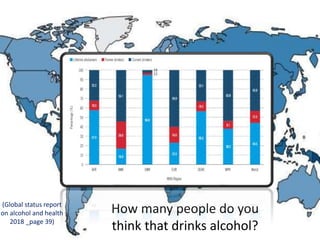
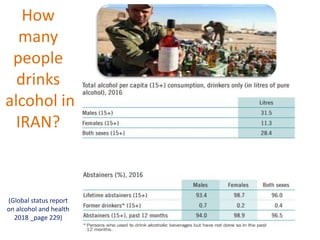
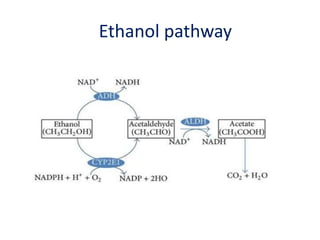
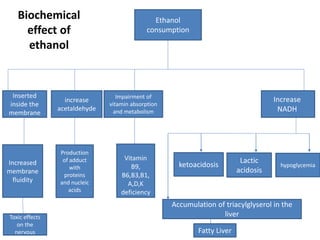
The document discusses the diverse effects of alcohol, including its impact on health, society, and addiction. It highlights the risks associated with alcohol consumption such as injuries, violence, and various health complications affecting multiple body systems. While some beneficial effects of moderate alcohol consumption are mentioned, the overall tone emphasizes the significant negative consequences and importance of addressing alcohol-related issues.