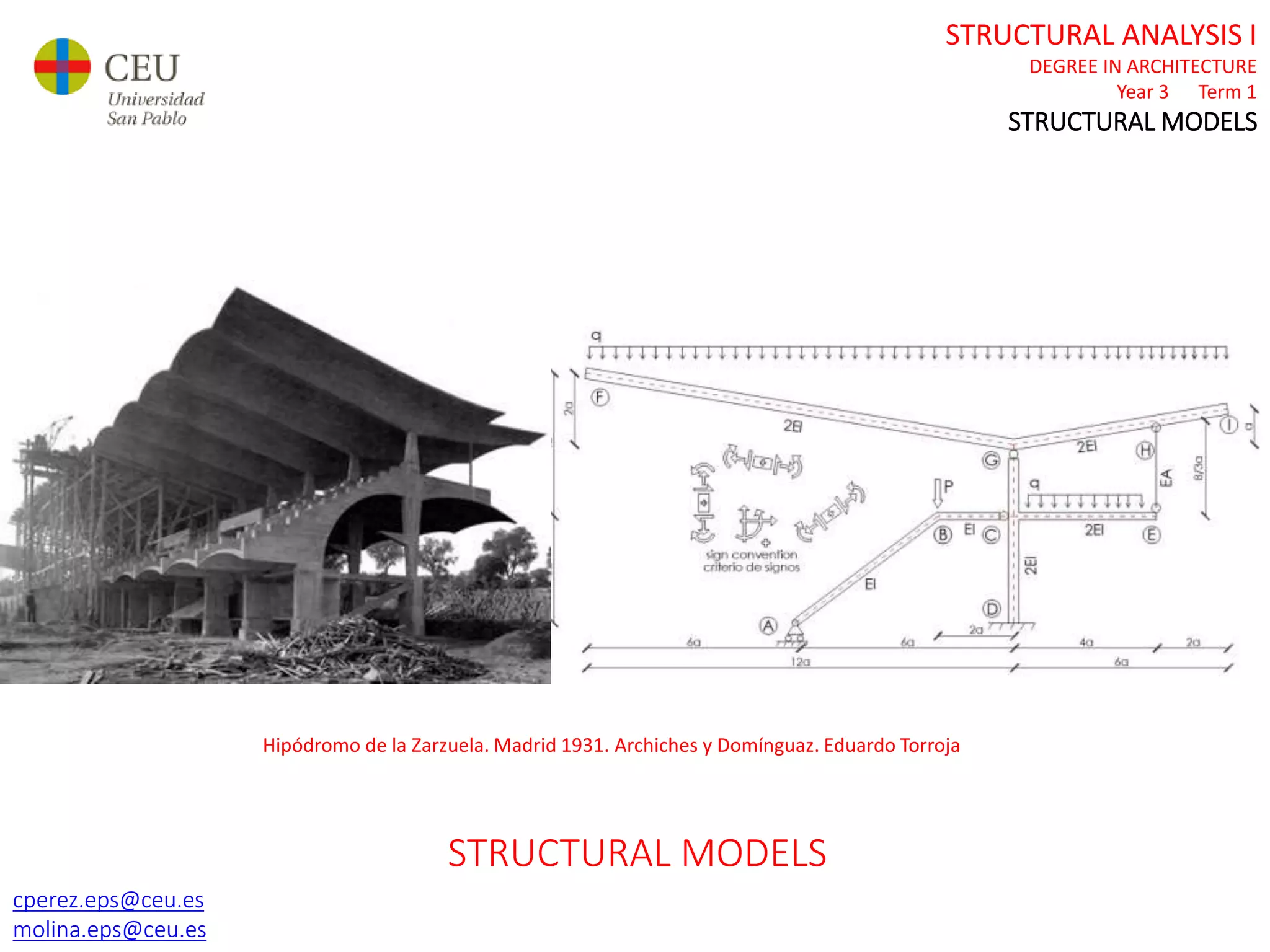
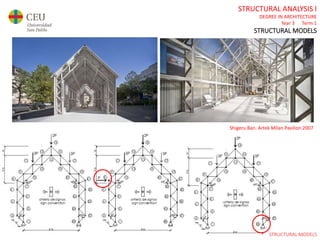
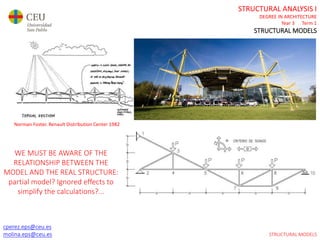
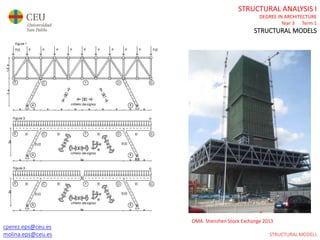
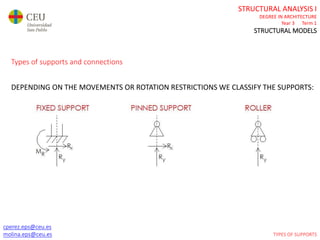
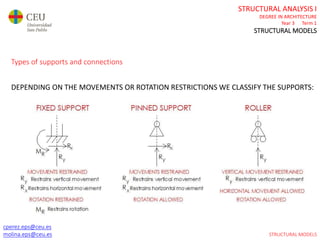
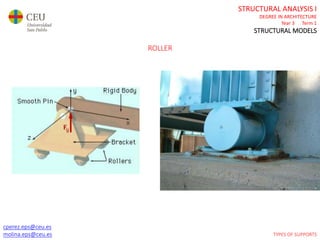
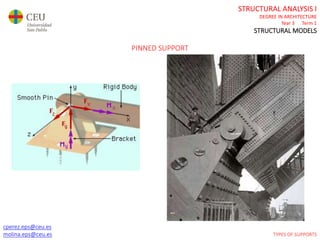
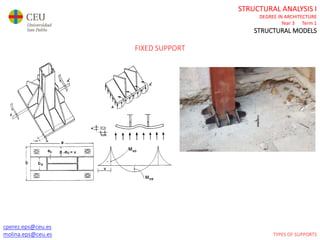
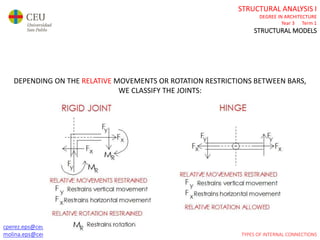
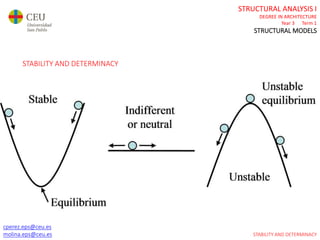
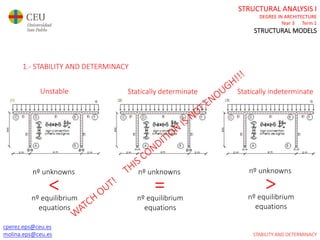
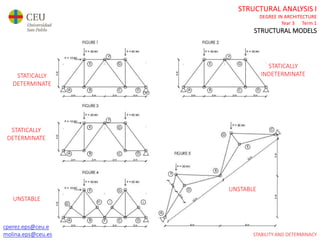
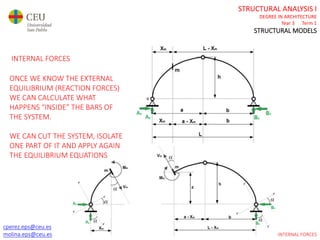
