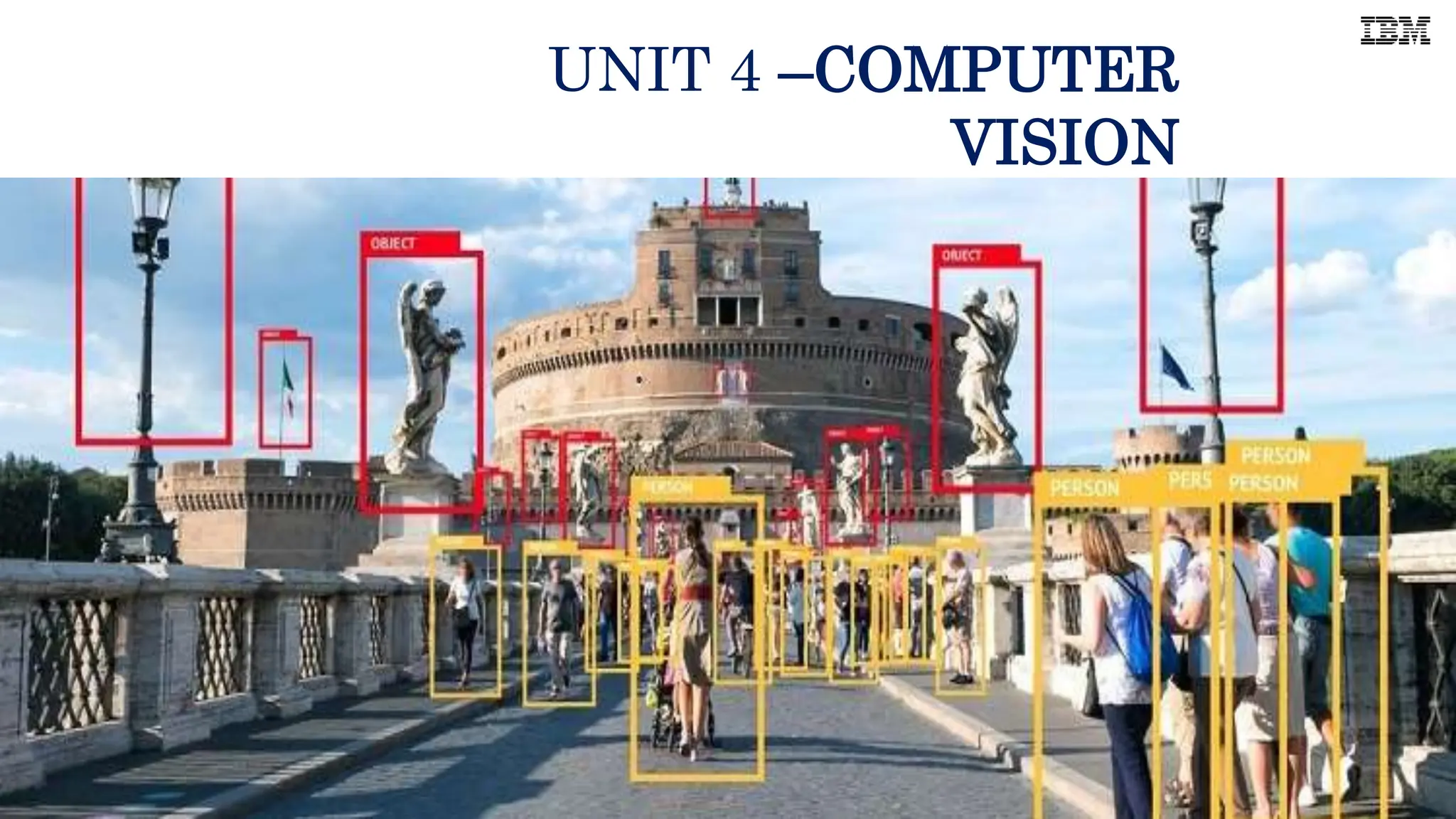
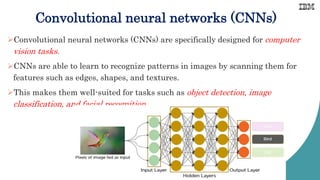
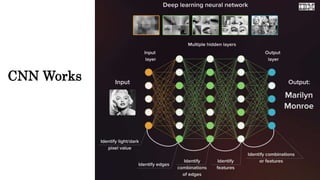
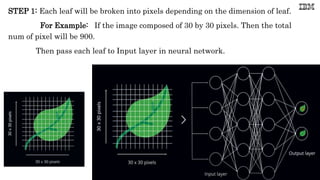
Computer vision involves developing algorithms to allow computers to understand visual data from images and videos. It includes tasks like image recognition, object detection, and facial recognition. Convolutional neural networks are commonly used for computer vision tasks as they can learn patterns in images by scanning for features. Python libraries like OpenCV provide tools for computer vision applications and allow reading, displaying, and processing images using functions for operations like resizing, cropping, and flipping.








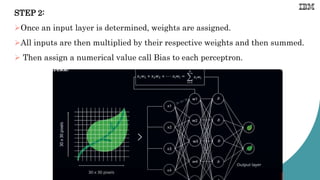
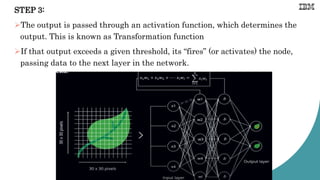
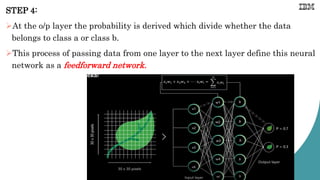
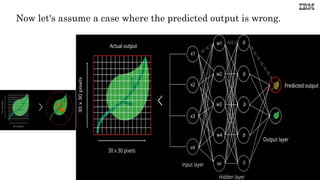




![Example:
import cv2
img= cv2.imread(r'C:/Users/ibmtr/OneDrive/Desktop/Elon.jpg’)
print('Image dimensions:', img.shape)
cv2.imshow('image',img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
OUTPUT:
Image dimensions: (1080, 1920, 3)
[Note:1080-height of the image
1920- width of the image
3-number of color channels in the image (Red, Green, and Blue)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aiunit4-srcasjoc-231228170311-65b9ac13/85/AI-UNIT-4-SRCAS-JOC-pptx-enjoy-this-ppt-22-320.jpg)
