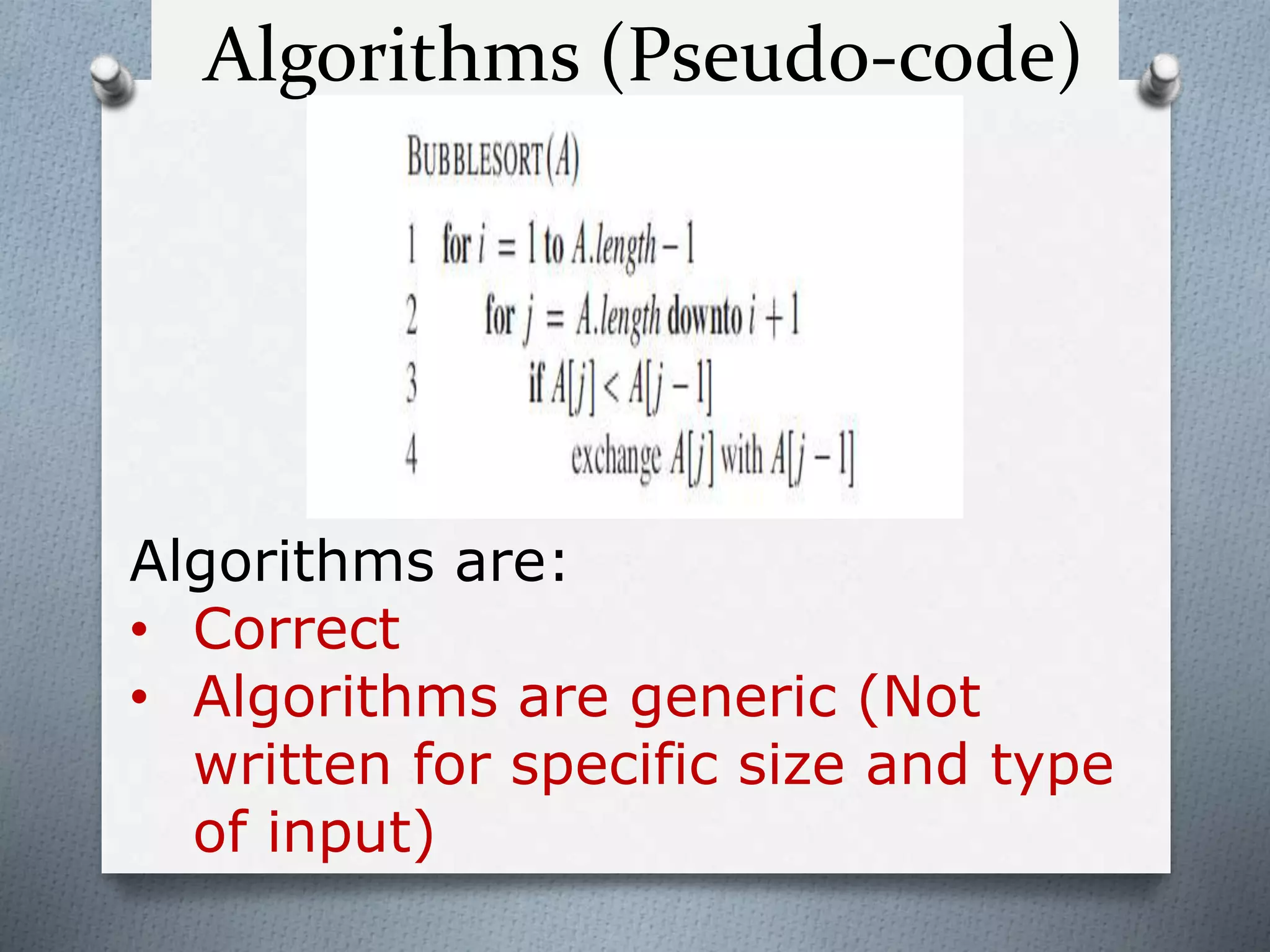
The document summarizes an algorithm lecture that covered the following topics:
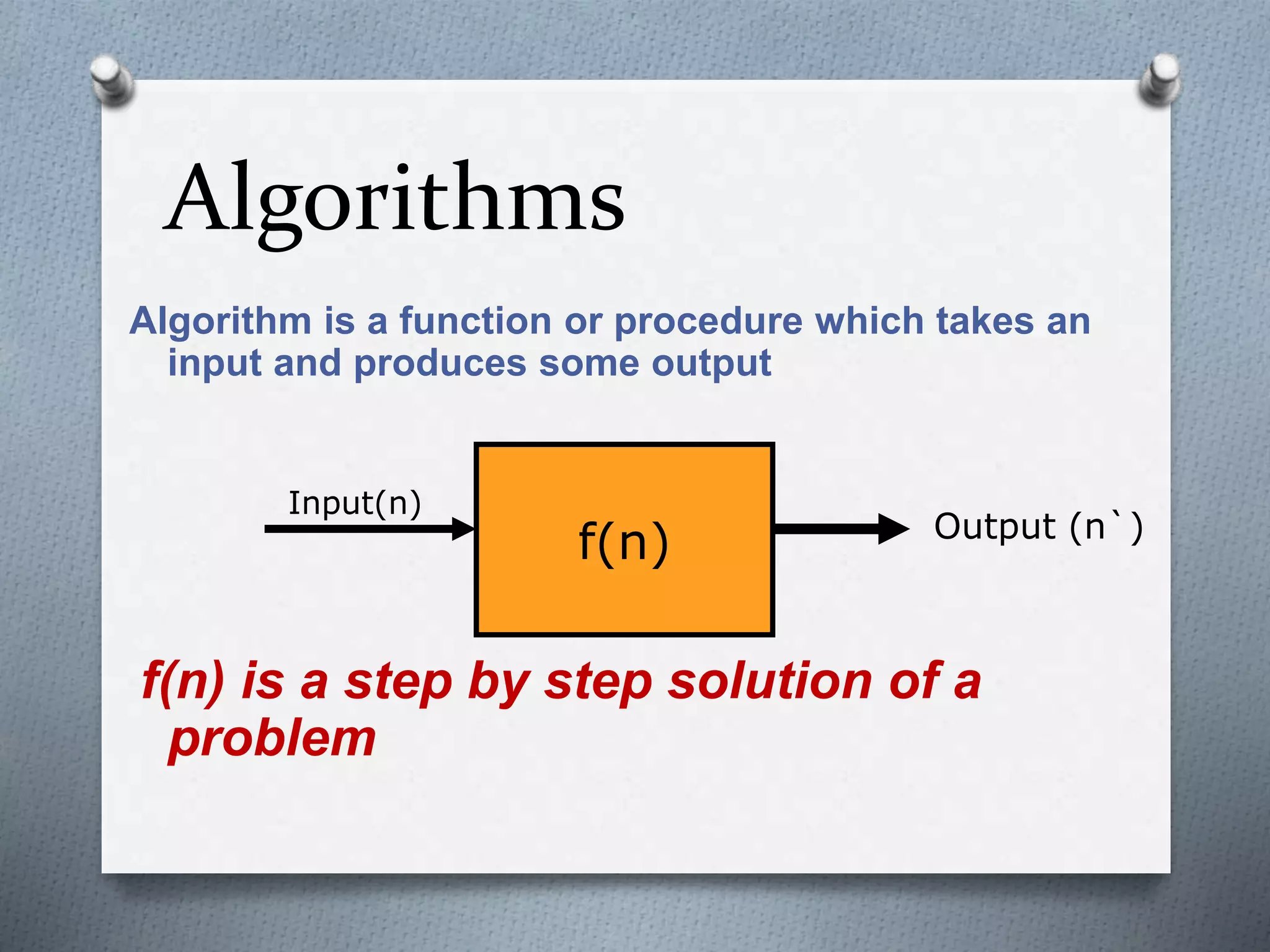
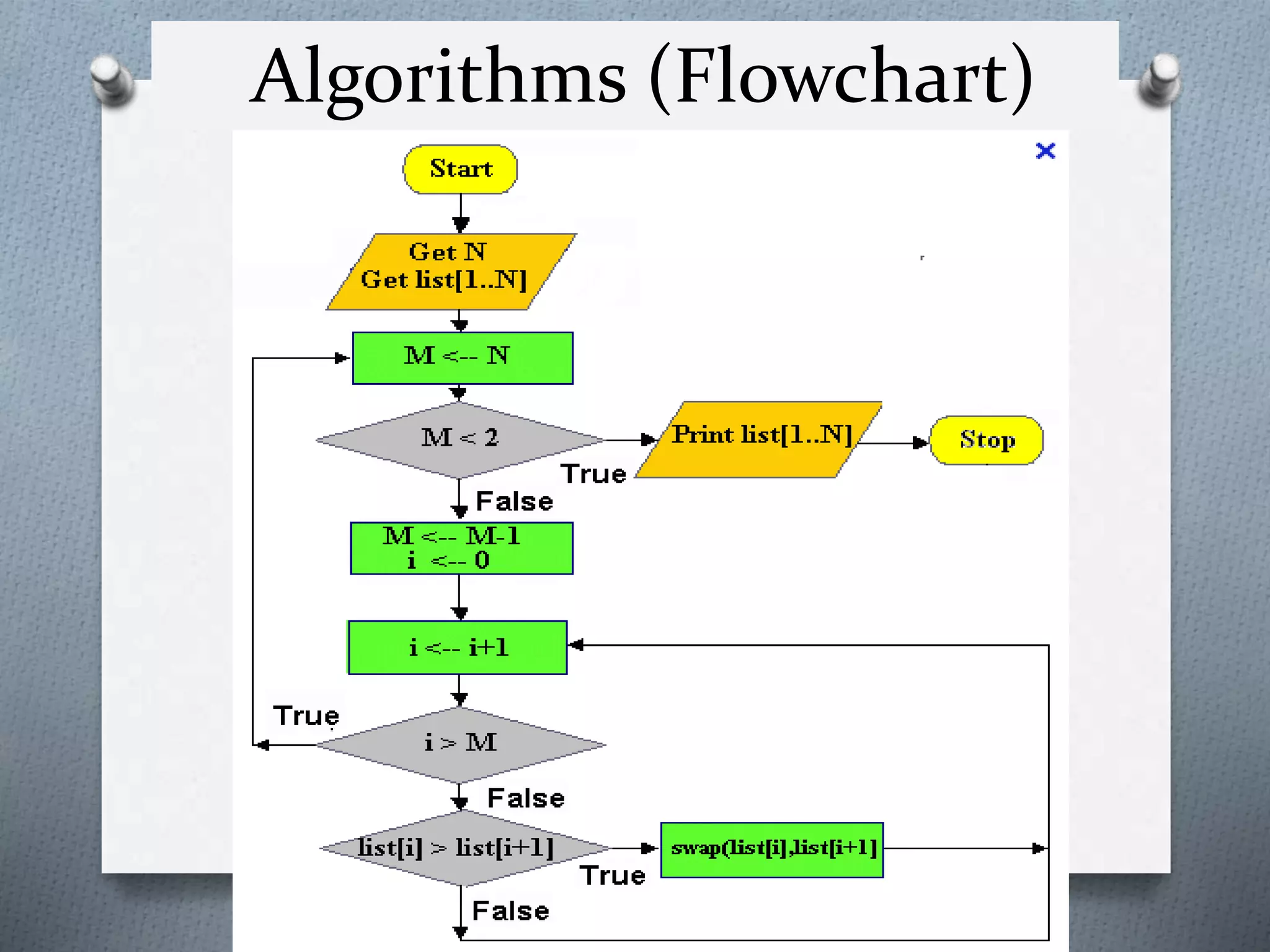
