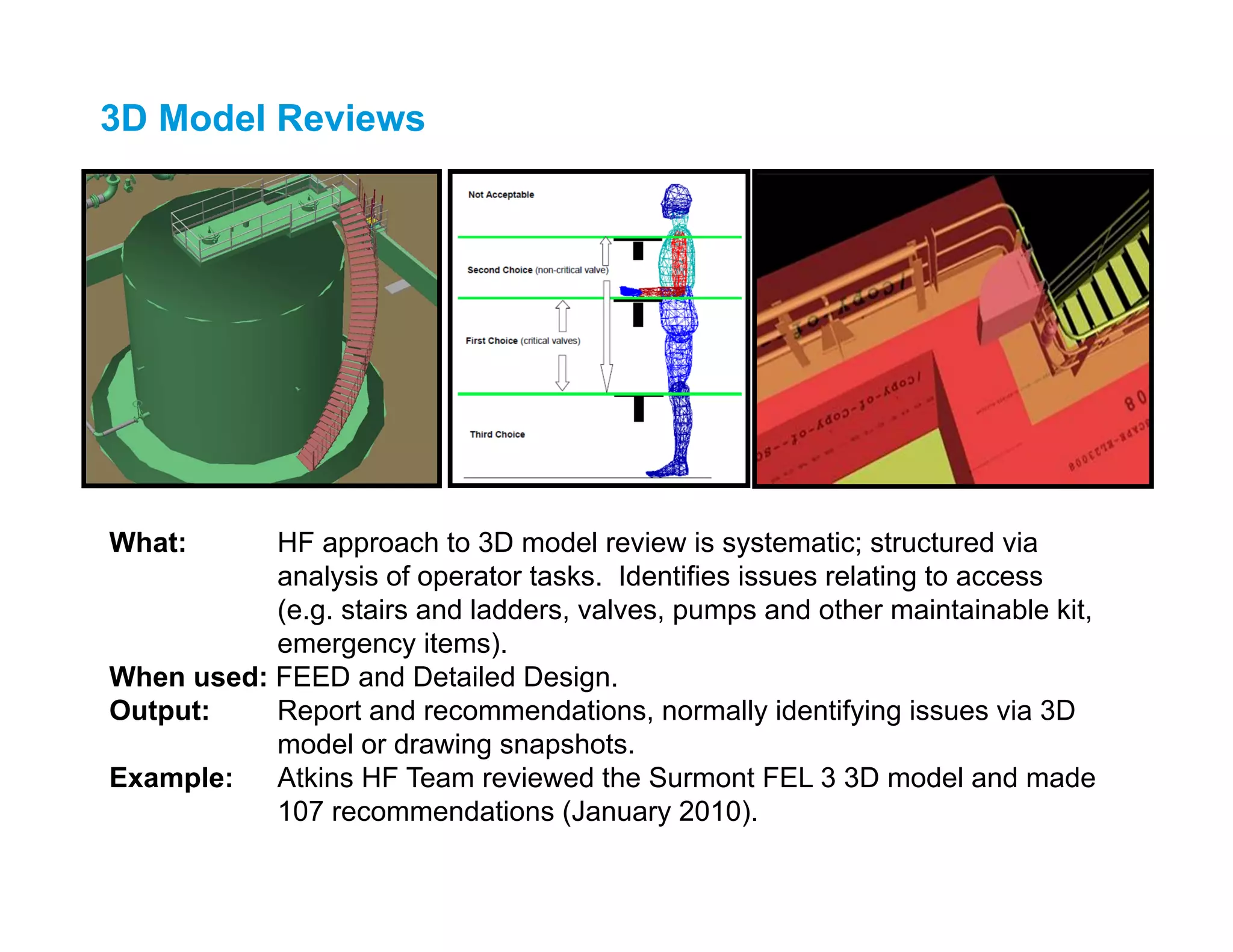
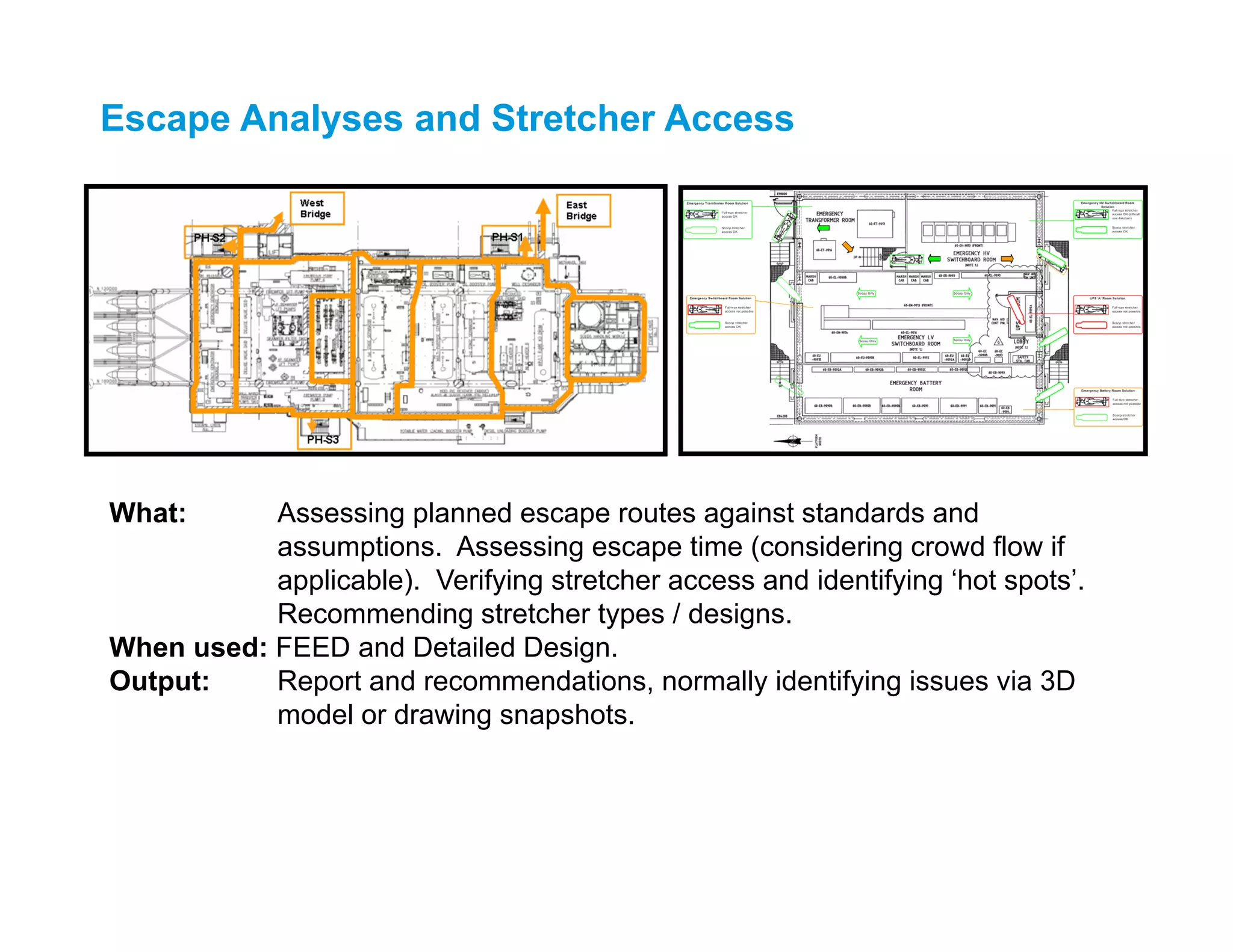
This document describes several 3D model review and human factors analysis techniques, including:
1) 3D model reviews which identify issues relating to access, maintenance, and emergency equipment.
2) Escape route analyses and stretcher access assessments.
3) Control room design integration to facilitate tasks, communication, and movement.
4) Alarm management workshops to properly configure alarm systems.
5) Crane and truck cabin assessments to evaluate design.
6) Hazard identification techniques to find equipment, procedure, and human-job mismatch problems.
7) Fatigue management guidance and shiftwork design recommendations.
8) Developing effective safety culture through assessment and workforce engagement.