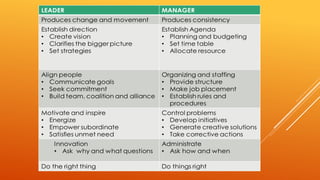
The document discusses leadership, defining it as a process where one person influences others. It outlines different leadership styles and qualities of effective leaders, including integrity, vision, communication and relationships. It distinguishes between the roles of a leader and manager. Ethics are described as important for leadership decision-making and can affect employee morale. The passage provides an overview of the construction company RAPDL, noting its focus on teamwork and communication under the transformational leadership of its executive director.