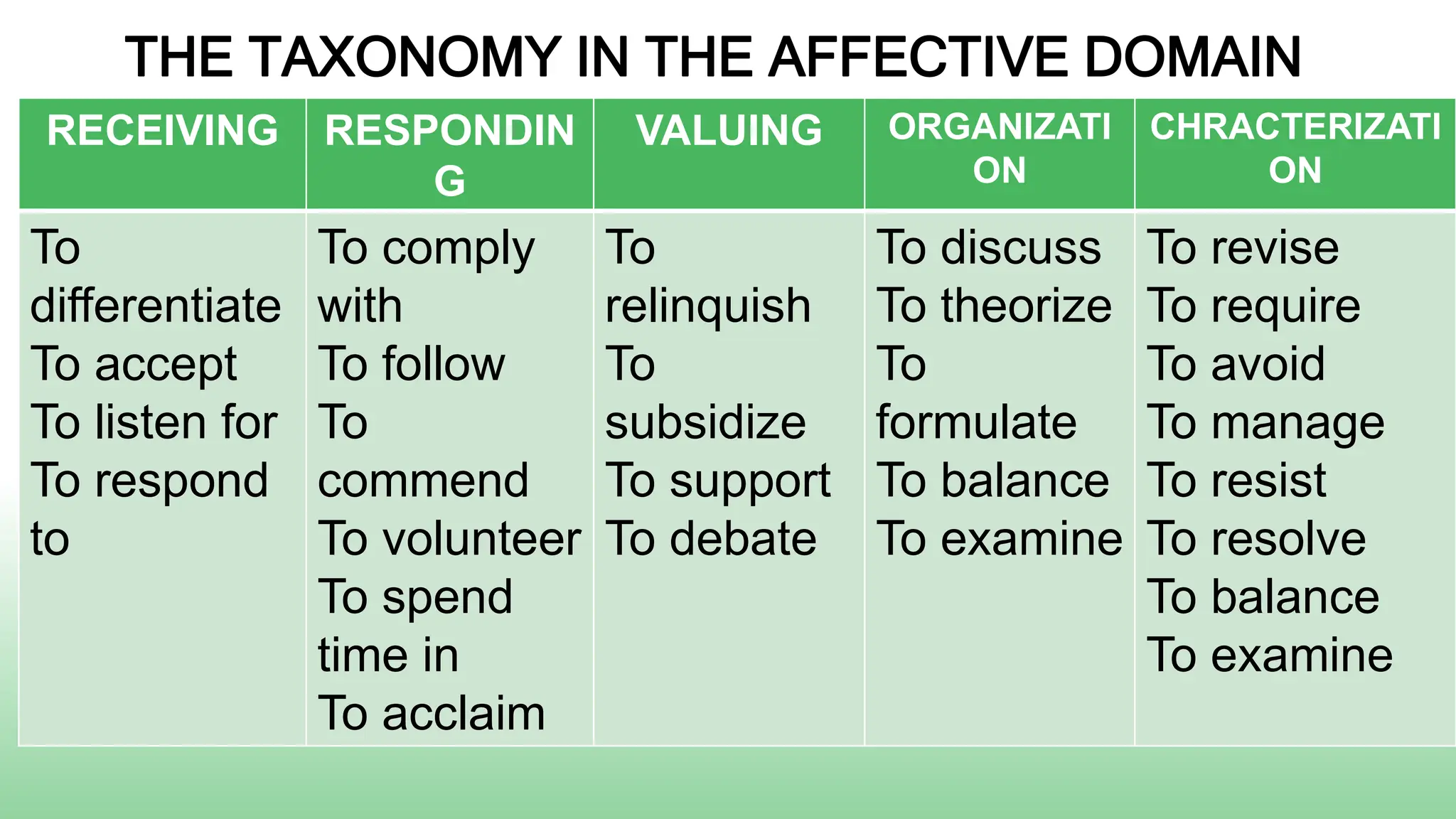
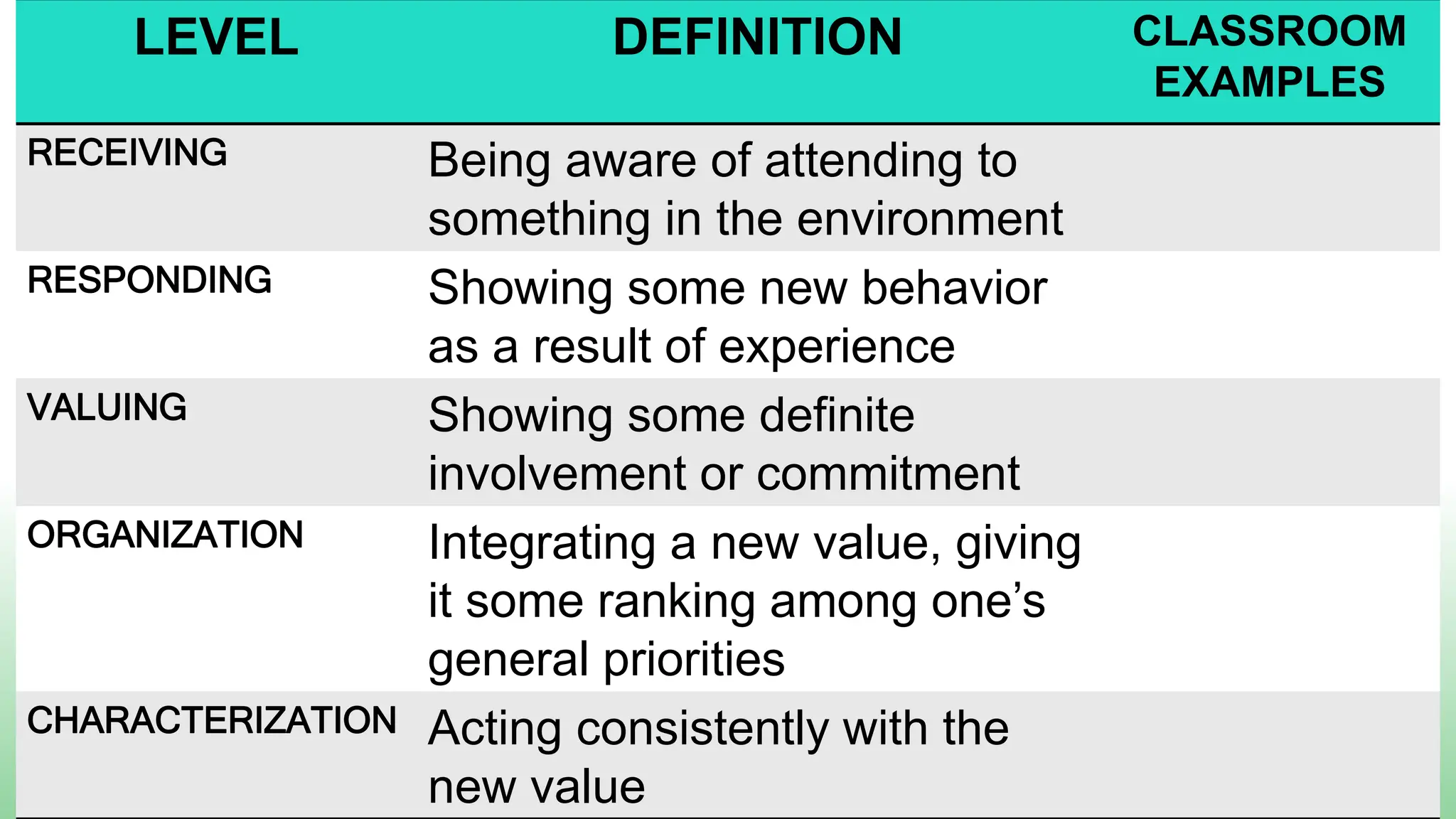
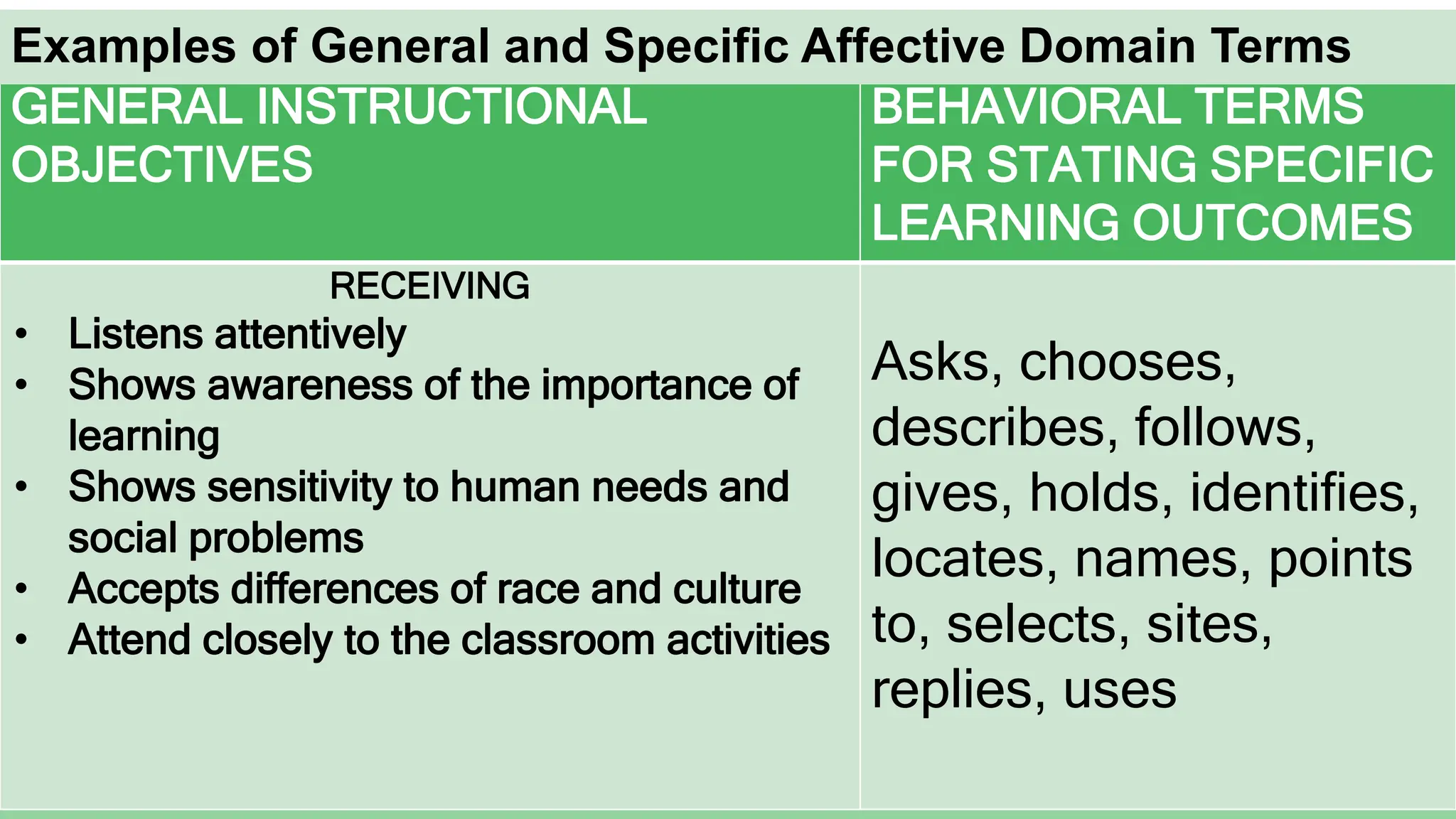
