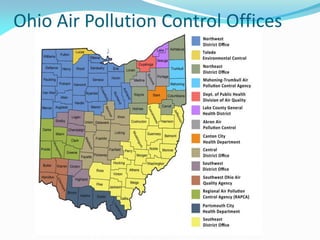
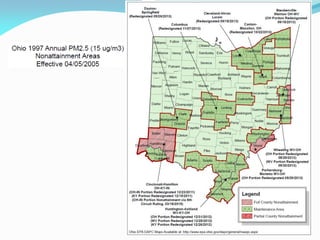
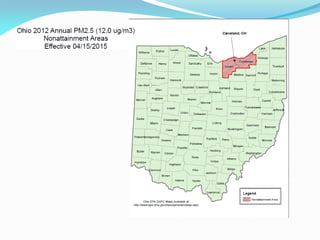
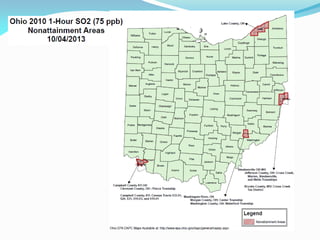
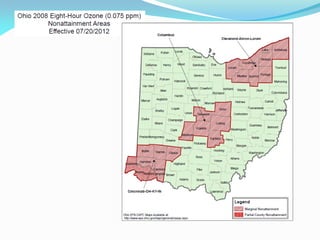
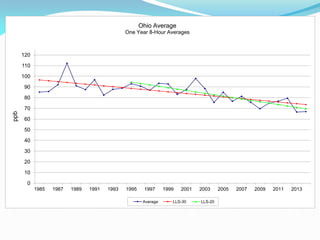
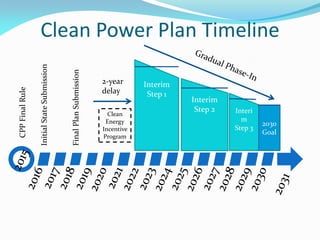
The document outlines the Ohio EPA's air pollution control program, detailing its structure, compliance strategies, permit processes, and the challenges it faces, particularly regarding new ozone standards and the Clean Power Plan. It emphasizes the agency's commitment to efficiency, consistency, and transparency while providing various online services to facilitate compliance for businesses. Additionally, it highlights successes in the oil and gas sector, including swift permit issuances, and the agency's proactive stance in addressing emerging air quality issues.