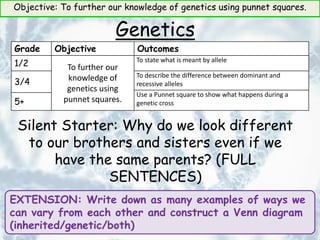
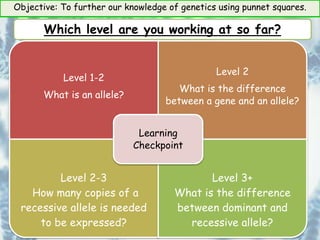
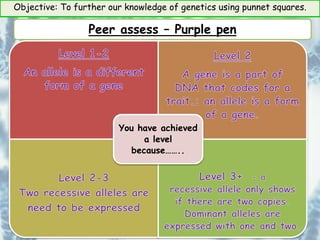
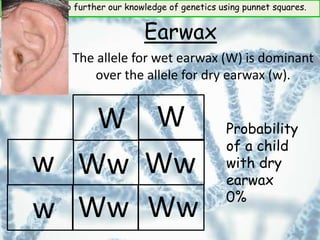
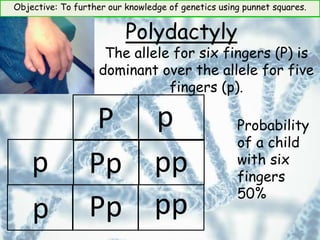
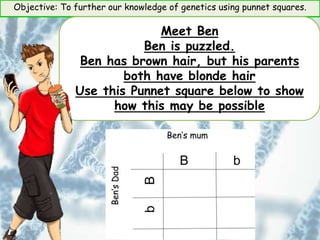
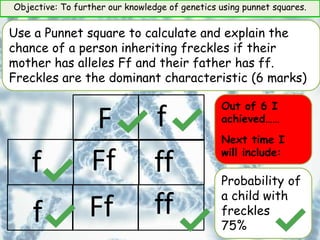
This document provides information about genetics and Punnett squares. It begins with learning objectives related to furthering knowledge of genetics using Punnett squares. It then provides information about genes, alleles, dominant and recessive traits, and examples of genetic crosses and Punnett squares. The document seeks to build understanding of concepts like what genes and alleles are, the difference between dominant and recessive, and how to use Punnett squares to determine the probabilities of inheriting certain traits. Various practice problems and self-assessment questions are included to help solidify these genetics concepts.