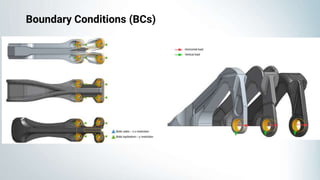
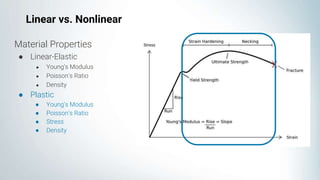
This document discusses linear and nonlinear analysis of an aircraft engine bearing bracket. It begins by describing the problem setup, geometries, boundary conditions, and material properties used. It then discusses when to use linear versus nonlinear solvers, focusing on high deformation levels, modeling time-dependent simulations, complex boundary conditions, and geometries. The document also covers the three types of nonlinearity: material, geometric, and boundary nonlinearity. It notes nonlinear systems do not follow the superposition principle. In the post-processing questions section, it lists some potential questions about the performance and deformation of different models.