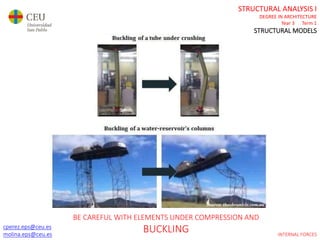
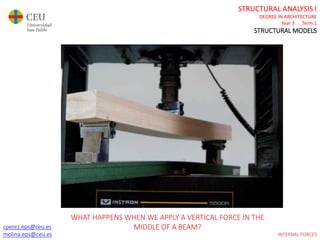
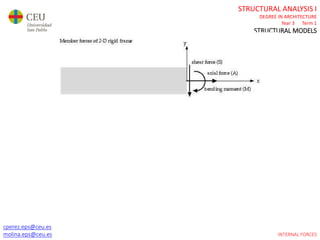
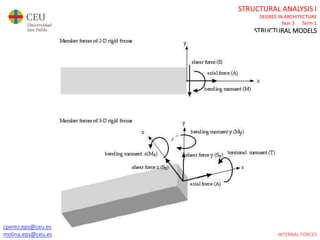
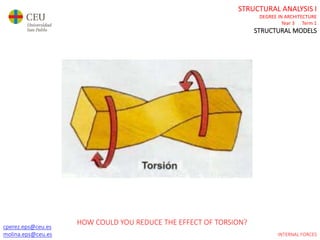
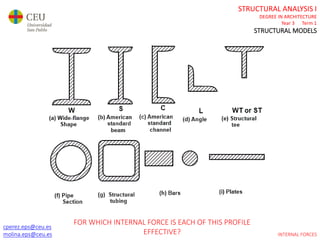
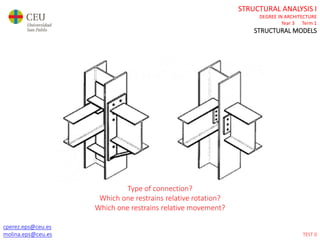
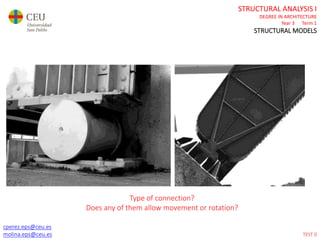
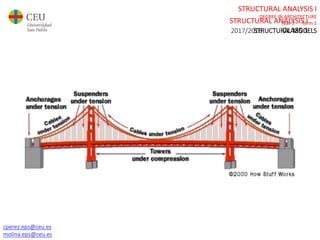
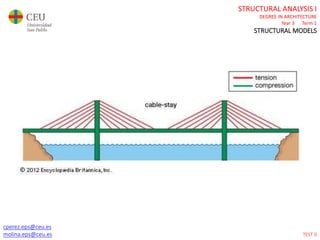
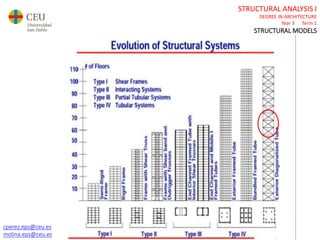
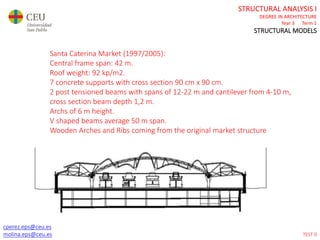
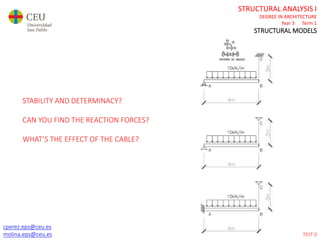
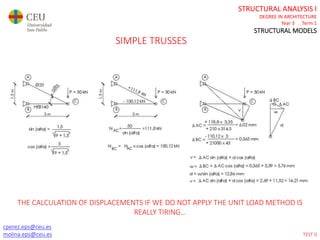
