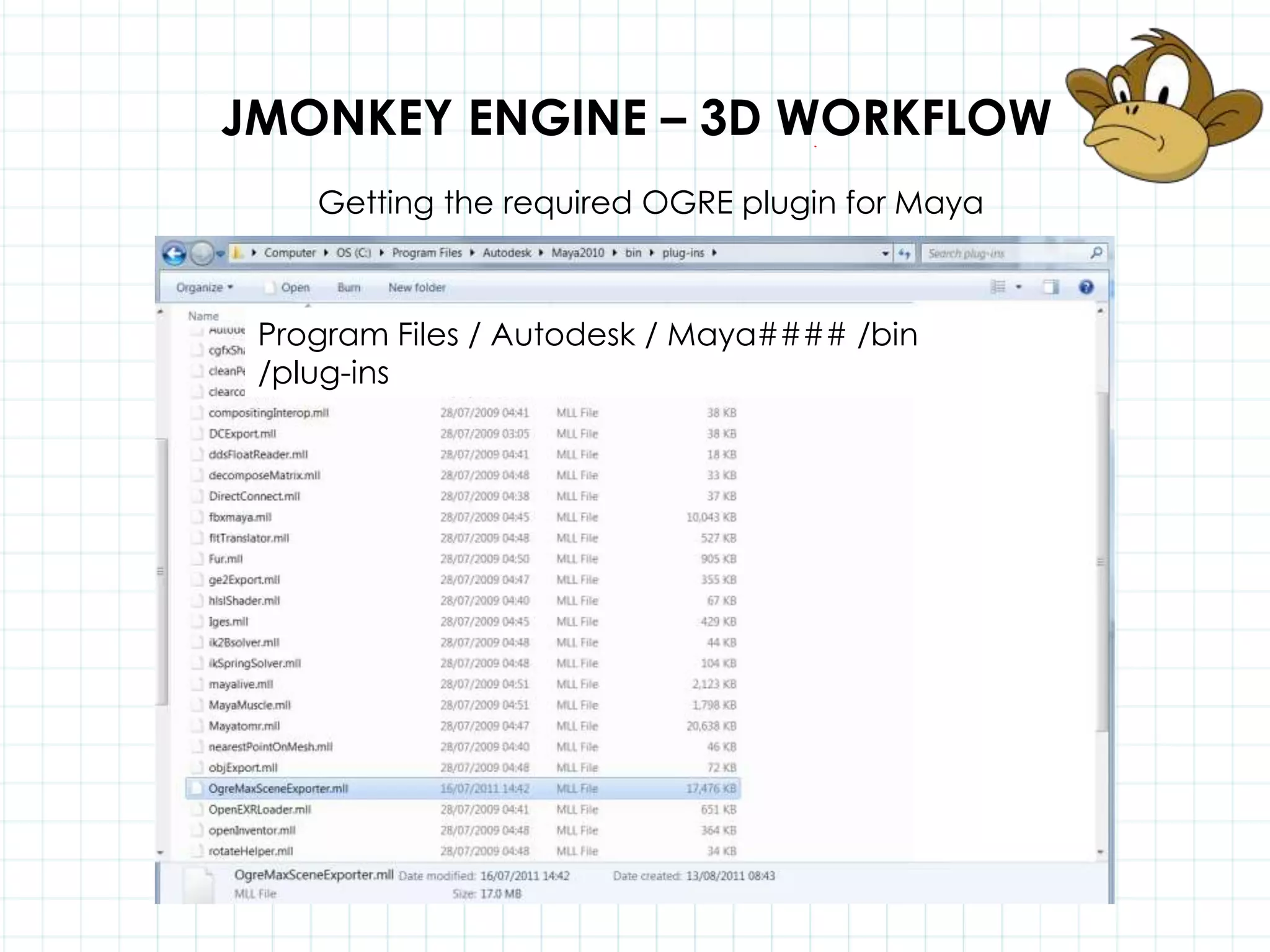
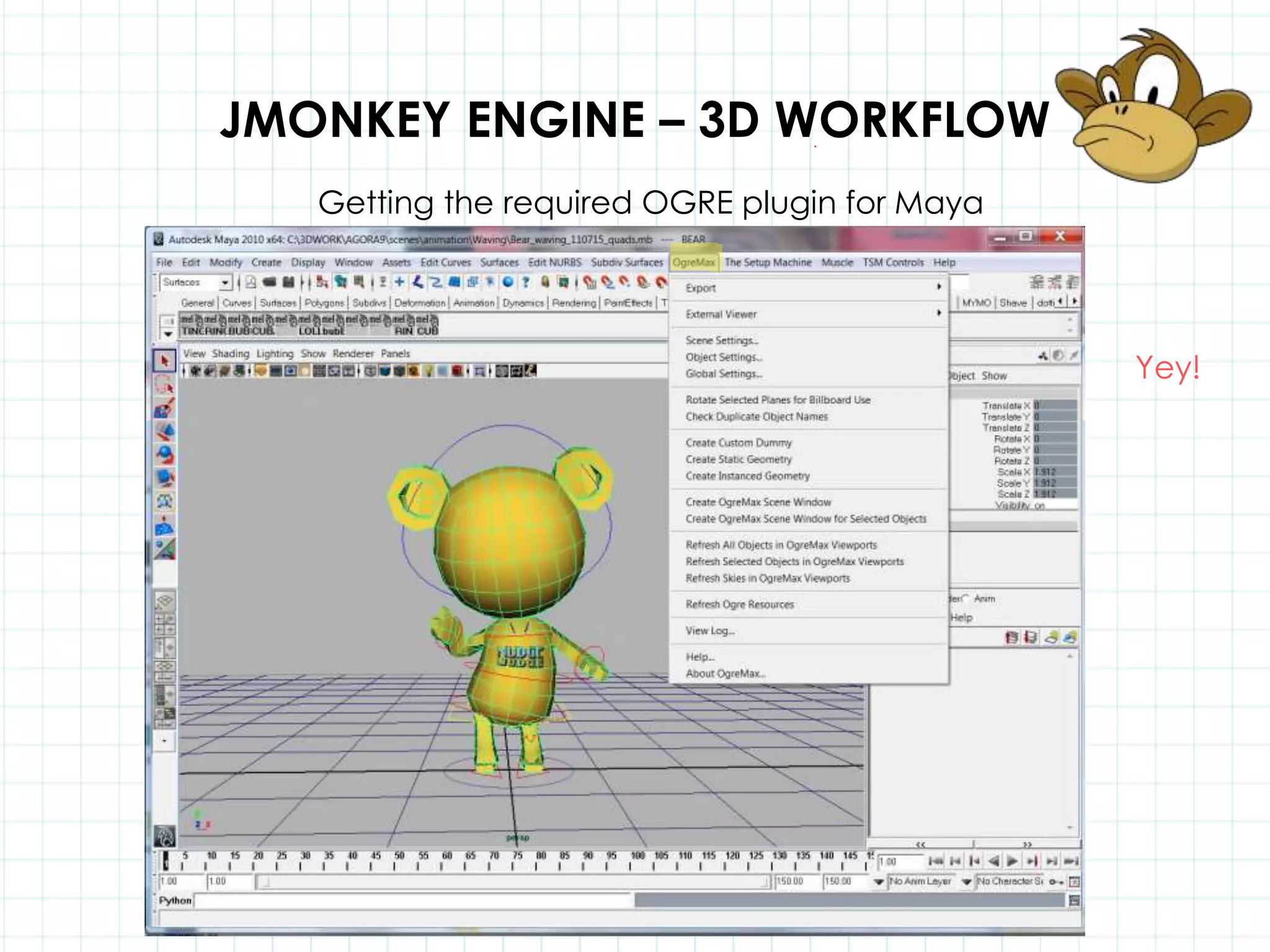
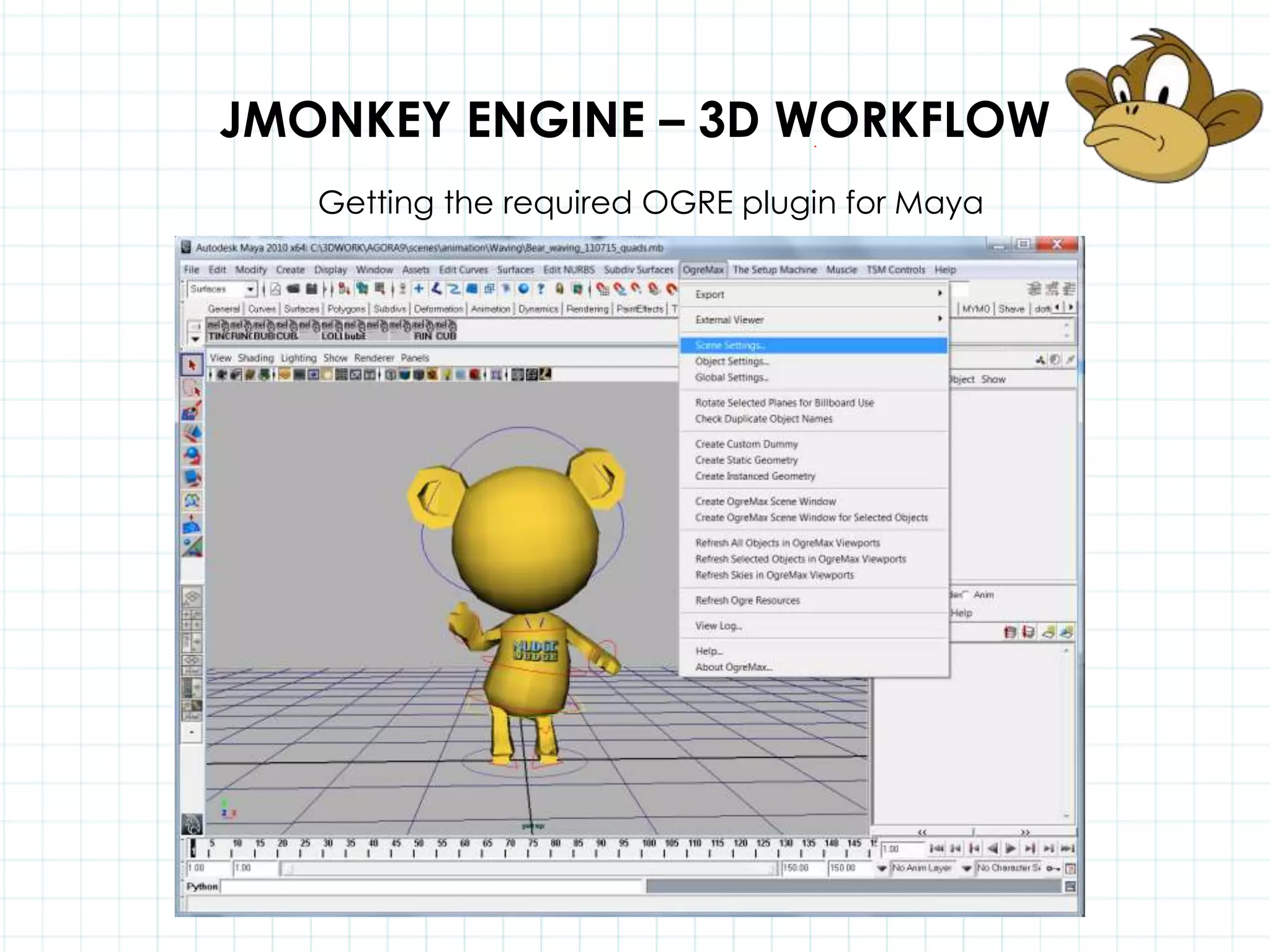
