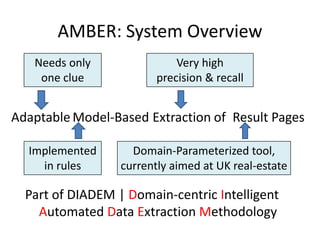
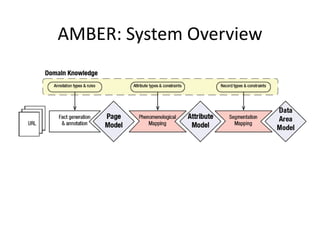
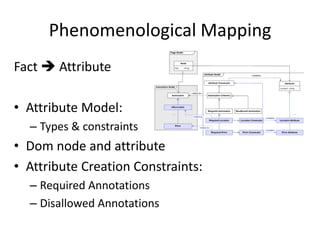
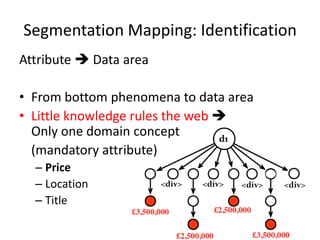
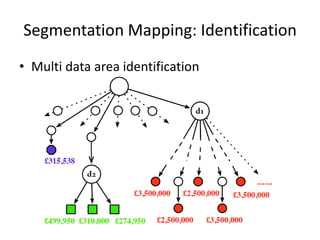
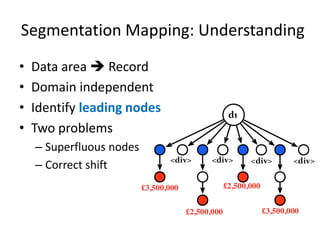
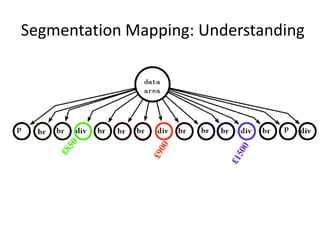
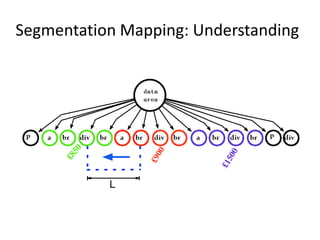
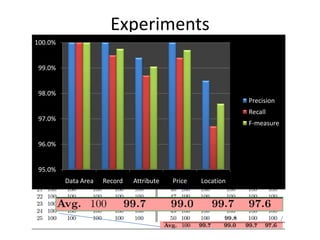
The document describes AMBER, a system for extracting structured data from result pages using little domain knowledge. AMBER uses a browser to extract the DOM tree and annotate facts. It maps facts to attributes and attributes to data areas using domain-specific rules. Experiments show AMBER achieves very high precision and recall of over 99% in extracting attributes like price and location from real estate pages. Current work involves testing AMBER on other domains and improving the system using visual information and probabilistic logic programming.