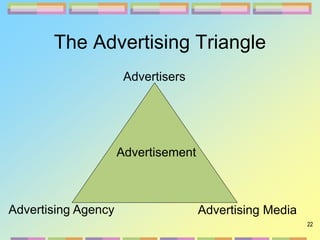
The document provides an overview of the history and roles of advertising. It discusses how advertising has evolved from the pre-industrial era through the current global interactive age. It also describes the main components of the advertising industry including advertisers, advertising agencies, and advertising media. Additionally, it outlines different types of advertising and explains the functions and stages of the advertising cycle.