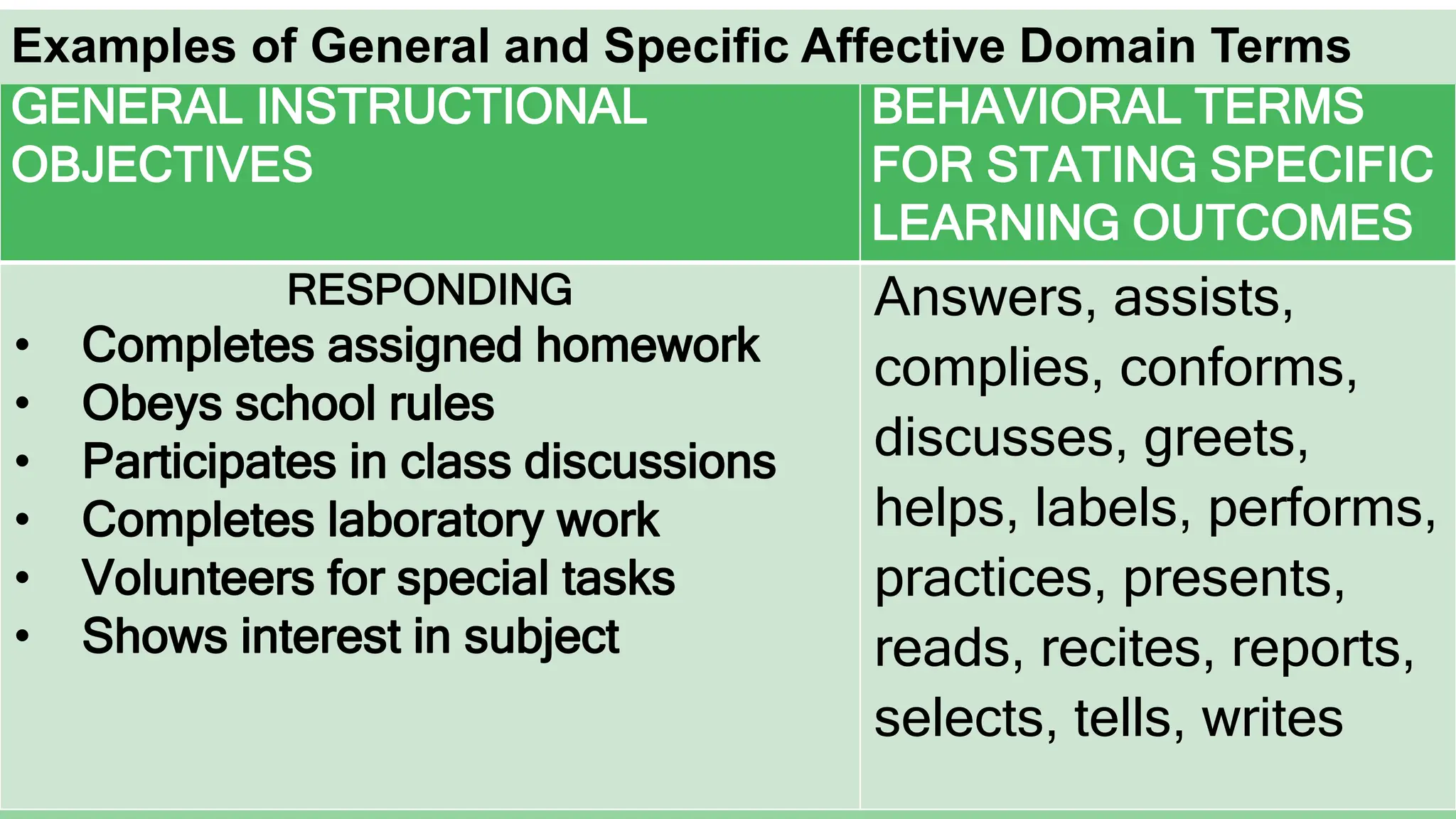
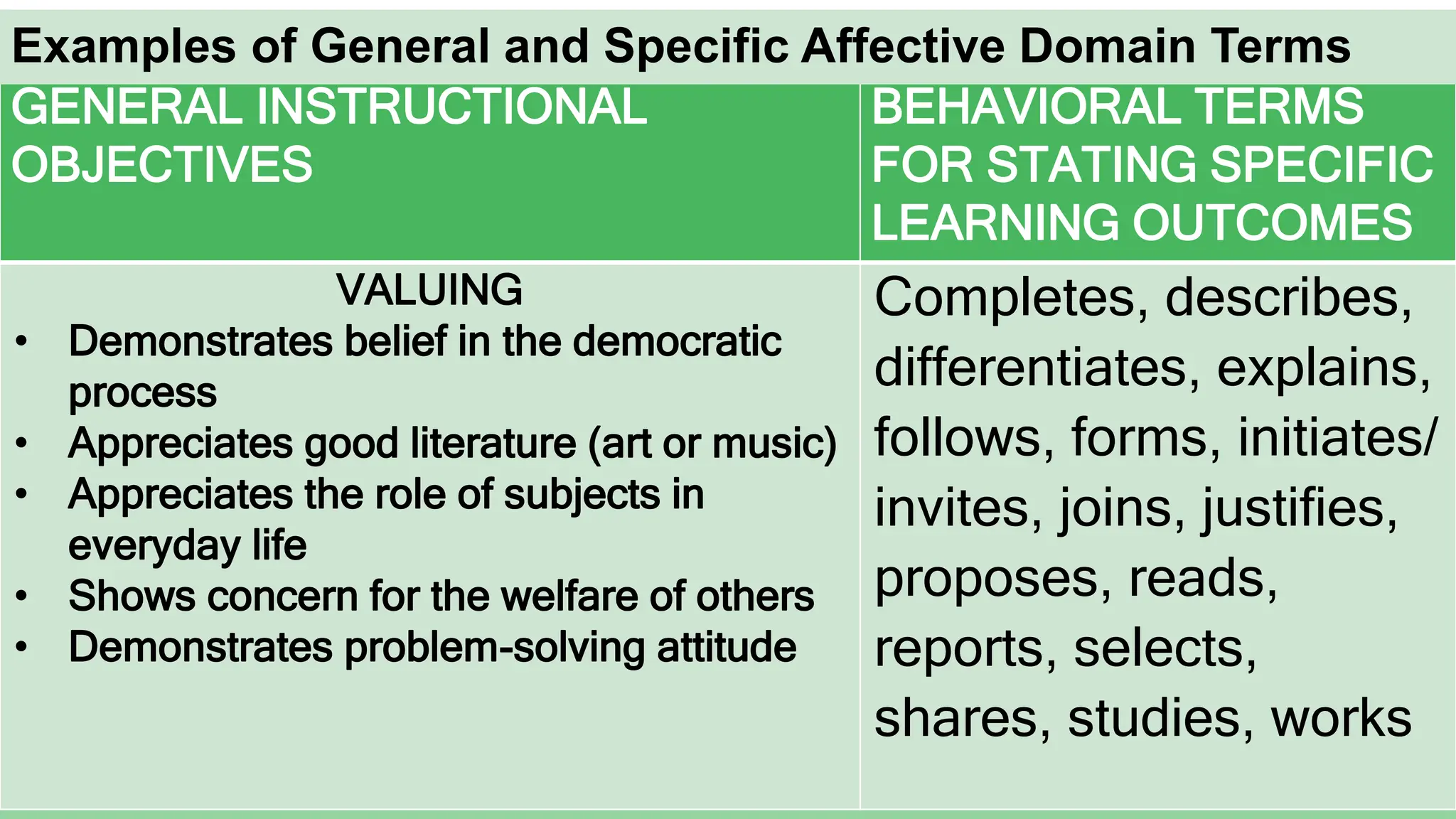
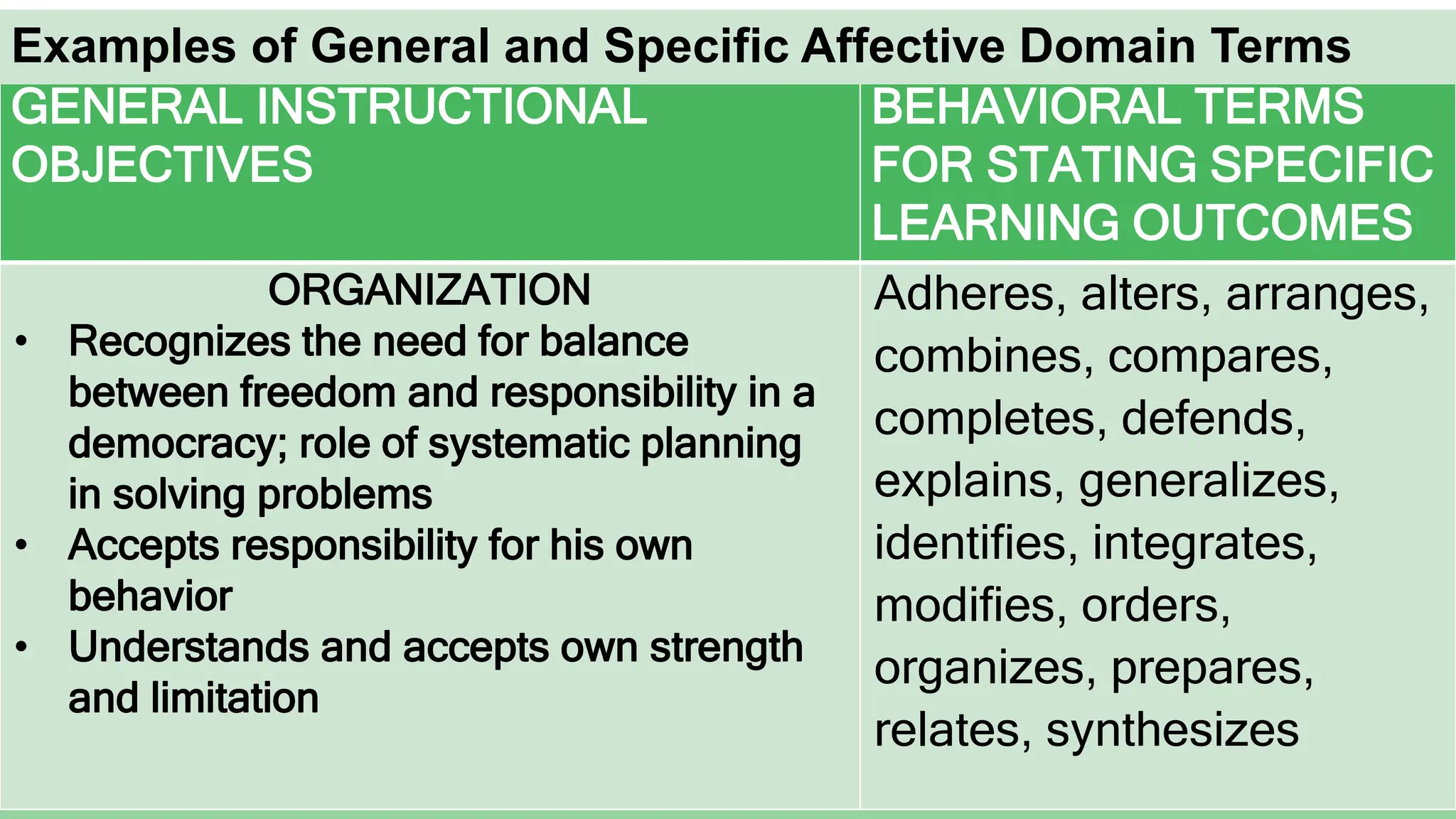
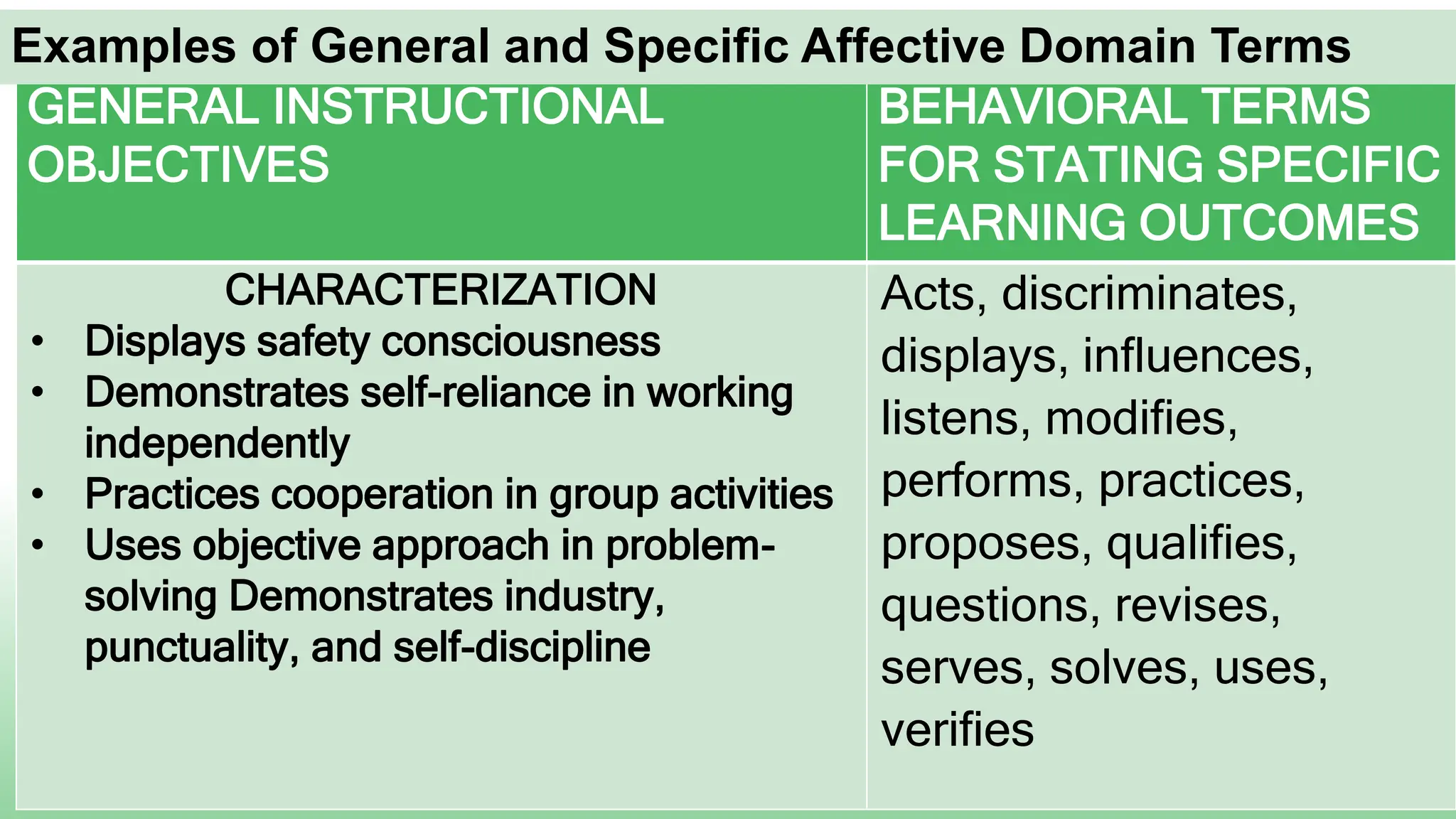