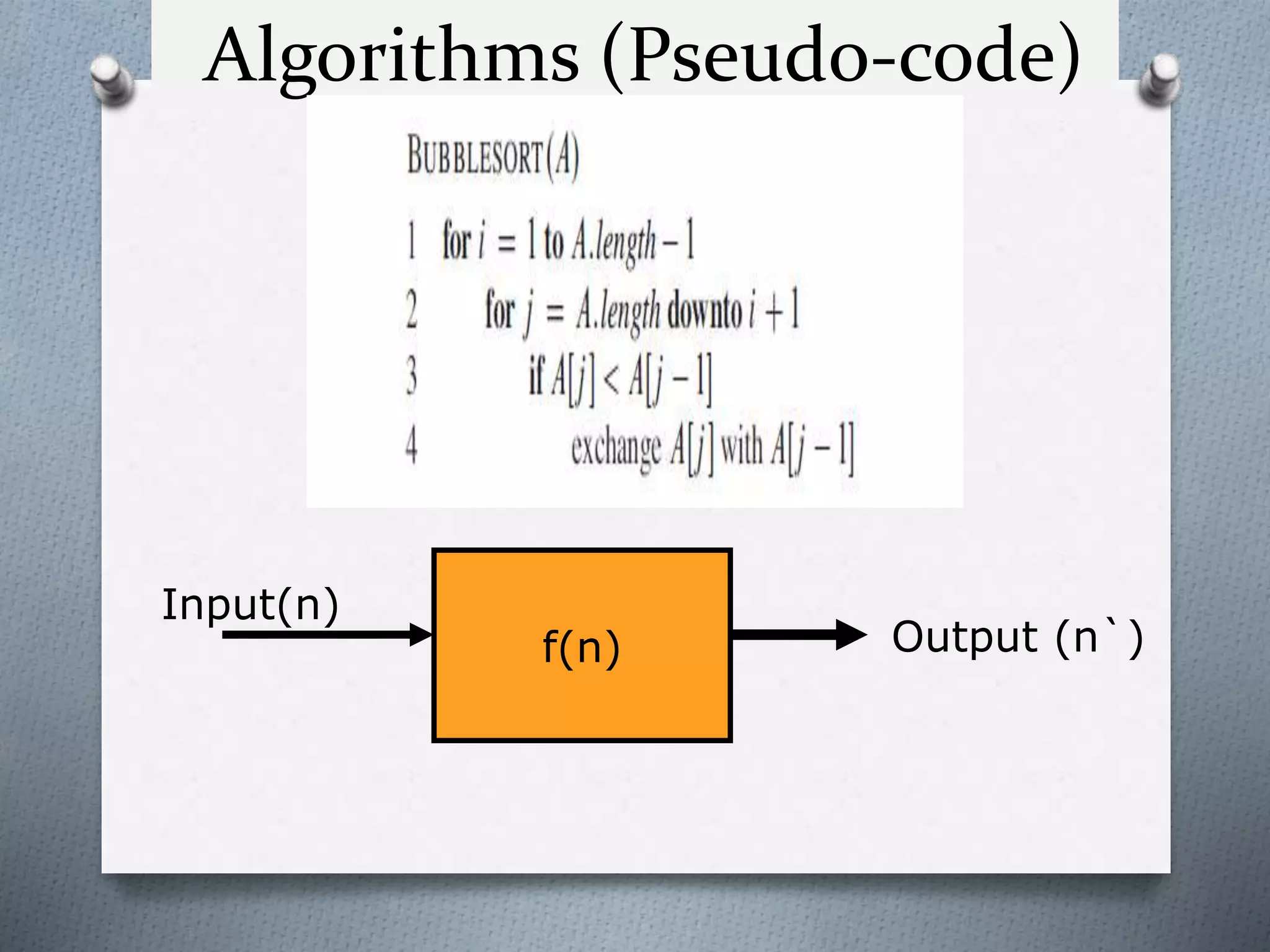
1. The definition of an algorithm as a well-defined computational function or procedure that takes input and produces output. Pseudo-code and flowcharts are common styles for writing algorithms.
2. The history of algorithms, which originated with the mathematician al-Khowarizmi in the 9th century.
3. An introduction to the course syllabus, which will cover sorting algorithms, advanced design techniques like dynamic programming and greedy algorithms, and graph algorithms and NP-complete problems.
