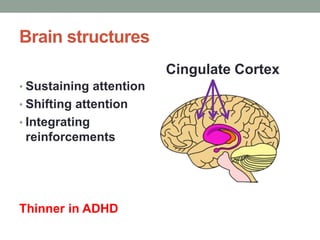
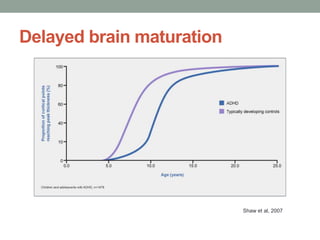
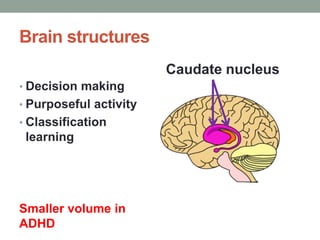
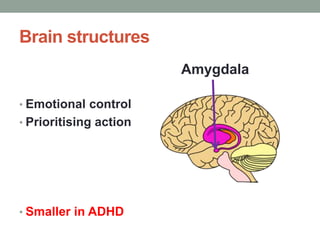
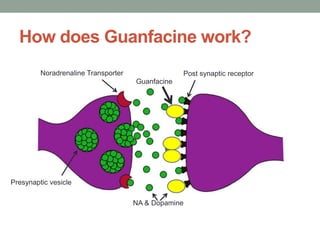
ADHD is associated with differences in brain structure, function, chemistry and maturation compared to those without ADHD. Core symptoms include inattention, hyperactivity and impulsivity. Common treatments target the brain's neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine. While genetics play a role, environment and brain plasticity also contribute to ADHD.