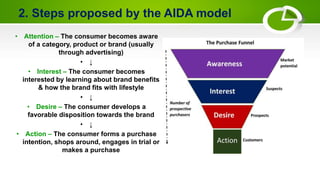
The AIDA model is a marketing communications model that describes the steps a consumer goes through in forming a purchase decision. It was developed by E. St. Elmo Lewis and includes the steps of Attention, Interest, Desire, and Action. The model proposes that marketers must first grab the consumer's attention, then spark their interest, develop desire for the product, and finally prompt them to take an action such as a purchase. However, the model has been criticized for being too linear and not accounting for post-purchase effects like satisfaction. Several variants of the AIDA model have also been developed over time.