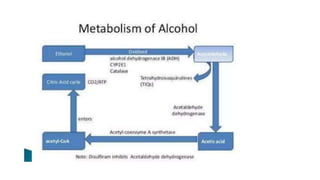
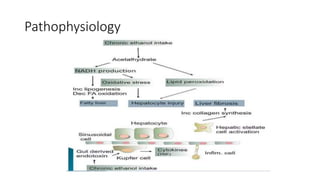
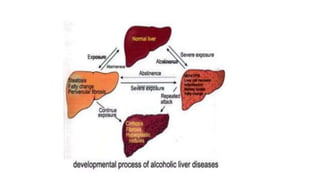
This document discusses alcoholic liver disease and its pharmacotherapeutic management. It notes that chronic excessive alcohol ingestion can lead to conditions like fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and cirrhosis. Symptoms may not appear initially but worsen with continued heavy drinking and include abdominal pain, weight loss, jaundice, and cognitive issues. Investigations show elevated liver enzymes. Complications include portal hypertension, varices, ascites, and hepatic encephalopathy. Management involves removing alcohol, diet changes, medications like diuretics for ascites, lactulose for encephalopathy, corticosteroids for hepatitis, and antioxidants like silymarin. Liver transplant is an option for severe cases.