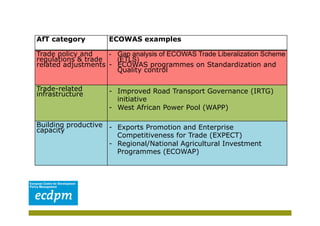
The document discusses the significance of Aid for Trade (AfT) in the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) and highlights existing regional AfT strategies. It outlines key lessons learned from these strategies, including the need for clear objectives and effective resource mobilization, while pointing out challenges like the coordination of resources and human capacity. Additionally, the document emphasizes the importance of developing a coherent ECOWAS AfT strategy that aligns with other regional and national plans.