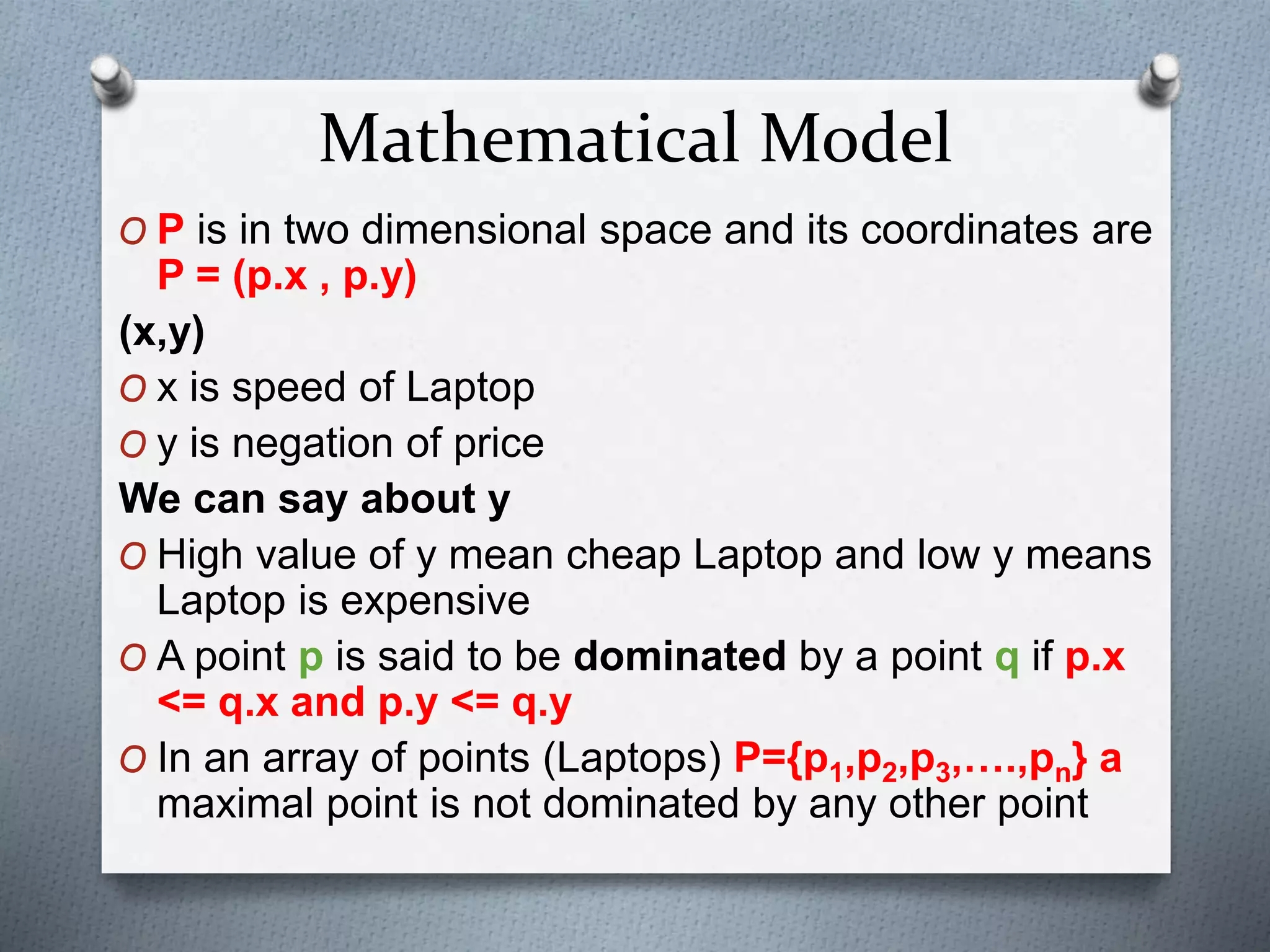
4. A selection problem example is used to demonstrate algorithm design and analysis procedures. The goal is to select the fastest laptops that are not






![Ovoid bubbleSort(int Size, number[]){
Ofor(int i=0;i<Size-1;i++){
O for(int j=0;j<Size-1;j++){
Oif(number[j]<number[j+1]){
O int temp=number[j];
O number[j]=number[j+1];
O number[j+1]=temp;
O }
O }
O}
Algorithms (c++ Code)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algolecture1-3-230924155142-608b3ce4/75/Algo_lecture1-3-pptx-9-2048.jpg)











![Searching
OSearching an elements from array
(Linear Search)
OLinearSearch( Record[1…..n], m)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algolecture1-3-230924155142-608b3ce4/75/Algo_lecture1-3-pptx-23-2048.jpg)
![Searching
LinearSearch( Record[1…..n], m)
1. k=false
2. for I =1 to n
3. if Record[i]==m
4. K=true;
5. break;
6. if k==true
7. print “Element found”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algolecture1-3-230924155142-608b3ce4/75/Algo_lecture1-3-pptx-24-2048.jpg)