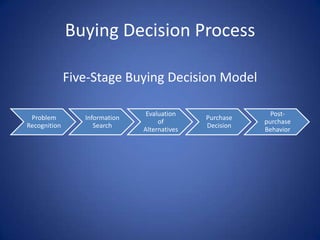
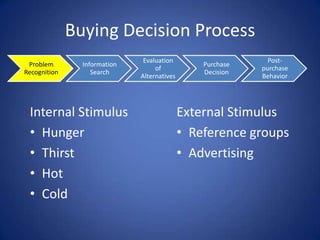
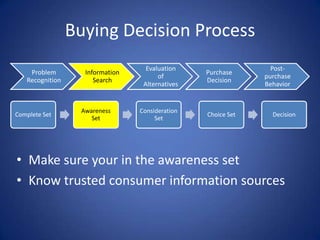
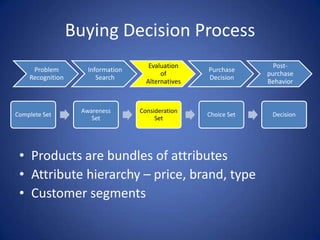
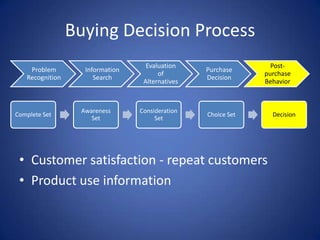
The document discusses the various influences on consumer buying decisions, including cultural, social, and personal factors. It highlights the significance of perception, motivation, learning, and memory in marketing strategy, as well as the stages of the buying decision process. Additionally, it addresses the importance of brand positioning, risk minimization, and customer satisfaction in driving repeat purchases.