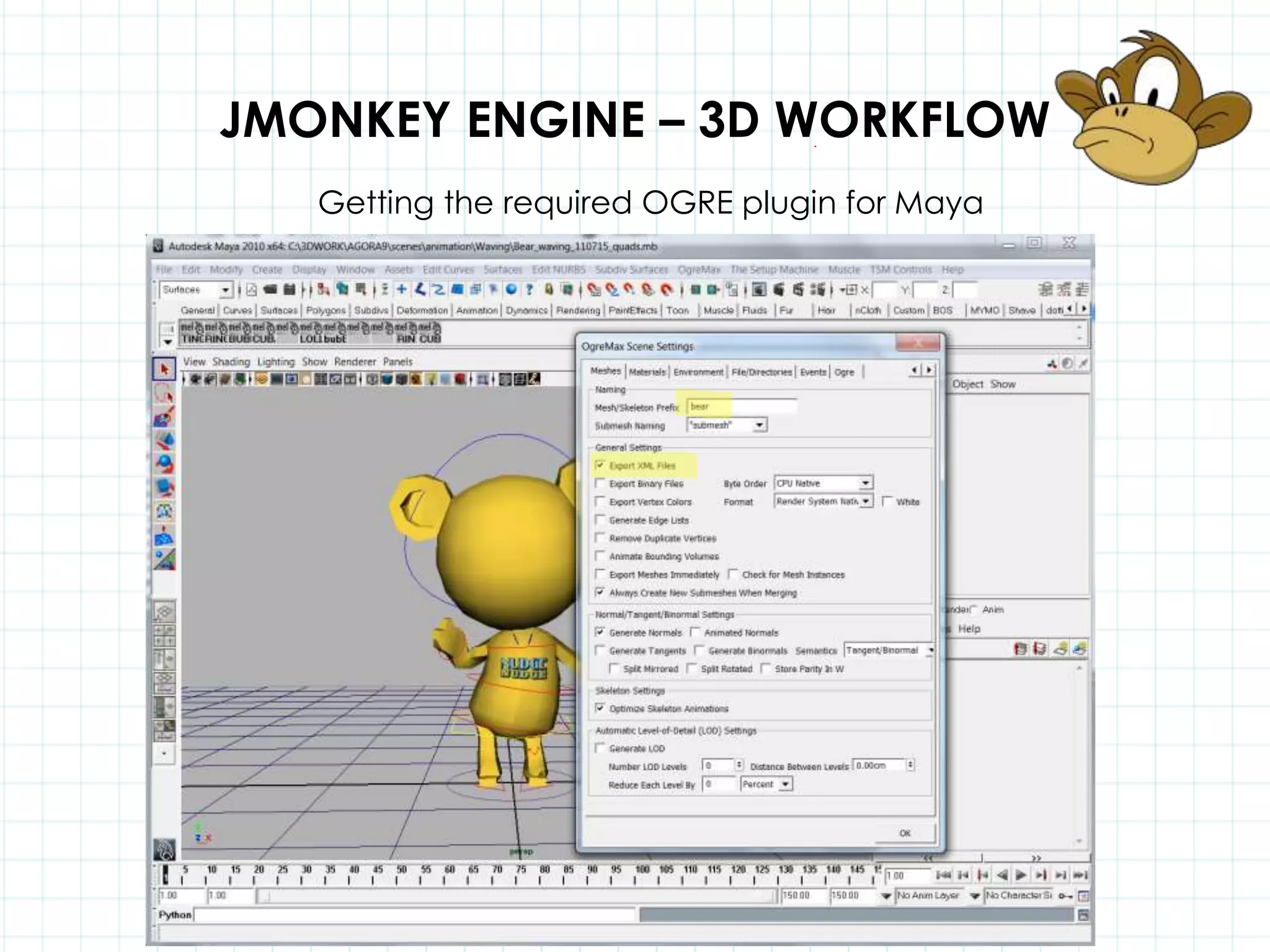
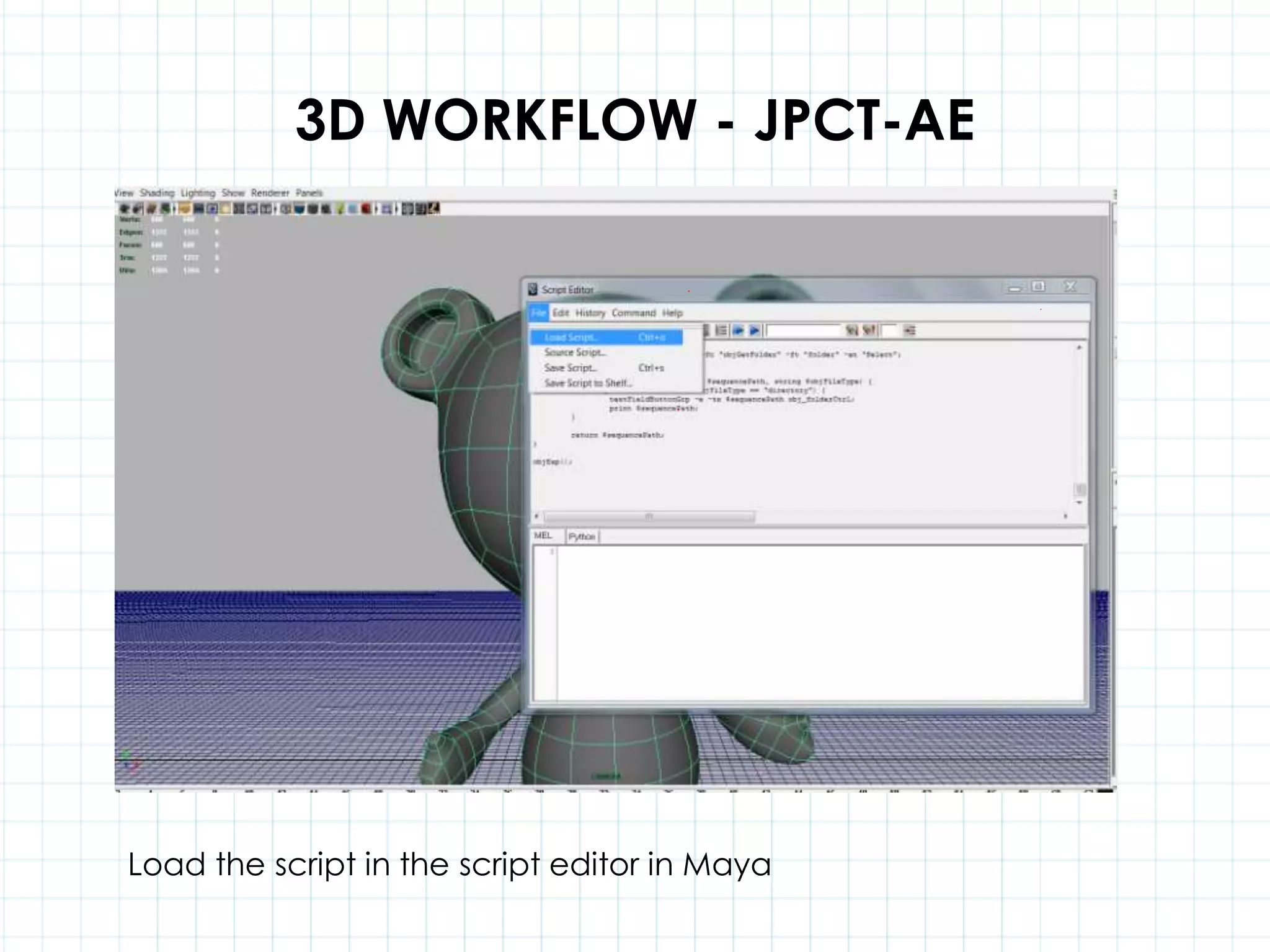
