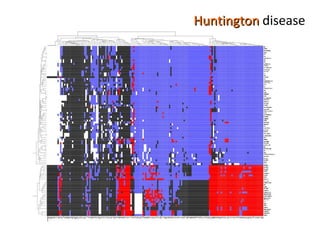
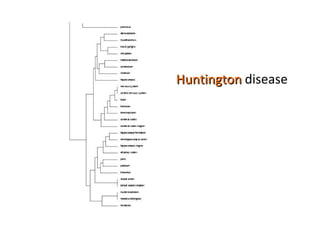
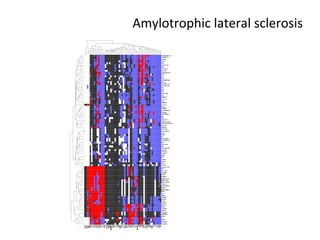
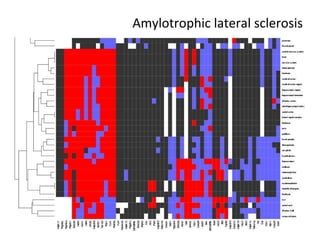
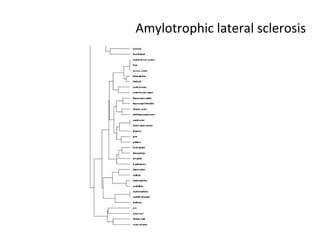
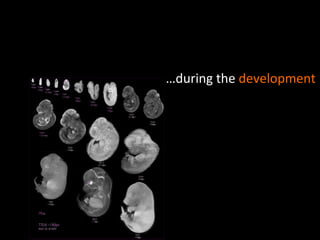
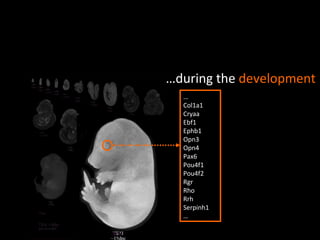
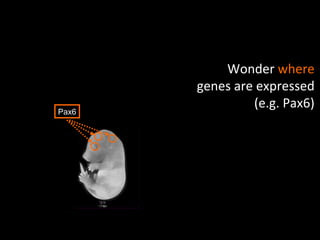
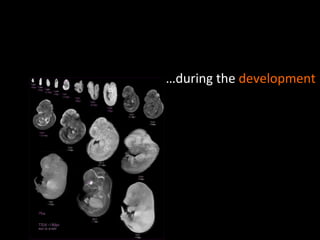
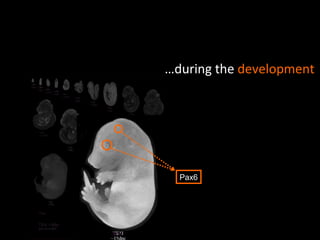
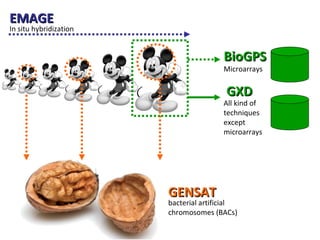
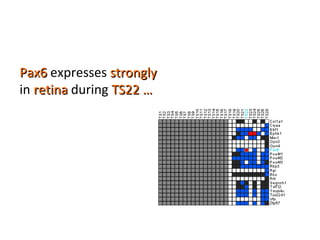
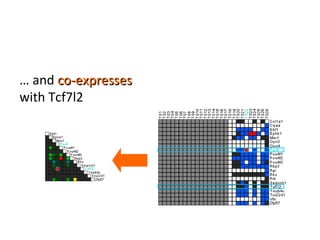
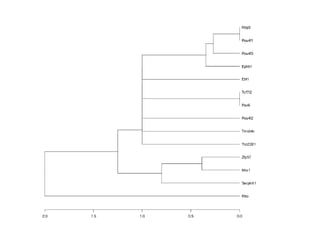
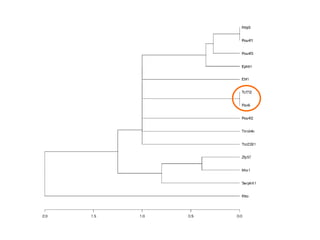
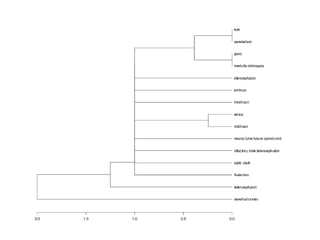
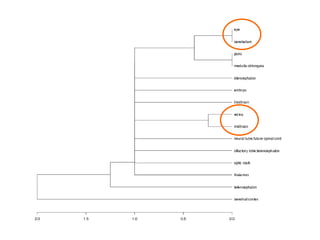
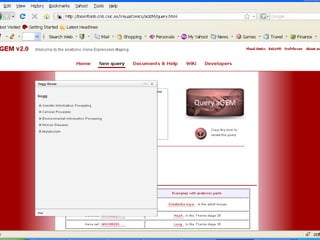
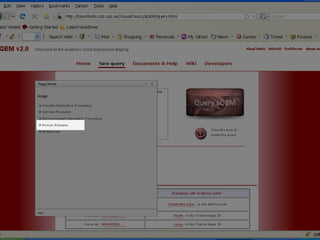
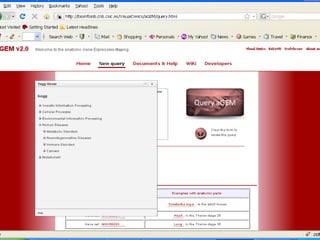
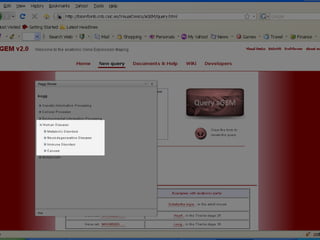
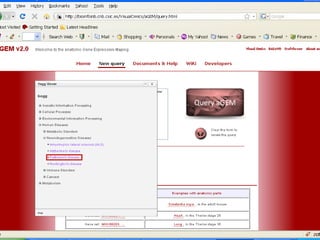
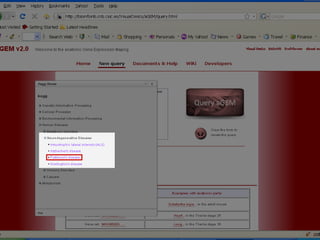
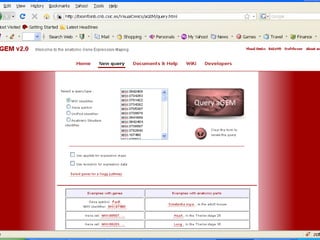
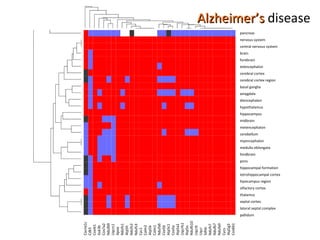
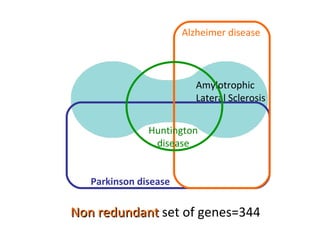
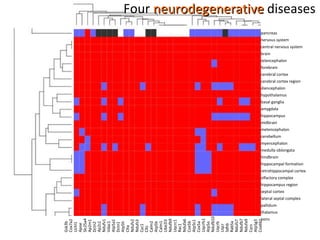
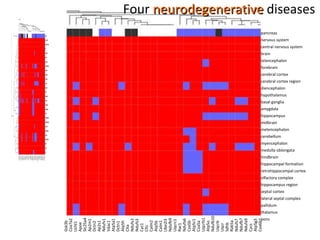
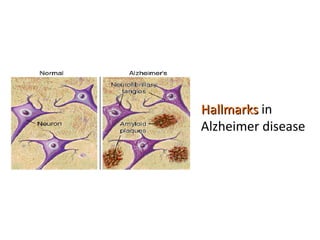
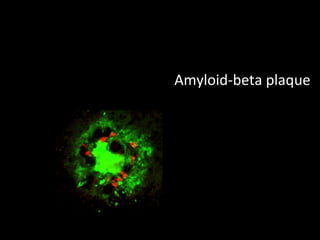
The document discusses gene expression patterns related to various neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and Huntington's disease. It notes that approximately 20% of neurodegenerative disorders are associated with diabetes mellitus. Several genes have been found to be commonly expressed across different brain regions and tissues involved in these diseases. The document also introduces aGEM, an integrative database for annotating gene expression patterns across anatomical structures.