Here is a sample specific objective showing the elevation of levels for the affective domain using the topic of environmental protection:
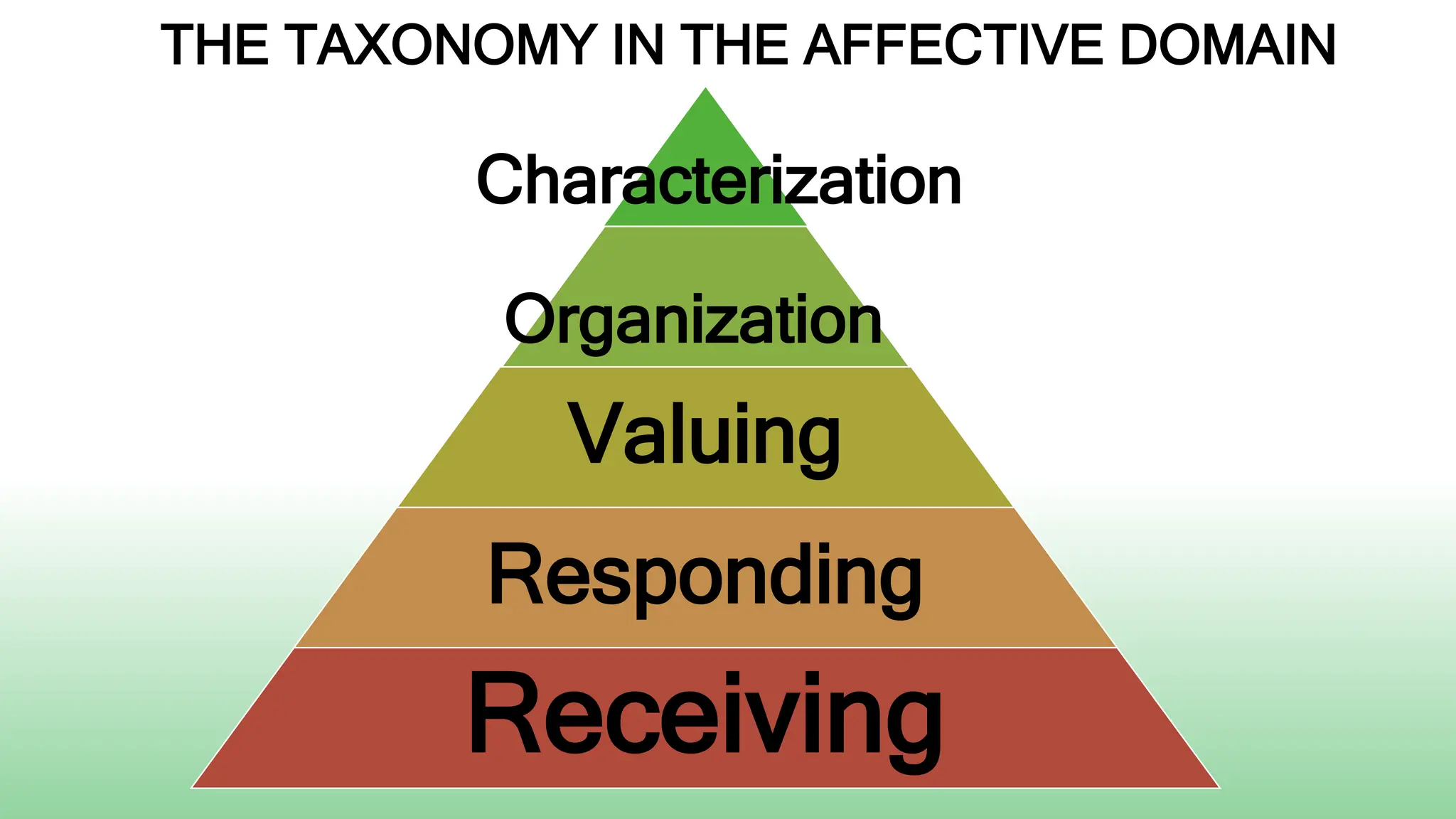
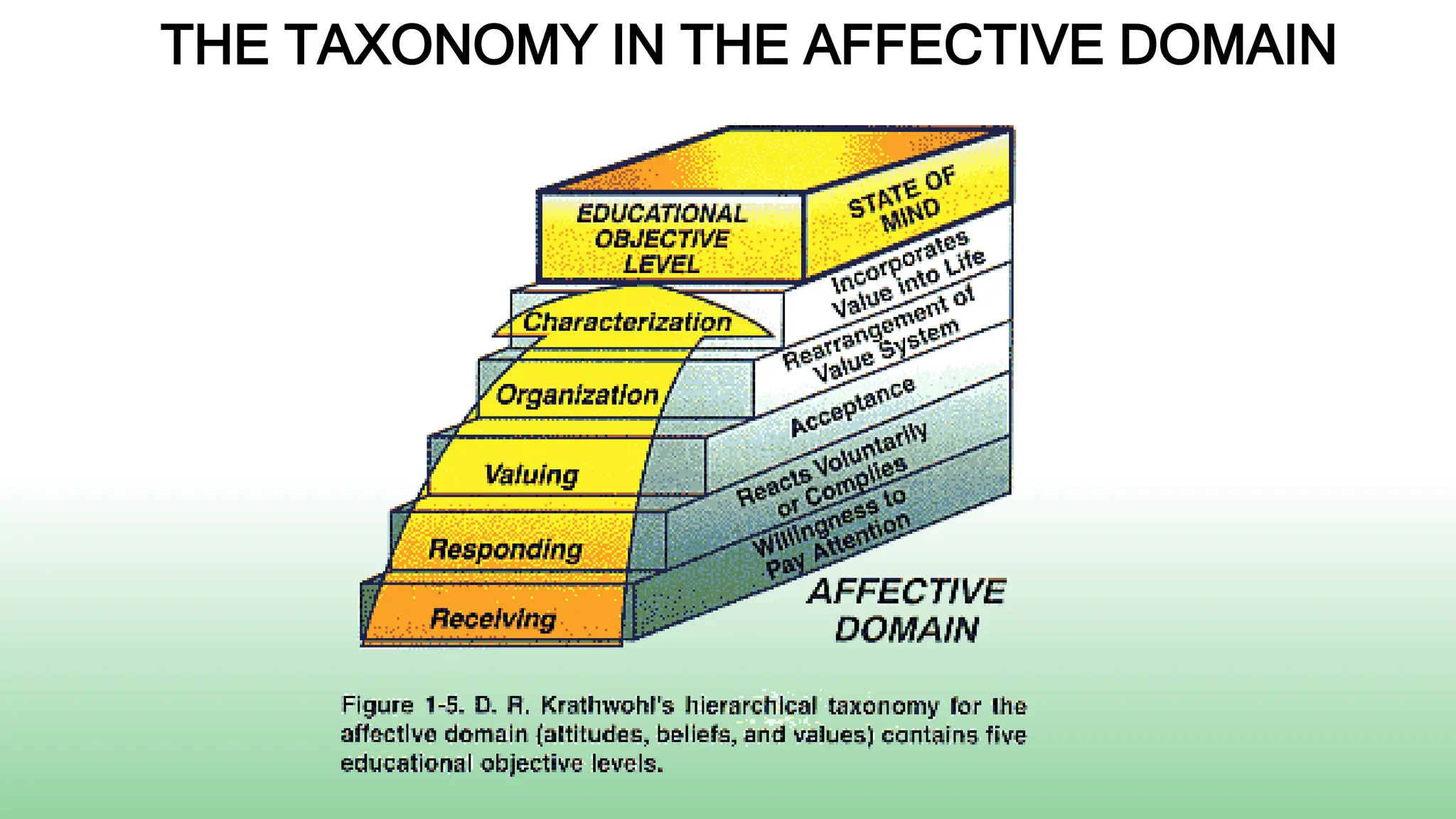
Receiving: Students will listen attentively during a lecture about the importance of environmental protection.
Responding: Students will complete a worksheet identifying 3 ways they can help reduce pollution in their community.
Valuing: Students will write a paragraph explaining why protecting the environment is important.
Organizing: Students will design an advocacy campaign to raise awareness about an environmental issue in their town.
Characterizing: Students will volunteer 5 hours over the semester to participate in a local environmental cleanup or conservation project.