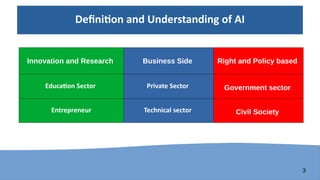
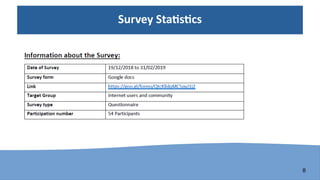
The document discusses the perspectives and challenges of artificial intelligence (AI) in developing nations, emphasizing the importance of human rights, inclusiveness, and ethical values in AI development. It highlights the current landscape of AI integration across various sectors, the challenges faced by developing nations, and the need for a collaborative governance framework. Recommendations include enhancing awareness, participation, and standardization of core values to adapt to and mitigate the challenges posed by AI.