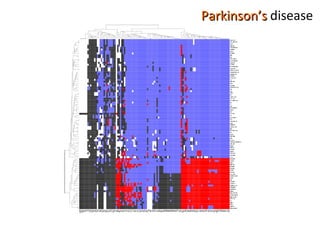
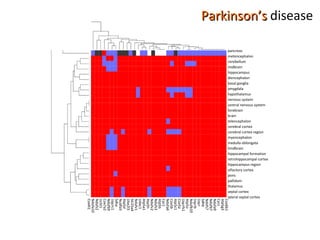
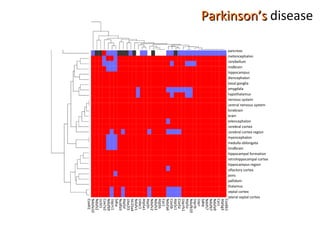














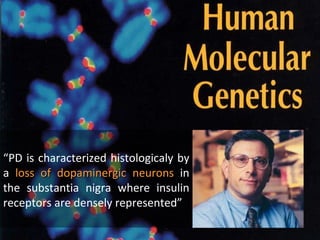
![“ Impaired glucose tolerance is frequently observed in Parkinson disease and affects up to 80% of patients. [...] therapy with levodopa seems to exacerbate glucose intolerance ”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/barcelona20091009def-091015072632-phpapp02/85/anatomic-Gene-Expression-Mapping-69-320.jpg)


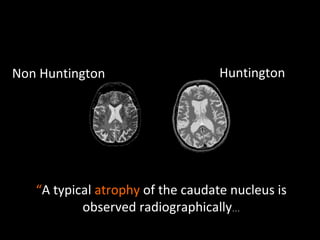








![http://agem.cnb.csic.es [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/barcelona20091009def-091015072632-phpapp02/85/anatomic-Gene-Expression-Mapping-82-320.jpg)