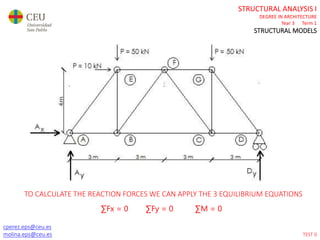
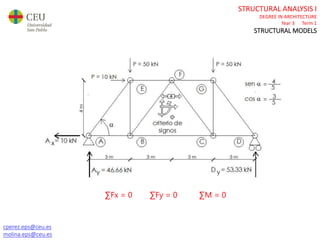
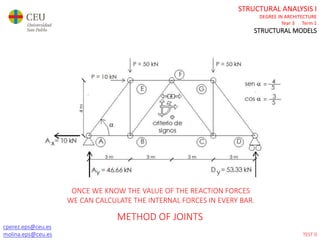
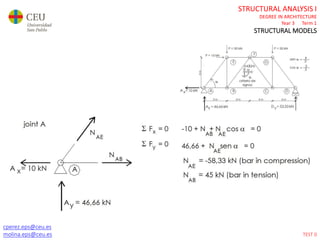
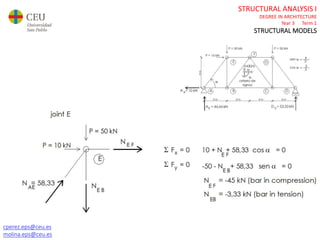
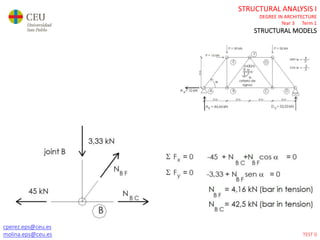
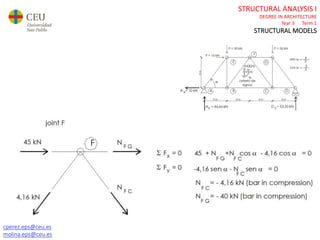
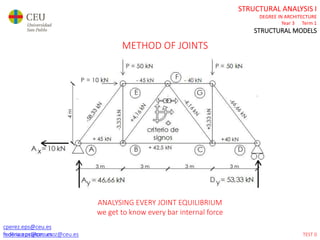
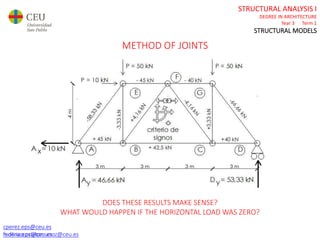
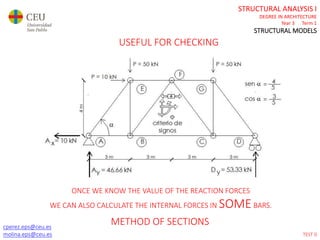
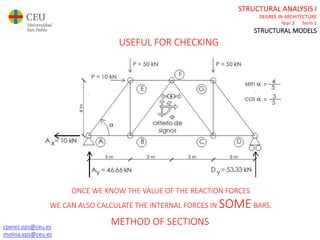
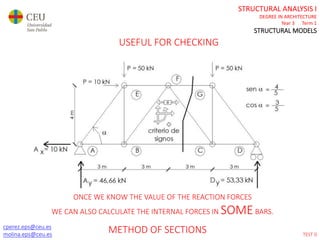
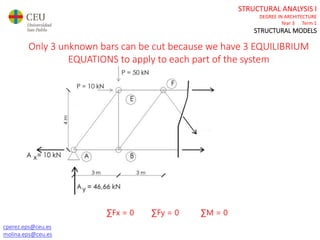
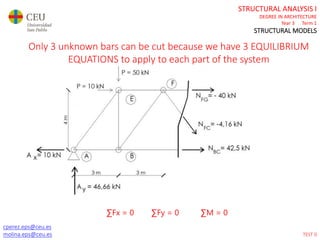