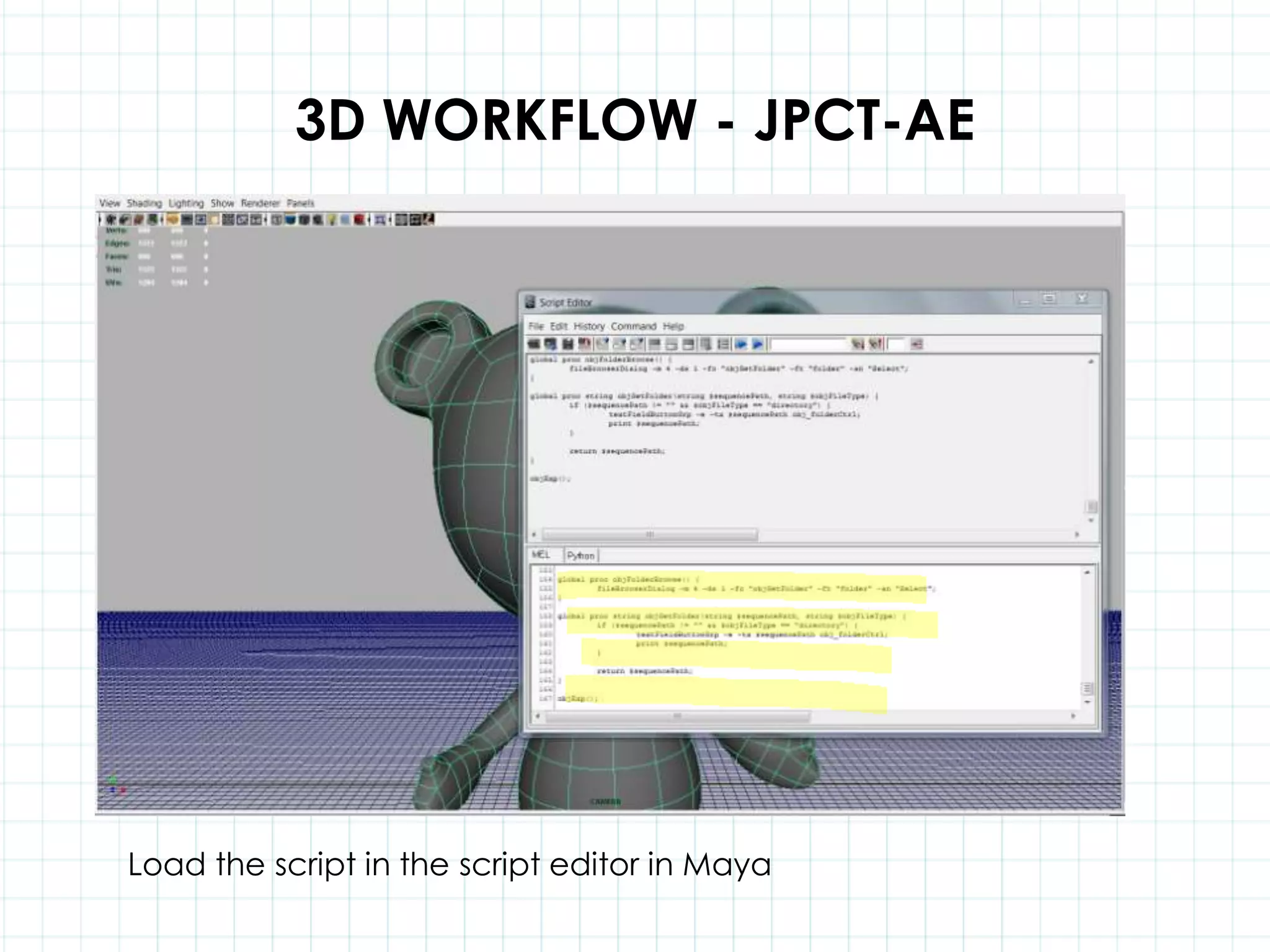
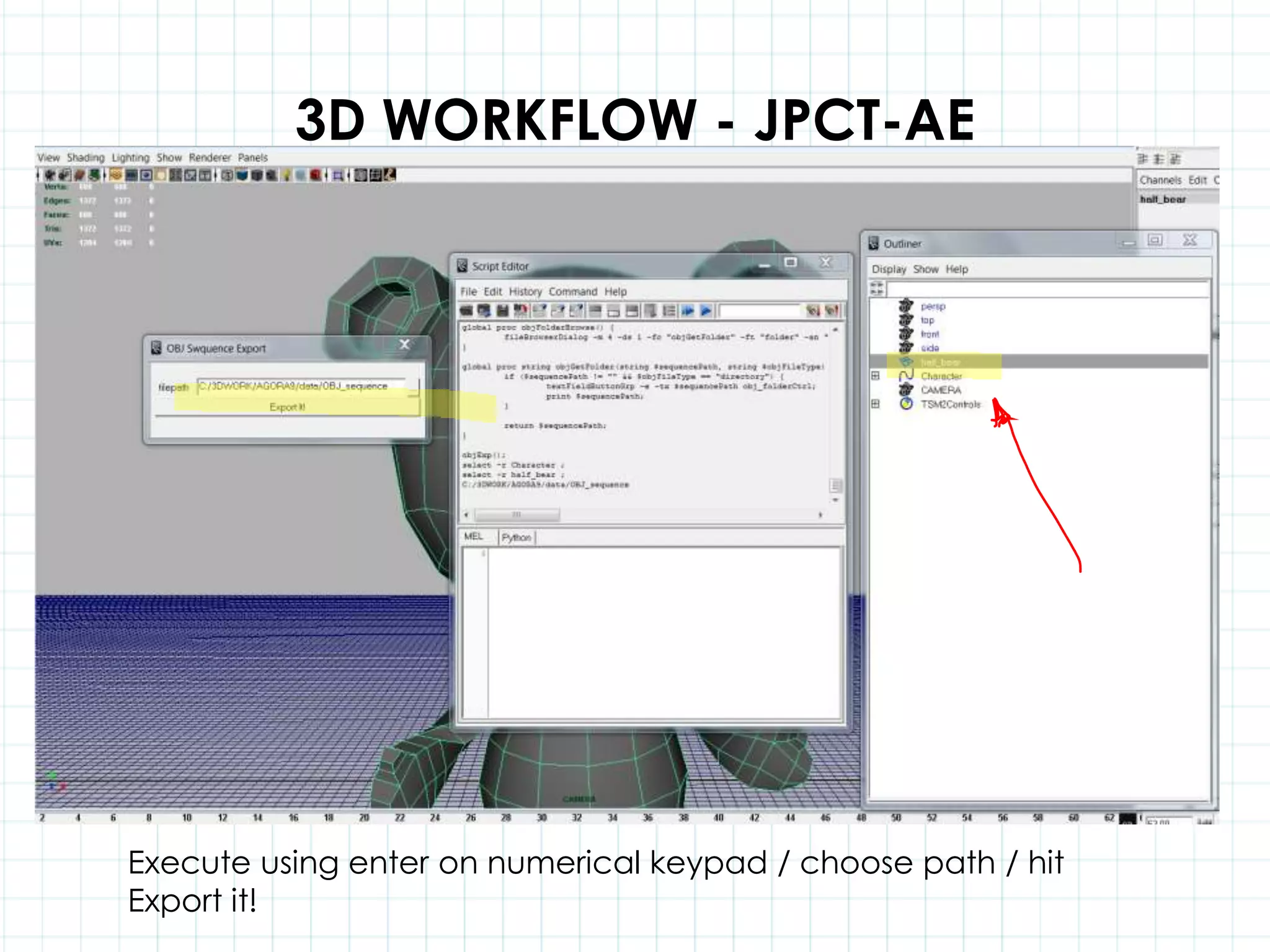
This document discusses 3D capabilities on the Android platform, including a history of Android and OpenGL ES. It provides information on jMonkeyEngine and jPCT-AE as 3D game engines for Android, and walks through workflows for importing 3D models into these engines from Maya, including using plugins and exporting OBJ/MTL sequences. Key steps discussed are installing Java JDK, configuring environment variables, importing models in j3o format for jMonkeyEngine or OBJ/MTL sequences for jPCT-AE.