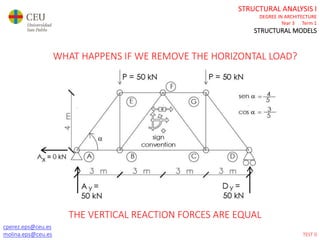
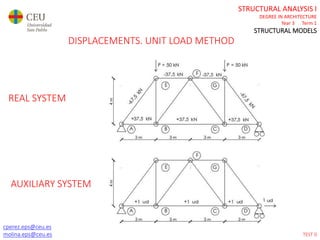
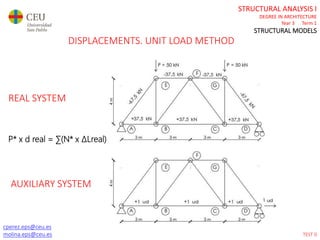
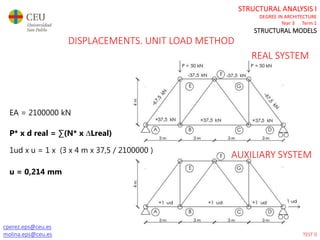
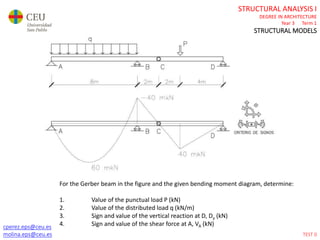
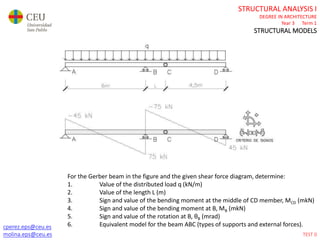
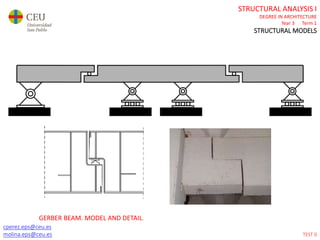
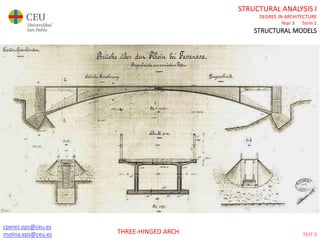
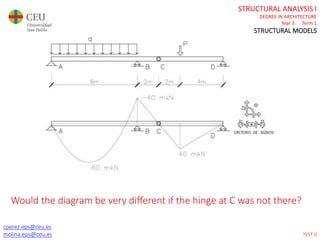
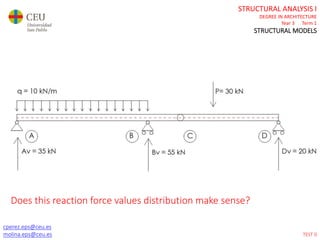
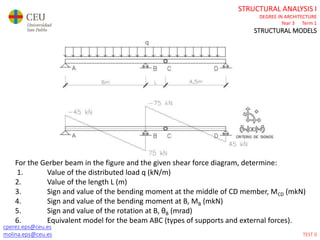
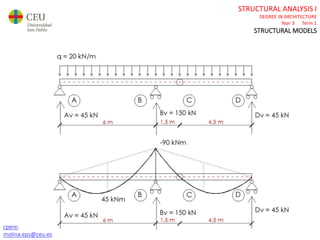
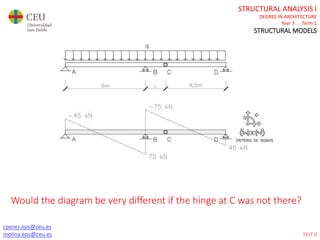
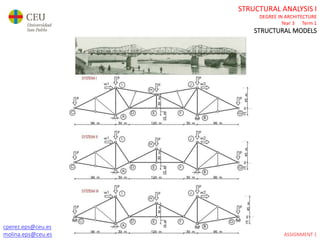
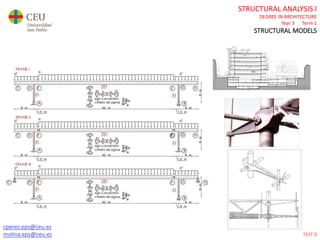
This document contains lecture slides for a Structural Analysis course. It discusses structural models, explaining that models are simplified representations of real structures used for calculations. It covers types of supports, loads, connections and joints in structural models. It also addresses structural stability, determinacy, and calculating internal forces like axial forces, shear forces, bending moments and torsion. Examples of structural models and buildings are provided throughout for illustration.